
COMPRESSOR MODELS
Doosan Infracore Portable Power
1293 Glenway Drive
Statesville, N.C. 28625
DoosanPortablePower.com
Book: 22893804 (12-2012) Rev C
T
D
T
ELECTRONIC SERVICE
MANUAL
HP675EWCU
XP750EWCU
HP750EWCU
XP825EWCU

1()
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION1.......ManualDescription
SECTION2.......GeneralInformationAndOperationalTheory
SECTION3.......ServiceTools
SECTION4.......ElectronicSystemsTroubleshooting
Procedures And Techniques
SECTION5.......SystemSchematicDiagrams
SECTION6.......ElectronicComponent Location Drawings
SECTION7.......IndividualCircuitDiagrams
SECTION8.......ElectricalConnector Information
SECTION9.......ElectricalPartsList
SECTION10......AlertsandShutdownsList
SECTION11......RecommendedSpareParts
SECTION 12 Software Information....

2()
SECTION 1
MANUAL DESCRIPTION
This manual contains all of the information concerning the electrical and electronic systems for
the HP750EWCU Family of compressors. It provides all information necessary to service, trou-
bleshoot and order parts for this machine.
It is organized into 12 sections.
Sections 2 -- 4 cover systems operation and troubleshooting procedures.
Sections 5 -- 7 have location diagrams, drawings of specific circuits and systems schematics.
Section 8 has information concerning the electrical connectors used, including removal and re-
placement.
Section 9 contains the parts list with ordering information.
Section 10 contains the list of Alerts and Shutdowns.
Section 11 contains a list of recommended spare parts for servicing.
Section 12 contains software information.

3()
SECTION 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
and
OPERATIONAL THEORY

4()
GENERAL INFORMATION AND OPERATIONAL
THEORY
General
The mid--range machine has an electronic monitor
and control system to provide discharge air pressure
control and engine and package monitor functions.
The system uses the WEDGE controller to perform
these functions. The electrical system connects all the
necessary switches, sensors and transducers to the
WEDGE controller in order for it to perform the monitor
and control functions.
WEDGE Controller
The WEDGE controller is the heart of the machine
monitor and control system. It provides data
collection, alarming and control functions for
compressor operations. It is a microcontroller based
unit with analog and digital inputs and outputs.
The W EDGE controller is attached to the back of the
control panel. The LED annunciators are part of the
front panel of the WEDGE. They can be seen through
the laminate on the front of the control panel.
The WEDGE is attached to the control panel with four
#10 size nuts.
The first function of the WEDGE controller is to scan all
analog and digital inputs at a fixed interval. These
inputs are scanned every 50 milliseconds. The analog
values are then compared against minimum and
maximum v alues and an ALERT or SHUTDOWN is
issued, if a value is out of range. The various ALERTS
and SHUTDOWNS are listed in Section 10 of this
manual.
The second function of the WEDGE controller is
machine discharge pressure control. The WEDGE
monitors the regulation system air pressure and varies
the engine throttle to maintain the setpoint discharge
air pressure. The setpoint pressure is set using the
regulator on the separator tank.
The third function of the WEDGE controller is to
communicate with the diesel engine via the J1939
CAN network. It retrieves diagnostic information over
J1939.

5()
FIGURE 2--1
MID RANGE MACHINE
WEDGE
Controller
CONTROL PANEL SWITCHES
GAUGES
24VDC HEATERS
ENGINE ECM DIAGNOSTIC
INTERFACE
ESTOP SWITCHES
SOLENOID VALVES
SPEED SENSOR
FUEL LEVEL SWITCH
PRESSURE TRANSDUCERS
TEMPERATURE SENSORS
BATTERY STARTING AND
CHARGING SYSTEM
W1
P2,P3
W1
P1
HOURMETER
CONTROL PANEL HARNESS
W1W1

6()
FIGURE 2--2
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
WEDGE TO ENGINE INTERFACE
CUMMINS ENGINE
J1--35
J1--34
J1--1
J1--37
J1--24
CUMMINS
ENGINE
CONTROLLER
J4--46
J4--47
J4--37
J4--39
J4--30
CAN HI
CAN LO
CANSHLD
J1--38
FREQ -- THT +
RANGE = 150 Hz (IDLE) to 375 Hz (Full Speed) AT 24VDC
KEY SWITCH
7()
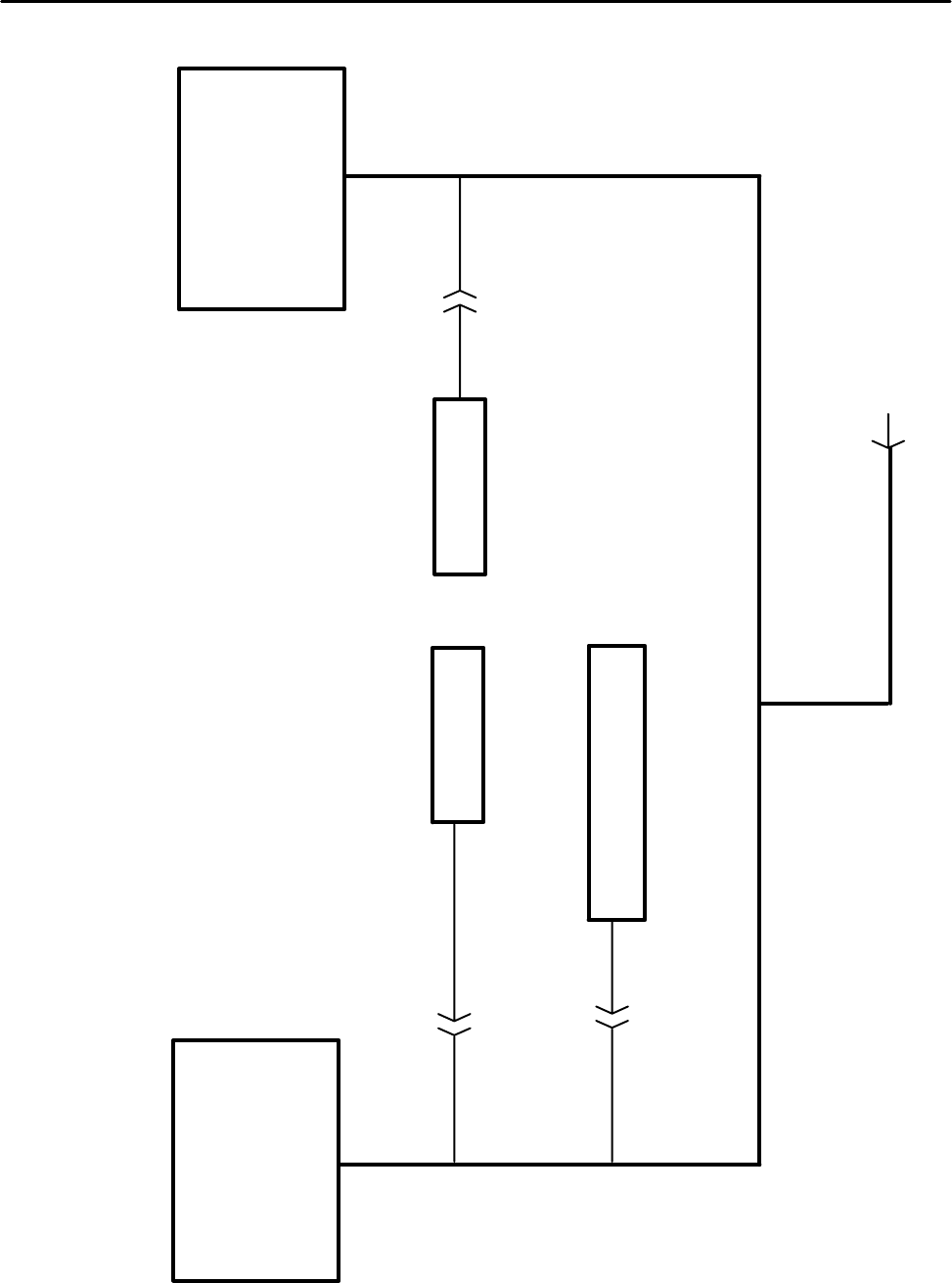
J1939 CAN COMMUNICATIONS SCHEMATIC
ENGINE
CONTROLLER
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
P14
TERMINATOR
TERMINATOR
ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS JACK
J11
TR1
TR2
CAN NODE WITH POWER
P15
P13
FIGURE 2--3

8()
The wedge uses the frequency throttle to communi-
cate with the engine. A s quare wave frequency signal
from 150 Hz to 375 Hz is sent from the WEDGE con-
troller to the engine controller.
The signal is a linear signal from 150 Hz at engine idle
to 375 Hz at maximum run speed.
Figure 2--2 shows the signals between the engine
controller and the WEDGE controller.
Sensors and Transducers
The electronics system contains sensors and trans-
ducers that are used to collect data from the compres-
sor. The temperature is measured by a thermistor.
This device exhibits a change in resistance as the tem-
perature changes. The resistance causes an input
voltage change to the WEDGE controller input and is
interpreted as a temperature change.
The electronics system also uses pressure transduc-
ers to measure compressor pressure changes. These
devices have an output signal of .45 VDC to 4.5 VDC,
corresponding to 0 psi and the maximum measured
psi for a particular device. The maximum pressure
transducer ranges are 100, 225 and 500 psi. The 100,
225 and 500 psi devices are gauge pressure devices.
These transducers are provided with 5 VDC excitation
to power the device. These are three wire devices: ex-
citation, signal and ground.
Digital Inputs and Outputs
The W EDGE controller scans digital inputs such as
switch contacts. These are either “ON” (24VDC) or
“OFF” (0 VDC). These digital inputs are connected to
switches within the package such as the key start
switch, air filter switches and IQ filter switches.
The WEDGE controller provides 24 VDC digital
outputs to control solenoids, start compressor and DC
heaters. These are 24 VDC “ON” and 0 VDC “OFF”.
They are current limited and short circuit protected.
Controller Outputs
The WEDGE controller has three types of outputs: fre-
quency, pulse width modulated (PWM) and 24 VDC
digital (ON /OFF). The frequency output is used as a
throttle signal for the engine.
The WEDGE controller varies the frequency from 150
Hz to 375 Hz, corresponding to idle to maximum
speed. The frequency signal is a 50% duty cycle, 24
VDC, square wave. This throttle signal is used with the
Cummins engine.
The PWM signal is used as a throttle signal for the Cat-
erpillar engine. It has a base frequency of 500 Hz and
the duty cycle varies from 10% to 90%.
Pressure Control
The discharge pressure is controlled by manipulating
the engine speed and compressor inlet valve position.
The inlet valve position is controlled pneumatically and
the engine speed is determined by the WEDGE con-
troller. The WEDGE measures the pneumatic system
regulation pressure and computes an engine throttle
setting. This throttle setting is sent to the engine via the
frequency throttle, PWM or J1939 throttle, depending
on which technique is used. The engine controller will
control engine speed to this throttle setting.
Electronic Engine
The mid--range machine contains an emissions
certified diesel engine. In order to meet the emissions
requirements, the engine has an electronic control
system.
The control system handles all monitor, alarm and
control functions for the engine. The WEDGE control-
ler communicates with the engine controller over the
J1939 CAN network.
The WEDGE controller sends throttle settings to the
engine and receives diagnostic and run time data from
the engine over the J1939 CAN network. A frequency
throttle interface is currently used with the engine.
Figure 2--2 shows the connections between the
WEDGE controller and the engine controller.

9()
J1939 Data Link
The CAN network is a single pair shielded cable
located with the W1 main harness. Figure 2--3 shows
a layout of the CAN harness or “backbone” as it is
referred to. The termination resistors (Terminator) are
important to prevent reflections on the transmission
line and must be in place for the network to function
properly. The shield from the cable is connected to the
machine metal at the WEDGE controller end.
This connection must be properly made with good
metal--to--metal contact between the wire terminal and
the machine metal.
The engine diagnostics connector is located on the left
side of the engine. This is used to connect the engine
manufacturer’s service tools to the CAN network. This
connector also provides 24 VDC to power these
service tools.
Electrical System
The electrical system consists of the wiring harnesses
and associated electrical devices such as relays,
switches, lights, solenoids and alarm horn. There are
two wiring harnesses on the machine. They are as fol-
lows:
22770879 W1 Chassis Main Harness
22784698 Control Panel Wiring Harness
The schematic diagrams show the connections for
these harnesses. Figure 2--1 is a system schematic
showing harness connection with devices and
controllers. Section 8 includes information on
connectors used in the harnesses.
The electrical circuits are protected using ATC style
fuses. A fuse should only be replaced with one of the
same rating. Replacing a fuse with one of a large
rating could lead to harness damage. If a fault occurs
and the circuit does not have the appropriate size fuse,
wires could be burned in the harness and damage
other circuits.

10()
KEY ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS FUNCTION
PT1:
PT1 is a 0--225 (or 0--500 depending upon machine model), psi gauge pressure transducer that measures
discharge air pressure.
PT2:
PT2 is a 0--100 psi gauge pressure transducer that measures regulation system pressure.
U1:
U1 is resistive level detector that measures the fuel level in the fuel tank.
It provides a continuous reading of fuel level. It also has a switch for low fuel level and low fuel shutdown.
These switches connect to WEDGE.
RT1:
RT1 is a 10K ohm Thermistor temperature sensor that measures separator tank temperature.
Its range is --30 to 255_ F.
RT2:
RT2 is a 10K ohm Thermistor temperature sensor that measures airend discharge temperature.
Its range is --30 to 255_F.
K1:
K1 is SPST, 24VDC relay used to activate the engine starter.
K2:
K2 is a SPDT, 24VDC relay used to s witch power.
K3:
K3 is a SPST, 24VDC relay used to power the engine air intake heater.
K4: K4 is a SPDT, 24VDC Relay used to power the IQ system option.

11()
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
OPERATING CONTROLS AND INSTRUMENTS
The operating controls and instruments are arranged on the control panel as shown above. A description of each
panel device is as follows:
1. Hourmeter: Records running time for
maintenance.
2. Compressor Discharge Pressure Gauge:
Indicates pressure in receiver tank.
3. Fuel Level Gauge: Indicates amount of fuel
in tank.
4. Power Switch: Activates systems for
STARTING and STOPPING.
5. Service Air Switch: After warm--up, PUSH.
Provides full air pressure at the service outlet.
Allows unit to warm--up at reduced pressure.
6. Engine Speed Gauge: Indicates engine
speed (RPM)
7. Discharge Air Temp. Gauge: Indicates
airend discharge temperature.
8. Engine Oil Pressure Gauge: Indicates
engine oil pressure.
9. Engine Water Temp Gauge: Indicates
coolant temperature.
10. Voltmeter: Indicates charging system
voltage.
11. Spare: Used for optional accessories.
12. Inlet Heater/Wait to Start Lamp: Indicates
engine manifold pre--heater is energized.
Wait until lamp extinguishes before engaging
starter.

12()
WEDGE DIAGNOSTIC DISPLAY
1 High Compressor Temp: Fault indicator lamp. Indicates shutdown due to high compressor temperature.
2. Low Engine Oil Pressure : Fault indicator lamp. Indicates shutdown due to low engine oil pressure.
3 . High Engine Coolant Temp: Fault indicator lamp. Indicates shutdown due to high engine water temperature.
4 . Low Fuel Level: Fault indicator lamp. Indicates shutdown due to low fuel level. Lamp blinkl warning.
5 . Low Battery Voltage:Alarm indicator lamp. Indicates battery or charging system requirer s ervice.
6 . Low Radiator Coolant Level: Alarm indicator lamp. Indicates engine coolant needs service.

13()
OPERATIONAL INFORMATION FOR LOW PRESSURE MACHINE
Power “ ON” at Control Panel:
1. Key switch signal (24VDC) supplied to engine controller by WEDGE controller
2. Frequency throttle signal OFF
3. Unloader solenoid valve (L2) is closed (de--energized)
Engine Start--up:
When the key is switched to the engine crank position:
1. Unloader solenoid valve (L2) is closed (de--energized).
2. Key switch signal (24VDC) is supplied to engine controller.
3. K1 auxiliary start relay is energized.
4. Run/Start solenoid valve (L1) is opened (energized).
Run/start solenoid stays open and unloader solenoid valve stays closed for 10 seconds after the key is
released if the engine does not start.
When the engine speed reaches 600 RPM (engine start declared):
1. Engine speed is set to 1500 RPM.
When the engine speed reaches 1450 RPM:
1. Unloader solenoid valve is opened (energized).(L2)
2. Run/Start solenoid valve is closed (de--energized). (L1)
When the separator tank pressure reaches 50 psi:
1. Run/Start solenoid valve is opened (energized). ( L1)
After 5 seconds:
1. Engine speed is set to idle (1200 RPM if air end discharge temperature is approximately 150 degrees
F or (if J1939 CAN is functioning) if the engine coolant is 100 degrees F. Otherwise, the engine idle
stays at 1500 RPM.
Loading:
When the “Service Air” switch is pushed:
1. Engine speed is set to 2000 RPM
When engine speed reaches 1900 RPM:
1. Run/Start solenoid valve is closed (de--energized).
After 2 seconds and if the regulation system pressure is 4 psi or greater:
1. Compressor pressure control is engaged.

14()
READING AND SETTING THE DISPLAY
UNITS
The WEDGE has four choices for display units:
_F, PSI
_C, Bars
_C, kPa
_C, Kg/cm2
To determine which units the WEDGE has been configured for:
1. With the machine power off (Key turned OFF)
2. Press and hold the “Service Air” Switch
3. Turn the key switch directly to the crank position.
4. Hold these switch positions until the 4 digit LED display on the WEDGE goes blank.
5. Release “Service Air” switch, release key switch to “ON”.
Units will be displayed for 2 seconds after which the current selection will be displayed as:
_F, PSI will be displayed as “PSI”
_C, Bars will be displayed as “bAr”
_C, kPa will be displayed as “HPA”
_C, Kg/cm2 will be displayed as “H9C”
To change the units setting:
1. With the WEDGE showing the current setting, press and release the “Service Air” switch until the desired setting
appears on the display.
2. Once it appears, do not release the “Service Air” switch. Hold it in the ON position until the WEDGE restarts.
This will select units selection that was displayed.
3. Release the “Service Air” switch. The compressor is ready to start.

15()
WEDGE SERVICE DIAGNOSTICS
The WEDGE controller provides a diagnostic capability that allows various internal parameters to be viewed on
the 4--digit LED display. These can be accessed with the machine stopped or while it is operating. If the machine
is stopped, the “Service Air” switch on the control panel is used to toggle through the list of parameters. If the ma-
chine is operating, the “ Start” position of the key switch is used. To view the parameters, toggle the switch or key
and a number (2--15) will appear on the LED display. After 3 seconds, it will extinguish and the parameter will be
displayed. The toggle only works in the ascending order direction, but it will wrap around and start over.
Display Parameter Remarks
2 RPM From Engine Flywheel Sensor
3 Engine RPM Filtered RPM Value
4 Reg. Sys. Pressure PSI
5 Sep. Tank Pressure PSI
6 Discharge Temperature Deg F
7 Sep. Tank Temperature Deg F
8 Engine Target RPM Wedge Signal to Engine
9 Machine Type *
10 Engine Coolant Temp. From CAN, Deg F
11 Engine Oil Temp. From CAN, Deg F
12 Engine Oil Pressure From CAN, PSI
13 Intake Manifold Temp. From CAN, Deg F
14 RPM From CAN
15 Fault Code List Cummins/CAT codes
16 Throttle Position
17 Boost Pressure
18 Engine Hours
19 Load at Speed Percent
20 Set Machine ID

16()
ENTERING MACHINE ID FOR WEDGE CONTROL SYSTEMS with V1.60 or Greater Software
For machines with the WEDGE controller mounted inside the control panel/instrument panel box, the “Service
Air” switch is used to enter the machine ID. Disconnect the fuel level gauge (located in the fuel tank) before
starting the process and reconnect once the process is completed.
For machines with the WEDGE controller mounted in the engine compartment, the rocker s witch beside the
WEDGE is used to enter the machine ID.
For the instructions below, the “Service Air” or rocker s witch will be referred to as the “data input switch”.
1. Examine the machine data plate to confirm the machine model.
Using the machine model and the machine models list on page 2 of this document, locate the proper
machine ID.
2. Turn power to the ”ON” position. Machine must not be operating.
3. Toggle the data input switch twice and the number “2” will appear on the WEDGE 4--digit LED display.
Continue to toggle the switch until the number “9” is reached. Read the machine ID on the
display, if it matches the proper machine ID in Step 1, stop. If not, proceed to step 4.
4. Continue to toggle the switch until number “19” is reached. Push and hold the data input switch and the
number “20” will appear. Continue to hold the switch. After 1 second, the current machine ID will appear in
the display. Continue to hold for 9 more seconds and a blinking “--” will appear. Release the switch.
5. Toggle the data input switch, the display will show “0”. Toggle the data input switch until the proper machine
ID appears on the display, then stop the toggle sequence.
6. Wait until the controller performs a reset function (or power up) (approximately 10 s econds). At reset, the
controller display first goes blank, then all annunciator LED’s light, the 4--digit LED display shows all 8’s,
the display then shows the installed software version and finally the display goes blank and the engine oil
pressure and alternator LED begin flashing. At this point the controller has stored the machine ID selected
in step 5.
7. Using the data input switch, toggle to service diagnostic number “9”.
The number “9” will appear for 1 second and then the machine ID will appear. The ID should be the same
as the one entered in steps 4--6. If not, go back to step 4 and enter the ID again.

17()
ESA Models/Wedge Machine
ID
Models
Machine ID
7/120,9/110. 10/105, 14/85 7
7/170. 10/125.14/115 8
9/230,9/270,9/300. 12/235 5
17/235,21/215 6
MSA Models/Wedge Machine
ID
Model Machine
ID
P425WJD, XP375 WJD, HP375WJD 7
VHP300WJD
P600WJD, HP450WJD, VHP400WJD 8
XP1060WCU, HP935WCU, MHP825WCU 5
VHP750WCU
XHP750WCU 6
MHP825WCAT, VHP750WCAT 2
XP1060HACAT,XP950HACAT
SHP825WCAT, XHP750WCAT. XHP650WCAT 3
HP1300CWCU,HP1600CWCU 0
XHP1170WCU 1
XHP1070AWCAT, XHP1170WCAT. XHP1170SCAT 4
HP1600WCAT 9
HP675EWCU, XP750EWCU, HP750EWCU, 10
XP825EWCU
SIRC Models/Wedge Machine
ID
Models
Machine ID
P1060WCAT, XP950WCAT, HP935WCAT 2
MHP825WCAT .VHP750WCAT
XHP750WCAT 3

18()
SECTION 3
SERVICE TOOLS

19()
SERVICE TOOLS
Service Tools
The following special tools are recommended to perform service procedures in this manual. The tools can
be purchased from Doosan Portable Power or other sources listed.
Tool Tool Description
22216691 Digital Multimeter (Fluke 87)
Used to measure electrical circuits; Volts, amps, ohms
54729660 Packard Weather--Pack Terminal Removal Tool
Used to repair Packard Electric Weather--Pack Connectors
54699632 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool (Blue)
Used to repair Deutsch connectors
54699640 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool (Red)
Used to repair Deutsch connectors
54699624 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool (Yellow)\
Used to repair Deutsch connectors
22216667 Deutsch Terminal Crimp Tool (HDT--48--00)
Used to crimp Deutsch connector terminals
54729710 Electrical Contact Cleaner
Used to clean electrical contacts and connectors
54729728 PDA Service Tool
Used to load software & extract service and fault logs
54699616 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool
Used to repair Deutsch connectors
54749544 RTD Simulator Plug
Used to test RTD circuits
54749551 Thermistor Simulator Plug
Used to test thermistor circuits for Intellisys controller systems
22073878 Thermistor Simulator Plug
Used to test thermistor circuits for WEDGE controller systems
54749635 Connector R epair Kit
Used to make connector repairs for Deutsch and Packard Electric Connectors
54699657 Deutsch Terminal removal Tool
Used to repair Deutsch connectors
54749643 Packard Metri--Pack Terminal Removal Tool
Used to repair Packard Electric onnectors

20()
22168868 Pressure Transducer Simulator
Used to test pressure transducer circuits
22147540 Test Adapter Kit Test adapters for various connectors to be
Used when making electrical measurements
22146393 Removal Tool Kit Assortment of most used Deutsch removal tools
22216675 Deutsch Crimp Tool (DTT --20--00)
Used to crimp Deutsch connector terminals
22216683 Packard Electric Crimp Tool (12155975)
Crimps 150 and 280 series pins
22255947 Packard Electric Crimp Tool (12039500)
Crimps 150 series pull to seat pins
22216709 Fluke Test Lead Set (TL20)
Contains needle probes, alligator clips, test leads
heat shrink tubing that are used on harnesses
22216725 Fluke Insulation Piercing Probe (AC--89)
Used to connect to a wire for measurements
22216733 Fluke Meter Case (C25)
Case for Fluke 87 meter including storage for test leads and probes
54740675 RS232 Heavy Duty Serial Cable
Connects lap top computer or PDA Service Tool
to WEDGE or Intellisys controller
22252969 Wire Terminal Kit
Contains a selection of terminals with
corresponding heat shrink tubing that are used on harnesses
22281588 Connector Wrench
22282107 5/32 “T” hex screwdriver wrench
22282172 1/4” Flex Shaft Nutdriver
Used to remove ECM connector on John Deere engines
22252993 WEDGE Connector Kit
Includes the 40--pin connector housing and pins for the harness connector
22253009 CAN Communications Adapter
Converts RS232 to J1939 CAN, used with lap top computer
or PDA Service Tool.
22253017 Adhesive Heat Shrink Assortment
Selection of most used heat shrink sizes

21()
22221303 Service Tool Kit
Kit consists of the following P/N’s: 22216691 22216667
22216675 22216683 54729660 54749643 54699657
22146393 22147540 22073878 54749635 22168868
22216709 22216725 22216733 54740675
22254775 ATC Fuse Assorlment Kit
Kit contains 5, 7--1/2, 10, 15,20,25, and 30 Amp fuses
22254734 Packard Crimp Tool (12014254) Crimps Sealed
Weather Pack Connector pins

22()
Tool No. Tool Description Tool Illustration
22216691
Digital Multimeter
54729660 Weather--Pack Terminal Removal Tool
54699632 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool (Blue)
54699640 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool (Red)
54699624 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool (Yellow)
22216667 Deutsch Crimp Tool

23()
54729710
Electrical Contact Cleaner
54729728 Virtual Technician Service Tool Kit
54699616 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool
54749544 RTD Simulator Plug
22073878 Thermistor Plug
54749635 Connector Repair kit
54699657 Deutsch Terminal Removal Tool

24()
54749643
Packard Metri--Pack Removal Tool
22168868 Pressure Transducer Simulator
22147540 Test Adapter Kit
22146393 Removal Tool Kit
22216675 Deutsch Crimp Tool
22216683 Packard Electric Crimp Tool

25()
22216709
Fluke Test Lead Set
22216725 Fluke Insulation Piercing Probe
(single probe)
22216733 Fluke Meter Case
54740675 RS232 Serial Cable
22252969 Wire Terminal Kit

26()
22281588
22282107
Connector Wrenches
22282172 1/4’’ Flex Shaft Nutdriver
22252993 WEDGE Connector Kit
22253009 CAN Communications Adapter
22253017 Adhesive Heat Shrink Assortment

27()
22255947
Packard Electric Crimp Tool
22254734 Packard Electric Crimp Tool

28()
SECTION 4
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS TROUBLESHOOTING
PROCEDURES AND TECHNIQUES

29()
General
A thorough analysis of the problem is the key to successful troubleshooting. The more information known
about a problem, the faster and easier the problem can be solved.
Troubleshooting charts are included to act as a guide to the troubleshooting process. They are organized so
the easiest and most logical things are performed first. It is not possible to include all the solutions to problems
that can occur or list all possible problems. The charts are designed to stimulate a thinking process that will
lead to solution of the problem.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps
• Collect all facts concerning the problem
• Analyze the problem thoroughly
• Relate the symptoms to the basic electrical / electronic systems and components
• Consider any recent repairs that could relate to the problem
• Double c heck before replacing components
• Review the controller fault log for clues as to the problem
• Determine the cause of the problem and make a thorough repair

30()
MEASURING VOLTAGE, RESISTANCE,
FREQUENCY AND DUTY CYCLE
General Measuring Guidlines:
Since the electrical system uses sealed connectors and splices, access of test points can be difficult. It is rec-
ommended that a test probe kit be used to access the signals to prevent damage to wires and connectors.
Back probing connectors and insulation piercing test probes can cause damage that can cause future failures.
Measuring Voltage:
A digital voltmeter is recommended to make measurements. Voltage measurements are made by connecting
the R ED + lead to the desired signal and the BLACK lead to the common. The test lead connections must be
secure or incorrect readings will result. Use circuit common for the Black lead, not chassis ground or other
metal connection. Circuit common will be any of the BROWN wires or battery negative can be used.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
DO NOT USE MACHINE FRAME, SHEET METAL, PIPING OR OTHER METAL COM-
PONENTS AS COMMON OR GROUND WHEN MAKING VOLTAGE OR FREQUENCY
MEASUREMENTS.
Measuring Resistance:
Extra care must be taken when making resistance measurements. Test probe connections are crucial to cor-
rect readings. Ensure the test probe makes a solid connection with the wire(s) or connector pin(s) under test.
the test probe kit may help with these types of measurements. Make sure system power is turned OFF while
making resistance measurements.
Measuring Frequency:
Frequency is measured in the same manner as voltage, but the meter is set for “HZ” or frequency. Good con-
nections are important or false readings will occur.
Measuring Duty Cycle:
To measure duty cycle, setup the meter as if measuring frequency or voltage. Select the “%” or duty cycle
function and take the measurements. As of the date of this writing, Fluke is the only known digital voltmeter
that has the duty cycle feature. The Fluke Model 87 Digital Meter has the duty cycle function.

31()
TROUBLE SHOOTING FLOW CHART
B
B
Control panel key is turned to “ON” position,
WEDGE controller annunciator lamps and 4
digit LED display do not come on
Check F1 fuse
Check operation of switch S1
Check wiring from S1 to WEDGE controller
Check battery voltage, ensure battery dis-
connect switch is turned ON
WEDGE controller annunciator lamps & 4
digit LED display initialize OK but alternator
lamp and engine oil pressure lamps do not
blink.
J1939 CAN communications not working –
Check for 24VDC key switch at engine, CAN
network wiring problem
Ensure 24VDC power to engine ECM
Check connector pins
Engine cranks but will not start
Ensure key switch (24VDC) at engine
Frozen fuel cooler or associated piping
Estop button pressed (ESA units) or
Estop jumpers not making connection
Clear active engine fault code
Engine does not crank when key turned to
crank position
Check switch S1
Check relay K1
Check starter solenoid
Check starter motor
Check WEDGE output to K1 relay
Check battery voltage
B
B
Compressor f ails to load
when “Service Air” switch pressed
Check Run/Start valve operation
Verify frequency throttle signal at engine
Check “Service Air” switch operation
32
COMPRESSOR FAULT CODES
DESCRIPTION AND TROUBLESHOOTING
Following, are the descriptions of the COMPRESSOR fault codes. These are indicated when the
“COMPRESSOR MALFUNCTION” lamp is illuminated. The compressor malfunction lamp is
shown on the control panel picture in Section 2 of this manual. It is indicated by Item number 9.
The engine fault codes are indicated by the “ENGINE MALFUNCTION” lamp that is located under
the “COMPRESSOR MALFUNCTION” lamp.
The engine fault codes are listed in Section 10 of this manual.
Be sure to determine which malfunction lamp is illuminated before beginning the troubleshooting
process.

33
COMPRESSOR CODE 1
Engine Speed Less Than 800 RPM
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an engine speed less than 800 RPM for 30 seconds.
Effect:
Code 1 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 1
Action Result
Check engine fault codes for an engine
shutdown. Check for engine fuel system
restriction (filter).

34
COMPRESSOR CODE 2
Engine Speed Greater Than the RPM limit.
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an engine speed greater than 2100 RPM for 30
seconds.
Effect:
Code 2 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 2
Action Result
Check engine fault codes for an engine
shutdown.

35
COMPRESSOR CODE 3
Engine Crank Time Exceeded
Explanation:
The engine crank time has exceeded 15 seconds.
Effect:
Code 3 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 3
Action Result
Crank engine for less than 15 seconds.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
36
COMPRESSOR CODE 5
Engine Oil Temperature
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an engine oil temperature greater than 252° F.
Effect:
Code 5 is an ALERT condition and will not halt machine operation.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 5
Action
Result
Step1:
Refer to the engine manufacturer’s service manual for
instructions.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
37
COMPRESSOR CODE 6
Engine Intake Manifold Temperature
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an engine intake manifold temperature greater than
180° F.
Effect:
Code 6 is an ALERT condition and will not halt machine operation.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 6
Action
Result
Step1:
Refer to the engine manufacturer’s service manual for
instructions.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
38
COMPRESSOR CODE 8
Water in Fuel
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received a water in fuel indication from the engine.
Effect:
Code 8 is an ALERT condition and will not halt machine operation.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 8
Action
Result
Step1:
Check the machine fuel system and engine fuel filters.
Step 2:
Refer to the engine manufacturer’s service manual for
instructions.
Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
39
COMPRESSOR CODE 10
Engine Not Responding To Throttle Command
Explanation:
The engine has not responded to a request from the WEDGE for engine speed
change during engine start. This ALERT will only occur during the idle speed
time, right after engine start.
Effect:
Code 10 is an ALERT condition and will not shutdown the machine. The
machine will not perform properly due to the low speed condition.
Throttle Circuits:
C
A
T
E
N
G
I
N
E
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
L
E
R
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
PWM
Throttle
J2-10 J1-38
Blu
W131
E
N
G
I
N
E
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
L
E
R
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
Analog
Throttle
J50-F2 J1-13
Blu
W054
Circuit Description:
J2-66
CUMMINS ENGINE
CONTROLLER
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
J40-30 W073 Freq Throttle Blue J1-38

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
40
As shown in the circuits above, the WEDGE provides three types of throttle
outputs: frequency, PWM and analog.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 10
Action
Result
Step1:
Measure the throttle signal at the engine connector.
If signal not present, check wiring
and verify throttle output at
WEDGE.
Step 2:
Engine may not be able to fuel properly due to restricted fuel
filters
Replace fuel filter (s)
Step 3:
Verify correct machine ID is installed.
Step 4:
Check connector pins at WEDGE controller and connector at
engine controller for corrosion.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
41
COMPRESSOR CODE 11
Too Many Start Attempts During Auto Start
Explanation:
The WEDGE has made three attempts to start the machine as commanded by
the Auto Start Stop controller. The machine failed to start.
Effect:
Code 11 is a SHUTDOWN condition and will shutdown the machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 11
Action
Result
Step1:
Check the machine fuel system and engine fuel filters.
Step 2:
Check the condition of the machine batteries.
Step 3:
Cycle machine power, activate the Auto Start input so the
machine will make another start attempt. Machine will go
through 3 crank cycles to attempt start before a Code 11 is
issued.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
42
COMPRESSOR CODE 29
Engine shut itself down: reason unknown
Explanation:
The engine has shut down. The WEDGE did not shut down the engine.
Effect:
Code 29 is a SHUTDOWN condition and will shutdown the machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 29
Action
Result
Step1:
Check the machine fuel system and engine fuel filters. Check
for loose fittings in the fuel piping that could allow air to be
drawn into the fuel system.
Step 2:
Verify the throttle signal from the WEDGE is continuously
supplied to the engine.
A quick drop in the throttle signal
could cause the engine to stop
Step 3:
Verify battery + and – connections to the engine controller,
inspect harness connections and measure voltage drop at
engine ECM.
Step 4:
In the case of the (John Deere) engine, check the
connections for the crank sensor which is mounted at the front
of the engine. Loose pin connections in the connector will
cause code 29.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
43
COMPRESSOR CODE 31
Low Air End Oil Pressure
Explanation:
The WEDGE received a closed contact from pressure switch S6, located
in the air end on the machine. This indicates a low oil pressure in the
air end.
Effect:
Code 31 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine. The
cause of the low air end oil pressure must be repaired to continue machine
operation.
S6 Pressure Switch Circuit:
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
J1-21
S9
Blu
Circuit Description:
Switch S6 is a 12 psi, normally open pressure switch. If the pressure falls below
12 psi, the switch will close, indicating to the WEDGE controller a low air end oil
pressure.
Component Location:
S6 is located in the back of the air end.
S6

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
44
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 31
Action
Result
Step1:
Check the air end oil pressure with a mechanical gauge.
If > 12 psi, replace S6
If not, there is a harness or
WEDGE problem.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
45
COMPRESSOR CODE 32
RT2, Discharge Temperature Sensor Fault
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an out of limits reading from the RT2 temperature
sensor. This reading could be on the high or low end of the range. It is
out of the normal range for temperature measurement.
Effect:
Code 32 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine.
RT2 Temperature Sensor Circuit:
R
T
2
T
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
S
e
n
s
o
r
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
1
2
J1-5
J1-6
Yel
Brn
W066
W025
Circuit Description:
The thermistor temperature sensor connects to the WEDGE controller as shown
in the schematic above. The temperature range of RT2 is –30 to 255 degrees F.
The thermistor is a 10K ohm device.
Component Location:
RT2 thermistor is located in the airend discharge pipe.
W003
W
00
4

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
46
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 32
Action
Result
Step1:
Substitute the thermistor simulator (PN # 22073878) for RT2
Use the WEDGE service diagnostics to read the value for RT2
It should be approximately 32 degrees F.
Should read approx. 32 Deg F
If not, there is a harness or
WEDGE problem.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
47
COMPRESSOR CODE 33
PT1 Pressure Transducer Sensor Fault
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an out of limits reading from the PT1 pressure
transducer. This reading could be on the high or low end of the range. It is
out of the normal range for pressure.
Effect:
Code 33 is an ALERT condition and will not shutdown the machine. If the
Transducer is defective, the machine could shutdown due to an out of
range pressure
PT1Pressure Transducer Circuit:
P
T
1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
T
r
a
n
s
d
u
c
e
r
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
Gnd
Sig
+5 VDC
A
C
B
J1-8
J1-7
Brn
Orn
Vio
W099
W098
W101
J1-10
Circuit Description:
The pressure transducer is a 3-wire device that connects to the WEDGE
controller as shown in the schematic above. The violet wire (W013) is the 5 VDC
excitation supply. This is spliced in the harness near the breakout for the
harness branch that goes to the separator tank. The “sig” wire is the output
signal that has a range o .45 to 4.5 volts DC. The pressure range of this
transducer is 0 – 225 psig.
Component Location:
PT1 pressure transducer is located in the top of the separator tank.
W
0
11
W
00
7
W
0
1
3

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
48
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 33
Action
Result
Step1:
Substitute the pressure transducer simulator (PN # 22168868)
for PT1. Use the WEDGE service diagnostics to read the value
for PT1. It should be approximately 30 – 50 psi.
Should read 30 – 50 psi.
If not, there is a harness or
WEDGE problem.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
49
COMPRESSOR CODE 34
Separator Tank Pressure Greater Than 20 psi at Crank
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received a pressure from PT1 that is greater than 20 psi at
The time of engine crank.
Effect:
Code 34 is a shutdown condition and will not allow the engine to crank. Once
The separator tank bleeds down below 20 psi, engine crank will be allowed.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
50
COMPRESSOR CODE 35
Machine Over Pressure Condition
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received a pressure from PT1 that is greater than the limit.
Effect:
Code 35 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine. The separator
tank high pressure has been exceeded.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 35
Action Result
Verify PT1 pressure transducer is reading
correctly.
The pressure simulator (PN#2216868) can
be substituted for PT1. This will verify
operation of harness and WEDGE controller.
Using the simulator, PT1 on the WEDGE
Diagnostics should read 30-50 psi.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
51
COMPRESSOR CODE 50
Separator Tank Temperature
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received a separator tank temperature from RT1 that is
greater than 247 degrees F.
Effect:
Code 50 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 50
Action
Result
Step1:
Check for package air inlet restrictions.
Step 2:
Check for dirty or clogged coolers.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
52
COMPRESSOR CODE 51
Machine ID Not Valid
Explanation:
The WEDGE has not received a reading from the machine ID.
Effect:
Code 51 is a shutdown condition and since a valid machine ID has not been
received the machine will shutdown.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
53
COMPRESSOR CODE 53
RT1, Separator Tank Sensor Fault
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an out of limits reading from the RT1 temperature
sensor. This reading could be on the high or low end of the range. It is
out of the normal range for temperature measurement.
Effect:
Code 53 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine.
RT1 Temperature Sensor Circuit:
R
T
1
T
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
S
e
n
s
o
r
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
1
2
J1-4
J1-6
Yel
Brn
W067
W024
Circuit Description:
The thermistor temperature sensor connects to the WEDGE controller as shown
in the schematic above. The temperature range of RT1 is –30 to 255 degrees F.
The thermistor is a 10K ohm device.
Component Location:
RT1 thermistor is located in the side of the separator tank.
W002
W006

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
54
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 53
Action
Result
Step1:
Substitute the thermistor simulator (PN # 22073878) for RT1
Use the WEDGE service diagnostics to read the value for RT1
It should be approximately 32 degrees F.
Should read approx. 32 Deg F
If not, there is a harness or
WEDGE problem.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
55
COMPRESSOR CODE 54
PT2 Regulation System Sensor Fault
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an out of limits reading from the PT2 pressure
transducer. This reading could be on the high or low end of the range. It is
out of the normal range for pressure.
Effect:
Code 54 is an ALERT condition and will not shutdown the machine.
PT2 Pressure Transducer Circuit:
P
T
2
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
T
r
a
n
s
d
u
c
e
r
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
Gnd
Sig
+5 VDC
A
C
B
J1-8
J1-9
Brn
Orn
Vio
W21
W100
W101
J1-10
Circuit Description:
The pressure transducer is a 3-wire device that connects to the WEDGE
controller as shown in the schematic above. The violet wire (W014) is the 5 VDC
excitation supply. This is spliced in the harness near the breakout for the
harness branch that goes to the separator tank. The “sig” wire is the output
signal that has a range o .45 to 4.5 volts DC. The pressure range of this
transducer is 0 – 100 psig.
Component Location:
PT2 pressure transducer is located in the pneumatic circuit near the compressor
inlet valve.
W
0
12
W
009
W
0
14

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
56
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 54
Action
Result
Step1:
Substitute the pressure transducer simulator (PN # 22168868)
for PT2. Use the WEDGE service diagnostics to read the value
for PT2. It should be approximately 30 – 50 psi.
Should read 30 – 50 psi.
If not, there is a harness or
WEDGE problem.

57
COMPRESSOR CODE 55
Estop Button
Explanation:
The WEDGE has received an indication that the emergency stop button has
been pressed.
Effect:
Code 55 is a shutdown condition and will shutdown the machine. If the machine
Is in the cranking mode when estop is pressed, the starter will be disengaged
simultaneously with engine key switch signal turn off.
Emergency Stop Button Circuit:
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
CUMMINS
ENGINE
CONTROLLER
S4
J1-28
J1-24
K1
J2-38
2
34
1
Yel
Vio
J1-22
Vio
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
CAT
ENGINE
CONTROLLER
S4
J1-28
J1-24
K1
J2-26
2
34
1
Yel
Vio
J1-22 Vio
S7
S7
J2-70
Pnk
Pnk
1
2
Pnk
Pnk
J4-39
1
2
3
4

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
58
Circuit Description:
The estop button is in series with the engine key switch signal and the auxiliary
start relay, K1. Pressing the button opens both of these circuits simultaneously.
The WEDGE reads a sense input that is connected to the estop button to
determine if the estop button is pressed.
Component Location:
The estop button is located above the machine control panel on the front of the
machine.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 55
Action
Result
Step1:
If the estop button is installed, determine if it is pressed.
Release the estop button to
operate the machine.
Step 2:
If the estop button is not installed, a jumper plug will be
installed in the harness at the connection point for the estop
button, P8.
Verify the jumper plug is functional
Step 3:
Perform a continuity check of the harness wires from the
WEDGE through the jumper plug to the engine connector.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
59
COMPRESSOR CODE 56
Minimum Pressure Not Met
Explanation:
The separator tank has not reached 50 psi within 20 seconds from time engine
starts.
Effect:
Code 56 is an ALERT condition and will not halt machine operation.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 56
Action
Result
Step1:
Check air piping system for restriction.
Step 2:
Verify engine speed has increased to full speed when Service
Air switch is pressed.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
60
COMPRESSOR CODE 70
Serial Communications
Explanation:
The WEDGE controller cannot communicate with an external computer over the
RS232 serial link.
Effect:
This code can only occur when a laptop computer or PDA Service Tool is
Connected to the WEDGE. The WEDGE may otherwise be functional and
This event may not be mission disabling.
RS232 Communications Circuit:
J
5
R
S
2
3
2
C
o
n
n
e
c
t
o
r
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
J5-B
J5-A
J1-33
J1-32
TXD
RXD
Circuit Description:
The RS232 serial communications link is used for re-programming the WEDGE controller and is
the communications port used with the PDA Service Tool. The J10 connector contains the
RS232 port. It is normally located very close to the WEDGE. There are two signals associated
with the RS232, TXD and RXD. TXD is the transmit signal and RXD is the received signal.
Component Location:
The J10 harness connector is located near the WEDGE controller.
J
1
0
-B
J10-
A
J10

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
61
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 70
Action
Result
Step1:
If the current RS232 device (laptop computer, etc.) will not
communicate with the WEDGE, substitute another RS232
device. Note: The second device must have proper software
loaded to communicate with the WEDGE.
If second device will not
communicate with WEDGE,
replace the WEDGE

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
62
COMPRESSOR CODE 71
CAN Communications
Explanation:
The WEDGE controller cannot communicate with the engine controller. The
J1939 CAN (Controller Area Network) broadcast of engine parameters cannot
be received.
Effect:
The WEDGE will not be able to display engine parameters using the diagnostic
Display function. The compressor will continue to operate since Code 71 is an
ALERT condition.
CAN Communications Circuit:
C
U
M
M
I
N
S
E
N
G
I
N
E
C
O
NT
R
O
L
L
E
R
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
CANH
CANL
SHLD
J2-46
J2-37
J2-36
J1-35
J1-34
J1-1
Yel
Grn
Gry
W151
W152
W199
C
AT
E
N
G
I
N
E
C
O
NT
R
O
L
L
E
R
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
CANH
CANL
SHLD
J2-17
J2-18
J2-16
J1-35
J1-34
J1-1
Yel
Grn
Gry
W151
W152
W150
J4-46 W150
J4-47
J4-37 W154
J2-50
J2-34
J2-42

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
63
J
o
h
n
D
e
e
r
e
E
N
G
I
N
E
C
O
NT
R
O
L
L
E
R
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
CANH
CANL
SHLD
J50-G1
J50-F1
J1-35
J1-34
J1-1
Yel
Grn
Gry
Circuit Description:
The CANH, CANL and SHLD wires are a cable that is located in the main harness. CANH refers
to CAN HI and CANL refers to CAN LO and SHLD is the shield of the CAN cable. This is the
cable that carries the communications between the engine and WEDGE controller and any other
devices that are connected to the CAN cable. This cable is also referred to as the CAN Network
since it may have multiple devices connected to it.
The CAN network has two terminating resistors, one located near the engine controller and one
near the WEDGE controller. The value of each of these resistors is 120 ohms. They are
connected in parallel, as shown below, across the network. The resistors are mounted in a
special Deutsch connector.
CUMMINS
ENGINE
CONTROLLER
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
R4
R5
CANH
CANL
Component Location:
The Cummins engine controller is located on the left side of the engine. Connector J4 is located
on the left side of the controller and is the OEM connector. The machine harness (P4) plugs into
the J4 connector. The CAT controller is located on the left side of the engine. The harness P4
connector plugs into the CAT J61 customer connector located near the controller.
The WEDGE controller is mounted to the machine control panel on the back side. Resistor TR2
is stubbed out of the harness near the engine controller and resistor TR1 is stubbed out of the
harness near the WEDGE controller.
TR2
TR1

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
64
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 71
Action Result
Step 1:
Verify P1 harness connector pins 34, 35, and 1 are firmly seated into
The connector at the WEDGE controller.
Step 2:
Verify P4 harness connector pins 46, 47, and 37 for Cummins engine
or pins 50, 34, and 42 for CAT engine are firmly seated into the
connector at the engine electronic controller.
Step 3:
Setup the digital multimeter to read ohms. (Refer to the section in this
manual on how to use the multimeter). Disconnect P1 harness
connector from the WEDGE controller. If the engine is a Cummins,
disconnect the P4 harness connector from the engine controller.
If the engine is a CAT engine, leave P2 connected to the engine
Controller.
Connect one of the multimeter test leads to P1-34 and the other test
Lead to P1-35.
Meter should read
approximately 60 ohms. If so,
go to Step 5. If not, go to Step
4.
Step 4:
If you did not get the results of Step 3, there is a problem with the wiring
harness. This problem could be a defective splice, broken wire or
defective wire connection at a pin. The CANH and CANL wires should
be tested for continuity from P1 to P2. The resistor stub outs should be
tested for continuity.
Make harness repairs as
necessary.
Step 5:
Setup the multimeter to read DC volts. (Refer to the section in this
manual on how to use the multimeter). The harness should be
connected to the engine controller and the WEDGE controller.
Turn the machine power to the “ON” position, but do not start the
engine. Using insulation piercing probes (P/N 22216725),
connect the red multimeter lead to P1-34 wire and connect the black
multimeter lead to the battery negative post or one of the brown wires
on the back of the control panel.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
65
Disconnect the test lead from P1-34 wire and connect to P1-35 wire.
Multimeter should read
approximately 2.5 volts DC.
Multimeter should read
approximately 2.5 volts DC.
If 2.5 volts cannot be read,
replace WEDGE controller. If
WEDGE controller is OK,
harness should be checked as
outlined in Step 4.

Book 22893804 (8-31-06) Rev. A
66
COMPRESSOR CODE 73
Auto Start Stop Controller Communications Failure
Explanation:
The WEDGE has not been able to communicate with the Auto Start Stop
controller for 17 seconds. A communications failure is determined.
Effect:
Code 73 is an ALERT condition and will not stop the machine. The Auto Start
system may not function properly due to communications failure.
TROUBLESHOOTING STEPS
Code 73
Action
Result
Step1:
If CAN communications is OK with the engine, check the CAN-
power stub connection for the Auto Start module. If CAN with
the engine is not working, check CAN wiring in harness.
Step 2:
Verify the Auto Start controller has power and ground.
Step 3:
Replace the Auto Start module.

67()
SECTION 5
SYSTEM SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS






72()
SECTION 6
ELECTRONIC COMPONENT
LOCATION DRAWINGS

73()
HARNESS CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
J1: Located on back of WEDGE controller
J4: 50 pin connector located on engine electronic controller
P5: 4 pin connector located on engine electronic controller
P13: 3 pin connector for termination resistor on CAN backbone near Engine electronic controller
J11: 9 pin connector for Cummins datalink service, located near engine controller
P15: 3 pin connector for termination resistor on CAN backbone nearWEDGE controller
P7: 4 pin connector for IQ System option located inside instrument panel
J10: 9 pin connector for RS232 communications, located behind control panel
P14: 6 pin CAN buss acc. option located inside front door on left side

74()
SECTION 7
INDIVIDUAL CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS

75()
J1--28
YEL
K1
STARTER
B1
24VDC
M
S
B+
BRN
YEL
-- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
CHART A1
ENGINE START CIRCUIT
P1--28
WEDGE
W070 Red--Yel
W076
W102
1
2
W071 RED
V1.5
W044
Estop
or
Jumper
W171
Yel

76()
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The WEDGE drives the engine starter through the auxiliary start
relay, K1.
K1 is mounted on the lifting bail near the engine.
K1 has a single set of contacts that connect to the starter solenoid.
The control signal leaving the WEDGE on J1--28 passes through the
W1 harness and through a jumper plug. The jumper plug is replaced
with an ESTOP switch for ESA versions.
If the starter will not engage during a crank cycle, check the voltage
at the coil of K1 during the crank cycle. It should be 14--22VDC. If
voltage is not at K1, check for voltage back through the ESTOP
jumper and to the WEDGE.
If voltage is at K1 coil, verify voltage is sent to the starter solenoid
by K1 contact.
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
Voltage available at the starter solenoid during a no--crank condition
indicates a starter problem.

77()
CHART B1
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
U1 FUEL SENDER CIRCUIT
The fuel sender is a resistive device that sends a 10--180 ohm signal to the fuel gauge
indicating fuel level. It also contains two switches, one for low fuel level and another
that will shutdown the machine when the fuel reaches this level. These two switch
inputs connect to the WEDGE controller.
If the fuel reading appears incorrect, check the fuel level in the tanks to see if it
corresponds with the gauge. If not, remove the fuel sender and disconnect t he
harness plug. Connect an ohmeter across terminals A and B on the Packard
Weather--Pack connector. Tilting the sender tube should produce resistance
reading between 10 and 180 ohms. If not, replace the sender.
The two switches can be checked with the sender removed from the tank. Use an
ohmeter to verify switch operation. Tilting the sender tube back and forth should
activate the switches.
o
C
o
D
o
E
o
F
ALERT
SHUTDOWN
U1
Fuel Level Sender
W098
BRN
W099
BRN
WEDGE
J1--17
P1--17
W016
BLU
W017
BLU
P1--18
J1--18
WEDGE
B
A
→
→
to control panel fuel level
to ground
W027
W100

78()
CHART C1
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
RT1 SEPARATOR TANK TEMPERATURE
CIRCUIT
J1--4
P1--4
YEL
1
2
BRN
P1--6
J1--6
RT1
SEPARATOR TANK
TEMP SENSOR
Separator tank temperature is read by RT1 thermistor. It is mounted in the side of the
separator tank and connects to the W1 harness. The temperature range is --30 to
255_F.
If the WEDGE Controller has an incorrect reading for the RT1 channel, disconnect the
thermistor and install the Thermistor Simulator Plug (PN# 22073878) into the harness
connector. Read the channel again and it should read 32 degrees F ± 5 degrees
(0C ± 3C). If the reading is correct, replace the thermistor. If not, disconnect the
WEDGE Controller P1 connector. Connect an ohmmeter between pins P1--4 and
P1--6. The ohmmeter should read 33.2K ohms ±1%. If the reading is correct, replace
the WEDGE Controller. If not, there is a problem with the W1 harness or the P1--4,
P1--6 connector pins.
W002
W006
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
--20 --4 25,490
--10 14 18,088
--5 23 12,221
0 32 9,369
5 41 7,240
15 59 4,427
25 77 2,786
40 104 1460
60 140 668.7
70 158 467.2
90 194 241.0
100 212 177.5
105 221 153.1
110 230 132.8
Tem p_C
Tem p_F
Resistance
(Ohms)

79()
CHART D1
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
RT2 AIREND DISCHARGE TEMP
J1--5
W1 P1--5
YEL
1
2
BRN
P1--6
J1--6
RT2
AIREND DISCHARGE
TEMP SENSOR
Airend discharge temperature is read by RT2 thermistor. It is mounted in the airend
discharge piping and connects to the W1 harness. The temperature range is --30 to
255_F.
If the WEDGE Controller has an incorrect reading for the RT2 channel, disconnect the
thermistor and install the Thermistor Simulator Plug (PN# 22073878) into the harness
connector. Read the channel again and it should read 32 degrees F ± 5 degrees
(0C ± 3C). If the reading is correct, replace the thermistor. If not, disconnect the
WEDGE Controller P1 connector. Connect an ohmmeter between pins P1--5 and
P1--6. The ohmmeter should read 33.2K ohms ±1%. If the reading is correct, replace
the WEDGE Controller. If not, there is a problem with the W1 harness or the P1--5,
P1--6 connector pins.
W003
W005
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
--20 --4 25,490
--10 14 18,088
--5 23 12,221
0 32 9,369
5 41 7,240
15 59 4,427
25 77 2,786
40 104 1460
60 140 668.7
70 158 467.2
90 194 241.0
100 212 177.5
105 221 153.1
110 230 132.8
Tem p_C
Tem p_F
Resistance
(Ohms)

80()
CHART E1
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
PT1
SEPARATOR TANK
PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
P1--8 BRN
P1--7 ORN
PT1 SEPARATOR TANK
PRESSURE CIRCUIT
J1--8
J1--7
J1--10
P1--10 VIO
A
C
B
5VDC+
SIG (+)
GND
The WEDGE reads separator tank pressure from PT1. It is a gauge pressure
transducer mounted on the separator tank. The WEDGE provides 5 VDC excitation
voltage to pin B (+5) and pin A (GND). The pressure signal on pin C connects to the
WEDGE input. The signal range is .45 to 4.5 volts. The transducer range is 0 to 225
psig, or 0--500 psig.
To verify the operation of PT1, connect a gauge in parallel with it. The test gauge
should be at least 1% accuracy to match the accuracy of PT1. Use the WEDGE
diagnostics to display the readings of PT1. If PT1 does not track the test gauge,
replace it.
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
W008
W007
W010
W1
HARNESS

81()
CHART F1
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
PT2
REGULATION SYSTEM
PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
P1--8 BRN
P1--9 ORN
PT2 REGULATION SYSTEM
PRESSURE CIRCUIT
J1--8
J1--9
J1--10
P1--10 VIO
A
C
B
5VDC+
SIG (+)
GND
The WEDGE reads regulation system pressure from PT2. It is a gauge pressure
transducer mounted near the inlet unloader. The WEDGE controller provides 5 VDC
excitation voltage to pin B (+5) and pin A (GND). The pressure signal on pin C
connects to the WEDGE input. The signal range is .45 t o 4.5 volts. The transducer
range is 0 to 100 psig.
To check the operation of PT2, connect a gauge in parallel with it. The test gauge
should be at least 1% accuracy to match the accuracy of PT2. Use the WEDGE
diagnostics to display the readings of PT2. If PT2 does not track the test gauge,
replace it.
W008
W009
W010
WEDGE
CONTROLLER
W1
HARNESS

82()
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DC HEATER CIRCUIT
A DC heater system is provided to prevent the orifices from freezing in cold tem-
peratures. It is turned on by control panel switch, S3. Fuse F1, a 20 amp fuse,
supplies power to the heaters.
+24V
“Heaters” switch on control panel
S3
W021
BLU
HR1--1
HR1
HR1--2
W097
BRN
GND
HR1 = Regulation Heater
CHART G1

83()
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
S4, S5 AIR FILTER SWITCHES
CHART I1
The WEDGE reads the air filter switches, S4 and S5. S5 is connected to the com-
pressor air filter and S4 is connected to the engine air filter. These are normally open
switches and close when the air filter restriction reaches 20 inches of water. The
switches provide a ground connection to an opto coupler input on the WEDGE con-
troller.
WEDGE
CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
To verify the circuit operation, another type of switch can be substituted for the filter
switch, or a wire jumper can be used to activate the circuit. Disconnect S4 and S5
and install the test switch or jumper. Closing the test switch or installing the jumper
should activate the circuit, and the “Air Filter” alarm light on the control panel should
light. Forcing the alarm lamp to turn on and off will verify proper circuit operation.
W001 BLU
P1--2 J1--2
W028
BLU
S5--1
S5
W029
BRN
S4--1
W093
BRN
S4

84()
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
U2 ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR
CHART K1
Pin
OutOfWater
In Water
U2
Coolant Sensor
P4
21 28 32
W1 Harness
W057 blu
W058 blu
W059 blu
AB C
The engine coolant level sensor is an impedance probe mounted in the radiator top
tank. The probe connects to the engine controller. The sensor is powered by a 5VDC
supply from the engine controller. The sensor connects to the engine controller at the
J4 connector, near the engine controller.
CIRCUIT
TROUBLESHOOTING
If the probe fails shorted, it can pull down the 5VDC supply and cause other sensors
to not function properly. If a sensor problem is suspected, check to see if engine
fault codes have been set.
The probe can be tested, using a container of water. Pin A connects to +5VDC, Pin
C to ground. Pin B is the output. Using a container of water, they should operate as
follows:
B5.0V
0V

85()
SECTION 8
ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR INFORMATION

86()
CONNECTOR PARTS INFORMATION
The following is a list of the connector parts used with the harnesses and devices on the machine. Most connectors
consist of 1 to 4 items per side (harness or device). The devices can be located on the schematics and then refer-
enced to this list. A connector repair kit, P/N 54749635, containing terminals and housings, is available for
repairs.
PART
Manufacturer Part No.
RT1, RT2
Plug, 2 Way Packard 22869515
TPA, 2 Way Packard 22969523
Seal, Cable Packard 54750567
Contact, Female Packard 22869531
PT1,PT2
Plug, 3 Way Packard 22869499
TPA, 3 Way Packard 22869754
Seal, Cable Packard 22869762
Contact, Female; 18AWG Packard 22869507
U1, Fuel Level
Plug, 6 Way Packard 22869416
Seal, Cable Packard 54750567
Contact, Female Packard 54750526
P1, Wedge Controller
Plug, 40 Way Deutsch 22868939
Socket, 16 AWG, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22869044
Socket, 16 AWG, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869069
Socket, 14 AWG, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22868947
P4, Cummins Engine Control
Plug, 50 Way Deutsch 22869580
Backshell, 50 Way Deutsch 22870026
Seal Cavity, Size 20 Deutsch 22870018
Socket, 20 AWG, Gold Stamp Deutsch 54699608
U2, Coolant Level Sensor
Plug, 3 Way Packard 22880926
TPA, 3 Way Packard 22870067
Seal, Cable Packard 54750682
Plug, Sealing Packard 22869465
Contact, Female Packard 54750674
P5, Cummins Power Connect
Plug, 4 Way Deutsch 22869986
Wedge, Lock, 4 Way Socket Deutsch 22870042
Socket, Size 12, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22880710

87()
P2 Control Panel
Plug, 12 Way Deutsch 22871842
Wedge Lock, 12 Way Deutsch 22871859
Socket Size 16, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22869044
P3 Control Panel: P14, Accessory Connector
Plug6Way Deutsch 22868988
Wedge Lock 6 Way Deutsch 22868996
Socket, Size 14, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22868947
Socket, Size 16, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869069
Socket, Size 16, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22869044
P7, IQ Option: P8, Emergency Stop Option
Plug, 4 Way Deutsch 22869002
Wedge Lock, 4 Way Deutsch 22869028
Socket, Size 16, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22869044
Socket, Size 16, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869069
P13, P15: Can Buss
Plug, 3 Way Deutsch 22869150
Wedge Lock, 3 Way Deutsch 22870000
Socket, Size 16, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869069
TR1, TR2: Can Terminator
Resister Plug Assembly Deutsch 54750633
J10 Wedge Comms
Receptacle, 9 Way Deutsch 22871875
Cap, Dust w/Lanyard Deutsch 22869085
Seal, Cavity, 12--16 AWG Deutsch 22868954
Pin, Size 16, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869093
J11 Data Link Service
Receptacle, 9 Way Deutsch 22869994
Cap, Dust, w/Lanyard Deutsch 22869085
Pin, Size 16, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869093
J8
Receptacle, 4 Way Deutsch 22869036
Wedge Lock, 4 Way, Pin Deutsch 22880876
Pin, Size 16, Gold Stamp Deutsch 22869093
G1, Engine Alternator
Plug, 4 Way Packard 22880918
TPA, 4 Way Packard 22870083
Seal, Cable Packard 54750682
Terminal, Female Packard 54750674
Seal, Cavity Packard 22869465

88()
F1, F2; Fuse Connectors
Connector, 2 Way; Fuse Packard 22871677
Cover, Fuse Packard 22871735
Terminal, Female; 12--10 AWG Packard 22869432
D1--D2; Diodes
Diode, Molded M/F Doosan 35376169
Connector, Over Mold; M/F Doosan 36882694
Shur RCPT .180 dia. AMP 22869606
Shur Plug .180 dia. AMP 22869598
M2 Control Panel
Housing, Connector; 3 Way Siemens VDO 22972089
Pin, Connector, 14--18 AWG AMP 22872097
J2 Control Panel
Receptacle, 12 Way Deutsch 22880942
Wedge Lock, 12 Way Deutsch 22880934
Seal, Cavity; Size 12--16 Deutsch 22868954
Pin, Size 16, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22880405
J3 Control Panel
Receptacle, 6 Way Deutsch 22869051
Wedge Lock, 6 Way Deutsch 22880959
Pin, Size 16, Tin Stamp Deutsch 22880405
Seal, Cavity; Size 12--16 Deutsch 22868954
S1 -- Key Switch
Plug, 4 Way Packard 22881966
TPA, 4 Way Packard 22871974
Terminal, Female Packard 22871982

89()
REMOVAL TOOL USAGE
Terminal
Part Number Manufacturer Removal Tool No.
54699525 Deutsch 54699624
22869044 Deutsch 54699632
22869069 Deutsch 54699632
22868947 Deutsch 54699624
22869093 Deutsch 54699632
22880405 Deutsch 54699632
22880413 Deutsch 54699624
54699608 Deutsch 54699640
22880710 Deutsch 54699624
22869531 Packard 54749643
22869507 Packard 54749643
54750526 Packard 54749643
54750674 Packard 54749643
54699525 Packard 54749643
22869044 Packard 54749643
22869432 Packard 54749643
22869424 Packard 54749643
22871982 Packard 54749643

90()
Deutsch DT Series Connector
(Note the orange wedgelock)
Packard Metri Pack Series Connector
(Note the green wire seals and blue Terminal
Position Assurance Connection)
Deutsch HD Series Connector
Deutsch DRC Series Connector
It is very important that connectors be properly
assembled. Use of the correct pin crimp tool is
required to ensure high quality terminations. The
manufacturer’s instructions must be followed as to
selection and use of crimp tools. Improper crimps
not only provide unreliable connections but can
damage the connector housing.
Troubleshooting Harnesses -- For extensive har-
ness troubleshooting, a detailed schematic will be
required. Splice location details can be very useful
since problems do occur at splices.
The proper test adapters are recommended for
harness troubleshooting. Some examples of these
are s hown in Section 2 concerning multimeters.
Use of these adapters will prevent harness dam-
age during testing.
The first item to perform during harness trouble-
shooting is a physical inspection of the harness
for damage. Look for cut or frayed conductors,
melted insulation and conductors pulled from con-
nectors.
The next item to check is connector pin seating.
Ensure the connector pins in the circuit under test
are properly seated in the connector housing. A
tug on the wire should confirm this.
If the harness is not physically damaged and all
connector pins are seated, perform a continuity
check of the circuit conductors. The ohmeter func-
tion of the multimeter can be used for this test.
Check to ensure there are not any ground
faults or conductor shorts to ground.
Finally, measure the signals on the circuit
under test. Start at the point of origin of the
signal and verify at as many points along the
harness as possible, ending at the termination
point.

91()
Use of Harness Tools
These pictures describe the proper methods of
use of harness tools.
Proper removal tool usage is shown in the above
picture. The removal tools are color coded as to
wire size. The Table below lists the colors and
wire sizes.
Removal
Tool Color Wire Size
P/N
Red 20--24 54699640
Blue 16--18 54699632
Yellow 12--15 54699624
Green 8--10 54699616
The w ire is placed into the slot on the removal tool
and the tool is slid along the wire inserted into the
back of the connector. Gently pull on the wire as
the tool is pushed into the connector. The pin
should release from the connector. To insert a pin,
push it into the connector until it locks.
Removal Tools
This picture shows the various removal tools for
the Deutsch connectors.
The following two pages will show how the
Deutsch crimp tools are to be used. One is used
for machined contacts and the other for stamped
and formed contacts.

92()

93()
94()
Engine electronic controller connector J4 location:
J4
OEM port connector P4 pinout viewed from connector mating face
(opposite wire side)
10
6
50
46
5
1
45
41
WEDGE connector (P1) pinout from connector back side (wire side)
01
12345 678910
31 32 33 34 35
36 37 38 39 40

95()
SECTION 9
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST

96()
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
Ref Designator Description Part Number
U2 Coolant Level Switch 22769186
Battery Disconnect Switch 36896975
PT1 0--225 psi pressure transducer 54496773
PT2 0--100 psi Pressure Transducer 36920825
K2 Relay, 24VDC SPDT 36892362
G2 Mag Speed Sensor 36785319
RT1, RT2 Thermistor Temperature Sensor 22806004
L1 Start / Run Solenoid Valve 36840841
L2 Unloader Solenoid Valve 36881944
S4,S5 Air Filter Switch 36847838
RP1 Engine Oil Press Sender 36870608
RT3 Air Discharge Temp Sender 35604180
K1 Auxiliary Start Relay 36853521
HR1 Regulator Heater 36854677
U1 Fuel Level Sender 22155451
D1--D2 Diode 35376169
K3 Engine Air Intake Heater Relay 36853521
WEDGE Controller 22173579
W1 Chassis H arness 22770879
Control Panel Harness 22784698
Negative Battery Cable 36780609
Positive Battery Cable 35582410
Positive Jumper Cable 54765383
Battery Jumper 35598986
F2 30 Amp Fuse 36786259
F1 20 Amp Fuse 36792083
IQ Wiring Harness 22840524
IQ Heater Harness 22460117
IQ Orifice Heaters 36841526
Actuator 36898310
RT5 Thermistor Temperature Sensor 36898922
K4 Relay, 24VDC SPDT 36892362
TCU IQ Controller 36920643
S8 Filter Switch 36899615
S9 Filter Switch 36899599
RT4 Engine Temperature Sender 35604180

97()
S6 Air End Oil Pressure Switch 36757581
HR3 Orifice Heater 36841526
CB1 Circuit Breaker 22101968
Engine Intake Air Heater Harness 22785349
Electric Brake Harness 36875508
Trailer Harness 22747786
S1 Panel Switch 22127385
S2 Panel Switch 22054076
S3 Panel Switch 22054050
DS1 Panel Lamp 22050553
M1 Hourmeter 22054175
M2 Fuel Level Gauge 22692602
M3 4 in 1 Gauge 22056394
M4 Discharge Air Pressure Gauge 36891216
M5 Tachometer Gauge 22055883

98()
SECTION 10
ALERTS AND SHUTDOWNS LIST

99()
ALERT/SHUTDOWN CONDITIONS Version 2.07
ALERT SHUTDOWN
CODE
LIGHT
(BLINKS)
Machine
ID
CODE
LIGHT
(STEADY)
DELAY
(sec)
Machine
ID
Engine Speed < Min. RPM 1 CPRSR Malf 30
All#
Engine Speed > Max. RPM 2 CPRSR Malf 30
All$
Engine Crank Time Exceeded 3 CPRSR Malf 0
All!
High Engine Oil Temperature 5 CPRSR Malf. 0--6
High Intake Manifold Temperature 6 CPRSR Malf. 0--7
Water In Fuel 8 CPRSR Malf. 5,6
Engine Not Responding to Throttle Cmd. 10 CPRSR Malf. All
Too Many Start Attempts during Autostart 11 CPRSR Malf 0 All
Engine Shuts Itself Down: reason unknown 29 CPRSR Malf 0 All
Low AE Oil Pressure 31 CPRSR Malf 20 0,2,5
Disch. Temp (RT2) Sensor Fault 32 CPRSR Malf 10 All
Separator Tank (PT1) Sensor Fault 33 CPRSR Malf. All
Separator Tank Pressure >20 PSI during start
attempt (Engine will not crank)
34 CPRSR Malf 0 0--10
Machine Over Pressure 35 CPRSR Malf 1 0--6
Safety Valve Open 36 CPRSR Malf 2 0--6
Sep. Tank Temp > 247 degrees F 50 CPRSR Malf 3 All
Machine ID Not Valid 51 CPRSR Malf 0 All
Sep. Tank Temp. (Rt1) Sensor Fault 53 CPRSR Malf 10 All
Reg. System Pressure (PT2) Sensor Fault 54 CPRSR Malf. All
Estop Button Pushed 55 CPRSR Malf. 0-- 6 55 CPRSR Malf 3 0--6
Minimum Pressure Not Met 56 CPRSR Malf. All
Serial Comm. Problem 70 CPRSR Malf. All
CAN Bus Problem 71 CPRSR Malf. All
Auto Start/Stop Module Failure -- No Comm
for 17 seconds
73 CPRSR Malf. All
Dedicated Lights:
Low Fuel Level Fuel Level 0--6 Fuel Level 3 All
Air Filter Restriction Soiled Filter
All^
Low Battery Voltage Battery Charging
Condition
All
Low Engine Oil Pressure Low Engine Oil
Pressure
All
Low Coolant Level Engine Coolant
Level
0,1,5, 6%
High Engine Coolant Temp High Engine
Temp
All
High Engine Coolant Temp High Engine
Temp
10 All
IQ Filter Restriction IQ Filter Re-
striction
3
0-- 6@
High Discharge Temp. (RT2 > 247 deg. F) High Comp.
Temp .
3 All
CAN D erived Data =

100()
Notes:
1) Max. crank time 0--6 = 15 sec; 7,8 = 30 sec.
2) IQ equipped machines
3) ID 0--6 = 800 RPM; 7,8 = 900
4) ID 0--6 = 1900 RPM; 7,8 = 2500
5) Via fault code 235
6) ID 7,8 Option
Machine ID:
0 = Viking HP CU
1=VikingXHPCU
2=EMULPCAT
3=EMUHPCAT
4=VikingXHPCAT
5=EMULPCU
6=EMUHPCU
7 = Zenith P425
8 = WW600
9=C15CAT150psi
10 = Triton CU

101()
FAULT CODES FOR QSC 8.3, QSL9 CUMMINS ENGINE
Fault Code Description
111 Engine Control Module -- Critical Internal Failure
115 Engine Speed/Position Sensor Circuit -- Lost both signals from Magnetic Pickup Sensor
122 Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor #1 Circuit -- Voltage above normal or Shorted High
123 Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor #1 Circuit -- Voltage below normal or Shorted Low
135 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit -- Voltage above normal or Shorted High
141 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit -- Votlage below normal or Shorted Low
143 Engine Oil Pressure Low -- Warning
144 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit -- Voltage above normal or Shorted H igh
145 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit -- Voltage below normal or Shorted Low
146 Engine Coolant Temperature High -- Warning
147 Frequency Throttle Signal -- Abnormal Frequency, Pulse Width, or Period
148 Frequency Throttle Signal -- Abnormal Frequency, Pulse Width, or Period
151 Engine Coolant Temperature High -- C ritical
153 Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor Circuit -- Voltage above normal, or shorted high
154 Intake Manifold Temperature Sensor Circuit -- Voltage below normal or shorted low
155 Intake Manifold Temperature #1 High -- Critical
187 Sensor Supply -- Voltage below normal or s horted low
195 Engine Coolant Level Sensor Circuit -- Voltage above normal or shorted high
196 Engine Coolant Level Sensor Circuit -- Voltage below normal or shorted low
197 Engine Coolant Level Low -- Warning
212 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor #1 Circuit -- Voltage above normal or shorted high
213 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor #1 Circuit -- Voltage below normal or shorted low
214 Engine Oil Temperature High -- Critical
221 Barometric Pressure Sensor Circuit -- Voltage above normal or shorted high
222 Barometric Pressure Sensor Circuit -- Voltage below normal or shorted low

102()
227 Sensor Supply Voltage #2 Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
231 Engine Coolant Pressure Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
232 Engine Coolant Pressure Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
233 Engine Coolant Pressure Low --Waming
234 Engine Speed High --Critical
235 Engine Coolant Level Low --Critical
238 Sensor Supply Voltage #3 Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
249 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
256 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
261 Engine Fuel Temperature High --Warning
263 Engine Fuel Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
265 Engine Fuel Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit-- Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
268 Fuel Pressure Sensor Circuit --Data Incorrect
271 High Fuel Pressure Solenoid Valve Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
272 High Fuel Pressure Solenoid Valve Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
275 Fuel Pumping Element (Front) --Mechanical System Malfunction
281 High Fuel Pressure Solenoid Valve --Mechanical System Malfunction
284 Engine Speed/Position Sensor (Crankshaft) Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or
Shorted Low
285 SAE J1939 Multiplexing PGN Timeout Error
286 SAE J1939 Multiplexing Configuration Error
287 SAE J1939 Multiplexing Throttle Error
295 Barometric Pressure Sensor Circuit --Data Incorrect
319 Real Time Clock Power Interrupt --Data Incorrect
322 Injector Solenoid Cylinder #1 Circuit --Current Below Normal, or Open Circuit
323 Injector Solenoid Cylinder #5 Circuit --Current Below Normal, or Open Circuit

103()
324 Injector Solenoid Cylinder #3 Circuit --Current Below Normal, or Open Circuit
325 Injector Solenoid Cylinder #6 Circuit --Current Below Normal, or Open Circuit
331 Injector Solenoid Cylinder #2 Circuit --Current Below Normal, or Open Circuit
332 Injector Solenoid Cylinder #4 Circuit --Current Below Normal, or Open Circuit
334 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit --Data Incorrect
342 Electronic Calibration Code Incompatibility --Out of Calibration
351 Injector Power Supply --Bad Intelligent Device or Component
352 Sensor Supply Voltage #1 Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
386 Sensor Supply Voltage #1 Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
415 Engine Oil Pressure Low --Critical
418 Water in Fuel Indicator High --Maintenance
422 Engine Coolant Level --Data Incorrect
425 Engine Oil Temperature --D ata Incorrect
428 Water in Fuel Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above N ormal, or Shorted High
429 Water in Fuel Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
433 Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor Circuit --Data Incorrect
435 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit --Data Incorrect
441 Battery Voltage Low --Warning
442 Battery Voltage High --Warning
449 Fuel Pressure High --Warning
451 In!ector Metering Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted
High
452 Injector Metering Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted
Low
488 Intake Manifold Air Temperature High --Warning
553 Injector Metering Rail Pressure High --Warning

104()
554 Fuel Pressure Sensor Error --Data Incorrect
559 Injector Metering Rail Pressure Low --Warning
595 Turbocharger Speed High --Warning
596 Electrical Charging System Voltage High --Warning
597 Electrical Charging System Voltage Low --Warning
598 Electrical Charging System Voltage Low --Critical
687 Turbocharger Speed Low --Warning
689 Primary Engine Speed Sensor Error --Data Incorrect
691 Turbocharger Compressor Inlet Temp Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted H igh
692 Turbocharger Compressor Inlet Temp Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
697 ECM Internal Temperature Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
698 ECM Internal Temperature Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
719 Extended Crankcase Blow--by Pressure Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
729 Extended Crankcase Blow--by Pressure Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or ShortedLow
731 Engine Speed/Position #2 Mechanical Misalignment --Mechanical System Malfunction
753 Engine Speed/Position #2 Camshaft Sync Error --Data Incorrect
778 Engine Speed Sensor (Camshaft) Error --Data Incorrect
951 Cylinder Power Imbalance Between Cylinders --Data Incorrect
1139 Injector Cylinder #1 --Mechanical System Malfunction
1141 Injector Cylinder #2-- Mechanical System Malfunction
1142 Injector Cylinder #3 --Mechanical System Malfunction
1143 Injector Cylinder #4 --Mechanical System Malfunction
1144 Injector Cylinder #5-- Mechanical System Malfunction
1145 Injector Cylinder #6 --Mechanical System Malfunction
1911 Injector Metering Rail Pressure High --Critical

105()
2111 Engine Coolant Temperature 2 Sensor Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
2112 Engine Coolant Temperature 2 Sensor Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
2113 Engine Coolant Temperature 2 High --Warning
2114 Engine Coolant Temperature 2 High --Critical
2115 Engine Coolant Pressure 2 Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
2116 Engine Coolant Pressure 2 Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
2117 Engine Coolant Pressure 2 Low-- Warning
2185 Sensor Supply Voltage #4 Circuit --Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
2186 Sensor Supply Voltage #4 Circuit --Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted Low
2215 Fuel Pump Delivery Pressure Low --Warning
2216 Fuel Pump Delivery Pressure High --Warning
2249 Injector Metering Rail Pressure Low-- Critical
2265 Fuel Priming Pump Control Signal Circuit --Voltage Above N ormal, or Shorted High
2266 Fuel Priming Pump Control Signal Circuit --Voltage Below N ormal, or Shorted Low
2292 Fuel Inlet Meter Device --High --Warning
2293 Fuel Inlet Meter Device --Low --Warning
2311 Fueling Actuator #1 Circuit Error --Condition Exists
2321 Engine Speed/Position Sensor #1 --Data Incorrect
2322 Engine Speed/Position Sensor #2-- Data Incorrect
2345 Turbocharger Speed --Abnormal Rate of Change
2555 Intake Air Heater #1 Circuit-- Voltage Above Normal, or Shorted High
2556 Intake Air Heater #1 Circuit --Voltage Below N ormal, or Shorted Low
2963 Engine Coolant Temperature High --Alert
2964 Intake Manifold Air Temperature High --Alert
2973 Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor Circuit --Data Incorrect

106()
SECTION 11
RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS
Quantity Description Part Number
1 WEDGE Controller 22173579
2 Thermistor Temperature Probe 22806004
3 0--100 psig Pres Transducer 36920825
3 0--225 psig Pres Transducer 54496773

107()
SECTION 12
SOFTWARE INFORMATION

108()
Software Updates
Software updates are available on a website for downloading. The website will always con-
tain the latest software revisions for all applications of Portable Power products. Software
files will be available for the Virtual Technician I (PDA based service tool), and Virtual Tech-
nician II PC based service tool.
Service Manuals
The website has Electrical/Electronics service manuals for all equipment requiring this
manual. They are stored in .PDF format and can be viewed or downloaded as needed.
Service Bulletins
Service Bulletins will be posted at the site as needed. These will describe any actions that
need to be taken involving hardware or software.

Revision History
Rev. EC Number Comments
A CN017781 Original Release
B
C CN026881 Doosan Reference Updates

©2012 Doosan Infracore Portable Power Printed in the U.S.A.
Doosan Infracore Portable Power
1293 Glenway Drive
Statesville, N.C. 28625
www.doosanportablepower.com
