
Trigonometry Practice 1 (Calculator) [123 marks]
[4 marks]
1a.
A ship leaves port A on a bearing of . It sails a distance of to point B. At B, the ship changes direction to a bearing of
. It sails a distance of to reach point C. This information is shown in the diagram below.
A second ship leaves port A and sails directly to C.
Find the distance the second ship will travel.
Markscheme
finding ( radians) (A1)
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
e.g.
correct substitution A1
e.g.
(km) A1
030
∘
25 km
100
∘
40 km
A C =
B
ˆ
110
∘
= 1.92
A = A + B − 2(AB)(BC) cosA C
C
2
B
2
C
2
B
ˆ
A = + − 2(25)(40)cos
C
2
25
2
40
2
110
∘
A = 53.9C
[3 marks]
1b.
Find the bearing of the course taken by the second ship.
Markscheme
METHOD 1
correct substitution into the sine rule A1
e.g. A1
bearing A1 N1
METHOD 2
correct substitution into the cosine rule A1
e.g. A1
bearing A1 N1
[3 marks]
=
sin B C
A
ˆ
40
sin
110
∘
53.9
B C =
A
ˆ
44.2
∘
=
074
∘
cosB C =
A
ˆ
− −
40
2
25
2
53.9
2
−2(25)(53.9)
B C =
A
ˆ
44.3
∘
=
074
∘

[3 marks]
2a.
The diagram below shows triangle PQR. The length of [PQ] is 7 cm , the length of [PR] is 10 cm , and is .
Find .
Markscheme
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
A1 N2
[3 marks]
P R
Q
ˆ
75
∘
P Q
R
ˆ
=
sin R
7
sin
75
∘
10
sin R = 0.676148…
P Q = 42
R
ˆ
.5
∘
[3 marks]
2b.
Find the area of triangle PQR.
Markscheme
(A1)
substitution into any correct formula A1
e.g.
(cm ) A1 N2
[3 marks]
P = 180 − 75 − R
P = 62.5
area ΔPQR = × 7 × 10 × sin(their P)
1
2
= 31.0
2
[2 marks]
3a.
The diagram below shows a circle centre O, with radius r. The length of arc ABC is and .
Find the value of r.
3π cm
A C =
O
ˆ
2π
9

Markscheme
evidence of appropriate approach M1
e.g.
(cm) A1 N1
[2 marks]
3π = r
2π
9
r = 13.5
[2 marks]
3b.
Find the perimeter of sector OABC.
Markscheme
adding two radii plus (M1)
(cm) ( ) A1 N2
[2 marks]
3π
perimeter = 27 + 3π
= 36.4
[2 marks]
3c.
Find the area of sector OABC.
Markscheme
evidence of appropriate approach M1
e.g.
area ( ) ( ) A1 N1
[2 marks]
× ×
1
2
13.5
2
2π
9
= 20.25π
cm
2
= 63.6
[7 marks]
4.
The following diagram shows a pole BT 1.6 m tall on the roof of a vertical building.
The angle of depression from T to a point A on the horizontal ground is .
The angle of elevation of the top of the building from A is .
Find the height of the building.
35
∘
30
∘

Markscheme
METHOD 1
appropriate approach M1
e.g. completed diagram
attempt at set up A1
e.g. correct placement of one angle
, A1A1
attempt to set up equation M1
e.g. isolate x
correct equation A1
e.g.
A1 N3
METHOD 2
A1
in triangle ATB, , A1A1
choosing sine rule M1
correct substitution
e.g. A1
A1
A1 N3
[7 marks]
tan30 =
h
x
tan35 =
h+1.6
x
=
h
tan 30
h+1.6
tan 35
h = 7.52
sin 30 =
h
l
=
A
ˆ
5
∘
=
T
ˆ
55
∘
=
h/sin30
sin 55
1.6
sin 5
h =
1.6×sin30×sin55
sin 5
h = 7.52
[3 marks]
5a.
A circle centre O and radius is shown below. The chord [AB] divides the area of the circle into two parts. Angle AOB is .
Find an expression for the area of the shaded region.
Markscheme
substitution into formula for area of triangle A1
e.g.
evidence of subtraction M1
correct expression A1 N2
e.g. ,
[3 marks]
r
θ
r × r sin θ
1
2
θ − sin θ
1
2
r
2
1
2
r
2
(θ − sin θ)
1
2
r
2

[5 marks]
5b.
The chord [AB] divides the area of the circle in the ratio 1:7. Find the value of .
Markscheme
evidence of recognizing that shaded area is of area of circle M1
e.g. seen anywhere
setting up correct equation A1
e.g.
eliminating 1 variable M1
e.g. ,
attempt to solve M1
e.g. a sketch, writing
(do not accept degrees) A1 N1
[5 marks]
θ
1
8
1
8
(θ − sin θ) = π
1
2
r
2
1
8
r
2
(θ − sin θ) = π
1
2
1
8
θ − sin θ =
π
4
sin x − x + = 0
π
4
θ = 1.77
[3 marks]
6a.
The following diagram shows a circle with centre O and radius 4 cm.
The points A, B and C lie on the circle. The point D is outside the circle, on (OC).
Angle ADC = 0.3 radians and angle AOC = 0.8 radians.
Find AD.
Markscheme
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N2
[3 marks]
=
AD
sin 0.8
4
sin 0.3
AD = 9.71 (cm)
[4 marks]
6b.
Find OD.

Markscheme
METHOD 1
finding angle (seen anywhere) (A1)
choosing cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N3
METHOD 2
finding angle (seen anywhere) (A1)
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N3
[4 marks]
OAD = π − 1.1 = (2.04)
O = + − 2 × 9.71 × 4 × cos(π − 1.1)
D
2
9.71
2
4
2
OD = 12.1 (cm)
OAD = π − 1.1 = (2.04)
= =
OD
sin(π−1.1)
9.71
sin 0.8
4
sin 0.3
OD = 12.1 (cm)
[2 marks]
6c.
Find the area of sector OABC.
Markscheme
correct substitution into area of a sector formula (A1)
e.g.
A1 N2
[2 marks]
area = 0.5 × × 0.8
4
2
area = 6.4 (c )
m
2
[4 marks]
6d.
Find the area of region ABCD.
Markscheme
substitution into area of triangle formula OAD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. , ,
subtracting area of sector OABC from area of triangle OAD (M1)
e.g.
A1 N2
[4 marks]
A= × 4 × 12.1 × sin 0.8
1
2
A= × 4 × 9.71 × sin 2.04
1
2
A= × 12.1 × 9.71 × sin 0.3
1
2
area ABCD = 17.3067 − 6.4
area ABCD = 10.9 (c )
m
2

[3 marks]
7a.
The circle shown has centre O and radius 3.9 cm.
Points A and B lie on the circle and angle AOB is 1.8 radians.
Find AB.
Markscheme
METHOD 1
choosing cosine rule (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g.
(cm) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of approach involving right-angled triangles (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. ,
(cm) A1 N2
METHOD 3
choosing the sine rule (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g.
(cm) A1 N2
[3 marks]
AB =
+ − 2(3.9)(3.9)cos1.8
3.9
2
3.9
2
− −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−
√
AB = 6.11
sin 0.9 =
x
3.9
AB = 3.9sin 0.9
1
2
AB = 6.11
=
sin 0.670…
3.9
sin 1.8
AB
AB = 6.11
[4 marks]
7b.
Find the area of the shaded region.

Markscheme
METHOD 1
reflex (A2)
correct substitution A1
area =34.1 (cm ) A1 N2
METHOD 2
finding area of circle (A1)
finding area of (minor) sector (A1)
subtracting M1
e.g. ,
area = 34.1 (cm ) A1 N2
METHOD 3
finding reflex (A2)
finding proportion of total area of circle A1
e.g. ,
area = 34.1 (cm ) A1 N2
[4 marks]
A B = 2π − 1.8
O
ˆ
(= 4.4832)
A = (3.9 (4.4832…)
1
2
)
2
2
A = π(3.9
)
2
(= 47.78…)
A = (3.9 (1.8)
1
2
)
2
(= 13.68…)
π(3.9 − 0.5(3.9 (1.8)
)
2
)
2
47.8 − 13.7
2
A B = 2π − 1.8
O
ˆ
(= 4.4832)
× π(3.9
2π−1.8
2π
)
2
× π
θ
2π
r
2
2
[3 marks]
8a.
The diagram below shows a triangle ABD with AB =13 cm and AD = 6.5 cm.
Let C be a point on the line BD such that BC = AC = 7 cm.
Find the size of angle ACB.

Markscheme
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing the cosine formula (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
radians A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of appropriate approach involving right-angled triangles (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
radians A1 N2
[3 marks]
cosA B =
C
ˆ
+ −
7
2
7
2
13
2
2×7×7
A B = 2.38
C
ˆ
(= )
136
∘
sin ( A B) =
1
2
C
ˆ
6.5
7
A B = 2.38
C
ˆ
(= )
136
∘
[5 marks]
8b.
Find the size of angle CAD.
Markscheme
METHOD 1
(A1)
evidence of choosing the sine rule in triangle ACD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1
A1 N3
METHOD 2
(A1)
evidence of choosing the sine rule in triangle ABD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1
A1 N3
Note: Two triangles are possible with the given information. If candidate finds leading to
, award marks as per markscheme.
[5 marks]
A D = π − 2.381
C
ˆ
(180 − 136.4)
=
6.5
sin 0.760…
7
sin A C
D
ˆ
A C = 0.836…
D
ˆ
(= 47.9 )
…
∘
C D = π − (0.760… + 0.836…)
A
ˆ
(180 − (43.5… + 47.9…))
= 1.54
(= )
88.5
∘
A C = (π − 2.381)
B
ˆ
1
2
( (180 − 136.4))
1
2
=
6.5
sin 0.380…
13
sin A C
D
ˆ
A C = 0.836…
D
ˆ
(= 47.9 )
…
∘
C D = π − 0.836… − (π − 2.381…)
A
ˆ
(= 180 − 47.9… − (180 − 136.4))
= 1.54
(= )
88.5
∘
A C = 2.31
D
ˆ
( )
132
∘
C D = 0.076
A
ˆ
( )
4.35
∘

[4 marks]
9a.
The following diagram shows the triangle ABC.
The angle at C is obtuse, , and the area is .
Find .
Markscheme
correct substitution into the formula for the area of a triangle A1
e.g. ,
attempt to solve (M1)
e.g. ,
( ) (A1)
A1 N3
[4 marks]
AC = 5 cm BC = 13.6 cm
20 c
m
2
A B
C
ˆ
× 5 × 13.6 × sin C = 20
1
2
× 5 × h = 20
1
2
sin C = 0.5882…
sin C =
8
13.6
= 36.031
C
ˆ
…
∘
0.6288… radians
A B =
C
ˆ
144
∘
(2.51 radians)
[3 marks]
9b.
Find AB.
Markscheme
evidence of choosing the cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N2
[3 marks]
(AB = + − 2(5)(13.6)cos143.968…
)
2
5
2
13.6
2
AB = 17.9
[1 mark]
10a.
The diagram below shows a quadrilateral ABCD with obtuse angles and .
AB = 5 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, AD = 4 cm , , , .
Use the cosine rule to show that .
A C
B
ˆ
A C
D
ˆ
B C =
A
ˆ
30
∘
A C =
B
ˆ
x
∘
A C =
D
ˆ
y
∘
AC =
41 − 40 cosx
− −−−−−−−−−
√

Markscheme
correct substitution A1
e.g. ,
AG
[1 mark]
25 + 16 − 40cosx
+ − 2 × 4 × 5 cosx
5
2
4
2
AC =
41 − 40 cosx
− −−−−−−−−−
√
[2 marks]
10b.
Use the sine rule in triangle ABC to find another expression for AC.
Markscheme
correct substitution A1
e.g. ,
(accept ) A1 N1
[2 marks]
=
AC
sin x
4
sin 30
AC = 4sin x
1
2
AC = 8sin x
4 sin x
sin 30
10c.
[6 marks](i) Hence, find x, giving your answer to two decimal places.
(ii) Find AC .
Markscheme
(i) evidence of appropriate approach using AC M1
e.g. , sketch showing intersection
correct solution , (A1)
obtuse value (A1)
to 2 dp (do not accept the radian answer 1.94 ) A1 N2
(ii) substituting value of x into either expression for AC (M1)
e.g.
A1 N2
[6 marks]
8sin x =
41 − 40 cosx
− −−−−−−−−−
√
8.682… 111.317…
111.317…
x = 111.32
AC = 8sin 111.32
AC = 7.45
10d.
[5 marks](i) Find y.
(ii) Hence, or otherwise, find the area of triangle ACD.

Markscheme
(i) evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
e.g.
correct substitution A1
e.g. , ,
A1 N2
(ii) correct substitution into area formula (A1)
e.g. ,
area A1 N2
[5 marks]
cosB =
+ −
a
2
c
2
b
2
2ac
+ −
4
2
4
2
7.45
2
2×4×4
= 32 − 32 cosy
7.45
2
cosy = −0.734…
y = 137
× 4 × 4 × sin 137
1
2
8sin 137
= 5.42
[2 marks]
11a.
The diagram below shows a circle with centre O and radius 8 cm.
The points A, B, C, D, E and F are on the circle, and [AF] is a diameter. The length of arc ABC is 6 cm.
Find the size of angle AOC .
Markscheme
appropriate approach (M1)
e.g.
A1 N2
[2 marks]
6 = 8θ
A C = 0.75
O
ˆ
[6 marks]
11b.
Hence find the area of the shaded region.

Markscheme
evidence of substitution into formula for area of triangle (M1)
e.g.
area (A1)
evidence of substitution into formula for area of sector (M1)
e.g.
area of sector (A1)
evidence of substituting areas (M1)
e.g. ,
area of shaded region A1 N4
[6 marks]
area = × 8 × 8 × sin(0.75)
1
2
= 21.8…
area = × 64 × 0.75
1
2
= 24
θ − absin C
1
2
r
2
1
2
area of sector − area of triangle
= 2.19 c
m
2
11c.
[2 marks]The area of sector OCDE is .
Find the size of angle COE .
Markscheme
attempt to set up an equation for area of sector (M1)
e.g.
(1.41 to 3 sf) A1 N2
[2 marks]
45 c
m
2
45 = × × θ
1
2
8
2
C E = 1.40625
O
ˆ
[5 marks]
11d.
Find EF .
Markscheme
METHOD 1
attempting to find angle EOF (M1)
e.g.
(seen anywhere) A1
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
EF A1 N3
METHOD 2
attempting to find angles that are needed (M1)
e.g. angle EOF and angle OEF
and A1
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution (A1)
e.g.
EF A1 N3
METHOD 3
attempting to find angle EOF (M1)
e.g.
(seen anywhere) A1
evidence of using half of triangle EOF (M1)
e.g.
correct calculation A1
e.g.
EF A1 N3
[5 marks]
π − 0.75 − 1.41
E F = 0.985
O
ˆ
EF =
+ − 2 × 8 × 8 × cos0.985
8
2
8
2
− −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−
√
= 7.57 cm
E F = 0.9853…
O
ˆ
O F (or O E) = 1.078…
E
ˆ
F
ˆ
=
EF
sin 0.985
8
sin 1.08
= 7.57 cm
π − 0.75 − 1.41
E F = 0.985
O
ˆ
x = 8sin
0.985
2
x = 3.78
= 7.57 cm
[2 marks]
12a.
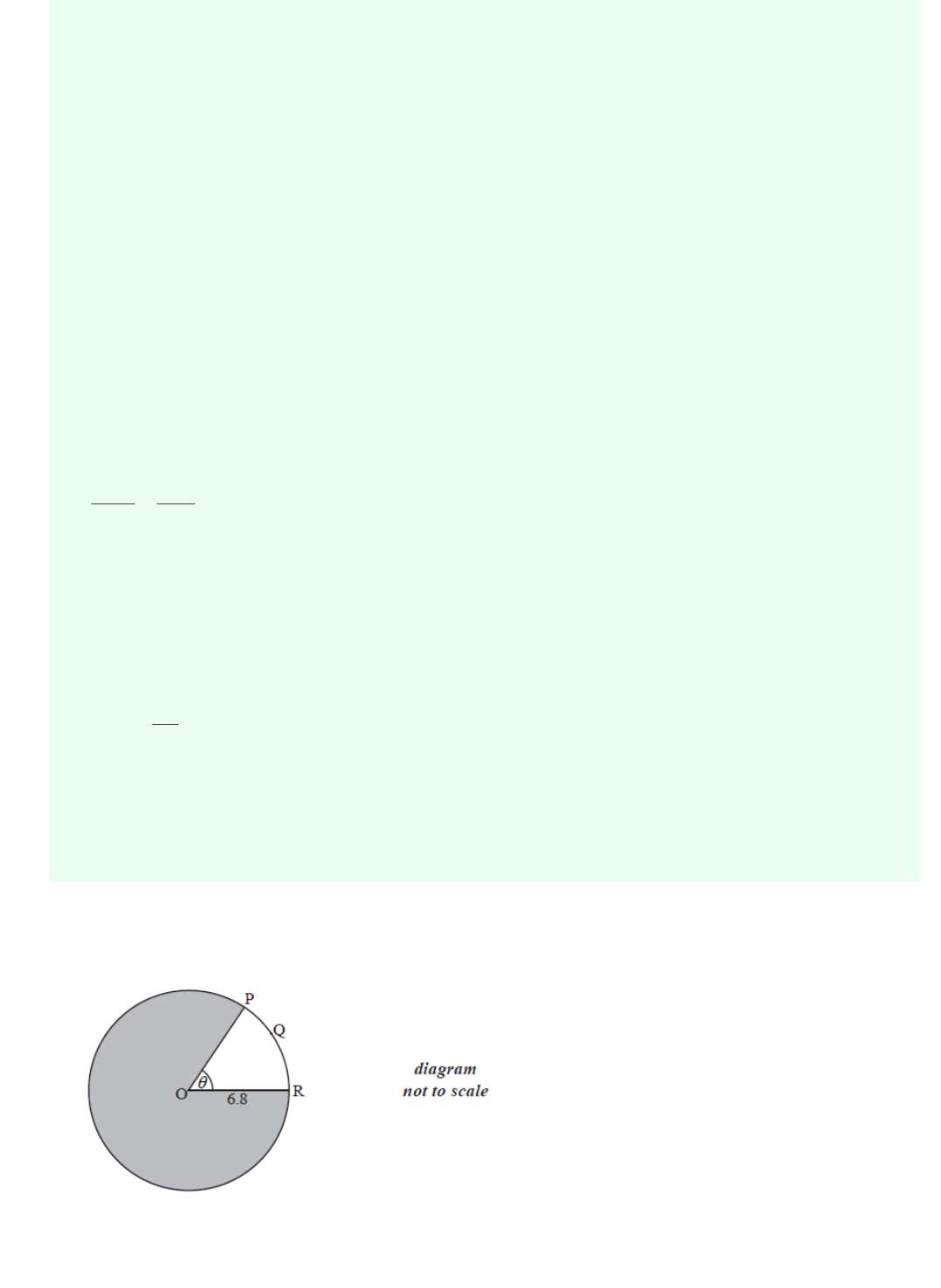
Consider the following circle with centre O and radius 6.8 cm.
The length of the arc PQR is 8.5 cm.
Find the value of .
θ

Markscheme
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. ,
(accept ) A1 N2
[2 marks]
8.5 = θ(6.8)
θ =
8.5
6.8
θ = 1.25
71.6
∘
[4 marks]
12b.
Find the area of the shaded region.
Markscheme
METHOD 1
correct substitution into area formula (seen anywhere) (A1)
e.g. ,
correct substitution into area formula (seen anywhere) (A1)
e.g. , 28.9
valid approach M1
e.g. ; ;
( ) A1 N2
METHOD 2
attempt to find reflex angle (M1)
e.g. ,
correct reflex angle (A1)
( )
correct substitution into area formula A1
e.g.
( ) A1 N2
[4 marks]
A = π(6.8
)
2
145.267…
A = (1.25)( )
1
2
6.8
2
π(6.8 − (1.25)( )
)
2
1
2
6.8
2
145.267… − 28.9
π − sin θ
r
2
1
2
r
2
A = 116
c
m
2
2π − θ
360 − 1.25
A B = 2π − 1.25
O
ˆ
= 5.03318…
A = (5.03318…)( )
1
2
6.8
2
A = 116
c
m
2
[4 marks]
13a.
Consider the triangle ABC, where AB =10 , BC = 7 and = .
Find the two possible values of .
Markscheme
Note: accept answers given in degrees, and minutes.
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
e.g.
correct substitution A1
e.g. ,
, A1A1 N1N1
Note: If candidates only find the acute angle in part (a), award no marks for (b).
[4 marks]
C B
A
ˆ
30
∘
A B
C
ˆ
=
sin A
a
sin B
b
=
sin θ
10
sin
30
∘
7
sin θ =
5
7
A B =
C
ˆ
45.6
∘
A B =
C
ˆ
134
∘
A C
ˆ

[2 marks]
13b.
Hence, find , given that it is acute.
Markscheme
attempt to substitute their larger value into angle sum of triangle (M1)
e.g.
A1 N2
[2 marks]
A C
B
ˆ
− (134.415 + )
180
∘
…
∘
30
∘
A C =
B
ˆ
15.6
∘
[3 marks]
14a.
The following diagram shows triangle ABC .
AB = 7 cm, BC = 9 cm and .
Find AC .
Markscheme
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
e.g.
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N2
[3 marks]
A C =
B
ˆ
120
∘
+ − 2ab cosC
a
2
b
2
+ − 2(7)(9)cos
7
2
9
2
120
∘
AC = 13.9
(= )
193
−−−
√
[3 marks]
14b.
Find .
B C
A
ˆ

Markscheme
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
e.g.
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
e.g.
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N2
[3 marks]
=
sin
A
ˆ
BC
sin
B
ˆ
AC
=
sin
A
ˆ
9
sin 120
13.9
=
A
ˆ
34.1
∘
cos =
A
ˆ
A +A −B
B
2
C
2
C
2
2(AB)(AC)
cos =
A
ˆ
+ −
7
2
13.9
2
9
2
2(7)(13.9)
=
A
ˆ
34.1
∘
[3 marks]
15a.
There is a vertical tower TA of height 36 m at the base A of a hill. A straight path goes up the hill from A to a point U. This
information is represented by the following diagram.
The path makes a angle with the horizontal.
The point U on the path is away from the base of the tower.
The top of the tower is fixed to U by a wire of length .
Complete the diagram, showing clearly all the information above.
4
∘
25 m
x m

Printed for North Hills Preparatory
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2015
International Baccalaureate® - Baccalauréat International® - Bachillerato Internacional®
Markscheme
A1A1A1 N3
Note: Award A1 for labelling with horizontal, A1 for labelling [AU] 25 metres, A1 for drawing [TU].
[3 marks]
4
∘
[4 marks]
15b.
Find x .
Markscheme
(A1)
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g.
A1 N3
[4 marks]
T U =
A
ˆ
86
∘
= + − 2(25)(36)cos
x
2
25
2
36
2
86
∘
x = 42.4
