
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 1 / 240
SAMSUNGELECTRONICSCo.,Ltd.
2016BusinessReport
FortheyearendedDecember31,2016
Certain statements in the document, other than purely historical information, including estimates, projections, statements relating to our business
plans, objectives and expected operating results, and the assumptions upon which those statements are based, are “forward-looking statements.”
Forward-looking statements are based on current expectations and assumptions that are subject to risks and uncertainties which may cause actual
results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements. A detailed discussion of risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results and
events to differ materially from such forward-looking statements is included in our financial reports available on our website.
See, also, 『Note on Forward-Looking Statements』 in preamble of 『II. Business Overview』.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 2 / 240
Table of Contents
Certification ......................................................................................................................................................................... 3
I. Corporate Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 4
II. Businesses Overview .................................................................................................................................................. 22
III. Financial Affairs ........................................................................................................................................................... 62
IV. Auditor’s Report ........................................................................................................................................................ 165
V. Management Discussion and Analysis .................................................................................................................... 167
VI. Corporate Governance ............................................................................................................................................. 175
VII. Information on Shareholders .................................................................................................................................. 186
VIII. Executives and Employees .................................................................................................................................... 192
IX. Affiliates and Subsidiaries ....................................................................................................................................... 200
X. Related Party Transactions ....................................................................................................................................... 230
XI. Other Information ...................................................................................................................................................... 234

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 3 / 240
Certification
Letter of Certification
We, Oh-Hyun Kwon and Sang-Hoon Lee, as CEO and executive of the company in charge of reporting, certify
that we have reviewed the annual business report of Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. for the year ended
December 31, 2016.
Based on our knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a
material fact necessary that would be misleading with respect to the period covered by this report.
Based on our knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in the report, fairly
present in all materials respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the company as
of, and for, the periods presented in this report.
We confirm that Samsung Electronics operates an Internal Accounting Management System, responsible for
establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls over financial reporting,
as defined in Article 2.2 and 2.3 of the External Audit Act. We have disclosed our most recent evaluation of
internal controls over financial reporting to the Company’s auditors and to the audit committee of the
Company’s board of directors.
Date: 2017. 4. 28

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 4 / 240
I. Corporate Overview
1. Overview
A. Legal, Commercial Name:
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
B. Date of Establishment:
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (“SEC”) was established as Samsung Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. on January 13,
1969, and held an initial public offering on June 11, 1975.
- SEC changed its name from Samsung Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. to Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. following a
resolution passed at the Annual General Meeting of Shareholders on February 28, 1984.
C. Address, Phone Number, and English Language Website of the Corporate Headquarter
- Address: 129, Samsung-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
- Phone Number: 82-31-200-1114
- Website: http:// www.samsung.com/sec
D. The Company is not subject to Article 2 of the Framework Act on Small and Medium Enterprises.
E. Core Businesses
- The Company (defined below) separately oversees three independent self-determining divisions (each a “Division”),
CE (Consumer Electronics), IM (Information Technology & Mobile Communications), and DS (Device Solutions).
Products in each Division are presented below:
Division Products
CE TV, Monitor, Refrigerator, Washing Machine, Air Conditioner, Medical Devices, etc.
IM HHP, Network System, Computer, etc.
DS DRAM, NAND Flash, Mobile AP, LCD panel, OLED panel, etc.
The Company is a global electronics company comprised of the headquarters in Korea and 169 subsidiaries (SEC and its
subsidiaries collectively, “Samsung Electronics” or the “Company”) across the world including nine (9) regional
headquarters for the CE and IM Divisions and five (5) regional headquarters for the DS Division.
[CE Division]
The CE Division is leading the global digital era by continuously offering new products with innovative technology,
unique design, and enhanced value propositions.
TV is the core product of CE. The Company has maintained its market leadership position for the past eleven (11)
consecutive years by leveraging competitive advantages in hardware such as LCD/LED TVs as well as software driven
product features within our Smart TV product portfolio.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 5 / 240
[IM Division]
The IM Division is at the forefront of mobile lifestyle innovation with consumer-friendly products such as the premium
‘GALAXY’ series, while driving the paradigm shift in the market beyond mobile convergence to focus on software.
The IM Division is focused on meeting market demand by enhancing mobile product differentiation through seamless
integration of key features from various product categories.
The IM Division expects increased convergence of mobile phones, digital media devices and personal computers, cameras
and other devices in smartphones and tablets, with both serving as replacements for certain devices. As a result, the IM
Division has made, and will continue to make, significant investments in research and development of new technologies,
products and services.
In addition to handheld phone (“HHP”) products including smartphones, the IM Division is also leading technological
development and standardization in the global networks system market including Long Term Evolution (“LTE”).
[DS Division]
The DS Division is comprised of the semiconductor sub-division and the display panel business. The semiconductor
sub-division (“Semiconductor Sub-Division”) is further divided into the memory business and the system LSI business.
The Company’s memory business unit (“Memory” or “Memory Business Unit”) manufactures and sells DRAM and
NAND products. The Company’s system LSI business unit (“System LSI”) manufactures mobile application processors
(“Mobile APs” or “APs”) and customized logic products. The display business (“DP Business Unit”) manufactures and
sells display panels (“DP”).
The Company is constantly working to increase its influence on end-product manufacturers and create new demand by
developing high quality components and through technological breakthroughs, as it has done with high-end 3D TV panels
and in memory components like DRAM by increasing capacity by increasing density.
The Memory Business Unit produces differentiated products and has maintained the top position in the global memory
market by continuously applying the latest advanced process technology ahead of the competition with each technological
iteration. The system LSI market is shifting from PCs to mobile devices and like its sibling, the System LSI business unit
plans to stay at the forefront of this market by offering differentiated products created using the latest advanced process
technology and through efficient inventory management.
The Company’s TFT-LCD business has been maintaining its position as a leader in the global flat panel display market by
developing evermore higher resolution panels that are more energy efficient and by producing these panels more cost
efficiently with a higher yield rate.
OLED is increasingly and rapidly replacing TFT-LCD in smart phones and other IT devices. The Company is also a
market leader in the OLED displays, reaping the benefits of its continued investment and technological breakthroughs.
☞ See 『II. Businesses Overview』, for more details about each Division.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 6 / 240
F. Affiliates
SEC is an affiliate of the Samsung group as defined under Korea’s Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act (“Samsung
Group”).
As of December 31, 2016, Samsung Group had a total of fifty-eight (58) domestic affiliates, reduction of seven (7)
affiliates (Nuri Solution, Samsung Fine Chemicals, S-EnPol, Hantok Chemicals, SDI-Chemical Co., Ltd., Jeongahm Wind
Power, Allat) and addition of three (3) affiliates (Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Financial Service, SDI-Chemical Co.,
Ltd., S-Printing Solution Co., Ltd.) when compared to December 31, 2015. Among the Samsung Group’s fifty-eight (58)
domestic affiliates, sixteen (16) affiliates including Samsung Electronics are listed, and forty-two (42) affiliates are
unlisted.
[As of December 31, 2016]
No. of
affiliates
Name of affiliates
Listed 16
Samsung C&T, Samsung Electronics, Samsung SDI, SEMCO, Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance,
Samsung Heavy Industries, Samsung Life Insurance, MULTICAMPUS,
Samsung Securities, Samsung SDS, Samsung Card, Samsung Engineering, S1,
Cheil Worldwide, Hotel Shilla, Samsung Biologics
Unlisted 42
Seoul Lakeside CC, Samwoo Architects & Engineers, CVnet Corporation,
Samsung Bioepis, Samsung Display, Samsung Corning Advanced Glass, SU Materials,
STECO, SEMES, Samsung Electronics Service, Samsung Electronics Sales,
Samsung Electronics Logitech, Suwon Samsung Bluewings FC, Samsung Medison,
Samsung Claim Adjustment Service, Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Service,
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Financial Service, Daejung Offshore Wind Power Co., Ltd.,
Samsung Futures, Samsung Asset Management, Saengbo, Samsung Life Service,
Samsung SRA Asset Management, Samsung Life Financial Service, SD Flex, Cheil Fashion Retail Co., Ltd.,
Natural9, Samsung Welstory, S-Printing Solution, SECUI, STM, S-Core, OpenHands,
Miracom, Samsung Card Customer Service, Human TSS, S-1CRM, Shilla Stay,
HDC Shilla Duty Free LTD, SERI, Samsung Lions, Samsung Venture Investment Corporation
Total 58
※ Effective March 11, 2016, CREDU changed its name to Multicampus Co., Ltd.
※ Effective April 1, 2016, Colombo Korea changed its name to Cheil Fashion Retail Co., Ltd.
※ Effective December 15, 2016, Allat was excluded from the Company group (sold its shares on September 30, 2016)
☞ See 『IX. Affiliates and Subsidiaries』 for more details about domestic and overseas affiliates.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 7 / 240
G. Subsidiaries Subject to Consolidated Financial Statements
As of December 31, 2016, Samsung Electronics’ consolidated subsidiaries totaled 169 with the addition of twenty (20)
newly established or acquired subsidiaries and the subtraction of ten (10) subsidiaries when compared to December 31,
2015. Below is the list of consolidated subsidiaries.
(Unit: KRW million)
Name of Subsidiaries
Date of
Establishment
Major business
Dec 31,
2015
Assets
%
ownership
Classified as
major
subsidiary
(Y/N)
Samsung Electronics America Inc. 1978.07 Sale of electronic goods 14,875,687 Over 50%
Y
NexusDX Inc. 2009.07 Medical equipment 9,513 Over 50%
N
NeuroLogica Corp. 2004.02 Medical equipment 210,095 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Receivables Corporation 1998.03 Receivable management 2,627,030 Over 50%
Y
Dacor Holdings, Inc. 1998.12 Holding Company 21,928 Over 50%
N
Dacor 1965.03
Production and sale of home
appliances
21,603 Over 50%
N
Dacor Canada Co. 2001.06 Sale of home appliances 515 Over 50%
N
EverythingDacor.com, Inc. 2006.06 Sale of home appliances 313 Over 50%
N
Distinctive Appliances of California, Inc. 2014.06 Sale of home appliances 389 Over 50%
N
Quietside LLC 2001.07 Sale of Air-conditioner 23,837 Over 50%
N
SmartThings, Inc. 2012.04 Sale of smart-home devices 214,616 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Oak Holdings, Inc. 2016.06 Holding company 0 Over 50%
N
Joyent, Inc. 2005.03 Cloud services 12,583 Over 50%
N
Samsung Pay, Inc. 2006.03
Develop and provide
mobile
payment services
300,278 Over 50%
Y
Stellus Technologies, Inc. 2015.11
Production and sales of storage
systems
0 Over 50%
N
Prismview, LLC (formerly YESCO Electronics LLC) 2007.10
LED display panel production and
sales
47,294 Over 50%
N
Samsung Semiconductor Inc. 1983.07
Sale of semiconductors and
display panels
8,288,391 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Canada Inc. 1980.07 Sale of electronic goods 465,801 Over 50%
Y
PrinterOn Inc. 2000.04 Sale of printing solutions 6,773 Over 50%
N
PrinterOn America Corporation 1986.04 Sale of printing solutions 74 Over 50%
N
AdGear Technologies Inc. 2010.08 Digital advertising platform 5,585 Over 50%
N
Viv Labs, Inc. 2012.09 Artificial Intelligence platform 24,582 Over 50%
N
NewNet Communication Technologies(Canada), Inc. 2009.07 Develop text messaging services 4,756 Over 50%
N
RT SV CO-INVEST, LP 2014.02 Investment in venture firms 13,557 Over 50%
N
Samsung Research America, Inc 1988.10 R&D 274,403 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Next LLC 2016.08 Holding company 0 Over 50%
N
Samsung Next Fund LLC 2016.08
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
0 Over 50%
N
Samsung International Inc. 1983.10 Production of TVs and monitors 51,164 Over 50%
N
Samsung Mexicana S.A. de C.V 1988.03 Production of electronic goods 884,512 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Austin Semiconductor LLC. 1996.02 Production of semiconductors 6,179,289 Over 50%
Y

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 8 / 240
Name of Subsidiaries
Date of
Establishment
Major business
Dec 31,
2015
Assets
%
ownership
Classified as
major
subsidiary
(Y/N)
Samsung Electronics Mexico S.A. De C.V. 1995.07 Sale of electronic goods 1,030,161 Over 50%
Y
SEMES America Inc. 1998.10 Semiconductor equipment 1,050 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Digital Appliance Mexico, SA de CV 2012.12 Production of electronic goods 435,513 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica Miami, Inc. 1995.05 Sale of electronic goods 194,088 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica (Zona Libre) 1989.04 Sale of electronic goods 318,028 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Venezuela, C.A. 2010.05 Marketing and services 4,599 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronica Colombia S.A. 1997.03 Sale of electronic goods 376,453 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Panama. S.A. 2012.07 Consulting 9,529 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronica da Amazonia Ltda. 1995.01
Production and sale of
electronic goods
3,114,334 Over 50%
Y
Simpress Comercio, Locacao e Servicos S.A. 2005.02 Sale of printing solutions 130,007 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Argentina S.A. 1996.06 Marketing and services 40,459 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Chile Limitada 2002.12 Sale of electronic goods 345,850 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Peru S.A.C. 2010.04 Sale of electronic goods 206,571 Over 50%
Y
Beijing Integrated Circuit Industry International Fund, L.P 2014.12 Investment in venture firms 18,707 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics (UK) Ltd. 1995.07 Sale of electronic goods 1,125,885 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics(London) Ltd. 1999.01 Holding company 7,627 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Holding GmbH 1982.02 Holding company 383,777 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Semiconductor Europe GmbH 1987.12
Sale of semiconductors and
display panels
904,359 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics GmbH 1984.12 Sale of electronic goods 1,820,922 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Iberia, S.A. 1989.01 Sale of electronic goods 642,393 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics France S.A.S 1988.01 Sale of electronic goods 908,971 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Hungarian Private Co. Ltd. 1989.10
Production and sale of
electronic goods
1,254,673 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Czech and Slovak s.r.o. 2010.01 Sale of electronic goods 133,947 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Italia S.P.A. 1991.04 Sale of electronic goods 768,278 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Europe Logistics B.V. 1991.05 Logistics 1,894,614 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. 1995.07 Sale of electronic goods 1,264,497 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Display Slovakia s.r.o. 2007.03 Display panel processing 156,256 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Romania LLC 2007.09 Sale of electronic goods 188,451 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Polska, SP.Zo.o 1996.04 Sale of electronic goods 457,516 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Portuguesa S.A. 1982.09 Sale of electronic goods 155,940 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Nordic Aktiebolag 1992.03 Sale of electronic goods 701,525 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Semiconductor Europe Ltd. 1997.04
Sale of semiconductors
and
display panels
90,287 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Austria GmbH 2002.01 Sale of electronic goods 289,807 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Switzerland GmbH 2013.05 Sale of electronic goods 145,143 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Slovakia s.r.o 2002.06 Production of TVs and monitors 1,888,341 Over 50%
Y

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 9 / 240
Name of Subsidiaries
Date of
Establishment
Major business
Dec 31,
2015
Assets
%
ownership
Classified as
major
subsidiary
(Y/N)
Samsung Electronics Baltics SIA 2001.10 Sale of electronic goods 69,023 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. 2008.10 Holding company 6,989,207 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Poland Manufacturing SP.Zo.o 2010.02 Production of home appliances 317,465 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Greece S.A. 2010.04 Sale of electronic goods 93,625 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Nanoradio Design Center 2004.02 R&D 24,043 Over 50%
N
Samsung Denmark Research Center ApS 2012.09 R&D 20,389 Over 50%
N
Samsung France Research Center SARL 2012.10 R&D 20,653 Over 50%
N
Samsung Cambridge Solution Centre Limited 2012.09 R&D 129,225 Over 50%
Y
PrinterOn Europe Limited 2013.11 Sale of printing solutions 76 Over 50%
N
Joyent Ltd. 2014.04 Cloud services 107 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Overseas B.V. 1997.01 Sale of electronic goods 105,859 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Rus LLC 1999.03 Marketing 7,104 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Rus Company LLC 2006.10 Sale of electronic goods 598,708 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Ukraine LLC 2004.01 Marketing 0 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Ukraine Company LLC 2008.09 Sale of electronic goods 107,816 Over 50%
Y
Samsung R&D Institute Rus LLC 2011.11 R&D 10,121 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Central Eurasia LLP 2008.09 Sale of electronic goods 82,420 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Caucasus Co., Ltd. 2014.10 Marketing 2,237 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Rus Kaluga LLC 2007.07 Production of TVs 608,200 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics West Africa 2010.03 Marketing 48,471 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics East Africa 2011.12 Marketing 40,347 Over 50%
N
Samsung Gulf Electronics Co., Ltd. 1995.05 Sale of electronic goods 952,236 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Egypt S.A.E 2012.07
Production and sale of
electronic goods
539,155 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Israel Ltd. 2012.09 Marketing 5,377 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Tunisia S.A.R.L 2012.09 Marketing 2,637 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Pakistan(Private) Ltd. 2012.11 Marketing 2,492 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics South Africa(Pty) Ltd. 1994.06 Sale of electronic goods 603,300 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics South Africa Production (pty) Ltd. 2014.07 Production of TV and monitors 38,848 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Turkey 1984.12 Sale of electronic goods 578,873 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Semiconductor Israel R&D Center, Ltd. 2007.10 R&D 37,860 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Levant Co.,Ltd. 2009.07 Sale of electronic goods 365,939 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Maghreb Arab 2009.11 Sale of electronic goods 100,686 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Japan Corporation 1975.12 Sale of electronic goods 656,101 Over 50%
Y
Samsung R&D Institute Japan Co. Ltd 1992.08 R&D 157,461 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Japan Co., Ltd. 2008.09 Sale of electronic goods 301,514 Over 50%
Y

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 10 / 240
Name of Subsidiaries
Date of
Establishment
Major business
Dec 31,
2015
Assets
%
ownership
Classified as
major
subsidiary
(Y/N)
Samsung Electronics Display (M) Sdn. Bhd. 1995.03
Production and sale of
electronic goods
246,755 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Medison India Private Ltd. 2009.01 Medical equipment 32 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics (M) Sdn. Bhd. 1989.09 Production of home appliances 117,879 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Vina Electronics Co., Ltd. 1995.01 Sale of electronic goods 350,158 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. 2006.07 Sale of electronic goods 4,227,798 Over 50%
Y
Samsung India Electronics Private Ltd. 1995.08
Production and sale of
electronic goods
3,723,127 Over 50%
Y
Samsung R&D Institute India-Bangalore Private Ltd. 2005.05 R&D 147,149 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Australia Pty. Ltd. 1987.11 Sale of electronic goods 431,714 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics New Zealand Limited 2013.09 Sale of electronic goods 53,454 Over 50%
N
PT Samsung Electronics Indonesia 1991.08
Production and sale of
electronic goods
964,021 Over 50%
Y
PT Samsung Telecommunications Indonesia 2003.03
Sale of telecom systems and
services
2,011 Over 50%
N
Thai Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. 1988.10
Production and sale of
electronic goods
1,889,410 Over 50%
Y
Laos Samsung Electronics Sole Co., Ltd 2016.09 Marketing 0 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Philippines Corporation 1996.03 Sale of electronic goods 197,197 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Display Vietnam Co., Ltd 2014.07 Display panel production 961,730 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Malaysia Electronics (SME) Sdn. Bhd. 2003.05 Sale of electronic goods 312,263 Over 50%
Y
Samsung R&D Institute BanglaDesh 2010.08 R&D 8,242 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Vietnam Co., Ltd. 2008.03 Production of electronic goods 7,829,507 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN Co., Ltd. 2013.03 Production of telecom products 6,571,798
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics HCMC CE Complex Co. Ltd,. 2015.02
Production and sale of
electronic goods
415,465 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Display Dongguan Co., Ltd. 2001.11 Display panel production 1,276,263
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Display TianJin Co., Ltd. 2004.06 Display panel production 958,820
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Hong Kong Co., Ltd. 1988.09 Sale of electronic goods 948,800
Over 50%
Y
Suzhou Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. 1995.04 Production of home appliances 637,485
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Suzhou Electronics Export Co., Ltd. 1995.04 Production of home appliances 385,732
Over 50%
Y
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. 1996.03 Sale of electronic goods 12,748,395 Over 50%
Y
Samsung Mobile R&D Center, China-Guangzhou 2010.01 R&D 52,046
Over 50%
N
Samsung Tianjin Mobile Development Center 2010.08 R&D 24,628
Over 50%
N
Samsung R&D Institute China-Shenzhen 2013.03 R&D 12,014
Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics Suzhou Semiconductor Co., Ltd. 1994.12 Semiconductor processing 836,562
Over 50%
Y
SEMES (XIAN) Co., Ltd. 2013.07 Semiconductor equipment 1,001
Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics (Shandong) Digital Printing Co., Ltd. 1993.03 Production of printers 853,982
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Huizhou Co., Ltd. 1992.12 Production of electronic goods 6,192,974
Over 50%
Y
Tianjin Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. 1993.04 Production of TV and monitors 858,675
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Taiwan Co., Ltd. 1994.11 Sale of electronic goods 1,253,480
Over 50%
Y

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 11 / 240
Name of Subsidiaries
Date of
Establishment
Major business
Dec 31,
2015
Assets
%
ownership
Classified as
major
subsidiary
(Y/N)
Beijing Samsung Telecom R&D Center 2000.09 R&D 65,595
Over 50%
N
Tianjin Samsung Telecom Technology Co., Ltd. 2001.03 Production of telecom products 2,075,123
Over 50%
Y
Shanghai Samsung Semiconductor Co., Ltd. 2001.10
Sale of semiconductor and display
panels
3,792,437
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Suzhou Computer Co., Ltd. 2002.09 Production of electronic goods 886,593
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Suzhou Module Co., Ltd 2002.09 Display panel processing 684,646
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Suzhou LCD Co., Ltd 2011.07 Display panel production 2,784,122
Over 50%
Y
Shenzhen Samsung Electronics Telecommunication Co., Ltd. 2002.02 Sale of telecom products 118,697
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Semiconductor (China) R&D Co., Ltd. 2003.04 R&D 24,818
Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics China R&D Center 2004.05 R&D 35,644
Over 50%
N
Samsung (China) Semiconductor Co., Ltd. 2012.09 Production of semiconductors 9,742,388
Over 50%
Y
Samsung SemiConductor Xian 2016.04
Sale of semiconductor and display
panels
0 Over 50%
N
Samsung Electronics (Beijing) Service Company Limited 2005.01 Services 160,151
Over 50%
Y
Tianjin Samsung LED Co., Ltd. 2009.05 LED production 349,963
Over 50%
Y
Tianjin Samsung Opto-Electronics Co., Ltd. 1994.02 Camera/camcorder production 125,762
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Display 2012.04
Production and sale
of display
panels
39,225,460 Over 50%
Y
SU Materials 2011.08
Production of display panel
component
26,131
Over 50%
N
STECO 1995.06
Production of semiconductor
component
73,744
Over 50%
N
SEMES 1993.01
Semiconductor/FPD manufacturing
equipment
717,229
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Service 1998.10 Electronics goods repair services 296,104
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Sales 1996.07 Sales of electronic goods 550,655
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Electronics Logitech 1998.04 Total logistics services 146,052
Over 50%
Y
Samsung Medison 1985.07 Medical equipment 315,073
Over 50%
Y
S-Printing Solution Co., Ltd. 2016.11 Sale of printing solutions 0 Over 50%
N
Mirero System 1994.01 Semiconductor S/W 17,446 Over 50%
N
SVIC #20 Venture Capital Union 2011.03
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
24,852
Over 50%
N
SVIC #21 Venture Capital Union 2011.11
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
181,200
Over 50%
Y
SVIC #22 Venture Capital Union 2011.11
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
163,503
Over 50%
Y
SVIC #23 Venture Capital Union 2012.10
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
29,364
Over 50%
N
SVIC #26 Venture Capital Union 2014.11
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
105,021
Over 50%
Y
SVIC #27 Venture Capital Union 2014.09
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
16,567
Over 50%
N
SVIC #28 Venture Capital Union 2015.02
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
64,453
Over 50%
N
SVIC #29 Venture Capital Union 2015.04
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
5,291
Over 50%
N
SVIC #32 Venture Capital Union 2016.08
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
0 Over 50%
N
SVIC #33 Venture Capital Union 2016.11
Investment in venture firms
and new technologies
0 Over 50%
N
※ Companies with over KRW 75 billion in total assets as of December 31, 2015, are classified as major subsidiaries.
※ See 『II. Businesses Overview』 for additional information about major business segments.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 12 / 240
(Changes in Subsidiaries)
AMER
Europe/
MEA/
CIS
Asia China
Domestic
Total Increase Decrease
Dec 31,
2011
26 51 25 30
24 156
Dec 31,
2012
30 61 23 32
20 166
[Domestic: 2]
Samsung Display Co., Ltd.,
SVIC #23 Venture Capital Union
[Americas: 8]
Samsung LED AMERICA, Inc.,
mSpot Inc.,
Nanoradio Inc.,
Samsung Electronics Panama. S.A,
Samsung Electroncis Corporative SA de CV,
Samsung Electronics Digital Appliance,
Mexico SA de CV, Nvelo, Inc.,
Newton Sub. Corp.
[Europe/MEA/CIS: 11]
Samsung LED Europe GmbH,
Samsung Nanoradio Design Center,
Nanoradio Hellas AE, General RF Modules AB,
Samsung Cambridge Solution Centre Limited,
Samsung Denmark Research Center ApS,
Samsung Electronics Egypt S.A.E,
Samsung Electronics Tunisia S.A.R.L,
Samsung Electronics Israel,
Samsung France Research Center SARL,
Samsung Electronics Pakistan(Private) Ltd.
[China: 2]
Tianjin Samsung LED Co., Ltd.,
Samsung (China) Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
[Domestic: 6]
Medison Healthcare,
Samsung Mobile Display Co., Ltd.,
S-LCD Co., Ltd.,
SVIC #7 Venture Capital Union
Prosonic Co., Ltd.,
SEHF Korea Co., Ltd.
[Americas: 4]
Samsung LED AMERICA, Inc.,
HX Diagnostics, Inc.,
HX Reagents, Inc.,
Nanoradio Inc.
[Europe/MEA/CIS: 1]
Samsung LED Europe GmbH
[Asia: 2]
Samsung Asia Private Ltd.,
Samsung Medison Japan Co., Ltd.
Dec 31,
2013
25 55 22 33
18 153
[Americas: 2]
NeuroLogica Corp.,
Intellectual Keystone Technology LLC.
[Europe/MEA/CIS: 1]
Samsung Electronics Switzerland GmbH
[Asia: 2]
Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN Co., Ltd.,
Samsung Electronics New Zealand Ltd.
[China: 3]
Samsung Network R&D Center China-Shenzhen,
Samsung R&D Institute China-Xian,
SEMES (XIAN) Co., Ltd.
[Domestic: 2]
Secron, GES
[Americas: 7]
Newton Sub. Corp., mSpot, Inc., Deltapoint
Cardiac Diagnostics, Inc., Samsung Medison
America, Inc., Intellectual Keystone Technology
LLC., Samsung Medison Brasil Ltda., Samsung
Electronics Corporativo, SA de CV
[Europe/MEA/CIS: 7]
Samsung Telecoms (UK) Ltd., Samsung LCD
Netherlands R&D Center B.V, Samsung LCD
Netherlands R&D Center (UK) Limited,
General RF Modules AB, Samsung Medison
France S.A.S., Samsung Opto-Electronics
GmbH, Samsung Medison Italia S.r.l.
[Asia: 3]
Samsung Electronic Philippines Manufacturing
Corp., Batino Realty Corporation, TNP
Small/Medium Size & Venture Enterprises Growth
Promotion Investment Limited
Partnership(TSUNAMI)
[China: 2]
Samsung LCD Netherlands R&D Center
(HK)Limited, Medison (shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Dec 31,
2014
30 56 22 32
18 158
[Domestic
: 2]
SVIC #26 Venture Capital Union
SVIC #27 Venture Capital Union
[America: 6]
RT SV CO-INVEST, LP, Quietside LLC,
SmartThings, Inc., PrinterOn Inc., PrinterOn America
Corporation, 1397011 Ontario Ltd.
[Europe/MEA/CIS: 3]
PrinterOn Europe Limited, Samsung Electronics South
Africa Production(pty) Ltd., Samsung Electronics Caucasus
Co., Ltd.
[Asia : 1]
Samsung Display Bac Ninh
[Domestic: 2]
Samsung Blue Wings, World Cyber Games
[America: 1]
1397011 Ontario Ltd.
[Europe: 2]
Samsung Medison Europe B.V
Nanogen Recognomics GmbH
[Asia: 1]
Medison Medical Systems India Private Ltd.
[China: 1]
Medison Medical Equipment Shanghai Co., Ltd..

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 13 / 240
Dec 31,
2015
33 55 24 30
17 159
[Domestic : 2]
SVIC #28 Venture Capital Union
SVIC #29 Venture Capital Union
[America: 6]
Simpress Comercio, Locacao e Servicos S.A.,
Samsung Pay, Inc. (formerly LooPay, Inc.),
YESCO Electronics LLC,
Paymate Global, Inc.,
Beijing Integrated Circuit Industry International Fund,
Stellus Technologies
[Asia: 2]
Samsung Electronics HCMC CE Complex Co. Ltd.
Future Technology & Service
[Domestic: 3]
RAY
High Pioneer Private Investment Trust #1,
SVIC #6 Venture Capital Union
[America: 3]
Samsung Telecommunications America LLC.,
Paymate Global, Inc.,
Nvelo, Inc.
[China: 2]
Samsung Electronics Hainan Fiberoptics Co.,Ltd
Samsung Medison Shanghai Medical Instrument
Co., Ltd
[Europe: 1]
Nanoradio Hellas AE
Dec 31,
2016
44 53 23 29
20 169
[Domestic : 4]
SVIC #32 Venture Capital Union
SVIC #33 Venture Capital Union
Mirero System, S-Printing Solution Co., Ltd.
[America: 13]
Samsung Oak Holdings, Inc., Joyent, Inc.,
Joyent Canada, Inc., AdGear Technologies Inc.,
Samsung Next LLC, Samsung Next Fund LLC,
Dacor Holdings, Inc., Dacor, Dacor Canada Co.,
EverythingDacor.com, Inc.,
Distinctive Appliances of California, Inc.,
Viv Labs, Inc.,
NewNet Communication Technologies(Canada), Inc.
[Europe: 1]
Joyent Ltd.
[Asia: 1]
Laos Samsung Electronics Sole Co., Ltd
[China: 1]
Samsung SemiConductor Xian
[Domestic : 1]
SVIC #14 Venture Capital Union
[America: 2]
Grandis, Inc., Joyent Canada, Inc.
[Europe/CIS: 3]
Samsung Russia Service Centre,
SonoAce Deutschland GmbH
Samsung Electronics Kazakhstan LLP
[Asia: 2]
Samsung Telecommunications Malaysia,
Future Technology & Service
[China: 2]
Samsung R&D Institute China-Xian,
Samsung Electronics Shanghai
Telecommunication Co., Ltd.
※ AMER = America; MEA = Middle East and Africa, CIS = Commonwealth of Independent States

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 14 / 240
H. Credit Rating
SEC’s credit rating is assessed by two external credit ratings agencies. As of December 31, 2016, SEC’s credit ratings are:
“A1” and investment outlook is stable, as rated by Moody’s; and “A+” and investment outlook is stable, as rated by S&P.
Date Securities Ratings Credit Rating Agency Rating Range Note
’14.08 Corporate bond A+ S&P (USA) (AAA ~ D)
Annual
Review
’14.10 Corporate bond A1 Moody’s (USA) (Aaa ~ C)
’15.05 Corporate bond A1 Moody’s (USA) (Aaa ~ C)
’15.09 Corporate bond A+ S&P (USA) (AAA ~ D)
’16.07 Corporate bond A+ S&P (USA) (AAA ~ D)
’16.08 Corporate bond A1 Moody’s (USA) (Aaa ~ C)
2. Company History
(The Information disclosed below outlines major changes to the Company such as asset transfers, M&A, and security offerings)
2011.01.01 Merged with Samsung Electronics Gwangju
2011.02.16 Acquired shares of Prosonic (100%) and Medison (43.5%)
2011.04.29 Acquired additional shares of Medison (22.3%)
2011.07.01 Transferred solar cell business to Samsung SDI
2011.07.22 Samsung Information System America (“SISA”), a subsidiary of SEC, acquired shares of Grandis (100%)
2012.01.19 Acquired remaining shares of S-LCD Corporation (50%) from SONY
2012.04.01 Separated LCD business (established Samsung Display)
2012.04.01 Merged Samsung LED into SEC
2012.04.10 Samsung Electronics America (“SEA”), a subsidiary of SEC, issued USD $1 billion of corporate bonds.
2012.07.01 Samsung Mobile Display merged with S-LCD (a subsidiary of Samsung Display)
2012.09.01 Samsung Medison, a subsidiary of SEC, merged with Prosonic
2012.12.01 Merged SEHF Korea into SEC
2013.01.01 Merged SECRON with GES (a subsidiary of SEMES)
2013.01.28 SEA acquired shares of NeuroLogica (100%)
2014.01.15 Samsung Display disposed of stock of Samsung Corning Precision Materials and purchased convertible
preferred shares of Corning Incorporated
2014.08.18 SEA acquired shares of SmartThings (100%)
2015.01.01 SEA merged with Samsung Telecommunications America LLC (“STA”)
2015.02.23 SEA acquired shares of LoopPay (100%)
2016.01.28 Sold shares of Samsung Card (37.5%)
2016.06.24 SEA acquired shares of Joyent (100%)
2016.09.07 SEA acquired shares of Dacor (100%)
2016.10.07 SEA acquired shares of Viv Labs (100%)
2016.11.01 Spun-off printing solutions business (established S-Printing Solution Co., Ltd.)
※ The Samsung Electronics Headquarters Address is: 129, Samsung-ro (Maetan-dong), Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 15 / 240
(Important Changes in Management Executives)
Following the annual general meeting of shareholders on March 16, 2012, of the three Executive Directors with
expiring terms (Gee-Sung Choi, Yoon-Woo Lee, Ju-Hwa Yoon), Yoon-Woo Lee retired and Gee-Sung Choi and Ju-
Hwa Yoon were re-appointed. Oh-Hyun Kwon was newly appointed as Executive Director. In addition, of the three
Independent Directors with expiring terms (Dong-Min Yoon, Jae-Woong Lee, Oh-Soo Park), Jae-Woong Lee and Oh-
Soo Park retired and Dong-Min Yoon was re-appointed. Han-Joong Kim and Byeong-Gi Lee were newly appointed
as Independent Directors.
On June 8, 2012, Oh-Hyun Kwon succeeded Gee-Sung Choi as CEO.
On February 7, 2013, Independent Director Dong-Min Yoon retired (deceased).
On March 14, 2013, Executive Directors Gee-Sung Choi and Ju-Hwa Yoon resigned.
Following the shareholders’ meeting on March 15, 2013, Boo-Keun Yoon, Jong-Kyun Shin, and Sang-Hoon Lee were
newly appointed as Executive Directors. Independent Director In-Ho Lee was reappointed, and Kwang-Soo Song and
Eun-Mee Kim were newly appointed as Independent Directors.
On March 15, 2013, SEC appointed Executive Directors Boo-Keun Yoon and Jong-Kyun Shin as CEOs to serve
alongside incumbent CEO Oh-Hyun Kwon as co-CEOs.
On March 13, 2015, Executive Director Oh-Hyun Kwon and Independent Directors Han-Joong Kim and Byeong-Gi
Lee were reappointed at the annual general meeting of shareholders.
On March 11, 2016, Executive Directors Boo-Keun Yoon, Jong-Kyun Shin and Sang-Hoon Lee were reappointed at
the annual general meeting of shareholders. Of the three Independent Executive Directors with expiring terms (In-Ho
Lee, Kwang-Soo Song and Eun-Mee Kim), Eun-Mee Kim retired, and In-Ho Lee, Kwang-Soo Song were
reappointed. Jae-Wan Bahk was newly appointed as an Independent Director.
On October 27, 2016, Jae-Yong Lee was newly appointed as Executive Director at the Extraordinary General Meeting
of Shareholders and Executive Director Sang-Hoon Lee resigned.
As of April 28, 2017, (the “Reporting Date”), SEC’s BOD is comprised of four Executive Directors (Oh-Hyun Kwon,
Boo-Keun Yoon, Jong-Kyun Shin, Jae-Yong Lee) and five Independent Directors (In-Ho Lee, Han-Joong Kim, Kwang-
Soo Song , Byeong-Gi Lee and Jae-Wan Bahk).

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 16 / 240
(Changes in Organizational Structure)
In December 2012, following an organizational change, CE and IM businesses were upgraded to individual Division
status, and the IT Solution business was divided into Printing Solution and Computer businesses. The Printing
Solution business was incorporated into the CE Division and the Computer business was converted to a team unit and
integrated into the Mobile business under the IM Division. The Medical Device business team was upgraded to a
business unit within the CE Division.
In December 2013, the Digital Imaging business was reorganized as a team unit, and then was integrated with the
Mobile business unit. In December 2015, the LED business was reorganized as a team unit.
In November 2016, the Company spun off its printing solutions business and established S-Printing Solution Co., Ltd.
[As of December 2012]
Before After
Business
organization
DMC Division
(CE: Visual display, Digital appliances)
(IM: Mobile, IT solution, Network, Digital imaging)
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances, Printing
solution, Medical devices)
IM Division (Mobile, Network, Digital imaging)
DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, LCD,LED) DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP, LED)
Regional
headquarters
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest
Asia, Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest Asia,
Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan(DS)
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS), Japan
(DS)
[
As of December 2013]
Before After
Business
organization
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances, Printing
solution, Medical devices)
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances, Printing
solution, Medical devices)
IM Division (Mobile, Network, Digital imaging) IM Division (Mobile, Network)
DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP, LED) DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP, LED)
Regional
headquarters
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest
Asia, Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest Asia,
Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan(DS)
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan (DS)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 17 / 240
[
As of December 2015]
Before After
Business
organization
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances, Printing
solution, Medical devices)
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances, Printing
solution, Medical devices)
IM Division (Mobile, Network) IM Division (Mobile, Network)
DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP, LED) DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP)
Regional
headquarters
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest
Asia, Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest Asia,
Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan(DS)
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan (DS)
[As of December 2016]
Before After
Business
organization
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances, Printing
solution, Medical devices)
CE Division (Visual display, Digital appliances,
Medical devices)
IM Division (Mobile, Network) IM Division (Mobile, Network)
DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP) DS Division (Memory, SYS.LSI, DP)
Regional
headquarters
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest
Asia, Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Korea, North America, Latin America, Europe, CIS, Southwest Asia,
Southeast Asia, China, Middle East, Africa
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan(DS)
Americas(DS), Europe(DS), China(DS), Southeast Asia(DS),
Japan (DS)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 18 / 240
3. Changes in Paid-in Capital
No changes were reported during the past five (5) consecutive years.
4. Stock Information
A. Total Number of Shares
The total number of authorized shares according to the articles of incorporation is 500,000,000 (par value per share:
KRW 5,000). As of December 31, 2016, SEC has issued 140,679,337 shares of registered common stock and
20,513,427 shares of registered preferred stock without voting rights (excluding canceled shares).
SEC has
cumulatively canceled 14,930,000 shares of common stock and 3,380,000 shares of preferred stock in accordance with the
resolution of the board of directors.
As of December 31, 2016, the number of floating common stock is 122,697,651 shares and the number of floating
preferred stock is 17,283,734 shares, excluding treasury shares (of 17,981,686 shares of common stock and 3,229,693
shares of preferred stock).
[As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: Shares)
Classification
Type of Stocks
Note
Common Preferred Total
I. Number of authorized shares 400,000,000
100,000,000
500,000,000 -
II. Number of shares issued 155,609,337
23,893,427
179,502,764 -
III. Number of shares decreased 14,930,000
3,380,000
18,310,000 -
1. Capital Reduction -
-
- -
2. Number of shares canceled 14,930,000
3,380,000
18,310,000
Cancellation of
treasury shares
3. Redemption of redeemable shares -
-
- -
4. Others -
-
- -
IV. Number of outstanding shares (II-III) 140,679,337
20,513,427
161,192,764 -
V. Treasury shares 17,981,686
3,229,693
21,211,379 -
VI. Number of floating shares (IV-V) 122,697,651
17,283,734
139,981,385 -
※ Shares of SEC’s common stock carry voting rights but preferred stock do not carry voting rights.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 19 / 240
B. Treasury Shares
In 2016, Samsung Electronics acquired 4,699,197 shares of common stock and 1,264,099 shares of preferred stock for
enhancing shareholder return, and retired 6,620,000 shares of common stock and 2,320,000 shares of preferred stock.
As of December 31, 2016, SEC holds 17,981,686 shares of common stock and 3,229,693 shares of preferred stock as
treasury shares.
On Oct 29, 2015, SEC announced plans for a KRW 11.3 trillion share buyback program for purposes of enhancing
shareholder return. The first stage of the repurchase program, which amounts to KRW 4.3 trillion, was completed in
January 2016. The second stage, which was approximately KRW 3.1 trillion, was completed in April 2016 and SEC
repurchased shares worth approximately KRW 2.1 trillion in the third stage in July. The fourth stage, which was
approximately KRW 1.9 trillion, was completed in September 2016.
[As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: Shares)
Acquisition method
Share
type
Period-
beginning
shares
Change
Period-end
shares
Acquisition
(+)
Disposal
(-)
Cancellation
(-)
Intra-market direct acquisition
(Within dividend related capital gains limit)
Common
19,902,489
4,699,197
- 6,620,000
17,981,686
Preferred
4,285,594
1,264,099
- 2,320,000
3,229,693
Tot al
Common
19,902,489
4,699,197
- 6,620,000
17,981,686
Preferred
4,285,594
1,264,099
- 2,320,000
3,229,693
C. Types of Registered Stock
SEC has two types of registered equity securities: 1) common stock; 2) non-voting and non-cumulative preferred stock.
The shareholders of preferred stock are entitled to dividend payments of an additional 1% of par value compared to
shareholders of common stock. As of December 31, 2016, the total number of outstanding preferred stock is 20,513,427
shares.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 20 / 240
5. Voting Shares
SEC has 140,679,337 shares of common stock outstanding, which represents 28.1% of the total number of authorized
shares of 500 million (500,000,000). There are 20,513,427 shares of preferred stock outstanding (with no voting rights).
SEC holds 17,981,686 shares of common stock (with no voting rights) in its treasury, and 12,506,577 shares of common
stock are held by SEC’s affiliates and have limited voting rights under applicable laws. Thus, the total number of shares
with voting rights is 110,191,074.
[As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: Shares)
Classification Share type
Number
of shares
Note
Number of outstanding shares (A)
Common 140,679,337
-
Preferred 20,513,427
-
Shares with no voting rights (B) Common 17,981,686
Treasury stock according to Korean Commercial Act
Shares with no voting rights according
to Articles of Incorporation (C)
Preferred 20,513,427
3,229,693 shares of preferred treasury stock included
Shares with limited voting rights
under relevant laws (D)
Common 12,479,184
Restricted by the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act:
10,622,814 shares held by Samsung Life Insurance &
1,856,370 shares held by Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance
Common 27,393
Restricted by the Insurance Business Act: Shares held by
Samsung Life Insurance in certain special accounts
Shares with voting rights
(F = A - B - C - D)
Common 110,191,074
-
Preferred -
-
※ Pursuant to Korea’s Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act, shareholders with limited voting rights (D) can exercise certain
rights in accordance with related laws, including the right to vote on agendas such as the appointment or dismissal of directors and
revisions to the Articles of Incorporation.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 21 / 240
6. Shareholder Return
As a part of the Company’s shareholder return policy, a portion of the profits have been returned to shareholders by way
of dividends and shareholder value has been increased through open market purchases of floating shares (share
repurchase). The Company carefully considers strategic investments for sustainable growth, business performance, and
cash flows in determining the level of total shareholder return.
Dividends paid in the most recent three (3) fiscal years are as follows:
(Unit: Shares / %)
Classification 2016 2015 2014
Par value per share (won) 5,000
5,000 5,000
Net profit (million won) 22,415,655
18,694,628 23,082,499
EPS (won) 157,967
126,305 153,105
Total cash dividend (million won) 3,991,892
3,068,737 2,999,972
Total stock dividend (million won) -
- -
Dividend payout ratio (%) 17.8
16.4 13.0
Cash dividend yield (%)
Common 1.6
1.6 1.5
Preferred 2.0
1.9 1.9
Stock dividend yield (%)
Common -
- -
Preferred -
- -
Cash dividend per share (won)
Common 28,500
21,000 20,000
Preferred 28,550
21,050 20,050
Stock dividend per share (share)
Common -
- -
Preferred -
- -
※ June quarterly dividend of 2016 is KRW 141,539 million (KRW 1,000 per share), and paid as interim dividends of previous years.
Interim dividends of 2015 and 2014 are KRW 148,916 million (KRW 1,000 per share) and KRW 75,408 million (KRW 500 per
share), respectively.
※ EPS denotes basic earnings per common share.
※ For further information relating to the calculation of basic EPS, see Earnings Per Share in 『2. Note to Consolidated Financial
Statements』 in 『Ⅲ. Financial Affairs』.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 22 / 240
II. Businesses Overview
1. Overview
Note on Forward-Looking Statements
This report includes forward-looking statements that relate to future events and can be generally identified by phrases
containing words such as “believes,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “foresees,” “forecasts,” “estimates” or other words or
phrases of similar meaning. These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and may involve
known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may affect the Company’s actual results, performance,
achievements or financial position, making them materially different from the actual future results, performance,
achievements or financial position expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements.
Uncertain events that could positively or negatively affect the Company’s management condition and financial
performance include:
• Trends of financial markets domestically and abroad, including changes in exchange rates and interest rates
• The Company’s strategic decision making, including disposals and purchases of businesses
• Unexpected sudden changes in core businesses such as CE, IM, Semiconductor, and DP
• Other changes domestically and abroad that can affect management condition and financial performance
The Company assumes no obligation to revise or update this report to reflect risks or uncertainties that arise after the
reporting period.
A. Business Overview by Division
In addition to our headquarters in Korea, Samsung Electronics is comprised of 169 subsidiaries across the world
responsible for sales and production. There are also nine (9) regional headquarters for Consumer Electronics (“CE”) and
Information Technology & Mobile Communications (“IM”) Divisions and five (5) regional headquarters for Device
Solutions (“DS”) Division.
The Company’s business Divisions are organized in a two-pronged business framework of set (brand products) and
component businesses. The set business is comprised of the CE and IM Divisions, and the component business is
comprised of the DS Division. The CE Division is responsible for the production and sales of TVs, monitors, refrigerators
and washing machines, and the IM Division focuses on the production and sales of handheld phones (such as
smartphones), network systems, and computers. The DS Division is comprised of the Semiconductor business which
manufactures and sells DRAM, Mobile APs, and other semiconductor and semiconductor-related products, and the
Display Panel (“DP Business Unit”) business which manufactures and sells TFT-LCD and OLED panels for TVs,
monitors, notebook PCs, and mobile devices.
<Major Products by Business Division>
Business Division Major Products
CE Division TV, Monitor, Refrigerator, Washing Machine, Air Conditioner, Medical Device, etc.
IM Division HHP, Network System, Computer, etc.
DS
Division
Semiconductor (Sub-
Division)
DRAM, NAND Flash, Mobile AP, etc.
DP Business Unit TFT-LCD, OLED, etc.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 23 / 240
The Company maintains its corporate headquarters and twenty (20) consolidated domestic subsidiaries in Korea.
The Company’s corporate headquarters in Korea is divided along Divisions and/or businesses, and are situated at the
following 5 locations: Suwon (CE Division and R&D Center); Gumi (IM Division); Giheung and Hwasung
(Semiconductor business); and Gwangju (Home Appliance business). The Company’s consolidated domestic subsidiaries
include Samsung Display for display panel production, Samsung Electronics Sales for domestic retail sales, Samsung
Electronics Service for after service care, and Samsung Electronics Logitech for logistics.
We have 149 overseas subsidiaries for product manufacturing, sales, and R&D.
In the Americas, we have 44 subsidiaries including SEA (New Jersey, United States) which is responsible for sales of set
products such as HHPs, SAMEX (Tijuana, Mexico) which is responsible for manufacturing TVs, and SAS (Austin,
United States) which is responsible for manufacturing semiconductor products.
In Europe, we operate 31 subsidiaries. This includes SEUK (UK) which is responsible for sales of set products in UK,
SEF (France), SEG (Germany), SEI (Italy), which are regional sales offices, SESK (Slovakia), SEH (Hungary) which are
TV manufacturing sites, and SEPM (Poland), which is responsible for manufacturing home appliances such as
refrigerators.
In Asia, we have 23 overseas subsidiaries, including SAPL (Singapore), SEAU (Australia), SEPCO (Philippines), and
SME (Malaysia), which are responsible for regional sales. In addition, we operate numerous production sites including
SEV·SEVT (Vietnam) for HHPs, SEHC (Vietnam) for TVs, and SIEL (India) for both TVs and HHPs.
We operate 29 subsidiaries in China, including regional sales operations in SCIC (Beijing) and SEHK (Hong Kong). We
also operate production and processing facilities sites in Tianjin and Suzhou (TSTC, SSEC, and SESS).
In addition, we have 22 production and sales subsidiaries across Africa, the Middle East and the CIS regions.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 24 / 240
[CE Division]
Industry Overview
Since the first public demonstration of a true television system in 1926 and subsequent mass production of Color TVs,
technological developments have led to products such as the Trinitron CRT (1967) and the flat CRT (1996). As the
penetration rate in major countries reached over 90%, the CRT TV business became stagnant. The industry regained
strong growth momentum following the launch of Flat Panel TVs (LCDs, PDPs), especially with the expansion of digital
broadcasting (UK/US 1998~).
Flat panel TVs (“FPTVs”) replaced the CRT driven by enhanced product performance with respect to design, picture
quality, etc., and a sharp decline in prices. In addition, 3D TVs were launched in 2010, and the rise of internet video
services (OTT, OVER-THE-TOP) along with increased consumer interest in smart devices from 2011 to 2012 led to the
birth of the Smart TV market.
In 2013, UHD TV, an innovative product with significantly enhanced resolution and picture quality, was launched, and in
2014, a new form factor Curved TV was released, indicating a constantly evolving TV market.
In 2016, overall TV demand was 222.74 million units, a 1.5% decline from the previous year. The demand in Latin
America decreased by approximately 23%, impacted by the expiration of a sales agreement with the Mexican government,
while Asian markets including China witnessed approximately 4% growth in demand. By product, LCD-TV (including
LED-TV) sold 221.50 million units, a decrease of 1.3% year-on-year, but UHD TV sales increased by 79% to reach 57
million units and large-size TVs (55-inches and above) sold 43 million units, a 42% growth from the previous year, due to
an increasing demand for high-resolution and large-size TVs. This trend also increased the average size of TVs sold to
41.5-inches, exceeding 40-inches for the first time. (Source: February ’17 IHS)
Market Condition
The trend towards large-size and high-resolution screens is accelerating due to intensified competition between
manufacturers. Accordingly, the market share of major manufacturers with high-quality products and brand power is
increasing. In addition, as consumer demand for high-resolution and slim design increases, LED TVs, with eco-friendly
LED back light units (“BLU”) which increases brightness and contrast as well as energy efficiency, has become the
mainstream of the market.
The Company has focused on smart TV sales based on forecasts that consumers’ desire to acquire internet information
from TVs will increase. The concentrated effort resulted in the launch of Smart TV in 2010 with various available
applications and resulted in strong market leadership. In 2012, the Company introduced a new market trend with the
introduction of the Smart Interaction™ system based on voice commands and command gestures for convenient
interaction with its proprietary Samsung Smart TVs. In 2013, the Company introduced a system that recommends TV
programs based on the user’s viewing history. In 2014, with the goal of enhancing the viewing experience of its Smart
TVs, the Company focused on increasing its usability, securing access to content, and strengthening the platform.
The Company recently saw the increasing need for TV as a comprehensive entertainment center that connects various
entertainment devices in the house due to the changing nature of content on TV. Accordingly, the Company achieved an
innovation in smart UX, enabling consumers to enjoy live broadcasts, OTT VOD service, cloud games and other services
in an easily accessible manner. In 2016, Smart TVs can automatically recognize connected devices, and control the
peripheral devices with a single remote. Also, they allow consumers to utilize even more diverse entertainment sources on
one screen in an easily accessible manner, providing users with an easier viewing experience.
< Market Share of the CE Division’s Main Product >
Product 2016 2015 2014
TV 21.6%
21.0% 22.6%
※ 2014, 2015 and 2016 market share data is from research firm, IHS (global market share in quantity).
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 25 / 240
Business Condition
We have maintained the top position in the overall TV market, FPTVs, and LCD TVs (in terms of market share) for
eleven consecutive years since 2006.
In 2009, we created the world’s first LED TV (LED BLU, ultra-slim/ultra-light, eco-friendly). In the first quarter of 2010,
we launched the world’s first 3D Total Solution that provides 3D TV/BDP/glasses/BD Title all-in-one, taking the lead in
the 3D TV market.
In addition, we launched “Samsung Apps,” the world’s first App Store for Smart TVs in 2010, and constantly added
various smart services in 2011, such as “Your Video”, “Social TV”, “Search All” and “Web Browser” services, to
consolidate Samsung’s leadership position in the Smart TV market. In 2012, by developing content in which new input
methods based on voice/gesture (Smart Interaction) is applied, we improved fitness and education services that every
member of family can enjoy. Samsung’s competitive edge in the Smart TV market has been further strengthened, driven
by the enhanced “All Share” function that allows the device to connect with other digital devices more easily.
In 2013, we released OLED and UHD TVs, which offer superior image quality and resolution compared to previous
models. Also, by launching a new Curved TV form factor in 2014 and the first nano-crystal technology (also as known as
quantum dot) SUHD TV in 2015, we continued to maintain our leading position in the industry with innovative premium
products.
In 2016, we released the 2
nd
-gen Quantum dot TV which offers excellent image quality and clear viewing even in bright
light by displaying one billion colors and emitting bright pure light. We also launched the SUHD TV which comes with
HDR 1000 technology that supports incredibly realistic and detailed images, as well as UHD TV equipped with Active
crystal color technology for bright, life-like images and expanded color range. Furthermore, we expanded shipments of
Curved TVs, which use our own curved form factor and increased the premium value, and enhanced our competitiveness
in image quality and design through bezel-less and 360-degree design for streamlined and clean back. Through these
efforts, we have maintained our leading position in the TV market during challenging economic conditions.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 26 / 240
[IM Division]
Industry Overview
In 2017, approximately 78% of the world’s population is expected to own a mobile phone, from 76% in 2016. (Source:
December ’16 Strategy Analytics)
The mobile phone industry started with the first generation analogue phones in the early 1980s. It evolved to second
generation digital, and to third generation mobile communication standards such as WCDMA. Today, fourth generation
LTE mobile communication technology with ultra-high-speed data transmission is becoming commonplace in the market,
and fifth generation mobile communication service is being prepared for commercialization. Also, as the market demand
is increasingly focused on smartphones, the competitive software and services including contents/service, application, UX,
Mobile Payment, A.I. is becoming more important, in addition to competitive hardware like high-performance AP,
AMOLED Display, high-resolution camera, sensor, and waterproof & dustproof feature.
Market Condition
In 2017, the global shipments of smartphones is expected to reach 1.54 billion units, increased by 6% from 1.45 billion in
2016. The tablet market is expected to decrease by 10%, declining to 190 million units in 2017 from 210 million units in
2016. (Source: Strategy Analytics. December ’16 data for Smartphone, March ’17 data for Tablet)
< Market share of the IM Division’s Main Product >
Product 2016 2015 2014
HHP 19.2%
20.7%
22.4%
※ 2014, 2015 and 2016 market share data are from the research firm, Strategy Analytics (global market share in quantity).
Business Condition
SEC aims to further consolidate its leadership position in the mobile device market. To this end, the Company is working
tirelessly to reinforce competitiveness of its products, service and B2B for future growth. For the smartphone business, the
Company is maintaining its no.1 position in the industry by constantly strengthening its diverse product lineups from
premium to mass market models. Going forward, the Company will solidify its market leadership in the premium
smartphone segment through new form factors such as flexible displays, differentiated designs and UX, and at the same
time, actively respond to the mid-range and entry level smartphone markets to increase overall market share. Furthermore,
the Company will actively address various consumer demands with wearable devices such as the Gear S3 and Gear VR, as
well as with accessories that improve user experience.
In addition, the Company will strive to enhance its status in the global market by constantly offering new value to its
customers based on the industry’s best R&D capabilities, and constantly making investments in mobile payment systems
such as our exclusive Samsung Pay service, and in future growth engines including cloud, Intelligence, and mobile B2B
services.
Based on the lessons we learned from the Galaxy Note 7 quality issue, we will continue to ensure that consumer safety is
our highest priority while pursuing innovation. To prevent a similar incident from occurring again, we have implemented
multi-layer safety measures and a thorough safety-check process, and formed an organization devoted to safety
verification. We will take this experience as a valuable lesson and work hard to enhance consumer trust.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 27 / 240
[DS Division]
- Semiconductor
Industry Overview
In general, semiconductor is divided into memory semiconductor that stores information and system LSI (non-memory
semiconductor) that logically processes information. Memory semiconductor is divided into RAM products that can be
written on and read, and ROM products that can only read. RAM is called volatile memory as the information is deleted
when the power is turned off. It is used for temporary loading and storage of application programs.
There are various types of system LSI products for various applications. CPUs (Central Processing Units) for PCs and
servers is the biggest market. System LSI products are used in many product categories such as household electronics,
telecommunications, network, and games. The Company manufactures Mobile APs for smartphone and tablets, image
sensors, and other customized system LSI semiconductor products.
The growth of thesemiconductor market is expected to be negatively impacted by slowing demand for mobile devices,
such as the low growth rate of the smartphone market and negative growth of the tablet market. However, the memory
market is expected to enjoy continuous growth fueled by increasing shipments of high-density information storage devices
like servers. Also, we expect future demand will grow rapidly from newly emerging markets, including IoT and
automotive applications. Supply and demand volatility is expected to decrease as the demand base becomes diversified.
Market Condition
The oversupply situation in the DRAM market has turned into a supply shortage, mainly due to increasing demand for
new mobile products and delays in the tech migration of suppliers. Meanwhile, concentrated demand on the Company is
likely remain in the short term as other manufacturers are experiencing delays in the stabilization of leading-edge process
and the development of high-performance and high-reliability products. Demand for NAND is expected to increase as
more NAND (in terms of gigabytes of installed memory) is included in new smartphones and the ever-increasing adoption
of solid state drives(“SSDs”) continues, but the chip market is expected to experience a prolonged supply shortage as
suppliers are close to the limits in migrating to the finer processes of Planar NAND and competitors are slow in expanding
Vertical NAND production.
< Market share of the Semiconductor Business’ Main Product >
Product 2016 2015 2014
DRAM 48.0%
45.3%
39.6%
※ 2014, 2015 and 2016 market share data is from research firm, DRAMeXchange (global market share in amount).
Business Condition
In the fourth quarter of 2016, the Company launched the world’s first 10nm-class DRAM products, and we are securing a
competitive position at least a year ahead of competitors. Furthermore, the Company is solidifying its leadership position
in the DRAM market by developing differentiated 10nm-class products and accelerating efforts to develop next-
generation DRAM. For NAND products, the Company is mass producing both planar and vertical NANDs, while
addressing customer demand for various NAND products in a timely manner. In particular, the Company is entering the
premium market by using technology that is ahead of its competitors to mass-produce 3
rd
generation 48-layer vertical
NAND and applying the product to high-performance SSDs. The Company is also expanding production of high-quality
3bit MLC products to maximize cost competitiveness.
In 2017, as the growth in the memory semiconductor market is expected to continue, the Company will expand into
differentiated products based on advanced processes and address each market segment with diverse product lineups to
continue to lead the market as the No.1 memory maker.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 28 / 240
- DP Business Unit
Industry Overview
Display products include TFT-LCD (Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting
Diode) panels.
OLED panels use organic materials which offer sharp contrast and color, high color gamut, and fast response rates. Such
differentiating features provide advantages in smartphone products, and as a result the market demand for under 10”
small-to-medium size OLED displays is growing sharply. Now the use of OLED is expanding to larger format displays
such as TVs and transparent displays.
A TFT-LCD panel is a liquid crystal based display that features a thinner and lighter profile, while maintaining high
resolution. It has a wide range of potential applications in devices of all sizes and functionality, from portable mobile
devices to large-size TVs featuring high resolution and brightness. The large panel TFT-LCD market grew rapidly from
first mainly being used in laptops, then monitors, and then TVs. However, the market growth rate has slowed recently due
to the high saturation rate of monitors and TVs.
The TFT-LCD and OLED businesses have high barriers to entry as they are capital intensive and require large-scale
production to realize economies of scale. These types of businesses are generally sensitive to business fluctuations.
Therefore, even if demand continuously increases, supply and demand balance tends to change regularly due to
competitive investment in facilities by producers. As such, when production capacity sharply increases, the average
selling price (“ASP”) of panels may decrease. In contrast, when supply cannot meet increasing demand, ASP may increase.
Market Condition
Most major display panel producers are based in Asia as indicated below:
- Korea: Samsung Display, LG Display, etc.
- Japan: Sharp, Japan Display, etc.
- Taiwan: AU Optronics, Innolux, etc.
- China: BOE, CSOT, Tianma, CEC Panda, etc.
The demand for OLED panels continued to grow, as major smartphone customers who pursue product differentiation
increasingly adopted OLED panels. Also, the trend towards using higher resolution and large panels lasted throughout the
year. This trend is expected to continue in 2017, and product categories will further expand to new technologies such as
flexible OLED.
Meanwhile, with regards to large-size panels, the UHD TV market grew last year and the trend toward large-size panels
continued under
stabilizing ASPs from improved supply-demand conditions. Although some risks remain such as intense
competition among competitors, the market conditions are projected to remain favorable for an extended period of time.
< Market Share of the DP Business’ Main Product >
Product 2016 2015 2014
Display Panel 17.1%
21.1% 20.9%
※ 2014, 2015 and 2016 market share data is from research firm, IHS (global market share, large-size panel in amount).
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 29 / 240
Business Condition
The Company is constantly upgrading technologies and improving productivity to strengthen business competitiveness.
For the mid to small-size OLED business, the Company is working to consolidate its leading position in the market by
actively responding to major customers’ demands, improving product mix, and expanding the customer base. For the
large-size LCD business, the Company aims to improve profitability by reinforcing competitiveness of high-end panels
such as ultra large-sized and UHD panels, and expanding shipments of differentiated products such as Frameless/Curved.
In 2017, we expect our smartphone manufacturing customers will increasingly adopt OLED panels in their products.
Accordingly, we will expand our flexibility in the supply of various products by reinforcing our technological leadership
and securing required capacity in accordance with the market demand.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 30 / 240
B. Financial Summary by Division
(Unit: KRW million, %)
Division Classification
2016 2015 2014
Amount Portion Amount Portion Amount Portion
CE
Total sales 109,672,506 22.8% 120,688,835 24.5% 124,916,892 25.3%
Internal sales 62,627,083 22.4% 73,793,424 25.2% 74,733,757 25.9%
Net sales 47,045,423 23.3% 46,895,411 23.4% 50,183,135 24.3%
Operating profit 2,638,002 9.0% 1,254,187 4.7% 1,184,325 4.7%
Total asset 49,675,022 13.6% 45,998,007 12.8% 43,116,374 12.8%
IM
Total sales 211,523,973 43.9% 222,023,600 45.0% 236,438,979 47.9%
Internal sales 111,221,861 39.7% 118,469,345 40.5% 124,674,435 43.3%
Net sales 100,302,112 49.7% 103,554,255 51.6% 111,764,544 54.2%
Operating profit 10,807,569 37.0% 10,142,022 38.4% 14,562,885 58.2%
Total asset 111,574,049 30.5% 98,463,323 27.4% 94,227,108 27.9%
DS
Semi-
conductor
Total sales 99,527,926 20.6% 90,600,806 18.4% 75,058,071 15.2%
Internal sales 48,370,924 17.3% 43,014,054 14.7% 35,328,169 12.3%
Net sales 51,157,002 25.3% 47,586,752 23.7% 39,729,902 19.3%
Operating profit 13,595,004 46.5% 12,787,297 48.4% 8,776,442 35.1%
Total asset 102,251,069 28.0% 98,989,253 27.6% 87,567,196 25.9%
DP Business
Unit
Total sales 55,884,739 11.6% 55,120,243 11.2% 52,227,615 10.6%
Internal sales 28,956,095 10.3% 27,633,382 9.4% 26,500,446 9.2%
Net sales 26,928,644 13.3% 27,486,861 13.7% 25,727,169 12.5%
Operating profit 2,226,626 7.6% 2,295,367 8.7% 660,181 2.6%
Total asset 57,240,065 15.6% 50,147,263 14.0% 46,826,533 13.8%
Total
Total sales 159,473,455 33.1% 149,974,731 30.4% 131,459,756 26.6%
Internal sales 81,325,252 29.0% 74,948,617 25.6% 65,669,950 22.8%
Net sales 78,148,203 38.7% 75,026,114 37.4% 65,789,806 31.9%
Operating profit 15,850,986 54.2% 14,887,262 56.4% 9,430,915 37.7%
Total asset 183,951,625 50.3% 174,264,841 48.5% 160,138,321 47.4%
※ Net sales reported here includes inter-divisional sales.
Cumulative net sales for 2016 were KRW 201,867 billion. By Division, CE reported net sales of KRW 47,045 billion
(23.3%) and IM reported net sales of KRW 100,302 billion (49.7%). The DS Division contributed approximately 38.7%
of net sales: KRW 51,157 billion (25.3%) by the Semiconductor Sub-Division and KRW 26,929 billion (13.3%) by the DP
Business Unit.
Cumulative operating profit for 2016 was KRW 29,241 billion. The CE Division accounted for 9.0% with KRW 2,638
billion, the IM Division accounted for 37.0% with KRW 10,808 billion and the DS Division accounted for 54.2% with
KRW 15,851 billion.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 31 / 240
Reasonable Allocation of Common SG&A (Selling General & Administrative) Expenses and Assets
(1) For common SG&A expenses, specific expenses that are allocable to a specific product/model are allocated to such
product/model. However, common expenses that cannot be attributed to a specific product/model category are reasonably
allocated throughout the Company based on an allocation standard (expense-to-sales ratio, number of personnel, etc.).
(2) For common assets, assets that can be directly allocated (inventory assets, fixed assets, investment assets, etc.) are
allocated to the corresponding organizational unit. Assets that are commonly managed are allocated to each Division
based on an allocation standard (expense-to-sales ratio, pre-tax profit, etc.).
2. Key Products and Services
A. Revenue
In 2016, the CE Division’s revenue of KRW 47,045 billion accounted for 23.3% of the total net revenue; the IM Division
accounted for 49.7% with KRW 100,302 billion; and the DS Division accounted for 38.7% with KRW 78,148 billion.
The Company’s net revenue by Division as of December 31, 2016 is as follows:
(Unit: KRW 100 million, %)
Division Major Products Net Revenue Portion
CE
TV, monitor, refrigerator, washing machine, air conditioner,
medical equipment, etc.
470,454
23.3%
IM HHP, network system, computer, etc. 1,003,021
49.7%
DS
Semiconductor DRAM, NAND flash, Mobile AP, etc. 511,570
25.3%
DP Business Unit TFT-LCD, OLED, etc. 269,286
13.3%
Sub-Total 781,482
38.7%
Others - -236,290
-11.7%
Total 2,018,667
100.0%
※ Includes sales between Divisions (on consolidated basis).
☞ See 『5. Sales and Distribution』 for sales by each product.
B. Average Selling Price (ASP) Changes
In 2016, the ASP of TVs declined by 5.1% compared to the previous year, and the ASP of memory products also declined.
The ASPs of HHPs increased by 1.3% compared to the previous year, but the ASP of display panels is on the decline as
companies increase their capacity, causing oversupply in the market.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 32 / 240
3. Key Raw Materials
(On consolidated basis as of December 31, 2016)
(Unit: KRW 100 million, %)
Division Type Item Specific usage Purchase price Portion Note (supplier)
CE
Raw material Display panel Color picture signaler 54,331 25.1%
AUO, BOE, etc.
Raw material Others 162,040 74.9%
Division Total 216,371 100.0%
IM
Raw material Baseband Chip CPU 34,821 10.3%
Qualcomm, etc.
Raw material Camera Module Mobile phone camera 34,432 10.2%
Samsung Electro-
Mechanics, etc.
Raw material Mobile display panel Color picture signaler 19,503 5.8%
Iljin Display, etc.
Raw material Others 249,998 73.8%
Division Total 338,754 100.0%
DS
Raw material Window Tempered glass 21,204 10.4%
BIEL, etc.
Raw material POL Polarizer plate 15,942 7.8%
Dongwoo Fine-
Chem, NITTO, etc.
Raw material Glass Glass substrate for display 14,090 6.9%
Corning Precision
Materials, etc.
Raw material Others 153,150 74.9%
Division Total 204,386 100.0%
Others 316 -
Total 759,827 -
※ Samsung Electro-Mechanics, the Camera module supplier, is an affiliate of Samsung Group.
For the CE Division, key raw materials include display panels for TVs and monitors and PDP modules. For the IM
Division, key raw materials include display panels, camera modules and baseband chips for mobile devices. For the DS
Division, key raw materials include glass, polarizers (“POL”) and window glass.
Large display panels for TVs and monitors are supplied by AU Optronics (AUO) and BOE (among others), mobile
display panels are supplied by Iljin Display and others, camera modules from Samsung Electro-Mechanics, and baseband
chips are supplied by Qualcomm and others. The Company manufactures display panels with glass and POLs supplied by
Corning Precision Materials and Dongwoo Fine-Chem.
(Raw Materials Price Trends)
The price of TV and monitor display panels, which are the major raw materials for the CE Division, declined 13% on
average since 2015. For the IM Division, since 2015, the price of mobile display panels have increased by 3%, and the
price of baseband chips have decreased by 12%.
For the DS Division, the price of wafers, which is one of its major raw
materials, has increased by around 8%, and the price of glass for display panels has increased by 1% since the previous
year.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 33 / 240
4. Production and Facilities
A. Production Capacity, Output, Utilization Rate
(Capacity)
(Unit: 1,000)
Division Item
2016 2015 2014
Quantity Quantity Quantity
CE TV 52,308
50,450 62,990
IM
HHP
447,200
497,050 523,750
DS
Memory 415,026,000
268,630,000 173,506,000
Display Panel 10,028
9,459 9,185
※ Global production capacity for major product categories
The CE and IM Divisions’ production capacity, by major product, is calculated as follows:
The average number of lines (x) the average output per hour (x) the average operation hours per day (x) the days of
operation
Memory production capacity for the DS Division is calculated as follows:
Converted output (1GB equivalent) ÷ the utilization rate.
Display panel production capacity is calculated as follows:
The total producible panel surface area ÷ the dimensions of eighth generation glass (2200x2500mm)
(Output)
(Unit: 1,000)
Division Item
2016 2015 2014
Quantity Quantity Quantity
CE TV 47,428
45,821 55,066
IM HHP 389,838
423,058 439,520
DS
Memory 415,026,000
268,630,000 173,506,000
Display Panel 8,307
8,284 8,252
※ Global output for major product categories
In 2016, the CE Division’s output of TVs was 47,428 thousand units (major production sites: Korea, China, Mexico,
Brazil, and Hungary). The IM Division’s output of HHPs was 389,838 thousand units (major production sites: Korea,
China, Vietnam, and Brazil). The DS Division’s memory output (1GB equivalent) was 415,026 million (major production
sites: Korea and China). The DS Division’s output of display panels was 8,307 thousand units (major production sites:
Korea, China, and Slovakia).

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 34 / 240
(Utilization Rate)
(Unit: 1,000)
Division Item
2016
Production capacity
2016
Actual output
Utilization Rate
CE TV 52,308
47,428 90.7%
IM HHP 447,200
389,838 87.2%
In 2016, CE and IM utilization rates were calculated as actual output relative to production capacity. The utilization rates
were 90.8% for TVs and 87.2% for HHPs.
(Unit: hours)
Division Item
2016
Potential
Production Time
2016
Actual
Production Time
Utilization Rate
DS
Memory
52,560
52,560 100.0%
Display Panel
82,944
82,944 100.0%
The DS Division operates memory and display panel production in three shifts (24 hours a day). Cumulative operating
days in 2016 including holidays were 366 days. The utilization rate was calculated as actual hours [366 days (x) number
of production lines (x) 24 hours] relative to production capacity.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 35 / 240
B. Production Facilities and Investment
(1) Key facilities for production and operation
The Company’s operational activities include manufacturing, development, marketing, and sales in Korea – including
operations in Seocho, Seoul, Suwon, Gumi, Giheung, Onyang, Gwangju – and 9 regional headquarters under the CE and
IM Divisions and 5 under the DS Division in North America, Europe, and China.
[Operations]
Region Headquarters Location
Korea
(11)
Seocho Seoul, Korea
Woomyeon Seoul, Korea
Suwon Suwon, Korea
Gumi1 Gumi, Korea
Gumi2 Gumi, Korea
Giheung Yongin, Korea
Onyang Asan, Korea
Hwaseong Hwaseong, Korea
Gwangju Gwangju, Korea
Cheonan Cheonan, Korea
Asan Asan, Korea
Overseas
(9 Regional Headquarters for
CE and IM Divisions)
North America New Jersey, US
Europe London, UK
China Beijing, China
Southeast Asia Singapore, Singapore
Southwest Asia New Delhi, India
CIS Moscow, Russia
Middle East Dubai, UAE
Africa Johannesburg, Republic of South Africa
Latin America Sao Paolo, Brazil
Overseas
(5 Regional Headquarters for
DS Division)
Americas San Jose, US
Europe Eschborn, Germany
China Shanghai, China
Southeast Asia Singapore, Singapore
Japan Tokyo, Japan

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 36 / 240
The Company’s property, plant and equipment include land, buildings and structures, machinery and equipment, and
construction in progress. As of December 31, 2016, their total book value is KRW 91,473 billion, which is an increase of
KRW 4,996 billion from year-end 2015. In 2016, new acquisitions of KRW 25,494 billion and depreciation of KRW
19,313 billion were recorded.
(Unit: KRW million)
Classification Land
Buildings and
Structures
Machinery and
Equipment
Construction
in –progress
Others Total
At 1 January 2016
Book value 7,848,432
22,453,296
43,077,879
10,970,052 2,127,451
86,477,110
Acquisition cost 7,848,432
32,850,110
147,315,096
10,970,052 6,303,834
205,287,524
Accumulated depreciation
(Including accumulated impairment loss)
-
(10,396,814)
(104,237,217)
- (4,176,383)
(118,810,414)
Increase
(Decrease)
General acquisition and capital expenditure 37,735
3,482,228
12,769,230
8,230,900 974,275
25,494,368
A
cquisition as a result of business
combination
-
-
4,492
240 2,271
7,003
Depreciation -
(1,631,089)
(16,814,751)
- (866,680)
(19,312,520)
Disposal/Discard (28,331)
(26,384)
(80,552)
(5) (66,684)
(201,956)
Impairment -
(2,805)
(370,574)
- (1,731)
(375,110)
Re-classification to assets held-for-sale -
(11,922)
(20,131)
(7,660) (45,156)
(84,869)
Others 11,843
112,502
(263,538)
(419,541) 27,749
(530,985)
Balance at
31 Dec 2016
Book value 7,869,679
24,375,826
38,302,055
18,773,986 2,151,495
91,473,041
Acquisition cost 7,869,679
36,474,462
155,285,378
18,773,986 6,769,149
225,172,654
Accumulated depreciation
(Including accumulated impairment loss)
-
(12,098,636)
(116,983,323)
- (4,617,654)
(133,699,613)
※ Others: Includes effects of changes in FX rates and effects of reduction in government subsidy.
※ Market value of major tangible assets is omitted as objective assessment is difficult.
※ Property, plant, and equipment above is presented on a consolidated basis.
(2) CAPEX
In 2016, the Company invested KRW 25.5 trillion in CAPEX, including upgrading production lines of the Semiconductor
Sub-Division and the DP Business Unit. The total CAPEX for 2017 is yet to be finalized, as the Company is still in the
process of considering many variables with respect to business environment and market conditions.
[CAPEX by Division]
(Unit: KRW 100 million)
Business Purpose Period Assets
Investment in
2016
Semiconductor
Establishment, addition,
upgrade
Jan '16 ~ Dec '16 Buildings, facilities 131,513
DP Business Unit
Establishment, addition,
upgrade
Jan '16 ~ Dec '16 Buildings, facilities 98,313
Other Other Jan '16 ~ Dec '16 Buildings, facilities 25,118
Total
254,944

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 37 / 240
5. Sales and Distribution
A. Sales
In 2016, the Company recorded KRW 201,867 billion of total revenue, an increase of 0.6% compared to the prior year. By
Division, when compared to 2015, CE Division’s revenue increased by 0.3%, IM Division’s revenue decreased by 3.1%
and DS Division’s revenue increased by 4.2%.
(Unit: KRW 100 million)
Division Sales types Product categories 2016 2015 2014
CE
Goods
Products
Service
Others
TV, monitor, air conditioner,
refrigerator, washing machine,
medical equipment, etc.
470,454
468,954 501,831
IM
Goods
Products
Service
Others
HHP,
Network System, Computer,
etc.
1,003,021
1,035,543 1,117,645
DS
Semiconductor
Goods
Products
Service
Others
DRAM,
NAND Flash, Mobile AP, etc.
511,570
475,868 397,299
DP Business Unit
Goods
Products
Service
Others
TFT-LCD,
OLED, etc.
269,286
274,869 257,272
Division total 781,482
750,261 657,898
Others Other revenue - -236,290
-248,223 -215,314
Total 2,018,667
2,006,535 2,062,060
※ Includes internal sales between Divisions.
□ Sales by Major Product
(Unit: KRW 100 million)
Classification 2016 2015 2014
TV 287,241
292,194 324,486
Mobile Devices
977,494
1,005,117 1,074,149
Memory 378,594
342,917 293,244
Display Panel 269,286
274,869 257,272
※ Including internal sales between Divisions.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 38 / 240
□ Sales by Type
(Unit: KRW 100 million)
Classification 2016 2015 2014
Products 2,006,326
1,988,452 2,036,716
Service and other Sales 12,341
18,083 25,344
Total 2,018,667
2,006,535 2,062,060
※ Other sales consists of royalty income and etc.
□ Sales by Region (on a separate basis)
(Unit: KRW 100 million)
Classification 2016 2015 2014
Korea 140,656
145,908 153,247
Americas 426,448
425,042 433,940
Europe 170,850
173,583 208,982
Asia and Africa 281,021
291,473 298,140
China 320,497
316,044 283,946
Total 1,339,472
1,352,050 1,378,255
B. Sales Channels
□ Korea
Seller Sales Channel Consumer
Manufacturer
(Facility)
Retailer
Consumer
Distributor (General Merchandise Store, Discount Store, Department Store, Home-Shopping, Internet)
Retailer Cooperative Joint Market, Sales Shop, Open Stores
Telecommunication Service Provider (SKT, KT, LG U+)
Direct Sales
□ Overseas
Seller Sales Channel Consumer
Production
Subsidiaries
Regional Sales Office
Retailer
Consumer
Dealer Retailer
Distributor Dealer Retailer
Telecommunication Service Provider
Regional Distribution Office
Regional Sales
Office
Retailer
Dealer Retailer
Distributor Dealer Retailer
Direct Sales
□ Sales Ratio by Channel
Channel Wholesale Retail Special/direct sale Others
Ratio 28% 26% 41% 5%
※ On a global basis

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 39 / 240
C. Sales Methods and Conditions
□ Domestic
Classification Channel Collection Incidental expense sharing
Exclusive Agency
- Credit agreement (Cash, 30 day credit)
(Credit applied within 100% of collateral)
- Case specific cost sharing as determined by mutual
agreement
Distributor
General Merchandise Store,
Discount Store, Department Store,
Home Shopping, Internet
Case specific and contract specific
- Case specific cost sharing as determined by mutual
agreement
Special/direct sale Corporate Clients, etc. Case specific and contract specific N/A
□ Overseas
Classification Channel Collection Incidental expense sharing
Retailer Retail store Case specific and contract specific
- Case specific cost sharing as determined by mutual
agreement
Dealer
General merchandise store,
Discount store, Department store
Case specific and contract specific
- Case specific cost sharing as determined by mutual
agreement
Distributor Direct sales to local distributors Case specific and contract specific
- Case specific cost sharing as determined by mutual
agreement
B2B Corporate Clients, etc. Case specific and contract specific N/A
D. Sales Strategy
○ Expand market leadership based on smart devices
○ Provide differentiated value to customers through brand, products, and service
○ Strengthen operational capabilities for customer/market
○ Enhance sales capabilities
E. Major Customers
In 2016, major customers included Apple, BestBuy, Deutsche Telekom, Sprint and Verizon (in alphabetical order). Sales
to our five major customers accounted for approximately 13% of total sales.
6. Long-term Contracts
As of December 31, 2016, there are no long-term contracts that have a significant impact on the Company’s financial
statement.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 40 / 240
7. Financial Risk Management
The Company’s financial risk management focuses on minimizing market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk arising from
operating activities. To mitigate these risks, the Company implements and operates a financial risk policy and program that
closely monitors and manages such risks.
The finance team mainly carries out the Company’s financial risk management. With the cooperation of the Company’s
Divisions, domestic and foreign subsidiaries, the finance team periodically measures, evaluates and hedges financial risks
and also establishes and implements global financial risk management policies.
Financial team employees are dispatched to the regional headquarters of located in the US, UK, Singapore, China, Japan,
Brazil and Russia to oversee application of global financial risk management policies at the local finance centers.
Financial assets subject to the Company’s financial risk management are as follows: cash and cash equivalents, short-term
financial instruments, available-for-sale financial assets, trade, and other receivables, and other financial assets. The
Company’s financial liabilities subject to financial risk management are as follows: trade and other payables, borrowings,
debentures, and other financial liabilities.
A. Market Risk
(1) Foreign Exchange Risk
The Company experiences currency gains and losses based on the different functional currency of each entity due to global
operations. As such, the Company is exposed to foreign currency volatility from exchange positions of currencies,
especially the US Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen, and Chinese Yuan.
To minimize foreign exchange risk arising from operating activities, the Company’s foreign exchange management
policy requires normal business transactions (including imports and exports) to be conducted in the local currency or for
the cash-in currency to be matched with the cash-out currency. The Company’s foreign exchange risk management
policy also defines foreign exchange risk, measuring period, ownership responsibilities, management procedures,
hedging period and hedge ratio.
The Company prohibits all speculative foreign exchange transactions. The Company has established a global foreign
exchange system to manage exposures related to receivables and payables denominated in foreign currencies.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s foreign currency exposure to its USD, Euro and Yen denominated financial
assets and liabilities, based on a hypothetical 5% currency rate change against the Korean won (KRW), are presented
below:
(Unit: KRW million)
Classification
Year-End 2016 Year-End 2015
Appreciation Depreciation Appreciation Depreciation
USD 222,149 (222,149) 143,266 (143,266)
EUR 138,084 (138,084) 19,626 (19,626)
JPY (61,294) 61,294 (15,120) 15,120

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 41 / 240
(2) Risk of Volatility in Equity Securities Held as Investment
The Company’s investment portfolio consists of direct and indirect investments in equity securities and is classified as
available-for-sale, which is in line with the Company’s strategy.
As of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, a price fluctuation in relation to marketable equity securities by 1%
would result in changes in other comprehensive income (before income tax) of KRW 23,622 million and KRW 46,748
million, respectively.
(3) Interest Rate Risk
Risk of changes in interest rate for a floating interest rate financial instrument is defined as the risk that the fair value of
future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates and the risk that cash
flows from investing/financing activities will fluctuate with changes in interest gain/loss. The Company is exposed to
interest rate risk mainly through interest bearing liabilities and assets. The Company has policies to minimize uncertainty
and expenses from changes in interest rates. In order to minimize interest rate related risks, the Company minimizes
external borrowings by facilitating cash pooling systems on a regional and global basis. The Company manages its
exposure to interest rate risks by regularly monitoring risk factors and timely resolution, and prevention, of issues.
(Unit: KRW million)
Classification
Year-End 2016 Year-End 2015
Interest Rate Increase Interest Rate Decrease Interest Rate Increase Interest Rate Decrease
Financial Assets 64,803 (64,803) 81,962 (81,962)
Financial Liabilities (9,123) 9,123 (22,314) 22,314
Net Effect 55,680 (55,680) 59,648 (59,648)
B. Credit Risk
Credit risk arises during the normal course of transactions and investing activities where clients or other parties fail to
discharge an obligation. The Company actively monitors its credit risk on a regular basis and determines a counterparty’s
credit limit periodically based on the counterparty’s financial conditions, default history, and other important factors.
Credit risk can arise from transactions with financial institutions which include financial instrument transactions such as
cash and cash equivalents, savings, and derivative instruments. To minimize such risk, the Company transacts only with
banks that have strong international credit ratings (S&P “A” and above), and all new transactions with financial
institutions with no prior transaction history are approved, managed and monitored by the SEC’s finance team and the
local finance center. The Company normally enters into financial agreements that do not: require guarantees for payment,
have restrictions on debt ratios or have acceleration provisions. The Company requires separate approval for contracts
with such restrictive provisions.
The Company estimates that its maximum exposure to credit risk is the carrying value of its financial assets, net of
impairment losses.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 42 / 240
C. Liquidity Risk
Due to large investments made by the Company, maintaining adequate levels of liquidity is critical. The Company strives
to achieve this goal by periodically forecasting its cash flow, estimating required cash levels, and managing income and
expenses.
The Company manages its liquidity risk by periodically forecasting projected cash flows. If abnormal signs are identified,
SEC works with the local finance center and provides liquidity support by utilizing its globally integrated finance
structures such as cash pooling. In addition, the Company maintains a liquidity management process which provides
additional financial support through the local finance center and the Company when necessary. The cash pooling program
allows sharing of surplus funds among entities and contributes to minimizing liquidity risk and strengthening the
Company’s competitive position by reducing capital operating expenses and finance expenses.
In addition, the Company mitigates liquidity risk by contracting with financial institutions with respect to bank overdrafts
and foreign trade finance and by providing payment guarantees to subsidiaries. For large scale facility investments,
liquidity risk is minimized by utilizing internal reserves and long term borrowings according to the capital injection
schedule.
As of year-end 2016, financial liabilities classified according to the term remaining from the Reporting Date until the due
date are as follows:
(1) Year-End 2016
(Unit: KRW million)
Under 3 mos. ~6 mos. ~1yr 1~5 yrs Over 5 yrs
Financial Liabilities 40,918,912 1,588,798 150,744 4,346,200 50,073
(2) Year-End 2015
(Unit: KRW million)
Under 3 mos. ~6 mos. ~1yr 1~5 yrs Over 5 yrs
Financial Liabilities 32,275,387 412,196 1,331,166 3,057,099 476,432
The above financial liabilities were classified according to the term remaining from the Reporting Date until the due date.
The cash flows included were not discounted at present value. Please note, as expiry of derivatives bought and sold is not
necessary for understanding liquidity requirements in a given period, its fair value of KRW 74,697 million (year-end 2015:
KRW 38,829 million) is included in the “under 3 mos.” figure. These derivatives contracts are managed based on their fair
value rather than expiration. Cash-settled derivatives are composed of currency forwards used for managing the
Company’s exchange rate risk.
The maximum amount of liquidity risk exposure due to payment guarantee and performance guarantee of affiliates (other
than the financial liabilities set forth above) is KRW 59,016 million (cf. year-end 2015: KRW 67,017 million).

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 43 / 240
D. Capital Risk Management
The purpose of capital management is to maintain a healthy capital structure. The Company uses debt ratio as an indicator
and measure of an appropriate capital structure. The debt ratio is calculated by dividing total liabilities by total equity in
the consolidated financial statements.
The Company’s capital risk management policy has not changed since the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015. The
Company has maintained “A+ ” and “A1” credit ratings from S&P and Moody’s, respectively.
The total liabilities to equity ratio as of year-end 2016 and year-end 2015 are as follows:
(Unit: KRW million)
December 31, 2016 December 31, 2015
Total liabilities 69,211,291
63,119,716
Total equity 192,963,033
179,059,805
Total liabilities to equity ratio 35.9%
35.3%

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 44 / 240
E. Fair Value Measurement
- Carrying amounts and fair values of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2016 and December 31,
2015 are as follows:
(Unit: KRW million)
Classification
December 31, 2016 December 31, 2015
Carrying amount Fair value Carrying amount Fair value
Financial assets
Cash and cash equivalents 32,111,442
(1)
22,636,744
(1)
Short-term financial instruments 52,432,411
(1)
44,228,800
(1)
Short-term available-for-sale
financial assets
3,638,460
3,638,460
4,627,530 4,627,530
Trade and other receivables 24,279,211
(1)
25,168,026
(1)
Long-term available-for-sale
financial assets
(2)
6,804,276
5,826,507
8,332,480 8,225,687
Other
(3)
3,459,863
919,071
3,546,434 1,070,839
Total Financial assets 122,725,663
108,540,014
Financial liabilities
Trade payables 6,485,039
(1)
6,187,291
(1)
Short-term borrowings 12,746,789
(1)
11,155,425
(1)
Other payables 10,225,271
(1)
7,625,490
(1)
Current portion of long-term
borrowings
1,232,817
(1)
221,548
(1)
Debentures 58,542
76,129
1,230,448 1,261,783
Long-term borrowings 1,244,238
1,225,455
266,542 242,603
Long-term other payables 3,009,659
3,022,821
2,719,674 2,581,985
Other
(3)
11,942,469
74,697
7,947,398 38,829
Total Financial liabilities 46,944,824
37,353,816
1
Assets and liabilities whose carrying amounts are reasonable approximations of their fair value are excluded from the
fair value disclosures.
2
Amount measured at cost (2016: KRW 977,769 million and 2015: KRW 106,793 million) is excluded, as the range of
reasonable fair value estimates are significant and the probabilities
of the various estimates cannot be reasonably
assessed.
3.
Assets of KRW 2,452,118 million (2015: KRW 2,349,454 million) and liabilities of KRW 11,867,772 million (2015:
KRW 7,908,569 million) are excluded from the fair value disclosures, as the carrying amounts are reasonable
approximations of their fair values.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 45 / 240
The following table presents the fair value of assets and liabilities, by Level (as defined below), measured as of the dates
indicated:
As of December 31, 2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Total balance
Assets
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets -
3,638,460
- 3,638,460
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
1
2,362,235
-
3,464,272 5,826,507
Other -
919,071
- 919,071
Liabilities
Debentures -
76,129
- 76,129
Long-term borrowings -
1,225,455
- 1,225,455
Long-term other payables -
2,680,119
342,702 3,022,821
Other -
74,697
- 74,697
December 31, 2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Total balance
Assets
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets -
4,627,530
- 4,627,530
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
1
4,674,753
78,189
3,472,745 8,225,687
Other -
1,055,240
15,599 1,070,839
Liabilities
Debentures -
1,261,783
- 1,261,783
Long-term borrowings -
242,603
- 242,603
Long-term other payables -
2,269,247
312,738 2,581,985
Other -
38,829
- 38,829
The levels of the fair value hierarchy (based on characteristics of the input variables) and its application to financial assets
and liabilities are described below.
ㆍLevel 1: Quoted market prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities
ㆍLevel 2: Fair valuation based on inputs that are observable in the market
(Other than quoted prices included within Level 1)
ㆍLevel 3: Fair valuation based on inputs that are unobservable in the market
The fair value of financial instruments traded in active markets is based on quoted market prices at the statement of
financial position date. A market is regarded as active if quoted prices are readily and regularly available from an
exchange, dealer, broker, industry group, pricing service, or regulatory agency, and those prices represent actual and
regularly occurring market transactions on an arm’s length basis. The quoted market price used for financial assets held by
the Company is the current bid price. These instruments are included in Level 1. Instruments in Level 1 include listed
equity investments classified as trading securities or available-for-sale financial assets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded on an active market (for example, over-the-counter derivatives)
is determined using valuation models. These valuation models maximize the use of observable market data where it is

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 46 / 240
available and rely as little as possible on entity specific information. If all significant inputs required to measure the fair
value of an instrument are observable, the instrument is included in Level 2.
If one or more of the significant inputs are not based on observable market data, the instrument is included in Level 3.
The Company performs fair value measurements required for financial reporting purposes, including Level 3 fair values,
and discusses valuation processes and results at least once every quarter in line with SEC’s quarterly reporting dates. The
Company recognizes changes in Levels at the end of the reporting period, if corresponding events or changes in
circumstances necessitating such reclassification have occurred.
Specific valuation methods used to value financial instruments include:
ㆍQuoted market prices or dealer quotes for similar instruments.
ㆍThe fair value of foreign exchange forward contracts is determined using, among other things, forward exchange rates
at the statement of financial position date, with the resulting value discounted back to present value.
Other methods, such as discounted cash flow analysis, are used to determine fair value for the remaining financial
instruments. For trade and other receivables, the book value approximates a reasonable estimate of fair value.
- Valuation Methods and Inputs
ㆍThe Company utilizes a present value method to discount future cash flows at a proper interest rate for corporate bonds,
government and public bonds, and bank debentures that are classified as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy.
ㆍThe following table presents the valuation methods and inputs used for major financial instruments classified as Level 3.
(In millions of Korean won)
Classification Fair Value
Valuation
Technique Level 3 Inputs
Input Range
(Weighted Average)
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
Maltani
(formerly Taewon Electric)
16,270 Discounted cash
flow
Permanent growth rate -1.00% ~ 1.00% (0%)
Weighted average cost of capital 7.45% ~ 9.45% (8.45%)
Samsung Venture
Investment
7,515 Discounted cash
flow
Permanent growth rate -1.00% ~ 1.00% (0%)
Weighted average cost of capital 21.31% ~ 23.31% (22.31%)
Coming Incorporated
convertible preferred shares
3,440,487 Trinomial model Risk adjusted discount rate 5.74% ~ 7.74% (6.74%)
Price volatility 27.8% ~ 33.8% (30.80%)
Long-term other payables
Contingent liabilities 342,702 Discounted cash
flow
Discount rate 3.81% ~ 4.65% (4.23%)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 47 / 240
- Changes in Level 3 Instruments:
(In millions of Korean won) 2016 2015
Balance as of January 1 3,488,344
3,548,095
Purchases -
119,297
Disposals (14,805)
(55,986)
Amount recognized in profit or loss (795)
3,530
Amount recognized in other comprehensive income 695,631
(304,012)
Other (704,103)
177,420
Balance as of September 30 3,464,272
3,488,344
(In millions of Korean won) 2016 2015
Balance as of January 1 312,738
-
Amount recognized in profit or loss 29,964
312,738
Balance as of September 30 342,702
312,738
- Sensitivity Analysis for Recurring Fair Value Measurements Categorized within Level 3
Sensitivity analysis of financial instruments is performed to measure favorable and unfavorable changes in the fair value
of financial instruments which are affected by inputs that are unobservable in the market, using a statistical technique.
When the fair value is affected by two or more input variables, such fair value is calculated using the most favorable or
most unfavorable input values.
The results of the sensitivity analysis for the effect on profit or loss from changes in inputs for each type of financial
instrument, which is categorized within Level 3 and subject to sensitivity analysis, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won) Favorable Changes Unfavorable Changes
Classification Profit or Loss
Equity
Profit or Loss Equity
Long-term available for sale
financial assets
1
-
194,732
- (227,857)
Long-term other payables
2
1,920
1,920
(1,932) (1,932)
Total
1,920
196,652
(1,932) (229,789)
1
For equity securities, changes in fair value have been calculated by increasing or decreasing the correlation between
growth ratio (-1% ~ 1%) and the discount rate, which are significant unobservable inputs.
2
For long-term other payables, changes in fair value have been calculated by increasing or decreasing the discount rate
by 10%, which are major variables that cannot be observed.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 48 / 240
8. Derivative Instruments and Put Options
(A) The value of derivative instruments of the Company and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 is presented below:
(Unit: KRW million)
Asset Liabilities Valuation Gain Valuation Loss
Put options - - - 794
Total - - - 794
※ The option values were calculated using appropriate valuation methodologies, including the Black-Scholes model
The Company and its subsidiaries hold convertible preferred shares of Corning Incorporated and its value as of
December 31, 2016 is as follows.
(Unit: KRW million)
Purchasing Price Fair Value Valuation Gain Valuation Loss
Convertible Preferred
Shares
2,434,320 3,440,487
1,006,167 -
※ Fair value is determined using Trinomial Tree model; valuation gain is reflected in equity (under other components of equity).
(B) To manage foreign exchange risk, SEC’s subsidiaries hedge their foreign currency positions by trading currency
forward contracts of such currencies. Overseas subsidiaries buy or sell currency forwards with less than one year
maturity through a bank to minimize such risks.
(C) As of December 31, 2016, the Company has 1,609 currency forward contracts involving 37 foreign currencies
including USD/EUR/JPY. Currency forwards as of December 31, 2016 are as follows.
(Unit: KRW million)
Asset Liabilities Valuation Gain Valuation Loss
Currency forwards 63,014 74,678
52,389 66,645
Total 63,014 74,678
52,389 66,645

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 49 / 240
9. Major Contracts
Account Item Contents
Ericsson
Contract type Patent cross-license agreement
Contract date 2014.01.25
Purpose and contents Secure operational advantage through mutual patent licensing
Google
Contract type Patent cross-license agreement
Contract date and period 2014.01.25 / indefinite term
Purpose and contents Secure business freedom through mutual patent licensing
Others Permanent license contract (including patent applications in the next 10 years)
Cisco
Contract type Patent cross-license agreement
Contract date 2014.01.23
Purpose and contents Secure business freedom through mutual patent licensing
Global Foundries
Inc.
Contract type Process technology license contract
Contract date 2014.02.28
Purpose and contents Expand customer base of 14nm process
InterDigital
Contract type Patent license agreement
Contract date 2014.06.03
Purpose and contents Secure business freedom through patent licensing
Sharp
Contract type Patent cross-license agreement
Contract date 2015.01.01
Purpose and contents Secure operational advantage through mutual patent licensing
Microsoft
Contract type Settlement Agreement
Contract date -
Purpose and contents End dispute over royalty payment
Nokia
Contract type Patent license agreement
Contract date 2016.07.12
Purpose and contents Secure business flexibility through patent licensing

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 50 / 240
HP
Contract type Sales of printing solutions business
Contract date 2016.09.12
Purpose and contents Concentrate on our core competencies and advance business structure
Others Transaction value: USD 1.05 billion
Harman
Contract type Acquisition of shares
Contract date 2016.11.14
Purpose and contents Strengthen business capabilities by acquiring the company’s shares
Others Transaction value: USD 8.02 billion
※ Information that may be referenced or used in other IP disputes, including contract amount, is not included.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 51 / 240
10. Research and Development Activities
A. Summary of Activities and R&D Expenditures
The Company is leading the global market by continuously developing creative and innovative products and the future
technology through shifting its way of thinking and understanding customer demand.
The Company is currently developing creative and innovative products and doing its utmost to cement its position in the
global IT industry and become a worldwide leader in industrial technology by creating and securing next-generation
technology.
[R&D expenses]
(Unit: KRW million)
2016 2015 2014
Total R&D expenditure 14,792,343
14,848,754 15,325,507
Accounting
Capitalization of development
expenses (intangible asset)
680,962
1,143,059 940,001
R&D costs (expenses) 14,111,381
13,705,695 14,385,506
R&D expenses/sales Ratio 7.3%
7.4% 7.4%
※ On a consolidated basis (in conformity with K-IFRS)
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s R&D expenses were KRW 14,792 billion. The Company capitalized KRW 681
billion and recognized KRW 14,111 billion as current expenditure.
B. R&D Organization and Operations
Korea
The Company operates three levels of R&D organizations; a business unit development team under each Division that
develops market ready technologies with a 1-2 year outlook, a research institute under each business unit that develops
mid-to-long term technology with a 3-5 year outlook, and the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology that develops
core technology as seeds for future growth engines.
Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology is the central research institute of Samsung Electronics that has been
established to lead the Company into the future and serve as an incubator of cutting-edge technology. It has a creative
R&D system and provides R&D direction for promising growth sectors at the Company level, exploring future growth
engines and strengthening technological competitiveness of core businesses.
Overseas
The Company operates R&D organizations in the US (SRA), the UK (SRUK), Russia (SRR), Israel (SRIL and SIRC),
India (SRI-Bangalore and SRI-Delhi), Japan (SRJ), China (SSCR, SRC-Beijing, SRC-Nanjing, SRC-Tianjin, and SRC-
Guangzhou) to carry out research activities for product development and basic technological research.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 52 / 240
※ As of December 31, 2016
※ Refer to 『G. Subsidiaries subject to consolidation』 in 『I. Corporate Overview』 for more details about overseas R&D organizations.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 53 / 240
C. R&D Results
Research Project Research Results and Expected Effect
In case applied to a product, name of
the product and application
Develop new smart card
product
□ Launched NFC with internal flash memory (e-flash)
- First to Use 45nm e-flash logic process, which improves density and power efficiency
compared to 90nm products
- Miniaturized products by supporting smallest antenna solution
- Enabled mobile POS through NFC chip as the first in the industry
※ POS (Point of Sales): point of sale information management system
□ Region : Global
□ Launch: Jan ‘14
□ Name : S3FWRN5
High-resolution low power
consumption
Tablet product technology
□ Mass produce high-resolution Tablet panel
□ Achieved low power consumption of tablet products and higher rate of production by
enhancing transmissivity
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘14
Mass produce 20nm
4GB
DDR3 DRAM
for server
□ First in the world to mass produce ultra-fine 20nm 4GB DDR3 DRAM
- Applied independently developed high-density/high-speed/low-power consumption
technology
- Enhanced productivity by 30% compare to 25nm
□ PC and server full line-up to be launched with 20nm 4GB DRAM
- Enhance competitiveness by launching the whole line-up including mobile in the future
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘14
□ Name : 4GB DDR3 DRAM
Develop
new ISOCELL
image sensor
□ Launched new 1600 megapixel ISOCELL image sensor
- Clear image even in dark places
- 16 megapixel / 30pfs per second (first in the industry)
- 16:9 aspect ratio FullHD resolution
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘14
□ Name : S5K2P2
Develop new Mobile AP
product
with HMP solution
□ Launched new Exynos 5 Octa (5422) product
- Enhance power efficiency by combining and utilizing 8 high-capacity/low-power
consumption cores through applying HMP solution
- Support WQHD and WQXGA ultra-high resolution
- Strengthen low-power consumption capacity by using automatic conversion to
power save mode and mobile video compression technology
□ Launched new Exynos 5 Hexa (5250) product
- Enhance power efficiency by combining and utilizing 6 high-capacity/low power
consumption cores through applying HMP solution
- Support WQXGA ultra-high resolution
□ Region : Global
□ Launch: Jan/Mar ‘14
□ Name : Exynos5250/
Exynos5422
UHD TV
HU9000
□ Ultimate Curved UHD TV that provides perfect immersive experience
- Adopted ergonomic Curved LED Panel
□ Clear differentiation values compare to competitors
- Smart Hub function with Multi-Link Screen added
- The only Evolutionary UHD TV
□ Premium design
- Ergonomic Curved Design
- eEnhance premium image through Immersive Viewing Experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch: Mar ‘14
□ Inch : 55"/65"
Mass produce
2
nd
generation
V-NAND based
1TB SSD for PC
□ First in the world to mass produce 2
nd
generation 3D V-NAND based 1TB SSD
- Opened up ‘the era of popularized 3D memory’ with 2
nd
generation V-NAND
- Target PC market after creating server market last year
□ Launched high-reliability, high-capacity, low-power consumption V-NAND SSD line-up
- Increased life by twofold and reduced power consumption by 20% compare to
existing SSD
- Launch ‘V-NAND SSD’ in 53 nations around the world starting in July
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : May ‘14
□ Name : 1TB, V-NAND SSD
Develop new ISOCELL
Image sensor
□ Develop 13 megapixel stacked ISOCELL image sensor
- Smaller chip size and wider circuit range by applying stacked structure
- Diversification of exposure with smart WDR function improves color in backlight
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jun ‘14
□ Name : S5K3M2
Develop new Mobile AP
product
□ Launched new Exynos 5 Octa (5430) product
- Increased power efficiency by applying 20nm low-power consumption HKMG process
- Enhanced performance by applying HMP solution and can work individually depending on
low power core needs
- Enhanced low power consumption property by using automatic conversion to power
save mode and mobile video compression technology
- Support WQHD and WQXGA ultra high-resolution
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jun ‘14
□ Name : Exynos 5430

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 54 / 240
Research Project Research Results and Expected Effect
In case applied to a product, name of
the product and application
UHD TV
(UN105S9WAF)
□ Product Concept
- Wide Curved(21:9) 105” UHD TV
- Need to solidify market leadership by introducing ultra-large size 105” UHD TV as
the first in the world
□ Spec and effects
- Adopted SDC 4200R 105" Wide Curved Panel
- Applied Golf-AP/MP Platform
- Provide the ultimate immersive and realistic viewing experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jul ‘14
□ Inch: 105”
LFD
QMD
□ Introduced Premium UHD Line Up
- Introduced high resolution UHD LFD lineup
- Applied SE13U Platform
- Applied spec to respond to LFD Usage
- Reduced additional investment costs by sharing TV HU7K design
□ Main functions
- Support full HD screen split in 4 (2/3/4 splits)
- DP 1.2 and SBB applicable
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Aug ‘14
□ Inch: 85”
Mass produce
PC/server
32 layer 3bit
3D V-NAND
□ Mass produced the world’s first 3bit 3D V-NAND based 1TB SSD
- Opened up the era of “popularized V-NAND SSD” with 3bit V-NAND
- Target the standard SSD market with V-NAND that has 50% higher productivity
□ Reinforced highly reliable, high-performance, low energy consuming V-NAND SSD lineup
- Launched mSATA and M.2 SSD lineups in addition to the existing 2.5”
- Launched '850 EVO SSD' in 53 nations around the world in Dec
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Oct ‘14
□ Inch: 128Gb 3bit
3D V-NAND
(850 EVO SSD)
Bendable TV
Nov
(UN78S9BAF)
□ World’s first Bendable UHD TV
- Secured technology leadership
□ Design
- Adopted Timeless Gallery Design
- Becomes an aesthetic object when power is off
□ Region : Domestic
□ Launch : Nov ‘14
□ Inch: 78”
Mass produce
mobile
20nm 8Gb
LPDDR4 DRAM
□ Mass produced the world’s first ultrafine 20nm 8Gb LPDDR4 DRAM
- Applied “highly integrated/ultrahigh speed/high-density” solution developed by the Company
- Created the world’s first 4GB market and took the lead
□ Led growth of the DRAM market by expanding 20nm DRAM lineup
- Plan to take the lead in the market by expanding next-generation lineups(8/6/4Gb) in the
future
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Dec ‘14
□ Inch: 8Gb LPDDR4 DRAM
Launch
new Mobile AP
product
□ Industry’s first 14nm FinFET process-based Mobile AP
- Compared to 20nm process, 14nm process has enhanced performance by 20%, reduced
power consumption by 30%, and improved productivity by 35%
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jan ‘15
□ Name: Exynos 7 Octa
Launch
new NFC
product
□ 4
th
generation NFC solution with enhanced RF performance
- Compared to 3
rd
generation products, doubled card mode and enhanced reader mode by 20%
□ Support mobile POS in smartphone environment
□ Applied 45nm embedded flash process
- Reduced customers’ product development and certification period
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jan ‘15
□ Name: S3FWRN5P
Mass produce
10nm-class
128GB UFS
for mobile
□ Mass produced the world’s first 128GB UFS memory for mobile
- Performance was enhanced by 12 times compared to memory card and 2.7 times
compared to eMMC
□ Lead the growth of the premium market by expanding the high-density memory market
- Launched high-density line up with twice the density (128/64/32GB)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘15
□ Name: 128GB UFS
(Internal memory card)Lau
Launch
SUHD TV
□ Curved SUHD TV : Provide the ultimate immersive experience
※ S: Spectacular, Smart, Stylish, Superb
□ Design : Chamfer Design (Real Metal)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘15
□ Inch: 65"/78"/88"

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 55 / 240
Research Project Research Results and Expected Effect
In case applied to a product, name of
the product and application
Mass produce
NAND-based
10nm-class
512GB M.2
NVMe SSD for PC
□ Mass produced world’s first 512GB M.2 NVMe SSD for the next generation PC
- Read speed of 2,260MB/s, 4 times faster than SATA SSD
- Took the lead in the mobile workstation and slim PC markets
□ Led the premium market by expanding the ultra-high speed, high-density SSD market
- Plan to target PC market in earnest by launching V- NAND based line ups in the future
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Apr ‘15
□ Name:
512GB
M.2 NVMe SSD
(SM951 SSD)
HAV(WAA)
WAM5500/ZA
□ Ambient Audio
Defined a new audio category with differentiated sound quality and sensible design
(Blending, conventional design)
- Provide the same sound quality through Wireless Audio 360 and Ring Radiator Tech
- Expand multi-room audio usability through compatibility with TV/AV products
- Provide sensible user experience by applying Analog Wheel
- Easy to understand setting information through Voice AUI
- Provide visual experience by applying OLED
□ Region : Americas
□ Launch : Aug ‘15
Launch
new
CMOS image sensor
□ Industry’s first 1.0um 16 mega-pixel mobile image sensor
- Provide the same image quality with 1.12um pixels by applying ISOCELL
- With camera module of under 5mm in height, mobile device design became slimmer
- Compared to 1.12um pixel sensor, module height decreased by 20%
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jul ‘15
□ Name: S5K3P3
Mass produce
3
rd
generation(48-layer)
256Gb
3D V-NAND
for SSD
□ Mass produced world’s first 3
rd
generation(48-layer) 3D V-NAND
- Began mass producing 256Gb in earnest, which has twice the degree of integration than
128Gb
- Took the lead in the PC, enterprise server, and datacenter SSD markets
□ Led ‘popularization of Tera SSD’ by expanding ultra-high-speed SSD line ups
- Target the market by expanding 3
rd
generation V-NAND based line ups
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Aug ‘15
□ Name: 256Gb 3D V-NAND
(3G 48-layer)
Mass produce
20nm DRAM-based
12Gb LPDDR4
mobile DRAM
for mobile
□ Mass produced world’s first next generation 12Gb LPDDR4 DRAM for mobile
- First to achieve 4,266Mbps, which is twice the speed of PC DRAM
- Took the lead in not only mobile but also PC, consumer electronics, and automobile
markets
□ Led the premium DRAM market by taking the lead in the ultra-high-speed DRAM market
- Plan to target the next generation DRAM market in the future by launching 6GB line ups
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Sep ‘15
□ Name: 12Gb LPDDR4
Mobile DRAM
(20nm DRAM)
LFD
OHD
□ Product Concept
- Satisfied market demand with accelerated digitization of outdoor Signage.
- Varied its sizes from 46” to 46”/55”
- Improved brightness to 2,500nit from 1,500nit and applied new panels which withstand
high-temperature
□ Specification
- Outdoor Kit product with Power Box
- Can operate in a wide range of temperature, from -30℃ to +50℃
(fans and heating films are applied)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Oct ‘15
□ Inch: 46”/55”
Mass produce
20nm DRAM-based
12GB 3D TSV DDR4
RDIMM for server
□ First to mass produce next-generation 128GB 3D TSV RDIMM for server
- 3D TSV technology doubled up the speed while reducing electricity consumption by 50%
- Surpassed the limit of DRAM module density for server (RDIMM/LRDIMM)
□ Leading the premium DRAM market with the next-generation line-up
- Will create new market by launching HBM2, following the TSV LRDIMM
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Nov ‘15
□ Name: 12GB 3D TSV
DDR4 RDIMM
(20nm DRAM)
System Air-Conditioner
(CAC)
AC9000K
□ Product features
- Developed the world-first Bladeless 360 Cassette-type air-conditioner
- Provides even distribution of air and minimized untouched area with circular air wave
- Increased space coverage to 83% from 44%
- Cold Draft Free (reduced sensory temperature gap to 0.2℃ from 7.9℃)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Dec ‘15
System Air-Conditioner
(DVM)
AM7500K
□ Product features
- Has the biggest capacity at the same size level
- Provided in Compact Size & improved installation and service (the width is 940mm, the
smallest in the market)
- Provides highest efficiency (increased China’s 12HP IPLV by 17%)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Dec ‘15
Mass produce
all-in-one
Bio-Processor Chip
□ Mass produced the industry’s first all-in-one Bio-Processor Chip
- Its all-in-one chip took up every steps from capturing signals to processing, by including
AEF, MCU, DSP, eFlash and PMIC
- Equipped with five AFEs and measures five different biometric signals: BIA (body fat), PPG
(heartbeat rate), ECG (electrocardiogram), skin temperature, and GSR (stress level)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Dec ‘15
□ Name: S3FBP5A

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 56 / 240
Research Project Research Results and Expected Effect
In case applied to a product, name of
the product and application
Mass produce
20nm DRAM-based
4GB HBM2
DRAM for HPC
□ Mass produced the world’s first next-generation 4GB HBM2 DRAM for HPC
- Improved system speed by 3.6x, board space savings of up to 97%
- Exceeded speed limitation through TSV technology with 37x higher density
□ Lead the growth of premium memory market with the launch of 8GB HBM2
- Continue to stay ahead in the network market, as well as graphic and HPC markets
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jan ‘16
□ Name: 4GB HBM2 DRAM
(20nm DRAM)
LFD
DCE
□ Specification and Effects
- Slim design though common use of mechanical engineering and panels of DBE model /
Provide light MagicInfo-E Solution by applying NT14 platform
- Slim Design: Bezel 9.5mm, Depth 49.9mm
- Provide USB Contents Player through MagicInfo-E Solution
- Strengthened controlling functions such as RJ45/RS232C
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jan ‘16
□ Inch: 32”/40”/48”/55”
LFD
TC2
□ Specification and Effects
- Enhanced competitiveness by upgrading CPU specifications
※ 1.0GHZ Dual Core → 2.2GHz Dual Core
- Provides more OS options by introducing 64bit WES7
- Added USB port (Serial Port → USB x 2)
※ Replaced the existing serial port with USB to Serial Adapter
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jan ‘16
□ Inch: 22”/24”
DVM System Air-
Conditioner
AM9100K
□ Product features
- Made an entrance into high-efficiency Inverter chiller market
- Efficiency (Europe): EER : 3.4 / ESEER: 5.7 (40% higher than competitor)
- Installment: 1.38㎡ (39% smaller than competitors)
- Operate in a wider range of temperature, from -25℃ to +48℃ (competitor: -15℃ to +43℃)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jan ‘16
Mass produce
3
rd
Generation (48-layer)
V-NAND based
256GB UFS
□ Mass produced the world’s first next-generation 256GB UFS for smartphone
- High-performance: up to 9 times faster than uSD card, twice as fast as SSD
- Provides high-speed, high-density solution with sub-micro size
□ Strengthen memory competitiveness though 256GB UFS market expansion
- Constantly lead high growth of UFS in internal storage market
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘16
□ Name: 256GB UFS
(3
rd
generation 48-layer 256Gb
V-NAND)
Mass produce
3
rd
Generation (48-layer)
V-NAND based
15.36TB SAS SSD
□ Mass produced the world’s first next-generation 15.36TB SAS SSD for server
- Provide 15.36TB SSD for the first time in the world through application of 256Gb V-NAND
- The highest density among single form factor storage devices
□ Focus on SAS market by constantly expanding high-density line-ups
- Expand enterprise market significantly following data center market
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘16
□ Name: 15.36TB SAS SSD
(3
rd
generation 48-layer 256Gb
V-NAND)
Mass produce
10nm-class (1x)
8Gb DDR4
DRAM for PC/server
□ Mass produced the world’s first 10nm-class 8Gb DDR4 DRAM
- Enhanced productivity and speed by above 30% compared to 20nm, save electricity by up
to 20%
- Exceeded limitation of migration, with our three distinctive innovative technology
□ Lead the market growth through high-density DRAM line-up expansion
- Continue to strengthen its dominance in the mobile market as well as PC and server
markets
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘16
□ Name: 8Gb DDR4 DRAM
(10nm-class DRAM)
LM
CF59
□ Specifications and Effects
- Circuits: Provides triple Interface (1 D-Sub/1HDMI/1DP)
- Mechanical Engineering: The 3-side bezel less technique gave birth to distinctive design
and provides seamless usage through multi-display
- Panel: Curved panel with a curvature of 1800R (4000R in 2015)
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘16
□ Inch: 27”
FDR Refrigerator
RF9500KF
□ Product features
- Create new demand and take leadership in the smart home appliances market by providing
new user experience which meets new consumer needs in IOT era
- Applied 21.5” LCD
- Provides Smart Things and Sticki Shopping features that all family members can share to
achieve a Smart Home.
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Feb ‘16
Exynos 8 Octa
□ 14nm 2
nd
generation process-based premium mobile SOC
- Enhanced performance and energy-saving effect
- Applied distinctive custom CPU core technology
- The first integrated one-chip solution with highest-specification LTE modem
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Name: S5E8990

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 57 / 240
Research Project Research Results and Expected Effect
In case applied to a product, name of
the product and application
Exynos 7
□ Industry’s first 14nm based mid to low-end mobile SOC
- Applied 14nm derivative process
- Enhanced energy-efficiency by 30%, compared to the existing 28nm products with same
performance level
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Name: S5E7870
Mobile Image Sensor
□ 1.2 megapixel mobile image sensor with dual pixel technology
- Phase-detection AF in all resolutions at high speed
- Auto-focus feature that is quick and accurate even in darker environments
- Maximized functions with Samsung isocell technology
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Name: S5K2L1
LFD
OHE
□ Specification and Effects
- Applied the existing outdoor specifications
- 110℃ TNI Panel made outdoor usage possible
- Internalized Quad-Core SoC to provide PC-less Solution
- Provides optimized brightness level through automatic illumination sensor, saving energy-
consumption and maximizing product life
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 24”
LM
CF39
□ Specification and Effects
- 16:9 ratio, the most optimal curvature of 1800R
- Offers distinctive design by applying round-type stand base and simple single hinge
- Simple and sensational design even on the back, maximizing the beauty of curved design
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 24”/27”
SUHD TV
(KS9000)
□ Curved SUHD TV
□ Design: Dignity, Bezel-less, Screw-less, Axis Stand
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W, S/W): Jazz-M, Tizen OS
- Image quality: UHD 120Hz, Curved, QD, Local Dimming
- Feature: Live and OTT combined Home helps easy access to TV content/service and
improves consumer experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 49"/55"/65"
SUHD TV
(KS8000)
□ Flat SUHD TV
□ Design : Dignity, Bezel-less, Screw-less, Axis Stand
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): Jazz-M, Tizen OS
- Image quality: UHD 120Hz, Flat, QD, Local Dimming
- Feature: Live and OTT combined Home helps easy access to TV content/service and
improves consumer experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 49"/55"/65"
SUHD TV
(KS7500/KS7000)
□ Curved SUHD TV
□ Design : Triumph, Bezel-less, Screw-less, Branch Stand
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): Jazz-M, Tizen OS
- Image quality: UHD 120Hz, Curved, QD, Local Dimming
- Feature: Live and OTT combined Home helps easy access to TV content/service and
improves consumer experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 43"/49”/55”/65”
UHD TV
(KU6500/KU6400)
□ UHD Curved TV
□ Design : Metal Design, Bolt-less Clean Back, Ultimate Slim Design
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): Jazz-M, Tizen OS
- Image quality: Wide Color Gamut
- Feature: Live and OTT combined Home helps easy access to TV content/service and
improves consumer experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 40”/43”/49”/55”/65”
UHD TV
(KU6000)
□ UHD Flat TV
□ Design : Minimalism Design, V-Shape stand
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): Jazz-M, Tizen OS
- Image quality: UHD Upscaling, Auto Contrast Enhancer, PurColor
- Feature:
New Smart TV feature provides easier access to TV content/service and improved
consumer experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Mar ‘16
□ Inch: 40"/43"/50"/55"/60"/65"
FHD TV
(K5100)
(K4100)
□ FHD Flat TV
□ Design : Louvre Design, Semi Edge Slim
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): XL1,NT14L,NT16L(Non-Smart)
- Image quality: FHD image quality enable consumers to watch various contents
- Feature:
Sport mode, USB 2.0
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Apr ‘16
□ Inch: 32"/40"/43"/49"/55"

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 58 / 240
Research Project Research Results and Expected Effect
In case applied to a product, name of
the product and application
SUHD TV
(KS9800)
□ Curved SUHD TV
□ Design : Dignity, Bezel-less, Screw-less, Axis Stand
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): Jazz-M, Tizen OS
- Image quality: UHD 120Hz, Curved, QD, Local Dimming
- Feature:
Live and OTT combined Home helps easy access to TV content/service and
improves consumer experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : May ‘16
□ Inch: 65"/78"/88"
UHD TV
(KU6300)
□ UHD Curved TV
□ Design : Minimalism Design, V-Shape stand
□ Specification and Effects
- Platform (H/W,S/W): Jazz-L, Tizen OS
- Image quality: UHD Upscaling, Auto Contrast Enhancer, PurColor, etc.
- Feature:
New Smart TV feature provides easier access to TV content/service and improves
user experience
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Jun ‘16
□ Inch: 40"/49"/55"/65"
HD-TV
(HE690)
□ Product Concept
- To penetrate the market by providing solutions and customized products for each market
segment
- Premium Smart TV for four to five-starred hotels
□ Specification and Effects
- HMS, SINC, REACH, H.Browser, Bluetooth Music Player, Ethernet Bridge(32”↑), Swivel
Stand
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Aug ‘16
□ Inch: 22"/24"/28"/32"/40"/49"/55"
Exynos 7 Quad
□ Connectivity integrated mobile SoC
- Increased performance by 70% and power efficiency by 30% vs. the previous 28nm
products
- Reduced the size by 20% by integrating major features such as the modem, connectivity
and PMIC.
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Aug ‘16
□ Name: S5E7570
Dishwasher
(DW9900M)
□ Product Concept
- 2
nd
Generation WaterWall technology
- Improved Zone booster
- Wi-Fi application and differentiated Rack feature
- Sump & New Filter System
- Hidden control, Touch Type display
□ Region : North America
□ Launch : Dec ‘16
Residential Air-conditioner
(AR5500M)
□ Product Concept
- Adopt environment-friendly (Low-GWP) R32 refrigerant to respond to market trends
- Applied S-Inv to strengthened the competitiveness of Inv-type products
- N-PFC, R32 8-pole compressor
□ Region : Global
□ Launch : Dec ‘16

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 59 / 240
11. Other Information
A. Intellectual Property Rights
In 2016, the Company invested KRW 14.8 trillion and registered 5,629 domestic and 15,193 overseas patents, including
approval for 5,518 US patents. As a result, the Company maintained second place in terms of numbers of patents
registered in US amongst global technology companies for eleven (11) consecutive years since 2006.
<Number of Patents Registered in Each Country (as of December 31, 2016, cumulative)>
(Unit: # of Patents)
Korea US Europe China Japan Others
Number 27,471
43,806
16,744
10,242
6,770 8,813
The Company registered its first US patent in 1984, and now holds 110,145 patents around the world.
<Number of Patent Registrations Per Year>
(Unit: # of Patents)
‘16 ‘15 ‘14 ‘13 ‘12 ‘11 ‘10 ‘09
Korea 3,452 2,984 3,970
2,762
2,013
1,610 1,612
1,485
US 5,518 5,072 4,952
4,676
5,081
4,894 4,551
3,611
These patents are mostly related to smartphone, smart TV, flash memory, and system LSI products for the Company’s
strategic business products or for future use. These patents not only protect the Company’s business but also play a role in
keeping similar technology and patents, as well as competitors, in check. Additionally, the Company is focusing on
securing early patents in new technologies ahead of others, in order to protect opportunities and have the freedom to
operate when entering new businesses.
The Company has also been focusing on securing design patents to protect its original design applied to smartphones and
LED TVs. In 2016, the Company acquired 1,635 US patents, in part for the aforementioned purposes.
B. Environmental regulations
The Company strictly abides by environmental regulations on products and in the workplace, as prescribed by law. In
addition, in accordance with “the low carbon green growth policy” of the Korean government, the Company reports “the
amount of CO2 emission and energy use” to the government and provides related information to stakeholders by
providing various reports, including the Samsung Sustainability Report.
(See 『9. Green Management』 of 『XI. Other Information』 for more details about Green Technology Certification.)
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 60 / 240
(Environmental Regulation of Products)
Environmental regulation of products are becoming stricter, reflecting the concerns of governments and regulators about
potential direct and indirect impact of products to consumers’ health and safety as consumers. Accordingly, the Company
is working to minimize the environmental impact throughout the entire life cycle of products from the development stage
of components and products to manufacturing, distribution, use, and disposal. The Company offers “Eco-Partner
Certification” to suppliers for components free of harmful substances, and runs an “eco-design evaluation” system to
reflect eco-friendly elements on products (reduced use of resources, energy and harmful substances, and the use of eco-
friendly materials) at the development stage, and operates a “waste electronics collection recycle system” in Europe,
North America, Korea, and India for collecting and recycling waste electronics. These activities are in line with domestic
and foreign environmental laws on electronics and are a differentiation factor for the Company and its products.
Relevant laws are as follows:
1. law on collection and· recycle of waste electronics (e.g., EU WEEE Directive)
2. limit on the use of harmful substances (e.g., EU RoHS Directive, REACH Regulation)
3. regulation on energy efficiency (e.g., EU ErP Directive)
(Environmental Regulations in the Workplace)
The Company operates environmental pollution prevention facilities to reduce air pollution, water pollution, and waste
disposal, and to minimize the discharge of pollutants, thereby minimizing impact on the surrounding environment.
Environmental management of workplace is supervised by the relevant government authorities. All production facilities,
domestic and overseas, have acquired the International Occupational Health and Safety Management System Certification
(ISO 14001, OHSAS18001) to strengthen compliance.
Major Relevant Domestic and International Laws are as follows:
1. Regulations related to emission of pollutants: Water Quality and Ecosystem Conservation Act, Clean Air
Conservation Act, Wastes Control Act, Noise and Vibration Control Act, Environmental Impact Assessment Act
2. Management of greenhouse gas emission: Act on Allocation and Trading of Greenhouse Gas Emission,
Framework Act on Low Carbon, Green Growth
3. Others: Toxic Chemicals Control Act, Act on the Registration and Evaluation, etc. of Chemical Substances, Odor
Control Law, Soil Environment Conservation Act

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 61 / 240
(Greenhouse gas emission and energy consumption management)
The Company is a “controlled entity” according to Article 42 of Korea’s “Framework Act on Low Carbon, Green
Growth.” Thus, the Company has been reporting the amount of greenhouse gas emission and energy consumption,
verified by a third-party, to the authorities and disclosing it to stakeholders according to Article 44 of the same Act since
May 2011.
The reported amount of greenhouse gas emission and energy use are provided below:
2016 2015 2014
Greenhouse gas
(Unit: tCO2e)
6,885,300
6,729,419 6,775,019
Energy
(Unit: TJ)
107,740
111,166 101,386
※ Domestic manufacturing facilities, office buildings, buildings owned by the Company, leased buildings, etc.
※ Reported Greenhouse gas emission excludes ozone depletion substances (ODS).
※ DP business was excluded from the calculation as Samsung Display was spun off from Samsung Electronics in 2012.
From 2015, in accordance with the Article 8 of the Act on the Allocation and Trading of Greenhouse-Gas Emission
Permits, the Company is an eligible business entity under the Act.
※ See 『9. Green Management』 in 『XI. Other Information』for Green Technology Certifications.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 62 / 240
III. Financial Affairs
1. Consolidated Financial Statements
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
December 31, December 31, December 31, December 31,
Notes 2016 2015 2016 2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Assets
Current assets
Cash and cash equivalents 4, 6, 7, 31 32,111,442 22,636,744 27,686,236 19,517,225
Short-term financial instruments 5, 6, 7, 31 52,432,411 44,228,800 45,206,818 38,133,728
Short-term available-for-sale
financial assets
6, 9, 31
3,638,460 4,627,530 3,137,052 3,989,820
Trade receivables 6, 7, 10, 31 24,279,211 25,168,026 20,933,347 21,699,677
Non-trade receivables 10 3,521,197 3,352,663 3,035,949 2,890,640
Advances 1,439,938 1,706,003 1,241,503 1,470,903
Prepaid expenses 3,502,083 3,170,632 3,019,469 2,733,694
Inventories 11 18,353,503 18,811,794 15,824,248 16,219,383
Other current assets 1,315,653 1,035,460 1,134,346 892,765
Assets held-for-sale 36 835,806 77,073 720,625 66,452
Total current assets
141,429,704 124,814,725 121,939,593 107,614,287
Non-current assets
Long-term available-for-sale
financial assets
6, 9, 31
6,804,276 8,332,480 5,866,594 7,184,200
Investment in associates and joint
ventures
12
5,837,884 5,276,348 5,033,378 4,549,226
Property, plant and equipment 13 91,473,041 86,477,110 78,867,346 74,559,893
Intangible assets 14 5,344,020 5,396,311 4,607,573 4,652,657
Long-term prepaid expenses 3,834,831 4,294,401 3,306,362 3,702,599
Net defined benefit assets 17
557,091
-
480,320
-
Deferred income tax assets 28 5,321,450 5,589,108 4,588,113 4,818,886
Other non-current assets 1,572,027 1,999,038 1,355,388 1,723,555
Total assets
262,174,324 242,179,521 226,044,667 208,805,303

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 63 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
December 31, December 31, December 31, December 31,
Notes 2016 2015 2016 2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Liabilities and Equity
Current liabilities
Trade payables 6, 31 6,485,039 6,187,291 5,591,350 5,334,634
Short-term borrowings
6, 8, 15,
31
12,746,789 11,155,425 10,990,183
9,618,121
Other payables 6, 31 11,525,910 8,864,378 9,937,550 7,642,798
Advances received 1,358,878 1,343,432 1,171,614 1,158,297
Withholdings 685,028 992,733 590,626 855,927
Accrued expenses 12,527,300 11,628,739 10,800,941 10,026,208
Income tax payable 2,837,353 3,401,625 2,446,344 2,932,855
Current portion of long-term
liabilities
6, 15, 16,
31
1,232,817 221,548 1,062,925 191,017
Provisions 18 4,597,417 6,420,603 3,963,857 5,535,794
Other current liabilities 351,176 287,135 302,781 247,565
Liabilities held-for-sale 36 356,388
-
307,275
-
Total current liabilities
54,704,095 50,502,909 47,165,446 43,543,216
Non-current liabilities
Debentures 6, 16, 31 58,542 1,230,448 50,474 1,060,883
Long-term borrowings 6, 15, 31 1,244,238 266,542 1,072,772 229,810
Long-term other payables 6, 31 3,317,054 3,041,687 2,859,938 2,622,519
Net defined benefit liabilities 17 173,656 358,820 149,725 309,372
Deferred income tax liabilities 28 7,293,514 5,154,792 6,288,411 4,444,422
Provisions 18 358,126 522,378 308,773 450,390
Other non-current liabilities 2,062,066 2,042,140 1,777,899 1,760,717
Total liabilities
69,211,291 63,119,716 59,673,438 54,421,329

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 64 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
Notes
December 31, December 31, December 31,
December 31,
2016 2015 2016 2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Equity attributable to owners of the
parent
Preferred stock 20 119,467 119,467 103,004 103,004
Common stock 20 778,047 778,047 670,826 670,826
Share premium 4,403,893 4,403,893 3,797,002 3,797,002
Retained earnings 21 193,086,317 185,132,014 166,477,524 159,619,385
Other components of equity 23 (11,934,586) (17,580,451) (10,289,907) (15,157,728)
Accumulated other comprehensive
income attributable to assets held-
for-sale
36 (28,810) 23,797 (24,841) 20,517
186,424,328 172,876,767 160,733,608 149,053,006
Non-controlling interests
6,538,705 6,183,038 5,637,621 5,330,968
Total equity
192,963,033 179,059,805 166,371,229 154,383,974
Total liabilities and equity
262,174,324 242,179,521 226,044,667 208,805,303

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 65 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
For the year ended December 31,
Notes 2016 2015 2016 2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Revenue
32 201,866,745 200,653,482 174,047,940 173,001,874
Cost of sales
24 120,277,715 123,482,118 103,702,512 106,465,323
Gross profit
81,589,030 77,171,364 70,345,428 66,536,551
Selling and administrative expenses 24, 25 52,348,358 50,757,922 45,134,348 43,763,086
Operating profit
29,240,672 26,413,442 25,211,080 22,773,465
Other non-operating income 26 3,238,261 1,685,947 2,792,003 1,453,610
Other non-operating expense 26 2,463,814 3,723,434 2,124,281 3,210,316
Share of profit of associates
and joint ventures
12 19,501 1,101,932 16,814 950,077
Financial income 27 11,385,645 10,514,879 9,816,615 9,065,847
Financial expense 27 10,706,613 10,031,771 9,231,159 8,649,315
Profit before income tax
30,713,652 25,960,995 26,481,072 22,383,368
Income tax expense 28 7,987,560 6,900,851 6,886,812 5,949,860
Profit for the year
22,726,092 19,060,144 19,594,260 16,433,508
Profit attributable to owners of the parent 22,415,655 18,694,628 19,326,604 16,118,363
Profit attributable to non-controlling interests 310,437 365,516 267,656 315,145
Earnings per share for profit attributable to
owners of the parent
(in Korean Won, in US dollars) 29
- Basic 157,967 126,305 136.2 108.9
- Diluted 157,967 126,303 136.2 108.9

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 66 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
For the year ended December 31,
Notes 2016 2015 2016
2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Profit for the year
22,726,092 19,060,144 19,594,260 16,433,508
Other comprehensive income
Items not to be reclassified to profit or loss
subsequently:
Remeasurement of net defined benefit liabilities,
net of tax
17, 23 963,602 263,978 830,810 227,600
Shares of other comprehensive income of
associates and joint ventures, net of tax
12, 23 50,438 24,069 43,487 20,752
Items to be reclassified to profit or loss
subsequently:
Changes in value of available-for-sale financial
assets, net of tax
9, 23 (23,839) (414,961) (20,554) (357,776)
Share of other comprehensive loss of associates
and joint ventures, net of tax
12, 23 (130,337) (65,330) (112,376) (56,327)
Foreign currency translation, net of tax
23 1,131,536 268,315 975,603 231,339
Other comprehensive income for the year, net
of tax
1,991,400 76,071 1,716,970 65,588
Total comprehensive income for the year
24,717,492 19,136,215 21,311,230 16,499,096
Comprehensive income attributable to :
Owners of the parent
24,310,814 18,804,189 20,960,595 16,212,826
Non-controlling interests
406,678 332,026 350,635 286,270

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 67 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(In millions of Korean won)
2015 KRW
Notes
Preferred
stock
Common
stock
Share
premium
Retained
earnings
Other
components
of equity
Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income
attributable
to assets held
-
for-sale
Equity
attributable
to owners of
the parent
Non-
controlling
interests Total
Balance as at January 1, 2015
119,467 778,047 4,403,893 169,529,604 (12,729,387) 80,101 162,181,725 5,906,463 168,088,188
Profit for the year - - - 18,694,628 - - 18,694,628 365,516 19,060,144
Changes in value of available-for-sale
financial assets, net of tax
9, 23 - - - - (348,068) (24,750) (372,818) (42,143) (414,961)
Share of other comprehensive income
(loss) of associates and joint
ventures, net of tax
12, 23 - - - - 12,686 (54,118) (41,432) 171 (41,261)
Foreign currency translation, net of tax 23 - - - - 266,061 (1,233) 264,828 3,487 268,315
Remeasurement of net defined benefit
liabilities, net of tax
17, 23 - - - - 258,983 - 258,983 4,995 263,978
Classified as held-for-sale 36 - - - - (23,797) 23,797 - - -
Total comprehensive income (loss)
- - - 18,694,628 165,865 (56,304) 18,804,189 332,026 19,136,215
Dividends 22 - - - (3,073,481) - - (3,073,481) (54,603) (3,128,084)
Capital transaction under common
control
- - - - (5,314) - (5,314) 423 (4,891)
Changes in consolidated entities - - - - - - - (152) (152)
Acquisition of treasury stock 23 - - - - (5,015,112) - (5,015,112) - (5,015,112)
Disposal of treasury stock 23 - - - - 3,406 - 3,406 - 3,406
Stock option activities 23 - - - - (806) - (806) - (806)
Others - - - (18,737) 897 - (17,840) (1,119) (18,959)
Total transactions with owners
- - - (3,092,218) (5,016,929) - (8,109,147) (55,451) (8,164,598)
Balance as at December 31, 2015
119,467 778,047 4,403,893 185,132,014 (17,580,451) 23,797 172,876,767 6,183,038 179,059,805

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 68 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(In thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
2015 USD
Preferred
stock
Common
stock
Share
premium
Retained
earnings
Other
components
of equity
Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income
attributable to
assets held
-for-
sale
Equity
attributable
to owners of
the parent
Non-
controlling
interests Total
Notes
Balance as at January 1, 2015
103,004 670,826 3,797,002 146,167,108 (10,975,179) 69,063 139,831,824 5,092,507 144,924,331
Profit for the year - - - 16,118,363 - - 16,118,363 315,145 16,433,508
Changes in value of available-for-sale
financial assets, net of tax
9, 23 - - - - (300,102) (21,339) (321,441) (36,335) (357,776)
Share of other comprehensive income
(loss) of associates and joint
ventures, net of tax
12, 23 - - - - 10,938 (46,660) (35,722) 147 (35,575)
Foreign currency translation, net of tax 23 - - - - 229,398 (1,065) 228,333 3,006 231,339
Remeasurement of net defined benefit
liabilities, net of tax
17, 23 - - - - 223,293 - 223,293 4,307 227,600
Classified as held-for-sale 36 - - - - (20,518) 20,518 - - -
Total comprehensive income (loss)
- - - 16,118,363 143,009 (48,546) 16,212,826 286,270 16,499,096
Dividends 22 - - - (2,649,932) - - (2,649,932) (47,078) (2,697,010)
Capital transaction under common
control
- - - - (4,582) - (4,582) 365 (4,217)
Changes in consolidated entities - - - - - - - (131) (131)
Acquisition of treasury stock 23 - - - - (4,323,991) - (4,323,991) - (4,323,991)
Disposal of treasury stock 23 - - - - 2,937 - 2,937 - 2,937
Stock option activities 23 - - - - (695) - (695) - (695)
Others - - - (16,154) 773 - (15,381) (965) (16,346)
Total transactions with owners
- - - (2,666,086) (4,325,558) - (6,991,644) (47,809) (7,039,453)
Balance as at December 31, 2015
103,004 670,826 3,797,002 159,619,385 (15,157,728) 20,517 149,053,006 5,330,968 154,383,974

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 69 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 KRW
Preferred
stock
Common
stock
Share
premium
Retained
earnings
Other
components
of equity
Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income
attributable
to assets held
-
for-sale
Equity
attributable
to owners of
the parent
Non-
controlling
interests Total
Notes
Balance as at January 1, 2016
119,467 778,047 4,403,893 185,132,014 (17,580,451) 23,797 172,876,767 6,183,038 179,059,805
Profit for the period
- - - 22,415,655 -
-
22,415,655 310,437 22,726,092
Changes in value of available-for-sale
financial assets, net of tax
9, 23 - - - - (87,706) (23,797) (111,503) 87,664 (23,839)
Share of other comprehensive income
(loss) of associates and joint
ventures, net of tax
12, 23 - - - - (80,146) 212 (79,934) 35 (79,899)
Foreign currency translation, net of tax 23 - - - - 1,160,316 - 1,160,316 (28,780) 1,131,536
Remeasurement of net defined benefit
liabilities, net of tax
17, 23 - - - - 926,280 - 926,280 37,322 963,602
Reclassification to assets held-for-sale
36 - - - - 29,022 (29,022) - - -
Total comprehensive income (loss)
- - - 22,415,655 1,947,766 (52,607) 24,310,814 406,678 24,717,492
Dividends 22 - - - (3,061,361) - - (3,061,361) (65,161) (3,126,522)
Capital transaction under common
control
- - - - (37) - (37) 12,272 12,235
Changes in consolidated entities
- - - - - - - 1,790 1,790
Acquisition of treasury stock
23 - - - - (7,707,938) - (7,707,938) - (7,707,938)
Retirement of treasury stock
23 - - - (11,399,991) 11,399,991 - - - -
Others
- - - - 6,083 - 6,083 88 6,171
Total transactions with owners
- - - (14,461,352) 3,698,099 - (10,763,253) (51,011) (10,814,264)
Balance as at December 31, 2016
119,467 778,047 4,403,893 193,086,317 (11,934,586) (28,810) 186,424,328 6,538,705 192,963,033

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 70 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(In thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
2016 USD
Preferred
stock
Common
stock
Share
premium
Retained
earnings
Other
components
of equity
Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income
attributable
to assets held
-
for-sale
Equity
attributable
to owners of
the parent
Non-
controlling
interests Total
Notes
Balance as at January 1, 2016
103,004 670,826 3,797,002 159,619,385 (15,157,728) 20,517 149,053,006 5,330,968 154,383,974
Profit for the period
- - - 19,326,604 - - 19,326,604 267,656 19,594,260
Changes in value of available-for-sale
financial assets, net of tax
9, 23 - - - - (75,619) (20,518) (96,137) 75,583 (20,554)
Share of other comprehensive income
(loss) of associates and joint
ventures, net of tax
12, 23 - - - - (69,101) 183 (68,918) 29 (68,889)
Foreign currency translation, net of tax 23 - - - - 1,000,415 - 1,000,415 (24,812) 975,603
Remeasurement of net defined benefit
liabilities, net of tax
17, 23 - - - - 798,631 - 798,631 32,179 830,810
Reclassification to assets held-for-sale 36 - - - - 25,023 (25,023) - - -
Total comprehensive income (loss)
- - - 19,326,604 1,679,349 (45,358) 20,960,595 350,635 21,311,230
Dividends 22 - - - (2,639,481) - - (2,639,481) (56,182) (2,695,663)
Capital transaction under common
control
- - - - (32) - (32) 10,581 10,549
Changes in consolidated entities
- - - - - - - 1,543 1,543
Acquisition of treasury stock
23 - - - - (6,645,724) - (6,645,724) - (6,645,724)
Retirement of treasury stock 23 - - - (9,828,984) 9,828,984 - - - -
Others
- - - - 5,244 - 5,244 76 5,320
Total transactions with owners
- - - (12,468,465) 3,188,472 - (9,279,993) (43,982) (9,323,975)
Balance as at December 31, 2016
103,004 670,826 3,797,002 166,477,524 (10,289,907) (24,841) 160,733,608 5,637,621 166,371,229

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 71 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
For the year ended December 31,
Notes 2016 2015 2016 2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Cash flows from operating
activities
Profit for the period
22,726,092 19,060,144 19,594,260 16,433,508
Adjustments 30 30,754,471 29,610,971 26,516,267 25,530,350
Changes in assets and liabilities
arising from operating activities
30 (1,180,953) (4,682,032) (1,018,209) (4,036,812)
Cash flows from operating activities
52,299,610 43,989,083 45,092,318 37,927,046
Interest received
1,405,085 2,151,741 1,211,453 1,855,215
Interest paid
(443,838) (748,256) (382,674) (645,141)
Dividends received
256,851 266,369 221,455 229,661
Income tax paid
(6,132,064) (5,597,176) (5,287,018) (4,825,842)
Net cash generated from operating
activities
47,385,644 40,061,761 40,855,534 34,540,939
Cash flows from investing activities
Net increase in short-term financial
instruments
(6,780,610) (5,762,783) (5,846,189) (4,968,627)
Proceeds from disposal of short-term
available-for-sale financial assets
3,010,003 2,143,384 2,595,201 1,848,009
Acquisition of short-term available-
for-sale financial assets
(2,129,551) (509,349) (1,836,082) (439,157)
Proceeds from disposal of long-term
financial instruments
789,862 3,999,710 681,013 3,448,519
Acquisition of long-term financial
instruments
(1,741,547) (132,733) (1,501,548) (114,441)
Proceeds from disposal of long-term
available-for-sale financial assets
2,010,356 200,502 1,733,313 172,871
Acquisition of long-term available-
for-sale financial assets
(1,498,148) (232,530) (1,291,692) (200,486)
Proceeds from disposal of associates
and joint ventures
2,280,203 278,009 1,965,973 239,697
Acquisition of associates and joint
ventures
(84,306) (137,917) (72,688) (118,911)
Disposal of property, plant and
equipment
270,874 357,154 233,545 307,935
Purchases of property, plant
and equipment
(24,142,973) (25,880,222) (20,815,884) (22,313,726)
Disposal of intangible assets
6,944 1,083 5,987 934
Purchases of intangible assets (1,047,668) (1,501,881) (903,291) (1,294,910)
Cash outflows from business
combinations
(622,050) (411,445) (536,327) (354,745)
Others
19,936 421,231 17,190 363,183
Net cash used in investing activities
(29,658,675) (27,167,787) (25,571,479) (23,423,855)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 72 / 240
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In millions of Korean won, in thousands of US dollars (Note 2.3))
For the year ended December 31,
Notes 2016 2015 2016 2015
KRW KRW USD USD
Cash flows from financing activities
Net increase(decrease) in short-term
borrowings
1,351,037 3,202,416 1,164,854 2,761,098
Acquisition of treasury stock
(7,707,938) (5,015,112) (6,645,724) (4,323,991)
Disposal of treasury stock
- 3,034 - 2,616
Proceeds from long-term borrowings and
debentures
1,041,743 192,474 898,183 165,950
Repayment of long-term borrowings and
debentures
(252,846) (1,801,465) (218,002) (1,553,209)
Payment of dividends
(3,114,742) (3,129,544) (2,685,506) (2,698,269)
Net increase(decrease) in non-controlling
interests
13,232 (25,312) 11,407 (21,823)
Net cash used in financing activities
(8,669,514) (6,573,509) (7,474,788) (5,667,628)
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
and cash equivalents
417,243 (524,487) 359,744 (452,209)
Net increase in cash and cash
equivalents
9,474,698 5,795,978 8,169,011 4,997,247
Cash and cash equivalents
Beginning of the period
22,636,744 16,840,766 19,517,225 14,519,978
End of the period
32,111,442 22,636,744 27,686,236 19,517,225

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 73 / 240
2. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. General Information
1.1 Company Overview
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (the “Company”) was incorporated under the laws of the Republic of Korea in 1969 and listed its
shares on the Korea Stock Exchange in 1975.
The Company and its subsidiaries (collectively referred to as the “Company”) operate three business divisions: Consumer
Electronics (“CE”), Information technology & Mobile communications (“IM”), and Device Solutions (“DS”). The CE division
includes digital TVs, monitors, air conditioners and refrigerators and the IM division includes mobile phones, communication
systems, and computers. The DS division includes products such as memory and system LSI in the semiconductor business
(“Semiconductor”), and LCD and OLED panels in the display business (“DP”). The Company is domiciled in the Republic of
Korea and the address of its registered office is Suwon, the Republic of Korea.
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with the International Financial Reporting Standards as
adopted by the Republic of Korea (“Korean IFRS”) 1110, Consolidated Financial Statements. The Company, as the controlling
company, consolidates its 169 subsidiaries, including Samsung Display and Samsung Electronics America (Note 1.2). The
Company also applies the equity method of accounting to its 38 affiliates, including Samsung Electro-Mechanics.
1.2 Consolidated Subsidiaries
(A) The consolidated subsidiaries as at December 31, 2016 are as follows:
Area Subsidiaries Industry
Percentage of
ownership
1
Domestic
Samsung Display (SDC) Manufacture and sale of display panels 84.8
SU Materials Manufacture of LCD components 50.0
STECO Manufacture of semiconductor components 70.0
SEMES Manufacture of semiconductor/FPD 91.5
Samsung Electronics Service Repair services for electronic devices 99.3
Samsung Electronics Sales Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Logitech General logistics agency 100.0
Samsung Medison Medical equipment 68.5
Samsung Venture Capital Union #20
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #21
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #22
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #23
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #26
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #27
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #28
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #29
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #32
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Samsung Venture Capital Union #33
Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.0
Mirero System
Quality control system of semiconductor
74.7
S-Printing Solution
Business of printing solutions
100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 74 / 240
Area Subsidiaries Industry
Percentage of
ownership
1
America
Samsung Electronics America (SEA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
NexusDX (Nexus) Medical equipment 100.0
Samsung Receivables (SRC) Credit management 100.0
NeuroLogica Medical equipment 100.0
Samsung Semiconductor (SSI) Sale of semiconductor/LCD 100.0
Samsung Electronics Canada (SECA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Research America (SRA) R&D 100.0
Samsung Mexicana (SAMEX) Manufacture of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung International (SII) Manufacture of TV/monitors 100.0
Samsung Austin Semiconductor (SAS) Manufacture of semiconductor 100.0
Samsung Electronics Mexico (SEM) Sale of electronic devices 99.9
SEMES America (SEMESA) Semiconductor equipment 100.0
Samsung Electronics Digital Appliance Mexico
(SEDAM)
Manufacture of electronic devices 99.9
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica Miami (SEMI) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica (SELA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Venezuela (SEVEN) Marketing and services 100.0
Samsung Electronica Colombia (SAMCOL) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Panama (SEPA) Consulting 100.0
Samsung Electronica da Amazonia (SEDA) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Argentina (SEASA) Marketing and services 100.0
Samsung Electronics Chile (SECH) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Peru (SEPR) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
RT SV CO-INVEST (RT-SV) Technology business, Venture capital investments
99.9
Quietside Sale of heating and cooling products
100.0
SmartThings Sale of smart home electronics
100.0
PrinterOn Sale of printing solutions
100.0
PrinterOn America Sale of printing solutions
100.0
Simpress Sale of printing solutions
100.0
Samsung Pay Develop and provide mobile payment service
100.0
Prismview (formerly YESCO Electronics) Manufacture and sale of LED displays
100.0
Beijing Integrated Circuit Industry International
Fund (Beijing Fund)
Venture capital investments
61.4
Stellus Technologies
Manufacture and sale of server semiconductor storage
system
100.0
Samsung Oak Holdings (SHI) Holding company 100.0
AdGear Technologies Digital advertising platforms 100.0
Joyent Cloud Services 100.0
Samsung Next Holding Company 100.0
Samsung Next Fund Technology business, Venture capital investments 100.0
Dacor Holdings Holding Company 100.0
Dacor Manufacture and sale of Home appliances 100.0
Dacor Canada Sale of Home appliances 100.0
EverythingDacor.com Sale of Home appliances 100.0
Distinctive Appliances of California Sale of Home appliances 100.0
Viv Labs
Research of AI technology 100.0
NewNet Communication Technologies Canada
RCS (Rich Communication Service) 100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 75 / 240
Area
Subsidiaries
Industry
Percentage of
ownership
1
Europe/CIS
Samsung Electronics (UK) (SEUK) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Holding (SEHG) Holding Company 100.0
Samsung Semiconductor Europe GmbH (SSEG) Sale of semiconductor/LCD 100.0
Samsung Electronics GmbH (SEG) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Iberia (SESA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics France (SEF) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Hungarian (SEH) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Czech and Slovak (SECZ) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Italia (SEI) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Logistics (SELS) Logistics 100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux (SEBN) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Display Slovakia (SDSK) Toll processing of LCD 100.0
Samsung Electronics Romania (SEROM) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Overseas (SEO) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Polska (SEPOL) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Portuguesa (SEP) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Nordic (SENA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Semiconductor Europe (SSEL) Sale of semiconductor/LCD 100.0
Samsung Electronics Austria (SEAG) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Slovakia (SESK) Manufacture of TV/monitors 100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding (SEEH) Holding Company 100.0
Samsung Electronics Poland Manufacturing (SEPM) Manufacture of home appliances 100.0
Samsung Electronics Greece (SEGR) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Nanoradio Design Center (SNDC) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Rus (SER) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Electronics Rus Company (SERC) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Ukraine (SEU) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Electronics Baltics (SEB) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Ukraine Company (SEUC) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung R&D Institute Rus (SRR) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Central Eurasia (SECE) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Rus Kaluga (SERK) Manufacture of TV 100.0
Samsung Electronics (London) Limited (SEL) Holding Company 100.0
Samsung Denmark Research Center (SDRC) R&D 100.0
Samsung France Research Center (SFRC) R&D 100.0
Samsung Cambridge Solution Centre (SCSC) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Switzerland GmbH (SESG) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
PrinterOn Europe Sale of printing solutions 100.0
Samsung Electronics Caucasus (SECC) Marketing 100.0
Joyent(UK) Cloud services 100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 76 / 240
Area
Subsidiaries
Industry
Percentage of
ownership
1
Middle East
and Africa
Samsung Electronics West Africa (SEWA) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Electronics East Africa (SEEA) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Gulf Electronics (SGE) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Egypt (SEEG) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Israel (SEIL) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Electronics Tunisia (SETN) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Electronics Pakistan (SEPAK) Marketing 100.0
Samsung Electronics South Africa (SSA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Turkey (SETK) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Semiconductor Israel R&D Center (SIRC) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Levant (SELV) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Maghreb Arab (SEMAG) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics South Africa Production
(SSAP)
Manufacture of TV/monitors 100.0
Asia
(Except China)
Samsung Japan (SJC) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung R&D Institute Japan (SRJ) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Japan (SEJ) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Display (M) (SDMA) Manufacture of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics (M) (SEMA) Manufacture of home appliances 100.0
Samsung Vina Electronics (SAVINA) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Asia Private (SAPL) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung India Electronics (SIEL) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung R&D Institute India-Bangalore (SRI-B) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Australia (SEAU) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Indonesia (SEIN) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Telecommunications Indonesia (STIN) Sale and services of communication systems 100.0
Thai Samsung Electronics (TSE) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 91.8
Samsung Electronics Philippines (SEPCO) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Malaysia Electronics (SME) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung R&D Institute Bangladesh (SRBD) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Vietnam (SEV) Manufacture of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN
(SEVT)
Manufacture and sale of communication equipment 100.0
Samsung Medison India (SMIN) Medical equipment 100.0
Samsung Electronics New Zealand (SENZ) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Display Vietnam (SDV) Manufacture of LCD 100.0
Samsung Electronics HCMC CE Complex (SEHC) Manufacture and sale of electronic devices 100.0
Laos Samsung Electronics Sole(LSE) Marketing 100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 77 / 240
Area
Subsidiaries
Industry
Percentage of
ownership
1
China
Samsung Display Dongguan (SDD) Manufacture of LCD 100.0
Samsung Display Tianjin (SDT) Manufacture of LCD 95.0
Samsung Electronics Hong Kong (SEHK) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Suzhou Samsung Electronics (SSEC) Manufacture of home appliances 88.3
Samsung Suzhou Electronics Export
(SSEC-E)
Manufacture of home appliances 100.0
Samsung (China) Investment (SCIC) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Mobile R&D Center China-Guangzhou (SRC-
Guangzhou)
R&D 100.0
Samsung Tianjin Mobile Development Center (STMC) R&D 100.0
Samsung R&D Institute China-Shenzhen(SRC-Shenzhen) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics Suzhou Semiconductor (SESS) Toll processing of semiconductor 100.0
Samsung Electronics (Shandong) Digital Printing (SSDP) Manufacture of printers 100.0
Samsung Electronics Huizhou (SEHZ) Manufacture of electronic devices 99.9
Tianjin Samsung Electronics (TSEC) Manufacture of TV/monitors 91.2
Samsung Electronics Taiwan (SET) Sale of electronic devices 100.0
Beijing Samsung Telecom R&D Center (BST) R&D 100.0
Tianjin Samsung Telecom Technology (TSTC) Manufacture of communication equipment 90.0
Shanghai Samsung Semiconductor (SSS) Sale of semiconductor/LCD 100.0
Samsung Electronics Suzhou Computer (SESC) Manufacture of electronic devices 100.0
Samsung Suzhou Module (SSM) Toll processing of LCD 100.0
Samsung Suzhou LCD (SSL) Manufacture of LCD 60.0
Shenzhen Samsung Electronics Telecommunication (SSET) Manufacture of communication equipment 95.0
Samsung Semiconductor (China) R&D (SSCR) R&D 100.0
Samsung Electronics China R&D Center (SCRC) R&D 100.0
Samsung (China) Semiconductor (SCS) Manufacture of semiconductor 100.0
Samsung Electronics (Beijing) Service (SBSC) Services 100.0
Tianjin Samsung LED (TSLED) Manufacture of LED 100.0
Tianjin Samsung Opto-Electronics (TSOE) Manufacture of cameras/camcorders 90.0
SEMES (Xian) Semiconductor equipment 100.0
Samsung Semiconductor Xian (SSCX) Sale of semiconductor/LCD 100.0
1
Ownership represents the Company’s ownership of voting rights in each entity.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 78 / 240
(B) A summary of financial data of major consolidated subsidiaries is as follows:
(1) 2016
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Assets Liabilities Sales
Net Income
(Loss)
Samsung Display (SDC)
₩ 43,305,405 ₩ 8,361,256 ₩ 24,658,814 ₩ 1,498,628
Samsung Electronics America (SEA) 21,810,492 9,496,649 34,521,654 246,141
Samsung (China) Investment (SCIC) 13,632,938 11,672,755 8,792,750 298,373
Samsung (China) Semiconductor (SCS) 9,749,448 4,564,793 4,152,137 1,113,218
Samsung Electronics Vietnam (SEV) 9,134,023 1,258,948 19,426,334 2,046,280
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding (SEEH) 8,643,308 6,661,092 - 350,974
Samsung Semiconductor (SSI) 7,804,698 3,746,687 19,911,135 30,247
Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN (SEVT) 7,646,828 2,179,023 23,563,736 2,641,418
Samsung Electronics Huizhou (SEHZ) 6,174,579 1,106,633 12,971,475 764,426
Shanghai Samsung Semiconductor (SSS) 5,862,409 5,166,385 20,983,314 181,041
Samsung Asia Private (SAPL) 5,528,472 592,320 1,458,176 1,056,956
Samsung Electronica da Amazonia (SEDA) 5,200,799 1,510,972 6,092,245 966,821
Samsung Austin Semiconductor (SAS) 4,940,748 1,293,458 3,586,127 104,747
Samsung India Electronics (SIEL) 4,563,407 2,256,194 8,827,028 753,164
Samsung Display Vietnam (SDV) 3,165,239 3,437,791 5,230,581 (98,102)
Samsung Electronics Europe Logistics (SELS) 2,887,230 2,779,296 13,157,455 36,768
Samsung Suzhou LCD (SSL) 2,499,917 1,376,439 1,494,787 1,091
Thai Samsung Electronics (TSE) 2,079,865 364,518 4,069,078 198,980
Samsung Electronics Slovakia (SESK) 2,053,467 440,402 3,634,166 115,387
Samsung Electronics Taiwan (SET) 1,857,017 1,540,478 3,533,924 (36,178)
Samsung Electronics HCMC CE Complex (SEHC) 1,814,566 1,572,982 2,010,442 118,091
Samsung Electronics Hungarian (SEH) 1,743,979 633,975 2,441,881 89,712
Samsung Electronics GmbH (SEG) 1,621,827 1,618,305 6,257,480 2,187
Samsung Display Dongguan (SDD) 1,584,504 518,511 5,187,954 199,922
Samsung Electronics (UK) (SEUK) 1,526,879 1,103,579 4,731,464 107,243

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 79 / 240
(2) 2015
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Assets Liabilities Sales
Net Income
(Loss)
Samsung Display (SDC)
₩ 39,225,460 ₩ 6,586,259 ₩ 26,397,111 ₩ 1,673,165
Samsung Electronics America (SEA) 14,875,687 7,562,099 35,766,374 268,083
Samsung (China) Investment (SCIC) 12,748,395 11,040,055 11,461,304 (77,629)
Samsung (China) Semiconductor (SCS) 9,742,388 5,537,446 2,610,462 171,644
Samsung Semiconductor (SSI) 8,288,391 4,379,980 21,724,671 (32,056)
Samsung Electronics Vietnam (SEV) 7,829,507 1,155,075 18,431,838 1,948,071
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding (SEEH) 6,989,207 5,223,523 - (31,925)
Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN (SEVT) 6,571,798 3,940,926 19,379,347 1,592,920
Samsung Electronics Huizhou (SEHZ) 6,192,974 1,738,095 17,949,623 722,700
Samsung Austin Semiconductor (SAS) 6,179,289 2,746,852 3,045,453 94,698
Samsung Asia Private (SAPL) 4,227,798 504,256 1,392,926 957,734
Shanghai Samsung Semiconductor (SSS) 3,792,437 3,207,942 14,372,358 141,232
Samsung India Electronics (SIEL) 3,723,127 2,204,333 8,008,884 326,462
Samsung Electronica da Amazonia (SEDA) 3,114,334 1,021,869 5,634,385 322,939
Samsung Suzhou LCD (SSL) 2,784,122 1,634,304 1,024,881 76,099
Tianjin Samsung Telecom Technology (TSTC) 2,075,123 778,133 6,963,943 146,972
Samsung Electronics Europe Logistics (SELS) 1,894,614 1,793,917 12,943,676 (7,745)
Thai Samsung Electronics (TSE) 1,889,410 416,382 3,949,756 179,527
Samsung Electronics Slovakia (SESK) 1,888,341 373,886 3,480,848 107,968
Samsung Electronics GmbH (SEG) 1,820,922 1,762,978 6,047,305 (1,630)
Samsung Display Dongguan (SDD) 1,276,263 384,963 4,649,277 130,635
Samsung Electronics Benelux (SEBN) 1,264,497 291,332 2,148,502 42,790
Samsung Electronics Hungarian (SEH) 1,254,673 231,785 3,029,047 97,474
Samsung Electronics Taiwan (SET) 1,253,480 918,482 4,258,650 44,025
Samsung Electronics (UK) (SEUK) 1,133,512 745,126 4,656,990 106,413

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 80 / 240
(C) Changes in scope of consolidation
(1) Subsidiaries newly included in the consolidation for the year ended December 31, 2016:
Area Subsidiary Description
Domestic
Samsung Venture Capital Union #32 Incorporation
Samsung Venture Capital Union #33 Incorporation
Mirero System
Acquisition of shares
S-Printing Solution
Spin-off
America
Samsung Oak Holdings (SHI) Incorporation
AdGear Technologies Acquisition of shares
Joyent Acquisition of shares
Joyent Canada Acquisition of shares
Samsung Next
Incorporation
Samsung Next Fund
Incorporation
Dacor Holdings
Acquisition of shares
Dacor
Acquisition of shares
Dacor Canada
Acquisition of shares
EverythingDacor.com
Acquisition of shares
Distinctive Appliances of California
Acquisition of shares
Viv Labs Acquisition of shares
NewNet Communication Technologies Canada Acquisition of shares
Europe/CIS Joyent (UK) Acquisition of shares
Asia
(Except China)
Laos Samsung Electronics Sole (LSE) Incorporation
China Samsung Semiconductor Xian (SSCX) Incorporation
(2) Subsidiaries excluded from the consolidation for the year ended December 31, 2016:
A
rea Subsidiar
y
Descri
p
tion
Domestic Samsung Venture Capital Union #14 Liquidation
America
Grandis Liquidation
Joyent Canada Liquidation
Europe/CIS
Samsung Russia Service Centre (SRSC) Merger
1
SonoAce Deutschland (SDG) Liquidation
Samsung Electronics Kazakhstan(SEK)
Merger
4
Asia
(Except China)
Samsung Telecommunications Malaysia (STM) Liquidation
Future Technology & Service Liquidation
China
Samsung R&D Institute China-Xian (SRC-Xian) Merger
2
Samsung Electronics Shanghai Telecommunication (SSTC) Merger
3
1
Samsung Electronics Rus Company (SERC), a subsidiary of the Company, merged with Samsung Russia Service Centre (SRSC) on February 1,
2016.
2
Samsung (China) Semiconductor (SCS), a subsidiary of the Company, merged with Samsung R&D Institute China-Xian (SRC-Xian) in July,
2016.
3
Samsung (China) Investment (SCIC), a subsidiary of the Company, merged with Samsung Electronics Shanghai Telecommunication (SSTC) in
September, 2016.
4
Samsung Electronics Central Eurasia (SECE), a subsidiary of the Company, merged with Samsung Electronics Kazakhstan (SEK) in December,
2016.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 81 / 240
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these consolidated financial statements are set out below. These
policies have been consistently applied to all the years presented, unless otherwise stated.
2.1 Basis of Presentation
The
Company maintains its accounting records in Korean won and prepares statutory financial statements in the Korean language
(Hangul) in accordance with Korean IFRS. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been condensed, restructured
and translated into English from the Korean language financial statements.
Certain information attached to the Korean language financial statements, but not required for a fair presentation of the
Company's
financial position, financial performance or cash flows, is not presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
The consolidated financial statements of the
Company presented have been prepared in accordance with Korean IFRS. International
Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) have been adopted by the Korean Accounting Standards Board as Korean IFRS based on
standards and interpretations published by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Korean IFRS permits the use of critical accounting estimates in the preparation of the financial statements and requires management
judgments in applying accounting policies. The areas involving a higher degree of judgment or complexity, or areas where
assumptions and estimates are significant to the consolidated financial statements, are disclosed in Note 3.
2.2 Changes in Accounting Policy and Disclosures
(A) New and amended standards adopted by the
Company
The
Company applied the following amended and enacted standards for the annual period beginning on January 1, 2016:
Amendment to Korean IFRS 1001, Presentation of Financial Statements
Korean IFRS 1001 Presentation of Financial Statements clarifies that materiality applies to the exclusion or inclusion or
aggregation of the disclosures in the notes. The standard also clarifies that the share of OCI arising from equity-accounting should
be presented in total for items which will and will not be reclassified to profit or loss. Additional amendments are made in relation
to the particular ordering of the footnote disclosures. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the financial
statements.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 82 / 240
(B) New and amended standards not adopted by the
Company
The
Company expects that new standards, amendments and interpretations issued but not effective for the financial year beginning
January 1, 2016, and not early adopted, would not have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
Amendment to Korean IFRS 1007, Statement of Cash Flows
Amendments to Korean IFRS 1007 Statement of Cash flows requires disclosures that enable users of financial statements to
evaluate changes in liabilities arising from financing activities, including both changes arising from cash flows and non-cash
changes. The
Company will apply this amendment for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2017. The Company
is in the process of determining the impact of adopting the new Standard.
Korean IFRS 1109, Financial Instruments
The new standard for financial instruments issued on September 25, 2015 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after
January 1, 2018 with early application permitted. This standard will replace Korean IFRS 1039 Financial Instruments:
Recognition and Measurement. The
Company will apply the standards for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2018.
The standard requires retrospective application with some exceptions. For example, the entity is not required to restate prior
periods in relation to classification, measurement and impairment of financial instruments. The standard requires prospective
application of its hedge accounting requirements for all hedging relationships except the accounting for time value of options and
other exceptions.
Korean IFRS 1109 Financial Instruments requires all financial assets to be classified and measured on the basis of the entity’s
business model for managing financial assets and the contractual cash flow characteristics of the financial assets. A new
impairment model, an expected credit loss model, is introduced and any subsequent changes in expected credit losses will be
recognized in profit or loss. Also, hedge accounting rules amended to extend the hedging relationship, which consists only of
eligible hedging instruments and hedged items, qualifies for hedge accounting.
An effective implementation of Korea IFRS 1109 requires preparation processes including financial impact assessment,
accounting policy establishment, accounting system development and system stabilization. The impact on the
Company’s financial
statements due to the application of the standard is dependent on judgements made in applying the standard, financial instruments
held by the
Company and macroeconomic variables.
The
Company has performed a preliminarily assessment of the financial impacts of the implementation of Korean IFRS 1109 to the
2016 financial statements based on current situation and available information as at December 31, 2016. The expected impact of
application of the standard on the
Company’s financial statements are set out below. The Company will conduct further analysis of
detailed financial impacts based on additional information in the future, and the result of the preliminary assessment may change
depending on additional information available to the
Company.
(a) Classification and Measurement of Financial Assets
When implementing Korean IFRS 1109, the classification of financial assets will be driven by the
Company’s business model for
managing the financial assets and contractual terms of cash flow. The following table shows the classification of financial assets
measured subsequently at amortized cost, at fair value through other comprehensive income reserve and at fair value through
profit or loss. For hybrid (combined) instruments, if the
Company is unable to measure an embedded derivative separately from its
host contract, financial assets with embedded derivatives are classified in their entirety.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 83 / 240
Business model for the
contractual cash flows
characteristics
Solely represent payments of
principal and interest
All other
Hold the financial asset for the
collection of the contractual cash
flows
Measured at amortized cost
1
Recognized at fair value through
profit or loss
2
Hold the financial asset for the
collection of the contractual cash
flows and trading
Recognized at fair value through
other comprehensive income
reserve
1
Hold for trading
Recognized at fair value through
profit or loss
1
A designation at fair value through profit or loss is allowed only if such designation mitigates an accounting mismatch
(irrevocable).
2
A designation at fair value through other comprehensive income is allowed only if the financial instrument is the equity
investment that are not held for trading (irrevocable).
With the implementation of Korean IFRS 1109, the criteria to classify the financial assets at amortized cost or at fair value through
other comprehensive income are more strictly applied than the criteria applied under Korean IFRS 1039. Accordingly, the
financial assets at fair value through profit or loss may increase by implementing Korean IFRS 1109 and may result in an
increased fluctuation in profit or loss.
As at December 31, 2016, the
Company recognizes loan and trade receivables amounting to ₩112,219,719 million, financial assets
available-for-sales amounting to
₩10,442,736 million.
According to Korean IFRS 1109, debt investments are measured at amortized cost if: a) the objective of the business model is to
hold the financial assets for the collection of the contractual cash flows, and b) the contractual terms of cash flows solely represent
payments of principal and interest. As at December 31, 2016, the
Company recognized loan and trade receivables amounting to
₩112,219,719 million held at amortized costs.
According to the result of preliminary impact assessment, when applying Korean IFRS 1109 to the financial assets as at December
31, 2016, under the terms and conditions of the contracts, most financial assets consist of cash flows solely representing payments
of principal and interest on a due date. Where the
Company holds the financial assets for the collection of the contractual cash
flows, the financial assets are classified as accounts subsequently measured at amortized cost. In conclusion, it is expected that the
financial impact on the financial statements will be immaterial.
Korean IFRS 1109 measures debt investments at fair value through other comprehensive income of which terms of cash flows
solely represent payments of the principal and interest on a due date, where the purpose of holding debt investment is to collect
contractual cash flows and trade. As at December 31, 2016, the
Company has debt investments classified as available-for-sale
financial assets amounting to
₩3,743,173 million.
According to the result of preliminary impact assessment, when applying Korean IFRS 1109 to the debt investments classified as
available-for-sale as at December 31, 2016, most of the investments will be classified as financial instruments measured at fair
value through other comprehensive income.
According to Korean IFRS 1109, equity investments not being held for trading may be given an irrevocable election to be
classified as financial instruments measured at fair value through other comprehensive income at initial recognition and the
cumulative gain or loss previously recognized in other comprehensive income is not subsequently recycled from equity to profit or
loss as a reclassification adjustment. As at December 31, 2016, the
Company's equity investments classified as available-for-sale
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 84 / 240
financial assets amount to
₩6,699,563 million and the cumulative unrealized profit or loss on available-for-sale equity
investments amounting to
₩631,601 million was recycled from equity to profit or loss as a reclassification adjustment for the
2016 fiscal year.
As a result of the preliminary impact assessment, the
Company p will designate long-term investment equity investments, which
account for most of the available-for-sale equity instruments, as financial instruments measured at fair value through other
comprehensive income. Therefore, the financial impact to the financial statements is expected to be immaterial. As at December
31, 2016, the remaining cumulative profit or loss which is comprehensive income not subject to be subsequently recycled from
equity to profit or loss is
₩1,390,624 million.
According to Korean IFRS 1109, debt investments of which the contractual term of cash flows are not solely representing
payments of principal and interest or which are held for trading are classified as at fair value through profit or loss. Also equity
investments not designated at fair value through comprehensive income are measured at fair value through profit or loss. As at
December 31, 2016, the
Company has no debt or equity investments classified as financial instruments at fair value through profit
or loss.
According to the results of the preliminary impact assessment, as most of the financial assets held as at December 31, 2016 are
recorded at fair value through the profit and loss for the current term, the financial impact of adopting Korean IFRS 1109 is
expected to be immaterial.
(b) Classification and Measurement of Financial Liabilities
Korean IFRS 1109 requires the change in the liability’s fair value attributable to changes in the credit risk to be recognized in other
comprehensive income, unless this treatment of the credit risk component creates or enlarges a measurement mismatch. Amounts
presented in other comprehensive income are not subsequently transferred to profit or loss.
Under Korean IFRS 1039, all financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss recognized their fair value
movements in profit or loss. However, under Korean IFRS 1109, certain fair value movements will be recognized in other
comprehensive income thus profit or loss from fair value movements may decrease.
As at December 31, 2016, total financial liabilities account for
₩46,944,824 million of which ₩417,399 million are designated to
be measure at fair value through profit or loss, and for the 2016 fiscal year the
Company recognized loss of 61,221 million in
relation to financial liabilities measured at fair value through profit or loss.
According to the result of the preliminary impact assessment, financial liabilities measured at fair value through profit and loss for
the current terms as at December 31, 2016 have mostly short maturities and the credit risk fluctuation of financial liabilities is
insignificant. Therefore, it is expected that the impact of adopting Korean IFRS 1109 will not be significant.
(c) Impairment: Financial Assets and Contract Assets
Korean IFRS 1109 sets out a new forward looking ‘expected loss impairment model’ which replaces the incurred loss model in
Korean IFRS 1039 if there is objective evidence and applies to:
Financial assets measured at amortized cost
Debt investments measured at fair value through other comprehensive income, and
Certain loan commitments and financial guaranteed contracts.
Under Korean IFRS 1109, a credit event (or impairment ‘trigger’) no longer has to occur before credit losses are recognized. The
Company will always recognize (at a minimum) 12-month expected credit losses in profit or loss. Lifetime expected losses will be
recognized on assets for which there is a significant increase in credit risk after initial recognition.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 85 / 240
Stage
1
Loss allowance
1
No significant increase in credit risk after
initial recognition
2
12-month expected credit losses (expected credit losses that result from
those default events on the financial instruments that are possible within 12
months after the reporting date)
2
Significant increase in credit risk after initial
recognition
Lifetime expected credit losses (expected credit losses that result from all
possible default events over the life of the financial instruments)
3 Objective evidence of credit-impaired
1
The Company shall measure the loss allowance at an amount equal to Lifetime expected credit losses for contract assets or
trade receivables under the standard, Korean IFRS 1115 Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which do not contain a
significant financing component. However, the
Company elects to measure the loss allowance at an amount equal to Lifetime
expected credit losses for all contract assets or all trade receivables which contain a significant financing component in
accordance with Korean IFRS 1115. The
Company also elects to measure the loss allowance at an amount equal to Lifetime
expected credit losses for lease receivables.
2
If the financial instrument has low credit risk at the reporting date, the Company may assume that the credit risk has not
increased significantly since initial recognition.
Under Korean IFRS 1109, the asset that is credit-impaired at initial recognition would recognize all changes in lifetime expected
credit losses since the initial recognition as a loss allowance with any changes recognized in profit or loss.
Korean IFRS 1115, Revenue from Contracts with Customers
The
Company will apply Korean IFRS 1115 Revenue from Contracts with Customers issued on November 6, 2015 for annual
reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2018. This standard replaces Korean IFRS 1018 Revenue, Korean IFRS 1011
Construction Contracts, Interpretation 2031 Revenue-Barter Transactions Involving Advertising Services, Interpretation 2113
Customer Loyalty Programs, Interpretation 2115 Agreements for the Construction of Real Estate and Interpretation 2118
Transfers of assets from customers.
The
Company will apply the standard retrospectively to prior reporting periods presented in accordance with Korean IFRS 1008
Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors and apply the simplified transition method with no restatement
for completed contracts as at January 1, 2017.
The new standard is based on the principle that revenue is recognized when control of goods or services transfers to a customer –
so the notion of control replaces the existing notion of risks and rewards. A new five-step process must be applied before revenue
from contract with customer can be recognized:
Identify contracts with customers
Identify the separate performance obligation
Determine the transaction price of the contract
Allocate the transaction price to each of the separate performance obligations, and
Recognize the revenue as each performance obligation is satisfied.
Based on the information available at the end of the reporting period, the Company is in the process of preliminary assessment of
the potential impact on the financial statements for the year 2016 when applying Korean IFRS 1115, and the interim results are set
out below. The Company will analyze more specific financial impacts based on additional information in the future.
(a) Identification of performance obligations
The
Company's IM (information technology & mobile communications) business consists of mobile phone, communication
systems and computers. The
Company manufactures and installs network communication systems, and provides them to customers.
In 2016, the related revenue from such activities did not account for a large portion of total revenue. When applying Korean IFRS
1115, performance obligation, such as network system production with customers, distinguished as technical support in the

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 86 / 240
integrated contract such as (1) product sales, (2) installation service, and (3) maintenance, were identified. The timing of revenue
recognition may change depending on whether each performance obligation is fulfilled at one time or over a period of time.
(b) Variable payment
As the
Company allows returns when selling products and merchandise, variability in payment may occur. When apply Korean
IFRS 1115, the
Company estimates the variable payment using an expectation-value method that is expected to better anticipate the
payments to which the company is entitled, and recognizes revenue by including variable payment in the transaction price only to
the amount that it is highly unlikely to reverse a significant portion of the cumulative revenue amount that has already been
recognized, at the end of the return period. Amounts not expected to be consideration received or receivable are recognized as a
refund liability.
(c) Distribution of transaction price
When applying Korean IFRS 1115, the
Company allocates transaction prices based on the relative individual selling prices to the
various performance obligations identified in a single contract. The
Company will use the 'Market Valuation Adjustment Approach'
to estimate the individual selling prices of each performance obligation and will use the 'Estimated Cost Plus Margin Approach',
which predicts the expected costs and adds the appropriate profits to the transactions.
2.3 Consolidation
The
Company prepares the consolidated financial statements in accordance with Korean IFRS 1110, Consolidated Financial
Statements.
(A) Subsidiaries
Subsidiaries are all entities (including special purpose entities) over which the
Company has control. The Company controls the
corresponding investee when it is exposed, or has rights, to variable returns from its involvement with the investee and has the
ability to affect those returns through its power over the investee. Consolidation of a subsidiary begins from the date the
Company
obtains control of a subsidiary and ceases when the
Company loses control of the subsidiary.
The
Company applies the acquisition method to account for business combinations. The consideration transferred is measured at the
fair values of the assets transferred, and identifiable assets acquired and liabilities and contingent liabilities assumed in a business
combination are initially measured at their fair values at the acquisition date. The
Company recognizes any non-controlling interest
in the acquiree on an acquisition-by-acquisition basis in the event of liquidation at the non-controlling interest’s proportionate share
of the recognized amounts of acquiree’s identifiable net assets. Acquisition-related costs are expensed as incurred.
Goodwill is recognized as the excess of (1) the aggregate of i) the consideration transferred, ii) the amount of any non-controlling
interest in the acquiree and iii) the acquisition-date fair value of the
Company’s previously held equity interest in the acquiree over
(2) the net identifiable assets acquired. If this consideration (1) is lower than the fair value of the acquiree’s net assets in (2), the
difference is recognized in profit or loss.
Balances of receivables and payables, income and expenses and unrealized gains on transactions between the
Company subsidiaries
are eliminated. Accounting policies of subsidiaries are changed where necessary to ensure consistency with the policies adopted by
the
Company.
(B) Changes in ownership interests in subsidiaries without change of control
Transactions with non-controlling interests that do not result in loss of control are accounted for as equity transactions – that is, as
transactions with the owners in their capacity as owners. The difference between fair value of any consideration paid and the
relevant share acquired of the carrying value of net assets of the subsidiary is recorded in equity. Gains or losses on disposals of
non-controlling interests are also recorded in equity.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 87 / 240
(C) Disposal of subsidiaries
If the
Company loses control of a subsidiary, any investment continuously retained in the subsidiary is re-measured at its fair value at
the date when control is lost and any resulting differences are recognized in profit or loss. Such fair value becomes the initial
carrying amount for the subsequent measurement of the retained interest accounted for as an associate, joint venture, or financial
asset. In addition, any amounts previously recognized in other comprehensive income in respect of such entity are accounted for as
if the
Company had directly disposed of the related assets or liabilities. As a result, the previously recognized other comprehensive
income are reclassified into profit or loss.
(D) Non-controlling interests
Each component of profit or loss and other comprehensive income is attributed to owners of the parent and to non-controlling
interests. Total comprehensive income is attributed to owners of the parent and to non-controlling interests even if this results in a
negative balance of non-controlling interests.
(E) Associates
Associates are all entities over which the
Company has significant influence but does not have control, generally investees of which
from 20% to 50% of voting stock is owned by the
Company. Investments in associates are initially recognized at acquisition cost
using the equity method. Unrealized gains on transactions between the
Company and its associates are eliminated to the extent of the
Company’s interest in the associates. If there is any objective evidence that the investment in the associate is impaired, the Company
recognizes the difference between the recoverable amount of the associate and its book value as impairment loss.
(F) Joint arrangements
A joint arrangement of which two or more parties have joint control is classified as either a joint operation or a joint venture. A joint
operator has rights to the assets, and obligations for the liabilities, relating to the joint operation and recognizes the assets, liabilities,
revenues and expenses relating to its interest in a joint operation. A joint venturer has rights to the net assets relating to the joint
venture and accounts for that investment using the equity method.
2.4 Foreign Currency Translation
(A) Functional and presentation currency
Items included in the financial statements of each of the
Company’s entities are measured using the currency of the primary
economic environment in which each entity operates (the “functional currency”). The consolidated financial statements are
presented in Korean won, which is the parent company’s functional and presentation currency.
(B) Transactions and balances
Foreign currency transactions are translated into the functional currency using the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the
transactions or valuation where items are re-measured. Foreign exchange gains and losses resulting from the settlement of such
transactions and from the translation at year-end exchange rates of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies
are recognized in profit or loss.
Exchange differences arising on non-monetary financial assets and liabilities such as equity instruments at fair value through profit
or loss and available-for-sale equity instruments are recognized in profit or loss and other comprehensive income, respectively, as
part of the fair value gain or loss.
(C) Translation into the presentation currency
The results and financial position of all the foreign entities that have a functional currency different from the presentation currency
of the
Company are translated into the presentation currency as follows:
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 88 / 240
Assets and liabilities for each statement of financial position presented are translated at the closing rate at the end of the
reporting date.
Income and expenses for each statement of income are translated at average exchange rates, unless this average is not a
reasonable approximation of the cumulative effect of the rates prevailing on the transaction dates, in which case income and
expenses are translated at the rate on the dates of the transactions.
All resulting exchange differences are recognized in other comprehensive income.
2.5 Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, deposits held at call with banks, and other short-term highly liquid investments
that are readily convertible to a known amount of cash and are subject to an insignificant risk of change in value.
2.6 Financial Assets
(A) Classification
The
Company classifies its financial assets in the following categories: financial assets at fair value through profit or loss, loans and
receivables, available-for-sale financial assets, and held-to-maturity financial assets. The classification depends on the terms of the
instruments and purpose for which the financial assets were acquired. Management determines the classification of its financial
assets at initial recognition.
(1) Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss
Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are financial assets held for trading. A financial asset is classified in this category
if acquired principally for the purpose of selling in the short-term. Derivatives not subject to hedge accounting and derivatives
separated from financial instruments, such as embedded derivatives, are also categorized as held for trading. Assets in this category
are classified as current assets.
(2) Loans and receivables
Loans and receivables are non-derivative financial assets with fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an active
market. They are included in current assets, except for those with maturities greater than 12 months after the end of the reporting
period which are classified as non-current assets.
(3) Available-for-sale financial assets
Available-for-sale financial assets are non-derivative financial assets that are either designated in this category or not classified in
any of the other categories. They are included in non-current assets unless an investment matures or management intends to dispose
of it within 12 months of the end of the reporting period.
(B) Recognition and measurement
Regular purchases and sales of financial assets are recognized on the trade date. At initial recognition, financial assets are measured
at fair value plus, in the case of financial assets not carried at fair value through profit or loss, transaction costs. Transaction costs of
financial assets carried at fair value through profit or loss are expensed in the statement of income. After the initial recognition,
available-for-sale financial assets and financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are subsequently carried at fair value.
Loans and receivables and held-to-maturity investments are subsequently carried at amortized cost using the effective interest
method.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 89 / 240
Changes in fair value of financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are recognized in profit or loss and changes in fair value
of available-for-sale financial assets are recognized in other comprehensive income. When the available-for-sale financial assets are
sold or impaired, the fair value adjustments recorded in equity are reclassified into profit or loss.
Interest on available-for-sale financial assets and held-to-maturity financial assets calculated using the effective interest method is
recognized in the statement of income as part of financial income. Dividends on available-for-sale financial assets are recognized in
the statement of income as part of other non-operating income when the
Company’s right to receive payments is established.
(C) Offsetting financial instruments
Financial assets and liabilities are offset, and the net amount reported in the statement of financial position, when there is a legally
enforceable right to offset the recognized amounts and there is an intention to settle on a net basis, or realize the asset and settle the
liability simultaneously.
(D) Derecognition of financial assets
If the
Company transfers a financial asset and the transfer does not result in derecognition because the Company has retained
substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the transferred asset due to a recourse in the event the debtor defaults, the
Company continues to recognize the transferred asset in its entirety and recognizes a financial liability for the consideration received.
The related financial liability is classified as ‘borrowings’ in the statement of financial position.
2.7 Impairment of Financial Assets
The
Company assesses at the end of each reporting period whether there is objective evidence that a financial asset or group of
financial assets is impaired. A financial asset or a group of financial assets is impaired and impairment loss is recognized only if
there is objective evidence and that loss event (or events) has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset or
group of financial assets that can be reliably estimated.
Impairment of loans and receivables is presented as a deduction in an allowance account. Impairment of other financial assets is
directly deducted from their carrying amount. The
Company writes off financial assets when the assets are determined to no longer
be recoverable.
The objective evidence that a financial asset is impaired includes significant financial difficulty of the issuer or obligor, a
delinquency in interest or principal payments, or the disappearance of an active market for that financial asset because of financial
difficulties. A significant and prolonged decline below its cost in the fair value of an available-for-sale equity instrument is also
objective evidence of impairment.
2.8 Trade Receivables
Trade receivables are amounts due from customers for merchandise sold or services performed in the ordinary course of business. If
collection is expected in one year or less, they are classified as current assets. If collection is expected beyond one year, they are
presented as non-current assets. Trade receivables are recognized initially at fair value and subsequently measured at amortized cost
using the effective interest method, less provision for impairment.
2.9 Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Cost is determined using the average cost method, except for
materials in transit. The cost of finished goods and work in progress comprises raw materials, direct labor, other direct costs and
related production overheads (based on normal operating capacity). It excludes costs of idle plant and abnormal waste. Net
realizable value is the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business, less applicable variable selling expenses.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 90 / 240
Inventories are reduced for the estimated losses arising from excess, obsolescence, and decline in value. This reduction is
determined by estimating market value based on future customer demand. The losses on inventory obsolescence are recorded as a
part of cost of sales.
2.10 Disposal Group Held-for-Sale
Non-current assets (or disposal groups) are classified as assets held-for-sale when their carrying amount is to be recovered
principally through a sale transaction and a sale is considered highly probable. The assets are measured at the lower of their carrying
amount and the fair value less costs to sell.
2.11 Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses. Historical cost
includes expenditures that are directly attributable to the acquisition of the items. Subsequent costs are included in the asset’s
carrying amount or recognized as a separate asset, as appropriate, only when it is probable that future economic benefits associated
with the item will flow to the
Company and the cost of the item can be measured reliably. The carrying amount of those parts that are
replaced is derecognized and repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
Depreciation on tangible assets is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the difference between their cost and their
residual values over their estimated useful lives. Land is not depreciated. Costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition,
construction or production of a qualifying asset, including capitalized interest costs, form part of the cost of that asset and are
amortized over the estimated useful lives.
The
Company’s policy is that property, plant and equipment should be depreciated over the following estimated useful lives:
Estimated useful lives
Buildings and structures 15, 30 years
Machinery and equipment 5 years
Other 5 years
The depreciation method, residual values and useful lives of property, plant and equipment are reviewed, and adjusted if appropriate,
at the end of each reporting period. An asset’s carrying amount is written down immediately to its recoverable amount if the asset’s
carrying amount is greater than its estimated recoverable amount. Gains and losses on disposals are determined by comparing the
proceeds with the carrying amount and are recognized within the statement of income as part of other non-operating income and
expenses.
2.12 Intangible Assets
Goodwill represents the excess of the cost of an acquisition over the fair value of the
Company’s share of the net identifiable assets
of the acquired subsidiary, associates, joint ventures and businesses at the date of acquisition. Goodwill on acquisitions of
subsidiaries and businesses is included in intangible assets and goodwill on acquisition of associates and joint ventures is included
in the investments in associates and joint ventures.
Intangible assets, except for goodwill, are initially recognized at their historical cost and carried at cost less accumulated
amortization and accumulated impairment losses.
Internally generated development costs are the aggregate costs recognized after meeting the asset recognition criteria, including
technical feasibility, and determined to have future economic benefits. Membership rights are regarded as intangible assets with an
indefinite useful life and not amortized because there is no foreseeable limit to the period over which the assets are expected to be

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 91 / 240
utilized. Intangible assets with definite useful lives such as trademarks and licenses, are amortized using the straight-line method
over their estimated useful lives.
The
Company’s policy is that intangible assets should be amortized over the following estimated useful lives:
Estimated useful lives
Development costs 2 years
Trademarks, licenses and other intangible assets 5 - 10 years
2.13 Impairment of Non-Financial Assets
Goodwill or intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are not subject to amortization and are tested annually for impairment.
Assets that are subject to amortization are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the
carrying amount may not be recoverable. An impairment loss is recognized for the amount by which the asset’s carrying amount
exceeds its recoverable amount. The recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s fair value less costs to sell and value in use. For
the purposes of assessing impairment, assets are grouped at the lowest levels for which there are separately identifiable cash flows
(cash-generating units). Non-financial assets other than goodwill for which an impairment charge was previously recorded are
reviewed for possible reversal of the impairment at each reporting date.
2.14 Financial Liabilities
(A) Classification and measurement
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss are financial instruments held for trading. Financial liabilities are classified in
this category if incurred principally for the purpose of repurchasing them in the near term. Derivatives that are not designated as
hedges or bifurcated from financial instruments containing embedded derivatives are also categorized as held-for-trading.
The
Company classifies non-derivative financial liabilities, except for financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss,
financial guarantee contracts and financial liabilities that arise when a transfer of financial assets does not qualify for derecognition,
as financial liabilities carried at amortized cost and presented as ‘trade payables’, ‘borrowings’, and ‘other financial liabilities’ in
the statement of financial position.
(B) Derecognition
Financial liabilities are removed from the statement of financial position when they are extinguished, for example, when the
obligation specified in the contract is discharged, cancelled or expires or when the terms of an existing financial liability are
substantially modified.
2.15 Trade Payables
Trade payables are amounts due to suppliers for merchandise purchased or services received in the ordinary course of business. If
payment is expected in one year or less, they are classified as current liabilities. If payment is expected beyond one year, they are
presented as non-current liabilities. Non-current trade payables are recognized initially at fair value and subsequently measured at
amortized cost using the effective interest method.
2.16 Borrowings
Borrowings are recognized initially at fair value, net of transaction costs, and are subsequently measured at amortized cost. Any
difference between cost and the redemption value is recognized in the statement of income over the period of the borrowings using
the effective interest method. If the
Company has an indefinite right to defer payment for a period longer than 12 months after the
end of the reporting date, such liabilities are recorded as non-current liabilities, otherwise, they are recorded as current liabilities.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 92 / 240
2.17 Provisions
A provision is recognized when the
Company has a present legal or constructive obligation as a result of a past event, it is probable
that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation, and a reliable estimate can be
made of the amount of the obligation. Provisions are not recognized for future operating losses.
Provisions are measured at the present value of the expenditures expected to be required to settle the obligation using a pre-tax rate
that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the obligation. The increase in the
provision due to passage of time is recognized as interest expense.
When it is probable that an outflow of economic benefits will occur due to a present obligation resulting from a past event, and the
amount is reasonably estimable, a corresponding provision is recognized in the financial statements. However, when such outflow is
dependent upon a future event that is not certain to occur, or cannot be reliably estimated, a disclosure regarding the contingent
liability is made in the notes to the financial statements.
2.18 Net Defined Benefit Liabilities
The
Company has a variety of retirement pension plans including defined benefit and defined contribution plans. A defined
contribution plan is a pension plan under which the
Company pays fixed contributions into a separate entity. The Company has no
legal or constructive obligations to pay further contributions if the fund does not hold sufficient assets to pay all employees the
benefits relating to employee service in the current and prior periods. For defined contribution plans, the
Company pays
contributions to annuity plans that are managed either publicly or privately on a mandatory, contractual or voluntary basis. The
Company has no further future payment obligations once the contributions have been paid. The contributions are recognized as
employee benefit expense when they are due. Prepaid contributions are recognized as an asset to the extent that a cash refund or a
reduction in the future payments is available.
A defined benefit plan is a pension plan that is not a defined contribution plan. Typically defined benefit plans define an amount of
pension benefit that an employee will receive on retirement, usually dependent on one or more factors such as age, years of service
and compensation. The liability recognized in the statement of financial position in respect to defined benefit pension plans is the
present value of the defined benefit obligation at the end of the reporting period less the fair value of plan assets. The defined
benefit obligation is calculated annually by independent actuaries using the projected unit credit method. The present value of the
defined benefit obligation is determined by discounting the estimated future cash outflows using interest rates of high-quality
corporate bonds that are denominated in the currency in which the benefits will be paid and that have terms to maturity
approximating to the terms of the related pension obligation.
Actuarial gains and losses resulting from the changes in actuarial assumptions, and the differences between the previous actuarial
assumptions and what has actually occurred, are recognized in other comprehensive income in the period in which they were
incurred. Past service costs are immediately recognized in profit or loss.
2.19 Financial Guarantee Contract
Financial guarantee contracts are contracts that require the issuer to make specified payments to reimburse the holder for a loss it
incurs because a specified debtor fails to make payments when due. Financial guarantees are initially recognized in the financial
statements at fair value on the date the guarantee was given. If the amount measured in subsequent periods exceeds the unamortized
balance of the amount initially recognized, the excess is classified as other financial liability.
2.20 Current and Deferred Tax
The tax expense for the period comprises current and deferred tax. Tax is recognized on the profit for the period in the statement of
income, except to the extent that it relates to items recognized in other comprehensive income or directly in equity, in which case
the tax is also recognized in other comprehensive income or directly in equity, respectively. The tax expense is calculated on the
basis of the tax laws enacted or substantively enacted at the end of the reporting period.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 93 / 240
Deferred tax is recognized for temporary differences arising between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying
amounts as expected tax consequences at the recovery or settlement of the carrying amounts of the assets and liabilities. However,
deferred tax assets and liabilities are not recognized if they arise from initial recognition of an asset or liability in a transaction other
than a business combination that at the time of the transaction affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss. Deferred tax
assets are recognized only to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profit will be available against which the temporary
differences can be utilized.
A deferred tax liability is recognized for taxable temporary differences associated with investments in subsidiaries, associates, and
interests in joint ventures, except to the extent that the
Company is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary
differences and it is probable that the temporary difference will not reverse in the foreseeable future. In addition, a deferred tax asset
is recognized for deductible temporary differences arising from such investments to the extent that it is probable the temporary
difference will reverse in the foreseeable future and taxable profit will be available against which the temporary difference can be
utilized.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset when there is a legally enforceable right to offset current tax assets against current tax
liabilities and when the deferred income taxes assets and liabilities relate to income taxes levied by the same taxation authority on
either the same taxable entity or different taxable entities where there is an intention to settle the balances on a net basis.
2.21 Derivative Instruments
All derivative instruments are accounted for at their fair value according to the rights and obligations associated with the derivative
contracts. The resulting changes are recognized in profit or loss in the year in which they are incurred. Certain derivatives that
qualify as cash flow hedges and hedges on net investments in foreign operations are recognized under equity.
2.22 Dividend
Dividend distribution to the
Company’s shareholders is recognized as a liability when the dividends are approved.
2.23 Share Capital
Common shares and preferred shares with no repayment obligations are classified as equity. When the
Company purchases its
common shares, the acquisition costs, including direct transaction costs, are deducted from equity until the redemption or reissuance
as treasury shares. Consideration received on the subsequent sale or issuance of treasury shares is credited to equity.
2.24 Revenue Recognition
Revenue mainly comprises the fair value of the consideration received or receivable for the sale of goods in the ordinary course of
the
Company’s activities. Revenue is shown net of value-added tax, returns, sales incentives and discounts and after eliminating
intercompany transactions.
The
Company recognizes revenue when the amount of revenue can be reliably measured; when it is probable that future economic
benefits will flow to the entity; and when specific criteria have been met for each of the
Company’s activities, as described below.
The
Company measures revenue by reliably estimating the contingencies associated with revenue based on historical results, taking
into consideration the type of customer, the type of transaction and the specifics of each arrangement.
Where multiple-element arrangements exist, the fair values of each element are determined based on the current market price of
each of the elements when sold separately. When the fair values of each element are indeterminable, the fair values of deliverables
which have already been provided are calculated in such way that the fair values of elements which are yet to be provided are
subtracted from total contract value of the arrangement.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 94 / 240
(A) Sales of goods
Sales of products and merchandise are recognized upon delivery when the significant risks and rewards of ownership of goods have
transferred to the buyer. Revenue is recognized net of discounts and returns, estimated at the time of sale based on past experience.
(B) Sales of services
Revenues from rendering services are generally recognized using the percentage-of-completion method based on the percentage of
costs to date compared to the total estimated costs, contractual milestones or performance.
(C) Interest income
Interest income is recognized using the effective interest method according to the time passed. When a loan or receivable is
impaired, the
Company reduces the carrying amount to its recoverable amount and continues unwinding the discount as interest
income. Interest income on impaired loans and receivables is recognized using the original effective interest rate.
(D) Royalty income
Royalty income is recognized on an accrual basis in accordance with the substance of the relevant agreements.
(E) Dividend income
Dividend income is recognized when the right to receive payment is established.
2.25 Government Grants
Government grants are recognized at their fair values when there is reasonable assurance that the grant will be received and the
Company will comply with the conditions attached to it. Government grants relating to costs are deferred and recognized in the
income statement over the period necessary to match them with the costs that they are intended to compensate. Government grants
relating to assets are recognized in liabilities as deferred income government grants and are credited to the income statement on a
straight– line basis over the expected lives of the related assets.
2.26 Earnings per Share
Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing net profit for the period available to common shareholders by the weighted-
average number of common shares outstanding during the year. Diluted earnings per share is calculated using the weighted-average
number of common shares outstanding adjusted to include the potentially dilutive effect of common equivalent shares outstanding.
2.27 Operating Segments
Operating segments are disclosed in the manner reported to the chief operating decision-maker. The chief operating decision-maker
is responsible for making strategic decisions on resource allocation and performance assessment of the operating segments. The
Management Committee, which makes strategic decisions, is regarded as the chief operating decision-maker.
2.28 Convenience Translation into United States Dollar Amounts
The
Company operates primarily in Korean won and its official accounting records are maintained in Korean won. The US dollar
amounts provided in the financial statements represent supplementary information solely for the convenience of the reader. All
Korean won amounts are expressed in U.S. dollars at the rate of ₩1159.83 to US $1, the average exchange rate for the year ended
December 31, 2016. Such presentation is not in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and should not be
construed as a representation that the Korean won amounts shown could be readily converted, realized or settled in US dollars at
this or at any other rate.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 95 / 240
2.29 Approval of the Consolidated Financial Statements
These consolidated financial statements were approved by the Board of Directors on January 28, 2016.
3. Critical Accounting Estimates and Assumptions
The
Company makes estimates and assumptions concerning the future. The estimates and assumptions are continuously assessed,
considering historical experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under
the circumstances. The resulting accounting estimates will, by definition, seldom equal the related actual results. The estimates and
assumptions that have a significant risk of causing a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the
next financial year are addressed below.
(A) Revenue recognition
The
Company uses the percentage-of-completion method in accounting for its fixed-price contracts to deliver installation services.
Use of the percentage-of-completion method requires the
Company to estimate the services performed to date as a proportion of the
total services to be performed. Revenues and earnings are subject to significant change, effected by early steps in a long-term
projects, change in scope of a project, cost, period, and plans of the customers.
(B) Provision for warranty
The
Company recognizes provision for warranty on products sold. The Company accrues provision for warranty based on the best
estimate of amounts necessary to settle future and existing claims. The amounts are estimated based on past experience.
(C) Fair value of derivatives and other financial instruments
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined by using a variety of methods and
assumptions that are mainly based on market conditions existing at the end of each reporting period.
(D) Net defined benefit liabilities
The net defined benefit liability depends on a number of factors that are determined on an actuarial basis using a number of
assumptions. Any changes in these assumptions will impact the carrying amount of the net defined benefit liability. The
Company, in
consideration of the interest rates of high-quality corporate bonds, determines the appropriate discount rate at the end of each year.
This is the interest rate that is used to determine the present value of estimated future cash outflows expected to be required to settle
the net defined benefit liability. The principal actuarial assumptions associated with the net defined benefit liability are based on the
current market expectations.
(E) Impairment of goodwill
At the end of each reporting period, the
Company tests whether goodwill has become impaired by comparing the carrying amounts
of cash-generating units to the recoverable amounts. The recoverable amounts of cash-generating units have been determined based
on value-in-use calculations, and these calculations are based on estimates.
(F) Income taxes
Income taxes on the
Company’s taxable income from operating activities are subject to various tax laws and determinations of each
tax authority across various countries throughout the world. There is uncertainty in determining the eventual tax effects on the
taxable income from operating activities. The
Company has recognized current tax and deferred tax at the end of the fiscal year
based on the best estimation of future taxes payable as a result of operating activities. However, the resulting deferred income tax
assets and liabilities may not equal the actual future taxes payable and such difference may impact the current tax and deferred
income tax assets and liabilities upon the determination of eventual tax effects.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 96 / 240
4. Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, deposits held at call with banks, and other short-term highly liquid investments
that are readily convertible to a known amount of cash and are subject to an insignificant risk of change in value.
Cash and cash equivalents as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, consist of the following:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Cash on hand
₩ 51,770 ₩ 40,337
Bank deposits and others 32,059,672 22,596,407
Total
₩ 32,111,442 ₩ 22,636,744
5. Financial Assets Subject to Withdrawal Restrictions
Financial instruments subject to withdrawal restrictions as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, consist of the following:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Short-term financial instruments
₩ 21,541 ₩ 14,032
Other non-current assets
28,828 23,015
6. Financial Instruments by Category
(A) Categorizations of financial assets and liabilities as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(1) As at December 31, 2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Assets at fair
value through
profit or loss
Loans and
receivables
Available-for-sale
financial assets Total
Assets
Cash and cash equivalents
₩ - ₩ 32,111,442 ₩ - ₩ 32,111,442
Short-term financial instruments - 52,432,411 - 52,432,411
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets - - 3,638,460 3,638,460
Trade receivables - 24,279,211 - 24,279,211
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets - - 6,804,276 6,804,276
Other 63,208 3,396,655 - 3,459,863
Total
₩ 63,208 ₩ 112,219,719 ₩ 10,442,736 ₩ 122,725,663

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 97 / 240
(In millions of Korean won)
Liabilities at fair
value through
profit or loss
Financial
liabilities
measured at
amortized cost
Other
financial liabilities Total
Liabilities
Trade payables
₩ - ₩ 6,485,039 ₩ - ₩ 6,485,039
Short-term borrowings - 1,817,021 10,929,768 12,746,789
Other payables - 10,225,271 - 10,225,271
Current portion of long-term liabilities - 1,232,817 - 1,232,817
Debentures - 58,542 - 58,542
Long-term borrowings - 1,244,238 - 1,244,238
Long-term other payables 342,702 2,666,957 - 3,009,659
Other 74,697 11,867,772 - 11,942,469
Total
₩ 417,399 ₩ 35,597,657 ₩ 10,929,768 ₩ 46,944,824
(2) As at December 31, 2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Assets at fair
value through
profit or loss
Loans and
receivables
Available-for-sale
financial assets Total
Assets
Cash and cash equivalents
₩ - ₩ 22,636,744 ₩ - ₩ 22,636,744
Short-term financial instruments - 44,228,800 - 44,228,800
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets - - 4,627,530 4,627,530
Trade receivables - 25,168,026 - 25,168,026
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets - - 8,332,480 8,332,480
Other 63,177 3,483,257 - 3,546,434
Total
₩ 63,177 ₩ 95,516,827 ₩ 12,960,010 ₩ 108,540,014
(In millions of Korean won)
Liabilities at fair
value through
profit or loss
Financial
liabilities
measured at
amortized cost
Other
financial liabilities Total
Liabilities
Trade payables
₩ - ₩ 6,187,291 ₩ - ₩ 6,187,291
Short-term borrowings - 2,416,977 8,738,448 11,155,425
Other payables - 7,625,490 - 7,625,490
Current portion of long-term liabilities - 221,548 - 221,548
Debentures - 1,230,448 - 1,230,448
Long-term borrowings - 266,542 - 266,542
Long-term other payables 312,738 2,406,936 - 2,719,674
Other 38,829 7,908,569 - 7,947,398
Total
₩ 351,567 ₩ 28,263,801 ₩ 8,738,448 ₩ 37,353,816

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 98 / 240
(B) Net gains or net losses on each category of financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as
follows:
(1) For the year ended December 31, 2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Financial Assets
Assets at fair
value through
profit or loss
Loans and
receivables
Available-for-
sale financial
assets Total
Gain on valuation (other comprehensive income)
₩ - ₩ - ₩ 607,762 ₩ 607,762
Gain(loss) on valuation/disposal (profit or loss) (24,573) (5,648) 953,416 923,195
Reclassification from other comprehensive income to profit or
loss
- - (631,601) (631,601)
Interest income - 1,475,357 28,961 1,504,318
Foreign exchange differences (profit or loss) - 772,552 - 772,552
Foreign exchange differences (other comprehensive income) - - (156,050) (156,050)
Dividend income - - 239,899 239,899
Impairment/reversal (profit or loss) - (135,046) (341,790) (476,836)
(In millions of Korean won)
Financial Liabilities
Liabilities at fair
value through
profit or loss
Financial
liabilities
measured at
amortized cost
Other financial
liabilities Total
Gain(loss) on valuation/disposal (profit or loss)
₩ (61,221) ₩ - ₩ - ₩ (61,221)
Interest expense - 351,009 236,822 587,831
Foreign exchange differences (profit or loss) - (623,777) (212,788) (836,565)
(2) For the year ended December 31, 2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Financial Assets
Assets at fair
value through
profit or loss
Loans and
receivables
Available-for-sale
financial assets Total
Loss on valuation (other comprehensive income)
₩ - ₩ - ₩ (906,547) ₩ (906,547)
Gain/(loss) on valuation/disposal (profit or loss) 4,168 (14,980) 132,223 121,411
Reclassification from other comprehensive income to profit o
r
loss
- - 491,586 491,586
Interest income - 1,665,521 95,636 1,761,157
Foreign exchange differences (profit or loss) - 147,455 - 147,455
Foreign exchange differences
(other comprehensive income)
- - (161,511) (161,511)
Dividend income - - 183,730 183,730
Impairment/reversal (profit or loss) - (65,051) (11,323) (76,374)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 99 / 240
(In millions of Korean won)
Financial Liabilities
Liabilities at fair
value through
profit or loss
Financial
liabilities
measured at
amortized cost
Other financial
liabilities Total
Gain on valuation/disposal (profit or loss)
₩ 315,873 ₩ - ₩ - ₩ 315,873
Interest expense - 567,181 209,330 776,511
Foreign exchange differences (profit or loss) - (436,676) 33,695 (402,981)
7. Credit Quality of Financial Assets
The credit quality of financial assets that are neither past due nor impaired is assessed by reference to external credit ratings as at
December 31, 2016 and 2015, as follows:
- Superior ability to repay: Aaa~Aa (Moody’s), AAA~AA (S&P, Fitch), A1 (Credit rating agencies in Korea)
- Strong ability to repay: A (Moody’s, S&P, Fitch), A2 (Credit rating agencies in Korea)
- Acceptable ability to repay: Baa (Moody’s), BBB (S&P, Fitch), A3 (Credit rating agencies in Korea)
- Currently having the ability to repay: Ba or below (Moody’s), BB or below (S&P, Fitch), B or below (Credit rating agencies
in Korea)
- Group 1: Customers not having experienced capital erosion or default risk
- Group 2: Customers having experienced capital erosion or default risk, where all default risk is relieved as the trade payables
are guaranteed by credit insurance or collateral.
(A) Trade receivables
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Counterparties with external credit rating:
Superior ability to repay
₩ 2,743,633 ₩ 3,346,722
Strong ability to repay 3,170,573 3,337,397
Acceptable ability to repay 3,839,674 3,285,587
Currently having the ability to repay 2,744,783 3,576,405
Subtotal 12,498,663 13,546,111
Counterparties without external credit rating:
Group 1 8,465,341 9,341,473
Group 2 239,626 137,973
Subtotal 8,704,967 9,479,446
Total
₩ 21,203,630 ₩ 23,025,557

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 100 / 240
(B) Cash equivalents and short-term financial instruments
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Superior ability to repay
₩ 9,319,341 ₩ 6,283,532
Strong ability to repay
70,916,126 57,377,674
Acceptable ability to repay
4,040,000 3,112,954
Currently having the ability to repay
171,393 17,293
Other
1
45,223 33,754
Total
₩ 84,492,083 ₩ 66,825,207
1
Short-term financial instruments held at financial institutions (such as Credit unions) without an external credit rating.
8. Transfer of Financial Assets
Trade receivables of the
Company have been discounted through factoring agreements with banks in 2016 and 2015. Collateral
(trade receivables and other) provided in such factoring transactions do not meet the requirements for asset derecognition as risks
and rewards are not
substantially transferred in the event the debtor defaults. Financial liabilities recognized in relation to these
transactions are included as short-term borrowings on the statement of financial position (Note 15).
The following table presents a breakdown of discounted trade receivables as at December 31, 2016 and 2015:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Carrying amount of the discounted trade receivables
1
₩ 10,929,
768
₩ 8,738,
448
Carrying amount of the related borrowings 10,929,768 8,738,448
1
The discounted trade receivables include intercompany balances.
9. Available-for-Sale Financial Assets
Changes in available-for-sale financial assets for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Balance as at January 1
₩ 12,960
,010
₩ 15,95
4,307
Acquisitions 17,804,905 8,213,756
Disposals (18,896,371) (9,746,482)
Valuation of available-for-sale financial assets 798,698 (1,218,782)
Impairment (326,672) (11,323)
Foreign exchange differences (156,050) (161,511)
Other
1
(1,741,784) (69,955)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 10,442,
736
₩ 12,960,
010
(A) Current portion
3,638,460 4,627,530
(B) Non-current portion
6,804,276 8,332,480

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 101 / 240
1
Due to increase in shareholding ratio for the year ended December 31, 2016, Samsung SDI and Cheil Worldwide were reclassified from
available-for-sale financial assets to investments in associates.
Changes in valuation gains (losses) recognized in equity (other comprehensive income) on available-for-sale financial assets for the
years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Balance as at January 1
₩ 2,008,223 ₩ 2,582,037
Fair value gains 798,698 (1,218,782)
Net gains transferred from equity (837,088) 644,968
Balance as at December 31 1,969,833 2,008,223
Deferred income tax and non-controlling interests (579,209) (506,096)
Total
₩ 1,390,624 ₩ 1,502,127
(A) Short-term available-for-sale financial assets
Details of short-term available-for-sale financial assets as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Beneficiary certificates
1
₩ 3,638,460 ₩ 1,606,320
Government bonds - 271,373
Bank debentures - 2,749,837
Total
₩ 3,638,460 ₩ 4,627,530
1
Details of beneficiary certificates as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Time deposits and others
₩ 3,638,460 ₩ 1,606,320
Total
₩ 3,638,460 ₩ 1,606,320
(B) Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
Details of long-term available-for-sale financial assets as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Equity securities - Listed
₩ 2,362,235 ₩ 4,674,753
Equity securities - Non-listed 4,337,328 3,498,655
Debt securities
1
104,713 159,072
Total
₩ 6,804,276 ₩ 8,332,480
1
The maximum exposure to credit risk of available-for-sale debt securities is the carrying value at the reporting date.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 102 / 240
(1) Equity securities - Listed
Details of listed equity securities as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won, number of shares and percentage)
2016 2015
Number of
Shares Owned
Percentage of
Ownership (%)
Acquisition
Cost
Book Value
(Market Value)
Book Value
(Market Value)
Samsung SDI
1
- -
₩ - ₩ - ₩ 1,534,745
SamsungHeavy Industries 65,930,982 16.9 473,727 609,862 441,331
Hotel Shilla 2,004,717 5.1 13,957 96,527 154,965
Cheil Worldwide
1
- - - - 300,124
iMarket Korea 647,320 1.8 324 6,732 16,377
SFA 1,822,000 10.2 38,262 117,519 90,098
Wonik Holdings
(formerly Wonik IPS)
2
3,518,342 4.6 30,821 23,714
81,949
Wonik IPS
2
3,701,872 9.0 32,428 96,989
ASML
3
6,297,787 1.5 363,012 851,395 1,331,450
Rambus
3
- - - - 65,039
Seagate Technology
3
- - - - 538,766
Sharp
3
- - - - 43,502
Wacom
8,398,400 5.2 62,013 26,647 39,330
BYD
4
52,264,808 1.9 528,665 449,872 -
Other
79,259 82,978 37,077
Total
₩ 1,622,468 ₩ 2,362,235 ₩ 4,674,753
1
Due to increase in shareholding ratio for the year ended December 31, 2016, Samsung SDI and Cheil Worldwide were reclassified from
available-for-sale financial assets to investments in associates.
2
For the year ended December 31, 2016, Wonik IPS split off from Wonik Holdings (formerly Wonik IPS).
3
For the same period above, the Company disposed all of its Rambus, Seagate Technology and Sharp shares and a portion of its
ASML shares.
4
For the same period above, the Company acquired 52,264,808 shares of BYD.
Acquisition cost includes impairment loss on available-for-sale financial assets recognized due to the decline in realizable value
below acquisition cost. The difference between the acquisition cost, net of impairment loss and the current fair value is recorded
within other components of equity, net of tax effects (unrealized gains or losses on available-for-sale financial assets).

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 103 / 240
(2) Equity securities - Non-listed
Details of non-listed equity securities as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won, number of shares and percentage)
2016 2015
Number of
Shares Owned
Percentage of
Ownership (%)
Acquisition
Cost
Book Value
2
Book Value
Kihyup Technology 1,000,000 17.2
₩ 5,000 ₩ 5,000 ₩ 5,000
Pusan Newport
1
- - - - 5,677
Samsung Venture Investment 980,000 16.3 4,900 7,515 7,207
Maltani
(formerly Taewon Lightning)
45,000 15.0 16,544 16,270 15,860
Corning Inc. 2,300 7.4 2,434,320 3,440,487 2,745,574
CSOT
1
- - - - 278,557
CSOSDT - 9.8 357,315 357,315 -
Nanosys 15,950,462 12.8 27,323 28,985 28,985
Other 542,205 481,756 411,795
Total
₩ 3,387,607 ₩ 4,337,328 ₩ 3,498,655
1
For the same period above, the Company disposed all of its Pusan Newport and CSOT shares.
2
Nonmarketable shares are measured at cost as the variability of estimated cash flow is significant and the probability of various estimates,
including discount rate, cannot be reasonably assessed.
Acquisition cost includes impairment loss on available-for-sale financial assets recognized due to the decline in realizable value
below acquisition cost. The difference between the acquisition cost, net of impairment loss and the current fair value is recorded
within other components of equity, net of tax effects (unrealized gains or losses on available-for-sale financial assets).
(3) Debt securities
Details of debt securities as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Corporate bonds
₩ 104,713 ₩ 159,072
Total
₩ 104,713 ₩ 159,072

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 104 / 240
10. Trade and Other Receivables
(A) Trade and other receivables as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
2016 2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Trade Non-Trade Trade Non-Trade
Receivables
₩ 24,704,524 ₩ 3,582,229 ₩ 25,520,385 ₩ 3,585,895
Less: Provisions for impairment (420,889) (25,503) (326,861) (49,291)
Receivables, net 24,283,635 3,556,726 25,193,524 3,536,604
Less: Non-current portion (4,424) (35,529) (25,498) (183,941)
Current portion
₩ 24,279,211 ₩ 3,521,197 ₩ 25,168,026 ₩ 3,352,663
The
Company transferred receivable balances to financial institutions in exchange for cash during the years ended December 31,
2016 and 2015. The outstanding balances of transferred receivables, amounting to ₩10,929,768 million and ₩8,738,448 million,
have been accounted for as collateralized borrowings as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively (Note 15).
(B) Movements in the provisions for impairment of receivables for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
2016 2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Trade Non-Trade Trade Non-Trade
Balance as at January 1
₩ 326,861 ₩ 49,291 ₩ 277,788 ₩ 9,894
Provisions for impaired receivables / (reversals of
unused amounts) 117,207 (19,209) 58,513 41,195
Receivables written off during the year as
uncollectible (20,421) (3,978) (2,963) (3,235)
Other (2,758) (601) (6,477) 1,437
Balance as at December 31
₩ 420,889 ₩ 25,503 ₩ 326,861 ₩ 49,291
(C) The aging analysis of trade and other receivables as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, is as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Receivables not past due
₩ 24,598,074 ₩ 26,052,236
Past due but not impaired
1
:
Less than 31 days overdue 2,281,693 1,986,756
Impaired:
31 days to 90 days overdue 881,736 405,310
Over 90 days overdue 525,250 661,978
Total
₩ 28,286,753 ₩ 29,106,280
1
The Company does not consider receivables that are overdue for less than or equal to 31 days as impaired.
(D) The maximum exposure to current credit risk is equivalent to the carrying amount of receivables as at December 31, 2016. The
Company has in place insurance contracts covering the Company’s major receivables, and has accrued provisions against
receivables in accordance with the overdue payment history for those receivables not covered by insurance contracts.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 105 / 240
11. Inventories
Inventories as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Gross Amount
Valuation
Allowance
1 Book Value Gross Amount
Valuation
Allowance Book Value
Finished goods
₩ 7,982,850 ₩ (2,077,511) ₩ 5,905,339 ₩ 5,956,413 ₩ (186,953) ₩ 5,769,460
Work in process 5,334,607 (317,223) 5,017,384 6,142,964 (363,661) 5,779,303
Raw materials and supplies 7,526,608 (1,032,442) 6,494,166 6,082,185 (222,923) 5,859,262
Materials in transit 936,614 - 936,614 1,403,769 - 1,403,769
Total
₩21,780,679 ₩ (3,427,176) ₩18,353,503 ₩19,585,331 ₩ (773,537) ₩18,811,794
1
Inventories for which the Company has suspended sales or production, are evaluated based on net realizable value. In addition, if the net
realizable value is less than the book value, then the difference is recorded as a valuation allowance.
The cost of inventories recognized as expense and included in ‘cost of sales’ for the year ended December 31, 2016, amounts to
₩119,611,006 million (2015: ₩122,679,069 million). The amount includes inventory valuation losses.
12. Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
(A) Changes in investments in associates and joint ventures for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Balance as at January 1
₩ 5,276,348 ₩ 5,232,461
Acquisition 84,306 137,917
Disposal
1
(1,343,936) (19,323)
Share of profit 19,501 1,101,932
Other
2
1,801,665 (1,176,639)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 5,837,884 ₩ 5,276,348
1
The Company sold its entire stake in Samsung Card for the year ended December 31, 2016.
2
Other consists of dividends, impairment and reclassification as assets held-for-sale. Due to increase in shareholding ratio for the year ended
December 31, 2016, Samsung SDI and Cheil Worldwide were reclassified from available-for-sale financial assets to investments in associates.
For the year ended December 31, 2015, Impairment losses on Samsung Card resulting from the decline in recoverable value below the book
value amounted to ₩1,126,958 million.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 106 / 240
(B) Major investments in associates and joint ventures as at December 31, 2016, are as follows:
(1) Investments in associates
Investee Nature of Relationship with Associate
Percentage of
Ownership
1
(%)
Principal Business
Location
Samsung Electro-Mechanics
Manufacture and supply electronic components including passive
components, circuit boards, and modules
23.7 Korea
Samsung SDS
Provide IT services including computer programming, system
integration and management
22.6 Korea
Samsung Biologics New business investment 31.5 Korea
Samsung SDI
2
Manufacture and supply electronics including secondary cell
batteries
19.6 Korea
Cheil Worldwide Advertising agency 25.2 Korea
1
Ownership represents the Company’s ownership of common stock in each entity.
2
The Company’s ownership of common stock outstanding is 20.3%.
(2) Investments in joint ventures
Investee Nature of Relationship with Joint Venture
Percentage of
Ownership
1
(%)
Principal Business
Location
Samsung Corning
Advanced Glass
Manufacture and supply industrial glass devices 50.0 Korea
1
Ownership represents the Company’s ownership of common stock in each entity.
(C) Details of investments in associates and joint ventures as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(1) Investments in associates
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
Investee Acquisition cost
Net asset value of
equity shares
1
Book value
Samsung Electro-Mechanics
₩ 359,237 ₩ 993,031 ₩ 997,022
Samsung SDS 147,963 1,161,197 1,185,703
Samsung Biologics 443,193 1,285,706 1,289,351
Samsung SDI 1,242,605 2,131,718 1,232,986
Cheil Worldwide 506,162 192,594 517,885
Other 642,536 182,279 390,438
Total
₩ 3,341,696 ₩ 5,946,525 ₩ 5,613,385
1
The Company’s portion of net asset value of associates is based on the Company’s ownership percentage.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 107 / 240
(In millions of Korean won)
2015
Investee Acquisition cost
Net asset value of
equity shares
1
Book value
Samsung Card
₩ 1,538,540 ₩ 2,504,778 ₩ 1,338,679
Samsung Electro-Mechanics 359,237 987,695 994,489
Samsung SDS 147,963 1,036,142 1,060,396
Samsung Biologics 545,665 1,300,185 1,310,202
Samsung SDI - - -
Cheil Worldwide - - -
Other 583,756 191,272 323,513
Total
₩ 3,175,161 ₩ 6,020,072 ₩ 5,027,279
1
The Company’s portion of net asset value of associates is based on the Company’s ownership percentage.
(2) Investments in joint ventures
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
Investee Acquisition cost
Net asset value of
equity shares
1
Book value
Samsung Corning Advanced Glass
₩ 215,000 ₩ 169,521 ₩ 169,485
Other 259,977 59,342 55,014
Total
₩ 474,977 ₩ 228,863 ₩ 224,499
1
The Company’s portion of net asset value of associates is based on the Company’s ownership percentage.
(In millions of Korean won)
2015
Investee Acquisition cost
Net asset value of
equity shares
1
Book value
Samsung Corning Advanced Glass
₩ 215,000 ₩ 188,431 ₩ 188,371
Other 259,977 104,440 60,698
Total
₩ 474,977 ₩ 292,871 ₩ 249,069
1
The Company’s portion of net asset value of joint ventures is based on the Company’s ownership percentage.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 108 / 240
(D) Details of the valuations of investments in associates and joint ventures under the equity method for the years ended December
31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won) 2016
Investee
Balance as at
January 1
Gain/loss on
valuation
Other
comprehensive
income/loss Other
1
Balance as at
December 31
Samsung Card
₩ 1,338,679 ₩ - ₩ - ₩ (1,338,679) ₩ -
Samsung Electro-Mechanics 994,489 1,738 9,641 (8,846) 997,022
Samsung SDS
1,060,396 105,424 28,620 (8,737) 1,185,703
Samsung Biologics 1,310,202 (66,212) (1,189) 46,550 1,289,351
Samsung SDI - (8,017) (1,602) 1,242,605 1,232,986
Cheil Worldwide - 4,375 7,348 506,162 517,885
Samsung Corning Advanced Glass
188,371 (18,742) (144) - 169,485
Other
384,211 935 (6,522) 66,828 445,452
Total
₩ 5,276,348 ₩ 19,501 ₩ 36,152 ₩ 505,883 ₩5,837,884
1
Other consists of acquisitions, disposals, dividends, impairment, reclassification and others
(In millions of Korean won)
2015
Investee
Balance as at
January 1
Gain/loss on
valuation
Other
comprehensive
income/loss Other
1
Balance as at
December 31
Samsung Card
₩ 2,354,026 ₩ 124,999 ₩ 29,831 ₩(1,170,177) ₩ 1,338,679
Samsung Electro-Mechanics
1,040,404 (2,877) (28,954) (14,084) 994,489
Samsung SDS
951,776 100,156 17,196 (8,732) 1,060,396
Samsung Biologics
293,975 886,439 (3,812) 133,600 1,310,202
Samsung Corning Advanced Glass
195,930 (7,785) 226 - 188,371
Other
396,350 1,000 (1,630) (11,509) 384,211
Total
₩ 5,232,461 ₩ 1,101,932 ₩ 12,857 ₩(1,070,902) ₩ 5,276,348
1
Other consists of acquisitions, disposals, dividends, impairment, reclassification and others

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 109 / 240
(E) Summary of the condensed financial information of major associates and joint ventures.
(1) A summary of condensed financial information of major associates, details of adjustments from the book value of investments
in major associates, and dividends received from major associates as at and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015,
is as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
Investee
Samsung Electro-
Mechanics Samsung SDS
Samsung
Biologics Samsung SDI
Cheil
Worldwide
1. Condensed financial information
Condensed statement of financial position:
Current assets
₩2,812,409 ₩4,548,448 ₩1,461,425 ₩3,958,266 ₩1,794,812
Non-current assets
4,850,220 2,293,556 6,071,580 10,942,046 356,619
Current liabilities
2,043,155 1,347,385 2,476,545 2,212,796 1,244,899
Non-current liabilities
1,281,889 203,495 974,089 1,723,405 130,248
Non-controlling interests
97,467 150,429 - 241,980 13,277
Condensed statement of comprehensive income:
Revenue 6,033,040 8,180,187 294,622 5,200,823 3,232,594
Profit from continuing operations
1
14,707 463,858 (176,832) (878,504) 88,263
Profit after tax from discontinued
operations
1
- - - 1,089,615 -
Other comprehensive income(loss)
1
41,212 35,664 108 (222,175) (13,711)
Total comprehensive income(loss)
1
55,919 499,522 (176,724) (11,064) 74,552
2. Details of adjustments from the book value of investments in associates
Net assets (a)
₩4,240,118 ₩5,140,695 ₩4,082,371 ₩10,722,131 ₩763,007
Ownership percentage (b)
2
23.4% 22.6% 31.5% 19.9% 25.2%
Net assets of equity shares (a x b) 993,031 1,161,197 1,285,706 2,131,718 192,594
Goodwill 7,081 26,801 3,645 - 325,291
Intercompany transactions and others
3
(3,090) (2,295) - (898,732) -
Book value of associates 997,022 1,185,703 1,289,351 1,232,986 517,885
3. Dividends from associates
Dividends
₩ 8,847 ₩ 8,736
- - -
1
Income (loss) attributable to owners of the parent.
2
Ownership percentage includes common and preferred stock.
3
Consists of unrealized gains and losses and other differences.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 110 / 240
(In millions of Korean won) 2015
Investee
Samsung Card
1
Samsung Electro-
Mechanics Samsung SDS Samsung Biologics
1. Condensed financial information
Condensed statement of financial position:
Current assets
₩19,070,997
₩2,729,971 ₩3,845,289 ₩ 192,854
Non-current assets
4,539,482 2,486,390 5,767,640
Current liabilities
12,382,672
1,768,254 1,389,915 1,911,669
Non-current liabilities
1,185,816 164,913 1,273,991
Non-controlling interests
- 93,268 188,091 -
Condensed statement of comprehensive income:
Revenue
₩3,302,194 ₩6,176,258 ₩7,853,459 ₩ 91,278
Profit from continuing operations
2
333,724 312,773 439,020 1,920,179
Profit after tax from discontinued operations
2
- (301,585) - -
Other comprehensive loss
2
79,656 (138,445) 70,670 (8,315)
Total comprehensive income
2
413,380 (127,257) 509,690 1,911,864
2. Details of adjustments from the book value of investments in associates
Net assets (a)
₩6,688,325 ₩4,222,115 ₩4,588,760 ₩2,774,834
Ownership percentage (b)
3
37.5% 23.4% 22.6% 46.8%
Net assets of equity shares (a x b) 2,504,778 987,695 1,036,142 1,300,185
Goodwill 17,181 7,081 26,801 5,531
Intercompany transactions and others
4
(56,322) (287) (2,547) 4,486
Impairment (1,126,958) - - -
Book value of associates 1,338,679 994,489 1,060,396 1,310,202
3. Dividends from associates
Dividends
₩ 43,393 ₩ 13,270 ₩ 8,736
-
1
Samsung Card does not present current and non-current assets and liabilities as separate classifications in its statement of financial position.
2
Income (loss) attributable to owners of the parent.
3
Ownership percentage includes common and preferred stock.
4
Consists of unrealized gains and losses and other differences.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 111 / 240
(2) A summary of condensed financial information of major joint ventures, details of adjustments from the book value of
investments in major joint ventures, and dividends from major joint ventures as at and for the years ended December 31, 2016
and 2015, is as follows:
(In millions of Korean won) Samsung
Corning Advanced Glass
Investee 2016 2015
1. Condensed financial information
Condensed statements of financial position
Current assets
₩ 170,614 ₩ 226,720
- Cash and cash equivalent 16,021 13,383
Non-current assets 209,881 183,313
Current liabilities 41,076 32,158
- Current financial liabilities
1
14,779 14,111
Non-current liabilities 377 1,013
Condensed statements of comprehensive income
Revenue 257,041 264,660
Depreciation and amortization 2,202 2,025
Interest income 1,433 1,182
Income tax expense (8,841) (2,100)
Loss from continuing operations
2
(37,531) (15,619)
Other comprehensive income (loss)
2
- 452
Total comprehensive loss
2
(37,531) (15,167)
1
Trade payables, other payables, and provisions are excluded.
2
Profit (loss) attributable to owners of the parent.
(In millions of Korean won) Samsung
Corning Advanced Glass
Investee 2016 2015
2. Details of adjustments from the book value of investments in joint ventures
Net assets (a)
₩ 339,042 ₩ 376,862
Ownership percentage (b)
50.0% 50.0%
Net assets of equity shares (a x b)
169,521 188,431
Intercompany transactions and others
1
(36) (60)
Book value of joint ventures
169,485 188,371
3. Dividends from joint ventures
Dividends
₩ -
₩ -
1
Consists of unrealized gains and losses and other differences.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 112 / 240
(3) Profit (loss) amounts attributable to owners of the parent from associates and joint ventures which are not individually material
for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follow:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Investee
Associates Joint ventures Associates Joint ventures
Profit(Loss) from continuing operations
1
₩ 4,993 ₩ (3,567) ₩ 173 ₩ 1,834
Other comprehensive income (loss)
1
(2,042) (4,505) 620 (233)
Total comprehensive income (loss)
1
₩ 2,951 ₩ (8,072) ₩ 793 ₩ 1,601
1
Income (loss) attributable to owners of the parent.
(F) Fair value of marketable investments in associates as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, is as follows:
(In millions of Korean won and
number of shares)
2016
2015
Number of shares held Market value Market value
Samsung Electro-Mechanics 17,693,084 898,809 1,112,895
Samsung SDS 17,472,110 2,437,359 4,437,916
Samsung Biologics 20,836,832 3,146,362
1
Samsung SDI 13,462,673 1,467,431
2
Cheil Worldwide 29,038,075 457,350
2
1
The Company does not disclose published price quotations of Samsung biologics for 2015 as Samsung Biologics listed its shares in 2016.
2
Due to increase in shareholding ratio for the year ended December 31, 2016, Samsung SDI and Cheil Worldwide were reclassified from
available-for-sale financial assets to investments in associates.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 113 / 240
13. Property, Plant and Equipment
(A) Changes in property, plant and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Land
Buildings and
Structures
Machinery
and E
q
ui
p
ment
Construction In
Pro
g
ress Other Total
Balance as at January 1
₩
7,848,432
₩22,453,296 ₩43,077,879 ₩10,970,052
₩2,127,451
₩86,477,110
Acquisition cost
7,848,432 32,850,110 147,315,096 10,970,052 6,303,834 205,287,524
Accumulated depreciation and
impairment
- (10,396,814) (104,237,217) - (4,176,383) (118,810,414)
Acquisitions and capital
expenditures
1
37,735 3,482,228 12,769,230 8,230,900 974,275 25,494,368
Business combinations
- - 4,492 240 2,271 7,003
Depreciation
- (1,631,089) (16,814,751) - (866,680) (19,312,520)
Disposals/Scrap
(28,331) (26,384) (80,552) (5) (66,684) (201,956)
Impairment
- (2,805) (370,574) - (1,731) (375,110)
Reclassification of assets held-
for-sale
- (11,922) (20,131) (7,660) (45,156) (84,869)
Other
2
11,843 112,502 (263,538) (419,541) 27,749 (530,985)
Balance as at December 31
₩
7,869,679
₩24,375,826 ₩38,302,055 ₩18,773,986
₩2,151,495
₩91,473,041
Acquisition cost
7,869,679 36,474,462 155,285,378 18,773,986 6,769,149 225,172,654
Accumulated depreciation and
impairment
- (12,098,636) (116,983,323) - (4,617,654) (133,699,613)
1
The capitalized borrowing costs are ₩17,644 million and the interest rate used to calculate the borrowing costs eligible for capitalization is
0.95%.
2
Other includes effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and effects of the offset related to government assistance.
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Land
Buildings and
Structures
Machinery
and Equipment
Construction In
Progress Other Total
Balance as at January 1
₩ 7,710,352
₩17,598,547 ₩ 37,751,890 ₩15,832,307 ₩ 1,979,854
₩ 80,872,950
Acquisition cost 7,710,352 26,474,937 127,603,897 15,832,307 5,664,513 183,286,006
Accumulated depreciation and
impairment - (8,876,390) (89,852,007) - (3,684,659) (102,413,056)
Acquisitions and capital
expenditures
1
318,540 6,389,558 22,233,244 (4,471,883) 1,048,603 25,518,062
Business combinations 246 1,757 3,498 47 29,228 34,776
Depreciation - (1,557,234) (17,191,280) - (914,027) (19,662,541)
Disposals/Scrap (78,449) (60,697) (208,505) (39) (226,004) (573,694)
Impairment - - (78,240) - (454) (78,694)
Other
2
(102,257) 81,365 567,272 (390,380) 210,251 366,251
Balance as at December 31
₩ 7,848,432
₩22,453,296 ₩ 43,077,879 ₩10,970,052 ₩ 2,127,451
₩ 86,477,110
Acquisition cost 7,848,432 32,850,110 147,315,096 10,970,052 6,303,834 205,287,524
Accumulated depreciation and
impairment - (10,396,814) (104,237,217) - (4,176,383) (118,810,414)
1
The capitalized borrowing costs are ₩11,061 million and the interest rate used to calculate the borrowing costs eligible for capitalization is
1.12%.
2
Other includes effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and effects of the offset related to government assistance.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 114 / 240
(B) Details of depreciation of property, plant and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Cost of sales
₩ 17,348,302 ₩ 17,877,592
Selling and administrative expenses and others
1,964,218 1,784,949
Total
₩ 19,312,520 ₩ 19,662,541
14. Intangible Assets
(A) Changes in intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
Intellectual
property rights
Development
cost Membership Goodwill Other Total
Balance as at January 1
₩ 1,342,104 ₩ 1,697,545 ₩ 184,915 ₩ 910,539 ₩ 1,261,208 ₩ 5,396,311
Internally generated (development
costs)
- 680,962 - - - 680,962
External acquisitions
275,288 - 802 4,922 85,694 366,706
Business combinations
70,199 - - 503,045 63,674 636,918
Amortization
(234,666) (748,573) - - (417,206) (1,400,445)
Sales/disposals
(49,700) - (1,005) - (2,257) (52,962)
Impairment
- (449,297) - (15,143) (9,054) (473,494)
Reclassification of assets held-
for-sale
(41,032) - (89) (41,650) (41,800) (124,571)
Other
1
(12,429) (19) (224) (18,133) 345,400 314,595
Balance as at December 31
₩ 1,349,764 ₩ 1,180,618 ₩ 184,399 ₩ 1,343,580 ₩ 1,285,659 ₩ 5,344,020
1
Other includes effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates, and others.
(In millions of Korean won)
2015
Intellectual
property rights
Development
cost Membership Goodwill Other Total
Balance as at January 1
₩ 1,340,481 ₩ 1,239,933 ₩ 182,415 ₩ 739,576 ₩ 1,283,068 ₩ 4,785,473
Internally generated (development
costs) - 1,143,059 - - - 1,143,059
External acquisitions
234,740 - 3,272 - 67,358 305,370
Business combinations
20,691 - - 316,724 36,809 374,224
Amortization
(232,103) (607,526) - - (428,687) (1,268,316)
Sales/disposals
(22,944) - (292) - (409) (23,645)
Impairment
(21,957) (76,703) - (178,696) (7,275) (284,631)
Other
1
23,196 (1,218) (480) 32,935 310,344 364,777
Balance as at December 31
₩ 1,342,104 ₩ 1,697,545 ₩ 184,915 ₩ 910,539 ₩ 1,261,208 ₩ 5,396,311
1
Other includes effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates, and others.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 115 / 240
(B) Goodwill
Goodwill is allocated to cash-generating units at the end of the reporting period. Details of goodwill as at December 31, 2016 and
2015, is as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
CE
₩ 532,669 ₩ 449,127
IM 644,468 290,338
Semiconductor 82,400 86,754
DP 80,299 80,299
Other 3,744 4,021
Total
₩ 1,343,580 ₩ 910,539
Goodwill impairment reviews are undertaken annually, and the recoverable amounts of cash-generating units have been determined
based on value-in-use calculations. These calculations use pre-tax cash flow projections based on financial budgets approved by
management covering a five-year period. Cash flows beyond the five-year period are extrapolated using the estimated growth rates
stated below. The growth rate does not exceed the long-term average growth rate for the industry. In addition, a constant growth
rate assumption is used for perpetual cash flow calculation.
(1) For the year ended December 31, 2016, The
Company recognized an impairment loss of ₩15,143 million relating to the
goodwill recorded by Samsung Electronics America (SEA) for which an associated inflow of economic benefits is no longer
expected.
(2) For the year ended December 31, 2015, pursuant to the results of the goodwill impairment reviews performed, the
Company
recognized an impairment of
₩79,277 million on goodwill recognized in LED division. The key assumptions used in
calculating the value-in-use were as follows:
(In percentage, %)
Key assumptions
Sales growth rate
1.1
Perpetual growth rate
1.0
Pre-tax discount rate
1
9.5
1
Pre-tax discount rate applied to the cash flow projections.
The sales growth rate was determined on the basis of past performance and expectations of market fluctuations. The discount rate
reflects specific risks related to the division.
(C) Details of amortization of intangible assets by line item for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Cost of sales
₩ 959,545
₩ 801,993
Selling and administrative expenses and others
440,900 466,323
Total
₩ 1,400,445
₩ 1,268,316

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 116 / 240
15. Loans
(A) Details of the carrying amounts of loans as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Financial
Institutions
Annual Interest Rates (%)
as at December 31, 2016 2016 2015
Short-term borrowings
Collateralized borrowings
1
Woori Bank and others
0.1 ~ 12.1
₩10,929,768 ₩ 8,738,448
Non-collateralized borrowings Citibank and others
0.5 ~ 18.9
1,817,021 2,416,977
Total
₩12,746,789 ₩11,155,425
Current portion of long-term
borrowings
Bank borrowings
US Bank and others
3.5 ~ 6.0
₩ 68
4
₩ 45
4
Financial lease liabilities
2
CSSD and others
1.1 ~ 15.7
18,599 15,652
Total
₩ 19,283 ₩ 16,106
Long-term borrowings
Bank borrowings
Citibank and others
LIBOR+0.4 ~ 19.8
₩ 1,179,111 ₩ 193,598
Financial lease liabilities
2
CSSD and others
1.1 ~ 15.7
65,127 72,944
Total
₩ 1,244,238 ₩ 266,542
1
Collateralized borrowings are secured by trade receivables (Note 8 and 10).
2
Leased property, plant and equipment were pledged as collateral (Note 19).
(B) Maturities of long-term borrowings outstanding as at December 31, 2016, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Long-term borrowings
For the Years Ending December 31
2017
₩ 19,283
2018
293,805
2019
903,193
2020
8,144
2021 and thereafter
39,096
Total
₩ 1,263,521

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 117 / 240
16. Debentures
Details of the carrying amount of debentures as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Korean won denominated debentures (A)
₩ -
₩ -
Foreign currency denominated debentures (B)
58,542 1,230,448
Total
₩ 58,542 ₩ 1,230,448
(A) Details of Korean won denominated debentures as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Issue Date Due Date
Annual Interest Rates (%)
as at December 31, 2016 2016 2015
Unsecured debentures 2011.11.17 2016.11.17 4.2
₩ - ₩ 200,000
Less: Current portion - (200,000)
Less: Discounts
- -
Total
₩ - ₩ -
The debenture has been issued by Samsung Display and will be repaid upon maturity.
(B) Details of foreign currency denominated debentures as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Issue Date
Due Date
Annual Interest Rates (%)
as at December 31, 2016 2016 2015
US dollar denominated straight
bonds
1
1997.10.2 2027.10.1 7.7
₩ 66,468
(US$55 million)
₩ 70,320
(US$60 million)
US dollar denominated
unsecured bonds
2
2012.4.10 2017.4.10 1.8
1,208,500
(US$1,000 million)
1,172,000 (US$1,000
million)
Less: Current portion (1,214,543) (5,860)
Less: Discounts (1,883) (6,012)
Total
₩ 58,542 ₩ 1,230,448
1
US dollar straight bonds are repaid annually for twenty years after a ten-year grace period from the date of issuance. Interest is paid semi-
annually.
2
Samsung Electronics America issued dollar denominated unsecured bonds. Repayment of these debentures is due on the date of maturity and
interest is paid semi-annually.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 118 / 240
(C) Maturities of debentures outstanding as at December 31, 2016, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
For the Years Ending December 31 Debentures
2017
₩ 1,214,543
2018
6,043
2019
6,043
2020
6,043
2021 and thereafter
42,296
Total
₩ 1,274,968
17. Net Defined Benefit Liabilities (Assets)
(A) Details of net defined benefit liabilities(assets) recognized on the statements of financial position as at December 31, 2016 and
2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Present value of funded defined benefit obligations
₩ 7,167,929
₩ 7,693,919
Present value of unfunded defined benefit obligations
110,885
138,860
Subtotal
7,278,814
7,832,779
Fair value of plan assets
(7,662,249)
(7,473,959)
Total
₩ (383,435)
₩ 358,820
(B) The amounts recognized in the statements of profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 relating to defined
benefit plans are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Current service cost
₩ 1,077,511
₩ 1,147,127
Net interest cost
11,221
8,595
Other
2,319
3,324
Total
₩ 1,091,051
₩ 1,159,046
(C) The amounts recognized as expense of defined contribution plans for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are
₩105,971 million and ₩96,611 million, respectively.
(D) The pension expenses related to defined benefit plans recognized on the statements of profit or loss for the years ended
December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Cost of sales
₩ 469,172
₩ 500,660
Selling and administrative expenses and others
621,879
658,386
Total
₩ 1,091,051
₩ 1,159,046

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 119 / 240
(E) Changes in the defined benefit obligations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Balance as at January 1
₩ 7,832,779
₩ 7,542,247
Current service cost
1,077,511
1,147,127
Interest cost
298,003
322,296
Remeasurement:
Actuarial gains or losses arising from changes in
demographic assumptions (41,608) 2,428
Actuarial gains or losses arising from changes in
financial assumptions (1,062,656) (315,630)
Other
(295,125)
(165,799)
Benefits paid
(474,112)
(700,205)
Foreign exchange differences
1,846
2,568
Other
1
(57,824)
(2,253)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 7,278,814
₩ 7,832,779
1
Other includes effects of reclassification as assets held-for-sale.
(F) Changes in the fair value of plan assets for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Balance as at January 1
₩ 7,473,959
₩ 7,340,905
Expected return on plan assets
286,782
313,701
Remeasurement factor of plan assets
(123,794)
(137,262)
Contributions by employer
498,504
292,951
Benefits paid
(422,249)
(320,106)
Other
1
(50,953)
(16,230)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 7,662,249
₩ 7,473,959
1
Other includes effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and reclassification as assets held-for-sale.
Expected contributions to post-employment benefit plans for the year ending December 31, 2017, are ₩1,196,040 million.
(G) Plan assets as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, consist of as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Debt instruments
₩ 7,635,150
₩ 7,445,277
Other
27,099
28,682
Total
₩ 7,662,249
₩ 7,473,959
Plan assets are mostly invested in instruments which have a quoted price in active markets.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 120 / 240
(H) The principal actuarial assumptions as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
2016 2015
Discount rate 0.4 ~ 8.2 % 0.7 ~ 8.2 %
Salary growth rate (including the effects of inflation) 1.5 ~ 10.0 % 1.5 ~ 10.0 %
(I) The sensitivity of the defined benefit obligations as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, to changes in the weighted principal
assumptions is as follows:
2016 2015
Discount rate
1% increases 90% 89%
1% decreases 111% 113%
Salary growth rate
1% increases 111% 112%
1% decreases 90% 89%
(J) The weighted average duration of the defined benefit obligations is 10.48 years.
18. Provisions
Changes in provisions for the year ended December 31, 2016, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Warranty (A)
Royalty
expenses (B)
Long-term
incentives (C) Other(D, E) Total
Balance as at January 1
₩ 1,664,526 ₩ 4,443,749 ₩ 753,553 ₩ 81,153 ₩ 6,942,981
Charged (credited) to the
statement of income
2,176,443 (1,047,548) 193,409 1,532,609 2,854,913
Payment
(2,087,361) (1,898,987) (220,402) (231,577) (4,438,327)
Other
1
(5,751) 90,823 (10,308) (478,788) (404,024)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 1,747,857 ₩ 1,588,037 ₩ 716,252 ₩ 903,397 ₩ 4,955,543
1
Other includes effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and reclassification as assets held-for sale.
(A) The
Company accrues warranty reserves for estimated costs of future service, repairs and recalls, based on historical experience
and terms of warranty programs.
(B) The
Company recognizes provisions for the estimated royalty expenses that are under negotiation with counterparties. The
timing and the amount of payment depend on the settlement of the negotiations.
(C) The
Company has a long-term incentive plan for its executives based on a three-year management performance criteria and
recognizes a provision for the estimated incentive cost for the accrued period.
(D) The
Company records provisions for the estimated expenses occurring from discontinuing production and sale of products.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 121 / 240
(E) The
Company makes provisions for the estimated expense for emissions in excess of the permits held by the Company for the
applicable years:
(1) Allocated amount of emission permits and estimated volume of emission as at December 31, 2016 are as follows:
(In 10 thousand tons)
2016
Allocated emission permits
1,080
Estimated volume of emission
1,148
(2) Changes in the emission permits for the year ended December 31, 2016 are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
Balance as at January 1
₩ 7,260
Addition
12,907
Used (5,100)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 15,067
(3) Changes in the provisions for emissions liabilities during the year ended December 31, 2015 are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
Balance as at January 1
₩ 7,947
Charged to the statement of income
9,845
Payment
(5,100)
Balance as at December 31
₩ 12,692
19. Commitments and Contingencies
(A) Guarantees
Details of guarantees of debt provided by the Company as at December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Guarantees of debt for housing rental
1
₩ 56,752 ₩ 64,753
1
Represents the maximum amount of debt guarantee which was provided for employees who took debt from financial institutions in order to
finance employee housing rental.
In addition to the guarantees described above, the Company provides guarantees for borrowings executed by Medicapital from Dime
Investment and two other companies in the amount of ₩ 2,264 million. In consideration of possibility to bear the liability, the
Company recognizes financial guarantee liabilities
(B) Leases
The
Company leases certain property, plant and equipment under various finance lease arrangements and recognizes the related
amounts as lease assets or liabilities. Assets with a net book value of ₩87,106 million (2015: ₩96,216 million) are treated as
finance lease agreements and are included in property, plant and equipment. Depreciation expense for the finance lease assets
amounted to ₩13,495 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 (2015: ₩12,916 million). Leased property, plant and
equipment were pledged as collateral (Note 15).

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 122 / 240
The minimum lease payments under finance lease agreements and their present value as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as
follows:
2016 2015
Minimum Lease
payments Present values
Minimum Lease
payments Present values
Within one year
₩ 25,928 ₩ 18,645
₩ 23,391 ₩ 15,652
From one year to five years
56,732 31,461
60,405 32,895
More than five years
56,249 33,620
69,194 40,049
Total
₩ 138,909 ₩ 83,726
₩ 152,990 ₩ 88,596
Present value adjustment (55,183) (64,394)
Finance lease payable
₩ 83,726 ₩ 88,596
(C) Litigation
(1) The litigation with Apple Inc. (“Apple”) is ongoing in the United States as at the reporting date. On August 24, 2012, the jury
determined that the
Company partially infringed Apple’s design and utility patent and should pay damages to Apple. However,
On March 1, 2013, the Judge ordered a new trial for a certain portion of the damages, ruling that it was originally
miscalculated. On November 21, 2013 a jury verdict was rendered on the recalculated damages amount, and on March 6, 2014,
the Judge made a final judgement to confirm the total damages and deny Apple’s bid for a permanent injunction against the
Company. The Company appealed the decision on the damages amount on March 7, 2014, and a hearing on the appeal was held
on December 4, 2014. On May 18, 2015, the appeals court affirmed in part and reversed in part a previous decision, and
remanded it. On June 17, 2015, the
Company petitioned for an en banc rehearing regarding the design infringement, and on
August 13, 2015, the federal court dismissed the
Company’s request. After the remand procedure, the Court of First Trial
announced a partial final judgment on the appeals on September 18, 2015. On October 13, 2015, the immediate appeal was
dismissed and on November 19, 2015, the Federal Circuit Court denied an en banc rehearing request. On December 11, 2015,
the
Company made payment for the damages. On December 14, 2015, the Company filed an appeal to the Supreme Court
regarding the design patent infringement ruling. Thereafter, the two parties have submitted in writing to the District court
details of supplemental damages incurred in connection with the ruling. On March 21, 2016, the Supreme Court granted the
design-related appeals filed by the
Company and on March 22, 2016, the Court of First Trial ordered all proceedings for review
of damages scheduled to commence March 28, 2016 suspended until the sentence rendered by the Supreme Court was
confirmed. On June 1, 2016, the
Company submitted the draft document in the design-related appeal, and on June 28, 2016,
several companies and organizations presented the document in support of the
Company. Apple filed a dissenting document on
July 29, 2016, and on August 5, 2016, several companies and organizations presented an advocative document. On August, 29,
2016, the
Company submitted a rebuttal letter. Oral statements for the appeal were held at the Supreme Court on October 11,
2016. On December 6, 2016, the Supreme Court issued a ruling citing the
Company appeal and returned the case to the Court of
Appeals. On February 7, 2017, the Court of Appeals reversed the case to the Court of First Trial.
Additionally, on May 5, 2014, the jury in another ongoing patent lawsuit determined that the
Company partially infringed
Apple’s utility patent and should pay damages to Apple. On November 25, 2014, the first trial judgment was pronounced to
confirm the jury’s verdict. The
Company appealed on November 25, 2014 and the rehearing was held on January 5, 2016. On
August 27, 2014, the Judge denied Apple’s request for a permanent injunction on the
Company’s product. However, on
September 17, 2015, the appellate court reversed and remanded a previous decision and on December 16, 2015, the Federal
Circuit Court denied an en banc hearing request of the
Company. On January 18, 2016, the Court of First instance ordered a
permanent injunction on the
Company’s product. The Company asserts that the Company’s product was designed around the
patent and thus has not infringed the patent. The final conclusion and the effect of the patent lawsuits with Apple are uncertain
as at the reporting date.
In August 2014, the
Company and Apple reached an agreement to withdraw from ongoing litigation in all regions other than the
United States, and the
Company has withdrawn all non-United States based lawsuits.
(2) The
Company is involved in claims, disputes, and investigations conducted by regulatory bodies at the reporting date,
including civil claims from some overseas buyers for price-fixing related to the sale of TFT-LCD. Although the outflow of
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 123 / 240
resources and timing of these matters are uncertain, the
Company believes the outcome will not have a material impact on the
financial condition of the
Company.
(3) In addition, during the normal course of business with numerous companies, the
Company has been involved in various
claims, disputes, and investigations conducted by regulatory bodies. Although the outflow of resources and timing of these
matters are uncertain, the
Company believes the outcome will not have a material impact on the financial condition of the
Company.
(D) Other commitments
As at December 31, 2016, the
Company has a trade financing agreement, trade notes receivable discounting facilities, and loan
facilities with accounts receivable pledged as collateral with 7 financial institutions, including Woori Bank, with a combined limit
of up to ₩10,116,485 million. In addition, the
Company has a trade financing agreement (up to ₩865,000 million and US$8,253
million), loan facilities with accounts receivable pledged as collateral and other financial agreements (up to ₩1,638,865 million
and JP¥180,000 million) with 23 financial institutions, including Shinhan Bank.
Samsung Display Co., Ltd entered into a collaboration agreement with Corning Incorporated on October 23, 2013 that includes a
condition relating to mutual loss preservation which can cause inflows or outflows of future economic benefits and the
Company has
recorded an estimated liability as a result of this commitment as at December 31, 2016 (Notes 6 and 31).

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 124 / 240
20. Share Capital
The
Company’s total number of authorized shares is 500,000,000 shares (₩5,000 per share). The Company has issued 140,679,337
shares of common stock and 20,513,427 shares of preferred stock as at December 31, 2016, excluding retired shares. Due to the
retirement of shares, the total par value of the shares issued is ₩805,964 million (common stock ₩703,397 million, preferred
stock ₩102,567 million), which does not agree with paid-in capital of ₩897,514 million.
Changes in the number of shares outstanding for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In number of shares)
Preferred stock Common stock
Balance as at January 1, 2015
19,722,484 130,204,596
Disposal of treasury stock through exercise
of stock options
- 5,000
Acquisition of treasury stock
(1,174,651) (2,812,748)
Balance as at December 31, 2015
18,547,833 127,396,848
Acquisition of treasury stock
(1,264,099) (4,699,197)
Balance as at December 31, 2016
17,283,734 122,697,651
The Company retired 6,620,000 shares of common stock and 2,320,000 shares of preferred stock of which acquisition cost is ₩11,399,991
million in total on the basis of the Board of Directors’ approval on October 29, 2015, January 28, 2016, April 28, 2016 and July 28, 2016.
21. Retained Earnings
Retained earnings as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, consist of as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Appropriated
₩ 143,007,192
₩ 131,539,594
Unappropriated
50,079,125
53,592,420
Total
₩ 193,086,317
₩ 185,132,014

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 125 / 240
22. Dividends
Details of interim and year-end dividends are as follows:
(A) Interim dividends (Record date: June 30, 2016 and 2015)
(In millions of Korean won and number of shares)
2016 2015
Number of shares eligible for dividends
Common stock
123,958,561 shares 129,312,651 shares
Preferred stock
17,580,920 shares 19,603,734 shares
Dividend rate
20% 20%
Dividend amount
Common stock
₩ 123,958 ₩ 129,313
Preferred stock
17,581 19,603
Total
₩ 141,539 ₩ 148,916
(B) Year-end dividends (Record date: December 31, 2016 and 2015)
(In millions of Korean won and number of shares)
2016 2015
Number of shares eligible for dividends
Common stock
122,697,651 shares 127,396,848 shares
Preferred stock
17,283,734 shares 18,547,833 shares
Dividend rate
Common stock
550% 400%
Preferred stock
551% 401%
Dividend amount
Common stock
₩ 3,374,185 ₩ 2,547,937
Preferred stock
476,167 371,884
Total
₩ 3,850,352 ₩ 2,919,821

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 126 / 240
23. Other Components of Equity
Other components of equity as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, consist of as follows::
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Treasury stock
₩ (9,750,326)
₩ (13,442,379)
Unrealized gains on available-for-sale financial assets
1,390,624
1,478,330
Share of other comprehensive income of associates and joint ventures
94,694
362,342
Foreign currency translation
(2,902,076)
(4,091,202)
Remeasurement of net defined benefit liabilities
(811,529)
(1,737,809)
Other 44,027 (149,733)
Total
₩ (11,934,586)
₩ (17,580,451)
The
Company repurchases registered common stock and non-voting preferred stock for the purpose of stock price stability and
increase in shareholder value. The
Company recognizes the repurchase amount in other components of equity. Treasury stock as at
December 31, 2016 and 2015, consists of as follows::
2016 2015
(In millions of Korean won and
number of shares)
Preferred Stock Common Stock Preferred Stock Common Stock
Number of shares 3,229,693 shares 17,981,686 shares 4,285,594 shares 19,902,489 shares
Acquisition cost
₩ 878,817 ₩ 8,871,509 ₩ 2,064,840 ₩ 11,377,539

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 127 / 240
24. Expenses by Nature
Expenses by nature for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Changes in finished goods and work in process
₩ 626,040 ₩ (1,310,244)
Raw materials used and merchandise purchased
73,512,658 77,774,274
Wages and salaries
19,269,035 18,366,965
Pension
1,197,022 1,255,657
Depreciation
19,312,520 19,662,541
Amortization
1,400,445 1,268,316
Welfare
3,495,336 3,852,929
Commission and service charges
8,002,513 8,439,586
Other expenses
45,810,504 44,930,016
Total
1
₩ 172,626,073 ₩ 174,240,040
1
Equal to the sum of cost of sales and selling and administrative expenses on the consolidated statements of income.
25. Selling and Administrative Expenses
Selling and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
1) Selling and Administrative Expenses
Wages and salaries
₩ 5,687,494 ₩ 5,542,701
Pension
288,767 295,652
Commissions and service charges
8,002,513 8,439,586
Depreciation
780,223 714,883
Amortization
221,593 255,708
Advertising
4,432,109 3,852,478
Sales promotion
7,080,554 7,101,937
Transportation
3,334,693 3,433,215
Warranty
3,752,603 2,849,567
Other
4,656,428 4,566,500
2) Research and development expenses
Total expenses 14,792,343 14,848,754
Capitalized expenses (680,962) (1,143,059)
Total
₩ 52,348,358 ₩ 50,757,922

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 128 / 240
26. Other Non-Operating Income and Expense
Details of other non-operating income for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Dividend income
₩ 239,899
₩ 183,730
Rental income
107,664
83,400
Gain on disposal of investments
2,053,744
262,073
Gain on disposal of property, plant and equipment
193,020
135,564
Gain on disposal of assets as held-for-sale
69,924
207,796
Other
574,010
813,384
Total
₩ 3,238,261
₩ 1,685,947
Details of other non-operating expense for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment
₩ 126,516 ₩ 161,510
Donations
407,087 446,391
Impairment losses on investments
341,790 1,890,097
Impairment losses on intangible assets
473,494 284,631
Other
1,114,927 940,805
Total
₩ 2,463,814 ₩ 3,723,434
27. Financial Income and Costs
(A) Details of financial income and costs for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Financial income
Interest income
Interest income from loans and receivables
₩ 1,475,357 ₩ 1,665,521
Interest income from available-for-sale financial assets
28,961 95,636
Foreign exchange differences
9,052,495 7,765,797
Gains from derivatives
828,832 987,925
Total
₩ 11,385,645 ₩ 10,514,879
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Financial costs
Interest expense:
Interest expense from financial liabilities measured at amortized cost
₩ 351,009 ₩ 567,181
Other financial liabilities 236,822 209,330
Foreign exchange differences 9,232,249 8,275,571
Losses from derivatives 886,533 979,689
Total
₩ 10,706,613 ₩ 10,031,771

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 129 / 240
(B) The
Company recognizes foreign exchange gains and losses arising from foreign currency transactions and translation as financial
income and costs.
28. Income Tax
(A) Income tax expense for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, consists of as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Current taxes:
Current tax on profits for the year
₩ 6,161,609 ₩ 5,707,937
Adjustments in respect to prior years (244,791) 1,077,780
Deferred taxes:
Changes in carryforward of unused tax credits (166,206) 35,128
Changes in temporary differences 1,869,700 (282,458)
Changes in carryforward of unused tax losses 397,329 321,583
Other (30,081) 41,369
Items charged directly to equity - (488)
Income tax expense
₩ 7,987,560 ₩ 6,900,851
(B) The tax on the Company’s profit before tax differs from the theoretical amount that would arise using the weighted average tax
rate applicable to profits of the
Company as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016
2015
Income before tax
₩ 30,713,652 ₩ 25,960,995
Tax calculated at weighted average of applicable tax rates
1
7,009,003 6,880,212
Tax effects of:
Permanent differences (687,901) 25,886
Temporary differences for which no deferred income tax was recognized
(12,825) (55,186)
Tax credits (608,218) (824,893)
Results of interest in subsidiaries, associates and joint ventures 2,288,893 560,668
Impact of changes in tax rates 1,280 6,291
Other (2,672) 307,873
Income tax expense
₩ 7,987,560 ₩ 6,900,851
1
The weighted average of statutory tax rates are applied to the respective profits of the Company applicable to each tax authority as at December
31, 2016 and 2015.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 130 / 240
(C) Changes in deferred income tax assets and liabilities resulting from the tax effect of temporary differences for the years ended
December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(1) 2016
Temporary Differences Deferred Income Tax Assets (Liabilities)
(In millions of Korean won)
Balance as at
January 1
Increase
(Decrease)
Balance as at
December 31
Balance as at
January 1
Increase
(Decrease)
Balance as at
December 31
Deferred tax arising from temporary differences
Special reserves appropriated for
tax purposes
₩ (7,368) ₩ 7,000 ₩ (368) ₩ (1,783) ₩ 1,694 ₩ (89)
Revaluation of land
(3,455,958) 11,704 (3,444,254) (836,342) 2,832 (833,510)
Investments in subsidiaries,
associates and joint ventures
1
(41,729,872) (17,540,434) (59,270,306) (5,173,897) (2,362,840) (7,536,737)
Depreciation
2,627,073 281,473 2,908,546 651,988 (7,862) 644,126
Accrued income
(309,545) 51,235 (258,310) (71,086) (7,885) (78,971)
Provisions and accrued expenses
13,322,516 136,265 13,458,781 3,519,564 (286,776) 3,232,788
Foreign currency translation
221,793 (56,235) 165,558 58,567 (13,960) 44,607
Asset impairment losses
652,768 574,585 1,227,353 160,975 140,231 301,206
Other
(193,612) 1,673,283 1,479,671 (14,734) 664,866 650,132
Subtotal
₩ (28,872,205) ₩ (14,861,124) ₩ (43,733,329) ₩ (1,706,748)
(1,869,700)
₩ (3,576,448)
Deferred tax arising from carryforwards
Unused tax losses
₩ 6,178,327 ₩ (1,486,967) ₩ 4,691,360 ₩ 1,495,976 ₩ (397,329) ₩ 1,098,647
Unused tax credits
631,362 242,093 873,455 555,041 166,206 721,247
Deferred tax recognized in other comprehensive income
Valuation of available-for-sale
financial instruments
₩ (1,976,829) ₩ 6,996 ₩ (1,969,833) ₩ (453,192) ₩ 6,436 ₩ (446,756)
Actuarial valuation
2,299,154 (1,275,595) 1,023,559 543,239 (311,993) 231,246
Subtotal
₩ 322,325 ₩ (1,268,599) ₩ (946,274) ₩ 90,047 ₩ (305,557) ₩ (215,510)
Deferred tax assets
₩ 5,321,450
Deferred tax liabilities
(7,293,514)
Total
₩ (1,972,064)
1
Deferred tax assets were not recognized if it is probable that the temporary differences will not reverse in the foreseeable future for investments
in subsidiaries, associates and joint ventures.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 131 / 240
(2) 2015
Temporary Differences Deferred Income Tax Assets (Liabilities)
(In millions of Korean won)
Balance as at
January 1
Increase
(Decrease)
Balance as at
December 31
Balance as at
January 1
Increase
(Decrease)
Balance as at
December 31
Deferred tax arising from temporary differences
Special reserves appropriated for tax
purposes
₩ (14,368) ₩ 7,000 ₩ (7,368) ₩ (3,477) ₩ 1,694 ₩ (1,783)
Revaluation of land
(3,475,692) 19,734 (3,455,958) (841,117) 4,775 (836,342)
Investments in subsidiaries,
associates and joint ventures
1
(31,469,156) (10,260,716) (41,729,872) (4,242,098) (931,799) (5,173,897)
Depreciation
2,609,052 18,021 2,627,073 643,194 8,794 651,988
Accrued income
(535,671) 226,126 (309,545) (132,237) 61,151 (71,086)
Provisions and accrued expenses
11,432,901 1,889,615 13,322,516 2,958,810 560,754 3,519,564
Foreign currency translation
98,788 123,005 221,793 25,516 33,051 58,567
Asset impairment losses
579,655 73,113 652,768 141,377 19,598 160,975
Other
(2,233,868) 2,040,256 (193,612) (539,174) 524,440 (14,734)
Subtotal
₩ (23,008,359) ₩ (5,863,846) ₩ (28,872,205) ₩ (1,989,206) ₩ 282,458 ₩ (1,706,748)
Deferred tax arising from carryforwards
Unused tax losses
₩ 7,465,339 ₩(1,287,012) ₩ 6,178,327 ₩ 1,817,559 ₩ (321,583) ₩ 1,495,976
Unused tax credits
739,448 (108,086) 631,362 590,169 (35,128) 555,041
Deferred tax recognized in other comprehensive income
Valuation of available-for-sale financial
instruments
₩ (2,549,385) ₩ 572,556 ₩ (1,976,829) ₩ (610,738) ₩ 157,546 ₩ (453,192)
Actuarial valuation
2,640,893 (341,739) 2,299,154 621,000 (77,761) 543,239
Subtotal
₩ 91,508 ₩ 230,817 ₩ 322,325 ₩ 10,262 ₩ 79,785 ₩ 90,047
Deferred tax assets
₩ 5,589,108
Deferred tax liabilities
(5,154,792)
Total
₩ 434,316
1
Deferred tax assets were not recognized if it is probable that the temporary differences will not reverse in the foreseeable future for investments
in subsidiaries, associates and joint ventures.
The Company periodically assesses its ability to recover deferred tax assets. In the event of a significant uncertainty regarding the
Company’s ultimate ability to recover such assets, deferred tax assets are recognized only to the extent that it is probable that future
taxable profit will be available against which the temporary differences can be utilized.
Temporary differences whose deferred tax effects were not recognized due to uncertainty regarding the ultimate realizability of
such assets as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Unused tax losses
1
₩ 58,969 ₩ 34,899
Unused tax credits
1
31,205 22,584
1
Expiry dates of unused tax losses and unused tax credits for which no deferred tax asset is recognized in the balance sheet are as
follows:

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 132 / 240
(In millions of Korean won)
2017
2018
2019 2020 and after
Undisposed accumulated deficit
-
₩ 58,969
Tax credit carryforwards
4,789 1,704 19,279 5,433
(D) The liquidity analysis of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities for the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 is as
follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Deferred tax assets
Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months
₩ 3,066,577 ₩ 2,401,806
Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months 2,254,873 3,187,302
Subtotal 5,321,450 5,589,108
Deferred tax liabilities
Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months (7,293,514) (5,154,792)
Subtotal (7,293,514) (5,154,792)
Total
₩ (1,972,064) ₩ 434,316
29. Earnings per Share
(A) Basic earnings per share
Basic earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are calculated as follows:
(1) Common stock
(In millions of Korean won, except per share data, and thousands of number of shares)
2016 2015
Profit attributable to owners of the Parent company
₩ 22,415,655 ₩ 18,694,628
Profit available for common stock 19,647,199 16,317,275
Weighted-average number of common shares outstanding 124,375 129,190
Basic earnings per share
₩ 157,967 ₩ 126,305
(2) Preferred stock
(In millions of Korean won, except per share data, and thousands of number of shares)
2016 2015
Profit attributable to owners of the Parent company
₩ 22,415,655 ₩ 18,694,628
Profit available for common stock 2,768,456 2,377,353
Weighted-average number of preferred shares outstanding 17,692 19,519
Basic earnings per preferred share
₩ 156,480 ₩ 121,798

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 133 / 240
(B) Diluted earnings per share
The
Company had one category of potentially dilutive common shares: stock options. Dilutive earnings per share is calculated by
adjusting the weighted average number of common shares outstanding to assume conversion of all dilutive potential common
shares. All remaining stock options were exercised during the year ended December 31, 2015, and as a result, basic earnings per
share and diluted earnings per share are the same for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Diluted earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, is calculated as follows:
(1) Common stock
(In millions of Korean won, except per share data, and thousands of number of shares)
2016 2015
Profit available for common stock and common stock equivalents
₩ 19,647,199 ₩ 16,317,276
Weighted-average number of shares of common stock and dilutive potential common stock
124,375 129,192
Diluted earnings per share
₩ 157,967 ₩ 126,303
(2) Preferred stock
(In millions of Korean won, except per share data, and thousands of number of shares)
2016 2015
Net income available for preferred stock and preferred stock equivalents
₩ 2,768,456 ₩ 2,377,352
Weighted-average number of shares of preferred stock and dilutive potential preferred stock
17,692 19,519
Diluted earnings per preferred share
₩ 156,480 ₩ 121,798

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 134 / 240
30. Cash Generated from Operations
(A) Adjustments and changes in assets and liabilities arising from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2016 and
2015, are as follows:
- Adjustments
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Adjustments for:
Income tax expense
₩ 7,987,560 ₩ 6,900,851
Financial income (3,521,050) (3,339,267)
Financial costs 2,500,020 2,466,042
Severance and retirement benefits 1,197,022 1,255,657
Depreciation 19,312,520 19,662,541
Amortization 1,400,445 1,268,316
Bad debt expenses 701,335 388,792
Dividend income (239,899) (183,730)
Gain on valuation of equity method investments (19,501) (1,101,932)
Gain on disposal of property, plant and equipment (193,020) (135,564)
Loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment 126,516 161,510
Obsolescence and scrapping of inventories 2,959,042 963,637
Gain on disposal of investments (2,053,744) (262,073)
Gain on disposal of assets as held-for-sale (69,924) (207,796)
Impairment losses on investments 341,790 1,890,097
Impairment losses on intangible assets 473,494 284,631
Other income/expense (148,135) (400,741)
Adjustments, total
₩ 30,754,471 ₩ 29,610,971
- Changes in assets and liabilities arising from operating activities
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Changes in assets and liabilities:
Decrease in trade receivables
₩ 1,473,776 ₩ 207,676
(Increase) decrease in other receivables
(160,500) 206,245
Decrease (increase) in advances
145,053 (40,938)
(Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses
(46,026) 611,089
Increase in inventories
(2,830,602) (2,616,203)
Increase (decrease) in trade payables
200,240 (1,871,175)
Increase in other payables
1,144,756 650,861
Decrease in advances received
(105,460) (76,233)
Decrease in withholdings
(302,901) (163,124)
Increase (decrease) in accrued expenses
1,136,440 (1,243,649)
(Decrease) increase in provisions
(1,604,824) 503,661
Payment of severance benefits
(474,112) (700,205)
(Increase) decrease in plan assets
(76,255) 27,155
Other
319,462 (177,192)
Changes in net working capital, total
₩ (1,180,953) ₩ (4,682,032)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 135 / 240
(B) The
Company’s statements of cash flows are prepared using indirect method. Significant transactions not affecting cash flows
for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Valuation of available-for-sale financial assets
₩ 798,698 ₩ (1,218,782)
Reclassification of construction in progress and machinery in transit to property,
plant and equipment 17,131,444 29,846,423
Reclassification of available-for-sale financial assets to assets held-for-sale
- 77,073
Valuation of investments in associates and joint ventures
36,152 12,857
Reclassification of current maturities of long-term borrowings
19,283 16,106
Reclassification of current maturities of bonds
1,214,543 205,860
Reclassification of available-for-sale financial assets to investment in associates
1,742,242 -
Reclassification of Printing Solutions division to held-for-sale
508,228 -
(C) The
Company reported cash receipts and payments arising from transactions occurring frequently and short-term financial
instruments, loans, and borrowings on a net basis.
31. Financial Risk Management
The
Company’s financial risk management focuses on minimizing market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk arising from operating
activities. To mitigate these risks, the
Company implements and operates a financial risk policy and program that closely monitors
and manages such risks.
The finance team mainly carries out the
Company’s financial risk management. With the cooperation of the Company’s divisions,
domestic and foreign subsidiaries, the finance team periodically measures, evaluates and hedges financial risk and also establishes
and implements the global financial risk management policy.
Also, financial risk management officers are dispatched to the regional headquarters of each area including the United States,
United Kingdom, Singapore, China, Brazil and Russia to operate the local finance center in accordance with global financial risk
management.
The
Company’s financial assets that are under financial risk management are comprised of cash and cash equivalents, short-term
financial instruments, available-for-sale financial assets, trade and other receivables and other financial assets. The
Company’s
financial liabilities under financial risk management are comprised of trade and other payables, borrowings, debentures, and other
financial liabilities.
(A) Market risk
(1) Foreign exchange risk
The
Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from various currency exposures, primarily with respect to the United
States, European Union, South America, Japan and other Asian countries. Revenues and expenses arise from foreign currency
transactions and exchange positions, and the most widely used currencies are the US Dollar, EU’s EURO, Japanese Yen and
Chinese Yuan. Foreign exchange risk management of the
Company is carried out by both SEC and its subsidiaries. To minimize
foreign exchange risk arising from operating activities, the
Company’s foreign exchange management policy requires normal
business transactions to be in local currency or for the cash-in currency to be matched up with the cash-out currency. The
Company’s foreign exchange risk management policy also defines foreign exchange risk, measuring period, controlling
responsibilities, management procedures, hedging period and hedge ratio.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 136 / 240
The
Company limits all speculative foreign exchange transactions and operates a system to manage receivables and payables
denominated in foreign currency. It evaluates, manages and reports foreign currency exposures to receivables and payables.
The foreign currency exposure to financial assets and liabilities of a 5% currency rate change against the Korean won are presented
below:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Increase Decrease Increase Decrease
USD
₩ 222,149 ₩ (222,149) ₩ 143,266 ₩ (143,266)
EUR
138,084 (138,084) 19,626 (19,626)
JPY
(61,294) 61,294 (15,120) 15,120
(2) Price risk
The
Company’s investment portfolio consists of direct and indirect investments in equity securities classified as available-for-sale,
which is in line with the
Company’s strategy.
As at December 31, 2016 and 2015, a price fluctuation in Company relation to marketable equity securities by 1% would result in
changes in other comprehensive income (before income tax) of ₩23,622 million and ₩46,748 million, respectively.
(3) Interest rate risk
Risk of changes in interest rates for floating interest rate financial instruments is defined as the risk that the fair value of
components of the statement of financial position, and future cash flows of interest income (expenses) of a financial instrument,
will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates. The
Company is exposed to interest rate risk mainly through interest
bearing liabilities and assets. The
Company’s position with regard to interest rate risk exposure is mainly driven by its floating
interest rate debt obligations and interest-bearing deposits. The
Company implemented policies and operates to minimize uncertainty
arising from changes in interest rates and finance costs.
In order to avoid interest rate risk, the
Company maintains minimum external borrowings by facilitating cash pooling systems on a
regional and global basis. The
Company manages exposed interest rate risk via periodic monitoring and handles risk factors on a
timely basis.
The sensitivity risk of the
Company is determined based on the following assumptions:
Changes in market interest rates that could impact the interest income and expenses of floating interest rate financial
instruments
Based on the above assumption, changes to profit and net equity as a result of 1% increases in interest rates on borrowings are
presented below:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Increase Decrease Increase Decrease
Financial assets
₩ 64,803 ₩ (64,803) ₩ 81,962 ₩ (81,962)
Financial liabilities
(9,123) 9,123 (22,314) 22,314
Net effect
₩ 55,680 ₩ (55,680) ₩ 59,648 ₩ (59,648)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 137 / 240
(B) Credit risk
Credit risk arises during the normal course of transactions and investing activities where clients or other parties fail to discharge an
obligation. The
Company monitors and sets the client’s and counterparty’s credit limit on a periodic basis based on the client’s and
counterparty’s financial conditions, default history and other important factors. Adequate insurance coverage is maintained for
accounts receivables related to trading partners situated in higher risk countries.
Credit risk can arise from transactions with financial institutions which include financial instrument transactions such as cash and
cash equivalents, savings, and derivative instruments. To minimize such risk, the
Company transacts only with banks which have
strong international credit rating (S&P A and above), and all new transactions with financial institutions with no prior transaction
history are approved, managed and monitored by the
Company’s finance team and the local finance center. The Company requires
separate approval for contracts with restrictions.
The
Company estimates that its maximum exposure to credit risk is the carrying value of its financial assets, net of impairment
losses.
(C) Liquidity risk
Due to large investments made by the
Company, maintaining adequate levels of liquidity risk is critical. The Company strives to
achieve this goal by periodically forecasting its capital balance, estimating required cash levels, and managing income and expenses.
The
Company manages its liquidity risk by periodically forecasting projected cash flows. If abnormal signs are identified, the
Company works with the local finance center and provides liquidity support by utilizing a globally integrated finance structure, such
as Cash Pooling. In addition, the
Company maintains a liquidity management process which provides additional financial support by
the local finance center and the
Company. The Cash Pooling program allows sharing of surplus funds among entities and contributes
to minimizing liquidity risk and strengthening the
Company’s competitive position by reducing capital operation expenses and
financial expenses.
In addition, the
Company mitigates liquidity risk by contracting with financial institutions with respect to bank overdrafts and
foreign trade finance, and by providing payment guarantees to subsidiaries. For large scale facility investments, liquidity risk is
minimized by utilizing internal reserves and long term borrowings according to the capital injection schedule.
The following table is an undiscounted cash flow analysis for financial liabilities that are presented on the statements of financial
position according to their remaining contractual maturity.
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Less than
3 months
4-6
months
7-12
months
1-5
years
More than
5 years
Financial liabilities
₩ 40,918,912 ₩ 1,588,798 ₩ 150,744 ₩ 4,346,200 ₩ 50,073
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Less than
3 months
4-6
months
7-12
months
1-5
years
More than
5 years
Financial liabilities
₩ 32,275,387 ₩ 412,196 ₩ 1,331,166 ₩ 3,057,099 ₩ 476,432
The table above shows the
Company’s financial liabilities based on the remaining period at the statement of financial position date
until the contractual maturity date. The amounts disclosed in the table are the contractual undiscounted cash flows. The
Company’s
trading portfolio of derivative instruments has been included at its fair value of
₩74,697 million (December 31, 2014: ₩38,829
million). These contracts are managed on a net-fair value basis rather than by maturity date. Net settled derivatives consist of

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 138 / 240
forward exchange contracts used by the
Company to manage the exchange rate profile.
The maximum liquidity risk exposure from those other than the above financial liabilities (e.g., payment guarantees for affiliated
companies and performance bonds) as at December 31, 2016 is
₩59,016 million (December 31, 2015: ₩67,017 million).
(D) Capital risk management
The purpose of capital management is to maintain a sound capital structure. The
Company monitors capital on the basis of the ratio
of total liabilities to total equity. This ratio is calculated by dividing total liabilities by total equity in the consolidated financial
statements.
The
Company’s capital risk management policy has not changed since the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015. As at December 31,
2016, the
Company has maintained an A+ and A1 credit rating from S&P and Moody’s, respectively, on its long term debt.
The total liabilities to equity ratios as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Total liabilities
₩ 69,211,291 ₩ 63,119,716
Total equity
192,963,033 179,059,805
Total liabilities to equity ratio 35.9% 35.3%

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 139 / 240
(E) Fair value estimation
(1) Carrying amounts and fair values of financial instruments by category as at December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
2016 2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Carrying amount Fair value Carrying amount Fair value
Financial assets
Cash and cash equivalents
₩ 32,111,442
1
₩ 22,636,744
1
Short-term financial instruments 52,432,411
1
44,228,800
1
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets 3,638,460 3,638,460 4,627,530 4,627,530
Trade receivables 24,279,211
1
25,168,026
1
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
2
6,804,276 5,826,507 8,332,480 8,225,687
Other
3
3,459,863 919,071 3,546,434 1,070,839
Total financial assets ₩ 122,725,663 ₩ 108,540,014
Financial liabilities
Trade payables
₩ 6,485,039
1
₩ 6,187,291
1
Short-term borrowings 12,746,789
1
11,155,425
1
Other payables 10,225,271
1
7,625,490
1
Current portion of long-term liabilities 1,232,817
1
221,548
1
Debentures 58,542 76,129 1,230,448 1,261,783
Long-term borrowings 1,244,238 1,225,455 266,542 242,603
Long-term other payables 3,009,659 3,022,821 2,719,674 2,581,985
Other
3
11,942,469 74,697 7,947,398 38,829
Total financial liabilities
₩ 46,944,824 ₩ 37,353,816
1
Assets and liabilities whose carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value are excluded from the fair value disclosures.
2
Amount measured at cost (2016: ₩977,770 million, 2015: ₩106,793 million) is excluded as the range of reasonable fair value estimates is
significant and the probabilities of the various estimates cannot be reasonably assessed.
3
Assets measured at cost of ₩2,452,118 million (December 31, 2015: ₩2,349,454 million) and liabilities measured at cost of ₩11,867,772
million (December 31, 2015: ₩7,908,569) are excluded as the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 140 / 240
(2) The following table presents the assets and liabilities, by level, that are measured or disclosed at fair value as at December 31,
2016 and 2015:
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Total balance
1) Assets
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets
₩ - ₩ 3,638,460 ₩ - ₩ 3,638,460
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets 2,362,235 - 3,464,272 5,826,507
Other - 919,071 - 919,071
2) Liabilities
Debentures - 76,129 - 76,129
Long-term borrowings - 1,225,455 - 1,225,455
Long-term other payables - 2,680,119 342,702 3,022,821
Derivatives - 74,697 - 74,697
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Total balance
1) Assets
Short-term available-for-sale financial assets
₩ - ₩ 4,627,530 ₩ - ₩ 4,627,530
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets 4,674,753 78,189 3,472,745 8,225,687
Other - 1,055,240 15,599 1,070,839
2) Liabilities
Debentures - 1,261,783 - 1,261,783
Long-term borrowings - 242,603 - 242,603
Long-term other payables - 2,269,247 312,738 2,581,985
Derivatives - 38,829 - 38,829
The levels of the fair value hierarchy and its application to financial assets and liabilities are described below.
ㆍ Level 1: Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
ㆍ Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or
indirectly
ㆍ Level 3: Inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (that is, unobservable inputs)
The fair value of financial instruments traded in active markets is based on quoted market prices at the statement of financial
position date. A market is regarded as active if quoted prices are readily and regularly available from an exchange, dealer, broker,
industry
Company, pricing service, or regulatory agency, and those prices represent actual and regularly occurring market
transactions on an arm’s length basis. The quoted market price used for financial assets held by the
Company is the current bid price.
These instruments are included in Level 1. Instruments included in Level 1 are listed equity investments classified as trading
securities or available-for-sale financial assets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market (for example, over-the-counter derivatives) is
determined by using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques maximize the use of observable market data where it is
available and rely as little as possible on entity specific estimates. If all significant inputs required to fair value an instrument are
observable, the instrument is included in Level 2.
If one or more of the significant inputs are not based on observable market data, the instrument is included in Level 3.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 141 / 240
The
Company performs the fair value measurements required for financial reporting purposes, including Level 3 fair values and
discusses valuation processes and results at least once every quarter in line with the
Company’s quarterly reporting dates. The
Company’s policy is to recognize transfers between levels at the end of the reporting period, if corresponding events or changes in
circumstances have occurred.
Specific valuation techniques used to value financial instruments include:
ㆍ Quoted market prices or dealer quotes for similar instruments.
ㆍ The fair value of forward foreign exchange contracts is determined using forward exchange rates at the statement of financial
position date, with the resulting value discounted back to present value.
Other techniques, such as discounted cash flow analysis, are used to determine fair value for the remaining financial instruments.
For trade and other receivables, the book value approximates a reasonable estimate of fair value.
(3) Valuation technique and the inputs
The
Company utilizes a present value technique to discount future cash flows at a proper interest rate for corporate bonds,
government and public bonds, and bank debentures that are classified as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy.
The following table presents the valuation technique and the inputs used for major financial instruments classified as Level 3.
(In millions of Korean won)
Classification
Fair
Value
Valuation
Technique Level 3 Inputs
Input Range
(Weighted Average)
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
Maltani
(formerly Taewon Lighting)
₩ 16,270
Discounted cash
flow
Permanent growth rate -1.00%~1.00%(0%)
Weighted average cost of capital 7.45%~9.45%(8.45%)
Samsung Venture Investment 7,515
Discounted cash
flow
Permanent growth rate -1.00%~1.00%(0%)
Weighted average cost of capital 21.31%~23.31%(22.31%)
Corning Incorporated convertible
preferred stock
3,440,487
Trinomial
model
Risk adjusted discount rate
Price volatility
5.74%~7.74%(6.74%)
27.8%~33.8%(30.80%)
Long-term other payables
Contingent financial liability 342,702
Discounted cash
flow
Weighted average cost of capital
3.81%~4.65%(4.23%)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 142 / 240
(4) Changes in Level 3 instruments for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Financial assets
Balance as of January 1
₩ 3,488,344 ₩ 3,548,095
Purchases
- 119,297
Disposals
(14,805) (55,986)
Amount recognized in profit or loss
(795) 3,530
Amount recognized in other comprehensive income(loss)
695,631 (304,012)
Others
(704,103) 177,420
Balance as at December 31
₩ 3,464,272 ₩ 3,488,344
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Financial liabilities
Balance as of January 1
\ 312,738 \ -
Amount recognized in profit or loss (29,964) 312,738
Balance as at December 31
\ 342,702 \ 312,738
(5) Sensitivity analysis for recurring fair value measurements categorized within Level 3
Sensitivity analysis of financial instruments is performed to measure favorable and unfavorable changes in the fair value of
financial instruments which are affected by the unobservable parameters, using a statistical technique. When the fair value is
affected by more than two input parameters, the amounts represent the most favorable or most unfavorable.
The results of the sensitivity analysis for the effect on profit or loss (before-tax amount for other comprehensive income or loss)
from changes in inputs for each financial instrument which is categorized within Level 3 and subject to sensitivity analysis, are as
follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Favorable Changes Unfavorable Changes
Classification Profit or Loss Equity Profit or Loss Equity
Long-term available-for-sale financial assets
1
₩ - ₩ 194,732 ₩ - ₩ (227,857)
Long-term other payables
2
1,920 1,920 (1,932) (1,932)
Total
₩ - ₩ 196,652 ₩ (1,932) ₩ (229,789)
1
For equtiy securities changes in their fair value are calculated with the correlation between growth ratio (-1% to 1%) and discount rate, which are
significant unobservable inputs.
2
The fair value long-term payables is calculated by increasing and decreasing the correlation between discount rate and volatility by 10% which
are significant unobservable inputs.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 143 / 240
32. Segment Information
(A) Operating segment information
The chief operating decision maker has been identified as the Management Committee. The Management Committee is responsible
for making strategic decisions based on review of the group’s internal reporting. The Management Committee has determined the
operating segments based on these reports.
The Management Committee reviews operating profits of each operating segment in order to assess performance and to make
decisions about allocating resources to the segment. The operating segments are product based and include CE, IM, Semiconductor,
DP and others.
Depreciation, amortization of intangible assets, and operating profit were prepared after the allocation of internal transaction
adjustments. Total assets and liabilities of each operating segment are excluded from the disclosure as these have not been provided
regularly to the Management Committee.
(1) For the year ended December 31, 2016
2016
DS
(In millions of
Korean won)
CE IM Total
1
Semi
conductor DP Total
1
Intercompany
elimination
within the group Consolidated
Total segment
revenue
₩109,672,506 ₩211,523,973 ₩159,473,455 ₩ 99,527,926 ₩55,884,739 ₩482,046,125 ₩ (280,179,380) ₩201,866,745
Intercompany
revenue
(62,627,083) (111,221,861) (81,325,252) (48,370,924) (28,956,095) (280,179,380) 280,179,380 -
Net revenue
2
47,045,423 100,302,112 78,148,203 51,157,002 26,928,644 201,866,745 - 201,866,745
Depreciation
560,095 1,303,509 17,041,961 12,548,152 4,271,617 19,312,520 - 19,312,520
Amortization
73,581 175,351 960,611 812,652 130,398 1,400,445 - 1,400,445
Operating profit
2,638,002 10,807,569 15,850,986 13,595,004 2,226,626 29,240,672 - 29,240,672
1
Includes other amounts not included in specific operating segments.
2
Segment net revenue includes intersegment revenues.
(2) For the year ended December 31, 2015
2015
DS
(In millions of
Korean won)
CE IM Total
1
Semi
conductor DP Total
1
Intercompany
elimination
within the group Consolidated
Total segment
revenue
₩120,688,835 ₩222,023,600 ₩149,974,731 ₩ 90,600,806 ₩ 55,120,243 ₩493,313,476 ₩ (292,659,994) ₩200,653,482
Intercompany
revenue
(73,793,424) (118,469,345) (74,948,617) (43,014,054) (27,633,382) (292,659,994) 292,659,994 -
Net revenue
2
46,895,411 103,554,255 75,026,114 47,586,752 27,486,861 200,653,482 - 200,653,482
Depreciation
600,216 1,175,340 17,244,351 12,481,198 4,534,914 19,662,541 - 19,662,541
Amortization
98,154 182,661 790,369 646,110 130,416 1,268,316 - 1,268,316
Operating profit
1,254,187 10,142,022 14,887,262 12,787,297 2,295,367 26,413,442 - 26,413,442
1
Includes other amounts not included in specific operating segments.
2
Segment net revenue includes intersegment revenues.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 144 / 240
(B) Regional information
The regional segment information provided to the Management Committee for the reportable segments as at and for the years ended
December 31, 2016 and 2015, is as follows:
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Korea America Europe
Asia and
Africa China
Intercompany
elimination
within the group Consolidated
Net segment revenue
20,201,828 68,728,575 38,253,185 39,099,991 35,583,166 - 201,866,745
Non-current assets
1
68,978,040 7,041,731 730,490 9,626,711 11,132,720 (483,191) 97,026,501
1
Total of non-current assets other than financial instruments, deferred tax assets, and investments in associates and joint ventures.
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Korea America Europe
Asia and
Africa China
Intercompany
elimination
within the group Consolidated
Net segment revenue
20,827,822 68,944,447 38,629,442 41,265,504 30,986,267 - 200,653,482
Non-current assets
1
63,691,863 7,600,852 709,513 7,596,102 12,820,469 (545,378) 91,873,421
1
Total of non-current assets other than financial instruments, deferred tax assets, and investments in associates and joint ventures.
33. Related Party Transactions
(A) Sale and purchase transactions
Sales and purchases with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, are as follows:
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Name of Company
1
Sales
Disposal of
fixed assets Purchases
Purchase of
fixed assets
Associates and Joint ventures
Samsung SDS
₩ 46,073 ₩ - ₩1,585,089 ₩ 199,728
Samsung Electro-Mechanics
27,516 23 2,280,953 -
Samsung SDI
2
59,322 397 1,072,830 32,576
Cheil Worldwide
3
672 - 214,061 -
Other
286,880 113 6,693,656 214,728
Total (Associates and Joint ventures)
420,463 533 11,846,589 447,032
Other related parties
Samsung C&T.
4
42,905 74 249,088 3,343,979
Other
231,878 1,557,589 763,500 398,514
Total (Other related parties)
274,783 1,557,663 1,012,588 3,742,493
Others
5
Samsung Engineering
15,677 - 17,627 2,485,027
S-1
35,846 - 323,792 37,590
Other
58,054 83,298 663,222 65
Total (Others)
109,577 83,298 1,004,641 2,522,682
1
Transactions with separate entities that are related parties of the Company.
2
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Samsung SDI was included in associates as the Company’s ownership of common outstanding stock
was increased.
3
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Cheil Worldwide was included in associates due to acquisition of shares.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 145 / 240
4
During the year ended December 31, 2015, Cheil Industries Inc. merged Samsung C&T and changed its name to Samsung C&T.
5
Although these entities are not related parties of the Company in accordance with Korean IFRS 1024, they belong to same enterprise group in
accordance with the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act.
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Name of Company
1
Sales
Disposal of
fixed assets Purchases
Purchase of
fixed assets
Associates and Joint ventures
Samsung SDS
₩ 38,885 ₩ - ₩1,615,824 ₩ 201,748
Samsung Electro-Mechanics
27,437 - 2,806,123 2
Other
319,090 3,526 5,541,899 323,363
Total (Associates and Joint ventures)
385,412 3,526 9,963,846 525,113
Other related parties
Samsung C&T.
2
9,630 - 113,098 1,850,655
Samsung SDI
59,879 326 1,518,575 24,606
Other
117,432 - 1,239,441 968,840
Total (Other related parties)
186,941 326 2,871,114 2,844,101
Others
3
Samsung Engineering
9,232 - 24,630 1,205,414
S-1
38,290 - 283,295 57,039
Other
77,706 88 817,212 143,981
Total (Others)
125,228 88 1,125,137 1,406,434
1
Transactions with separate entities that are related parties of the Company.
2
During the year ended December 31, 2015, Cheil Industries Inc. merged Samsung C&T and changed its name to Samsung C&T.
3
Although these entities are not related parties of the Company in accordance with Korean IFRS 1024, they belong to the same large enterprise
group in accordance with the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act.
(B) Balances of receivables and payables
Balances of receivables and payables arising from sales and purchases of goods and services as at December 31, 2016 and 2015, are
as follows:
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Name of Company
1
Receivables Payables
Associates and Joint
ventures
Samsung SDS
₩ 5,709 ₩ 362,062
Samsung Electro-Mechanics 1,143 108,469
Samsung SDI
2
89,721 76,211
Cheil Worldwide
3
456 436,624
Other
210,891 784,475
Total (Associates and Joint ventures)
307,920 1,767,841
Other related parties
Samsung C&T
4
231,089 435,505
Other 31,752 1,932,924
Total (Other related parties)
262,841 2,368,429
Others
5
Samsung Engineering
10,664 115,726
S-1
4,160 47,098
Other
3,058 28,841
Total (Others)
17,882 191,665
1
Balances due from and to separate entities that are related parties of the Company.
2
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Samsung SDI was included in associates as the Company’s ownership of common outstanding stock
was increased.
3
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Cheil Worldwide was included in associates due to acquisition of shares.
4
During the year ended December 31, 2015, Cheil Industries Inc. merged Samsung C&T and changed its name to Samsung C&T.
5
Although these entities are not related parties of the Company in accordance with Korean IFRS 1024, they belong to the same large enterprise
group in accordance with the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 146 / 240
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Name of Company
1
Receivables Payables
Associates and Joint
ventures
Samsung SDS
₩ 3,578 ₩ 311,648
Samsung Electro-Mechanics 608 216,869
Other
66,033 1,722,515
Total (Associates and Joint ventures)
70,219 2,251,032
Other related parties
Samsung C&T
2
208,576 1,430,098
Samsung SDI 90,221 106,507
Other 19,456 161,048
Total (Other related parties)
318,253 1,697,653
Others
3
Samsung Engineering
3,970 457,817
S-1
2,825 61,739
Other
4,546 385,649
Total (Others)
11,341 905,205
1
Balances due from and to separate entities that are related parties of the Company.
2
During the year ended December 31, 2015, Cheil Industries Inc. merged with Samsung C&T and changed its name to Samsung C&T.
3
Although these entities are not related parties of the Company in accordance with Korean IFRS 1024, they belong to the same large enterprise
group in accordance with the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act.
(C) During the year ended December 31, 2016, the
Company invested \84,306 million in associates and joint ventures including
\14,805 million in Samsung Biologics. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company invested \137,917 million in
associates and joint ventures. Also, the
Company invested \181,081 million in Samsung Heavy Industries which is not a related
party of the
Company in accordance with Korean IFRS 1024, the entity belongs to the same large enterprise group in
accordance with the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act.
(D) Key management compensation
Key management includes directors (executive and non-executive) and members of the Executive Committee. The compensation
paid or payable for employee services for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, consists of as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2016 2015
Salaries and other short-term employee benefits
₩ 16,822 ₩ 23,671
Termination benefits 840 560
Other long-term benefits 8,671 8,316

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 147 / 240
34. Information about Non-Controlling Interests
(A) Changes in accumulated non-controlling interests
The profit or loss allocated to non-controlling interests and accumulated non-controlling interests of subsidiaries that are material to
the
Company for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, is as follows:
2016
(In millions of Korean won)
Percentage of Non-
Controlling
Interests
Balance as at
January 1
Net Income
Dividends
Other
Balance as at
December 31
Samsung Display and its
subsidiaries
15.2%
₩ 5,642,413 ₩ 253,296 ₩ (13,472) ₩ 99,217 ₩ 5,981,454
2015
(In millions of Korean won)
Percentage of Non-
Controlling
Interests
Balance as at
January 1
Net Income
Dividends
Other
Balance as at
December 31
Samsung Display and its
subsidiaries
15.2%
₩ 5,360,192 ₩ 314,078 - ₩ (31,857) ₩ 5,642,413
(B) The summarized financial information for each subsidiary with non-controlling interests that are material to the
Company
before intercompany eliminations for the years December 31, 2016 and 2015 is as follows:
(1) Summarized consolidated statements of financial position
(In millions of Korean won)
Samsung Display and its subsidiaries
December 31, 2016 December 31, 2015
Current assets
₩ 17,208,126 ₩ 16,947,132
Non-current assets
30,421,181 25,161,235
Current liabilities
7,957,076 6,703,532
Non-current liabilities
3,191,759 1,260,822
Equity attributable to:
36,480,472 34,144,013
Owners of the parent
35,982,390 33,639,387
Non-controlling interests
498,082 504,626
(2) Summarized consolidated statements of comprehensive income
(In millions of Korean won)
Samsung Display and its subsidiaries
2016 2015
Sales
₩ 26,816,450 ₩ 27,446,419
Net income
1,618,023 1,841,637
Other comprehensive income(loss)
721,849 (233,527)
Total comprehensive income attributable to:
2,339,872 1,608,110
Owners of the parent
2,343,120 1,565,566
Non-controlling interests
(3,248) 42,544

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 148 / 240
(3) Summarized consolidated statements of cash flows
(In millions of Korean won)
Samsung Display and its subsidiaries
2016 2015
Cash flows from operating activities
₩ 6,800,635 ₩ 7,458,783
Cash flows from investing activities
(9,163,528) (8,045,005)
Cash flows from financing activities
2,563,830 653,266
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents
10,061 (2,563)
Increase in cash and cash equivalents
210,998 64,481
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period
385,863 321,382
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period
596,861 385,863
35. Business Combination
Significant business combinations for the year ended December 31, 2016 are as follow:
(A) Acquisition of Joyent
Samsung Electronics America, the
Company’s subsidiary, acquired 100% of the equity shares of Joyent on June 24, 2016.
(1) Overview of the acquired company
Name of the acquired company
Joyent, Inc. and 2 subsidiaries
Headquarters location San Francisco, CA, USA
Representative director Scott Hammond
Industry Cloud services
(2) Purchase price allocation
(In millions of Korean Won)
Amount
I. Consideration transferred
₩ 185,343
II. Identifiable assets and liabilities
Cash and cash equivalents
1,556
Short-term financial instruments
116
Trade and other receivables
3,646
Property, plant and equipment
5,625
Intangible assets
22,208
Other assets
24,582
Trade and other payables
(10,979)
Total net identifiable assets
46,754
III. Goodwill (I – II)
₩ 138,589
Had Joyent been consolidated from January 1, 2016, revenues would have increased by ₩9,721 million and net income would
have decreased by ₩5,386 million on the interim consolidated statement of income. The revenue and net loss contributed by
Joyent since acquisition amount to ₩14,142 million and ₩5,690 million, respectively.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 149 / 240
(B) Acquisition of Dacor
Samsung Electronics America, the
Company’s subsidiary, acquired 100% of the equity shares of Dacor on September 7, 2016.
(1) Overview of the acquired company
Name of the acquired company
Dacor Holdings, Inc. and 4 subsidiaries
Headquarters location City of Industry, CA, USA
Representative director Charles Huebner
Industry Manufacture and sale of home appliances
(2) Purchase price allocation
(In millions of Korean Won)
Amount
I. Consideration transferred
₩ 176,800
II. Identifiable assets and liabilities
Cash and cash equivalents 2,092
Short-term financial instruments 834
Trade and other receivables 5,786
Inventory 9,323
Property, plant and equipment 646
Intangible assets 67,313
Other assets 3,731
Trade and other payables (8,936)
Other liabilities (4,549)
Total net identifiable assets 76,240
III. Goodwill (I – II)
₩ 100,560
Had Dacor been consolidated from January 1, 2016, revenues would have increased by ₩38,979 million and net income would
have decreased by ₩35,193 million on the interim consolidated statement of income. The revenue and net loss contributed by
Dacor since acquisition amount to ₩16,239 million and ₩1,682 million, respectively.
(C) Acquisition of Viv Labs
Samsung Research America, the
Company’s subsidiary, acquired 100% of the equity shares of Viv Labs on October 7, 2016.
(1) Overview of the acquired company
Name of the acquired company
Viv Labs, Inc.
Headquarters location San Jose, CA, USA
Representative director Dag Kittlaus
Industry Research of AI technology

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 150 / 240
(2) Purchase price allocation
(In millions of Korean Won)
Amount
I. Consideration transferred
₩ 238,930
II. Identifiable assets and liabilities
Cash and cash equivalents
10,325
Short-term financial instruments
67
Trade and other receivables
284
Inventory
-
Property, plant and equipment
30
Intangible assets
33,038
Other assets
-
Trade and other payables
(1,874)
Other liabilities
(5,543)
Total net identifiable assets
36,327
III. Goodwill (I – II)
₩ 202,603
Had Viv Labs been consolidated from January 1, 2016, net income would have decreased by ₩6,770 million on the interim
consolidated statement of income. Net loss contributed by Viv Labs since acquisition amount to ₩3,424 million.
36. Non-current Assets Held-for-Sale (Assets of disposal group)
(A) Summary
(1) Sale of Samsung Fine Chemicals
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the
Company entered into an agreement with Lotte Chemical to sell all of its shares in
Samsung Fine Chemicals. The transaction was completed in February 2016.
(2) Sale of Samsung Biologics
During the year ended December 31, 2016, the
Company entered into an agreement with Samsung Biologics to sell all of its
shares. The transaction was completed in November 2016.
(3) Sale of printing solutions business segment
During the nine months ended December 31, 2016, the management of the
Company decided to sell printing solutions business
segment to HP Inc. The contract was entered into on September 12, 2016, and the transaction is expected to be completed within
1 year upon regulatory approval.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 151 / 240
(B) Details of assets and liabilities reclassified as held-for-sale, as at
December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
(In millions of Korean Won)
2016 2015
Assets held-for-sale
Trade receivables
₩ 182,738
₩ -
Inventories 270,642
-
Other current assets 115,037
-
Property, plant and equipment 84,869
-
Intangible assets 124,571
-
Investment -
77,073
Other non-current assets 57,949
-
Total 835,806
77,073
Liabilities held-for-sale
Current liabilities 272,726
-
Non-current liabilities 83,662
-
Total
₩ 356,388
₩ -
(C) Details of cumulative income or expense recognized in other comprehensive income relating to the disposal group classified as
held-for-sale as of
December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
(In millions of Korean Won)
2016 2015
Gain on valuation of available-for-sale securities
₩ - ₩ 23,797
Foreign exchange translation adjustment (28,810) -
Total
₩ (28,810) ₩ 23,797
37. Events after the Reporting Period
On January 24, 2017, the board of directors approved the share buyback and retirement of common and preferred stock, with the
estimated total number of shares to be repurchased of 1.28 million (common stock 1.02 million, preferred stock 0.26 million). All
repurchased shares will be retired after the buyback is completed. The purchase period will end on April 24, 2017.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 152 / 240
3. Other Financial Information
A. Matters of Interest
(1) Restatement of Financial Statements: N/A
(2) Acquisitions and Divestments (Separate only)
There are no major merger transactions in the past three fiscal years. For information on the business combinations and
divestitures of subsidiaries, please refer to the notes on the business combination and assets held for sale (assets of
disposal group) of the consolidated financial statements.
Details of split
Company Name: S-Printing Solution Corp.
Location: 129 Samsung-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do
Purpose of split: Improve S-Printing Solution competitiveness
Approval of split: October 27, 2016 (extraordinary meeting of shareholders)
Date of split: November 1, 2016
(Unit: KRW million)
Company Account
Forecast Actual
1st Year 2nd Year
1st Year 2nd Year
Actual Difference Actual Difference
S-Printing
Solution
Sales 2,094 14,160 2,186 4.40% - -
Operating
Income
-29 -1,359 -61 111.48% - -
Net Income -67 -1,486 -10 -84.72% - -
Difference rate of operating income was more than 110% due to the year-end bonus payments and difference of net
income was more than 80% due to the foreign exchange differences and etc.
Details of the above statement can be found in the “Important Matters Report“, published at DART
(http://dart.fss.or.kr/).
Split of S-Printing Solution business was reported on a separate basis.
(3) Information on the accounting treatment of the sales of assets and contingent liabilities relating to the asset backed
securities
- Domestic: As of December 31, 2016, the Company provided a debt guarantee of KRW 36,825 million to its
employees who took debt from financial institutions in order to finance employee housing rental. The Company’s
housing rental debt guarantee limit is KRW 56,752 million. The Company has provided guarantees for borrowings
executed by Medicapital from Dime Investment and two other companies in the amount of KRW 2,264 million.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 153 / 240
- Overseas :
(Unit: USD thousand)
Company Relationship Creditor
Guarantee Expiry
Date
Transactions
Limit of
Guarantee
Beginning of
period
Increase Decrease End of period
SEA Subsidiary SMBC, etc. 2017-12-16 1,000,000
-
- 1,000,000
2,425,000
SEM Subsidiary Santander, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
546,000
SAMCOL Subsidiary
Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 66,333
17252
- 83,585
156,000
SEDA Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-18 -
-
- -
769,000
SECH Subsidiary
Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
178,000
SEPR Subsidiary BBVA, etc. 2017-12-16 58,033
10,706
- 68,739
180,000
SSA Subsidiary
Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 126,001
-
91,674 34,327
335,000
SEMAG Subsidiary SocGen, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
110,000
SETK Subsidiary
BTMU, etc. 2017-12-16 134,625
53242
- 187,867
590,000
SECE Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 1,180
-
1,180 -
110,000
SEEG Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 -
-
- -
50,000
SEIN Subsidiary
BNP, etc. 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
186,000
SJC Subsidiary
Mizuho Bank, etc. 2017-12-16 107,656
-
107,656 -
900,040
SRJ Subsidiary SMBC 2016-02-28 20,734
-
20,734 -
-
SEUC Subsidiary
Credit Agricole, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
175,000
SEDAM Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 110,408
-
9082 101,326
391,000
SECA Subsidiary
Nova Scotia 2017-10-10 -
-
- -
11,105
SELA Subsidiary
Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
30,000
SEEH Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
727,000
SERK Subsidiary BNP, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
345,000
SELV Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
10,000
SAPL Subsidiary
BOA, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
411,000
SEV Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
15,000
SAVINA Subsidiary
SCB, etc. 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
71,000
SET Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
30,000
SCIC Subsidiary
HSBC, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
350,000
SME Subsidiary
SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
110,000
SAMEX Subsidiary
Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
5,000
SEASA Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
1,000
SSAP Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 14,267
-
3985 10,282
30,000
Simpress Subsidiary BNP 2017-11-08 36,356
8,173
- 44,529
60,000
SEHK Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 -
-
- -
2,000
SEPM Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 115,493
-
28,623 86,870
125,000
Total 1,791,086
89,373
262,934 1,617,525
9,434,145
※ SEC requires BOD approval for individual guarantees exceeding 2.5% of total equity. When the guarantee amount is between
0.1% and/or less than 2.5%, the approval decision is delegated to the Management Committee.
Refer to 3.Litigation (XI. Other Information Related to Investment Protection) or the notes to the consolidated financial
statements for the information on contingent liabilities.
(4) Other matters requiring attention in relation to the use of the financial statements: N/A

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 154 / 240
B. Allowance for Bad Debt
The allowances for bad debts over the past 3 years are as follows:
Bad debt allowance by account
(Unit: KRW million, %)
Period Account Receivables Amount
Allowance Amount Allowance (%)
2016
Trade receivables 24,699,961
420,750 1.7%
Short-term loans 7,208
67 0.9%
Other receivables 3,546546
25,349 0.7%
Advances 1,442,219
2,281 0.2%
Trade receivables (Long-term) 4,563
139 3.0%
Other receivables (Long-term) 35,683
153 0.4%
Advances (Long-term) 175,211
1,369 0.8%
Long-term loans 173,068
7,849 4.5%
Total 30,084,459
457,957 1.5%
2015
Trade receivables 25,494,637
326,611 1.3%
Short-term loans 8,570
80 0.9%
Other receivables 3,400,227
47,564 1.4%
Advances 1,709,840
3,837 0.2%
Trade receivables (Long-term) 25,747
249 1.0%
Other receivables (Long-term) 185,667
1,726 0.9%
Advances (Long-term) 422,884
793 0.2%
Long-term loans 180,839
2,334 1.3%
Total 31,428,411
383,194 1.2%
2014
Trade receivables 24,972,069 277,459 1.1%
Short-term loans 9,650 118 1.2%
Other receivables 3,549,692 9,817 0.3%
Advances 1,993,788 4,318 0.2%
Trade receivables (Long-term) 35,944 329 0.9%
Other receivables (Long-term) 9,419 77 0.8%
Advances (Long-term) 176,949 793 0.4%
Long-term loans 176,232 1,246 0.7%
Total 30,923,743 294,157 1.0%
※ Receivables amount is based on net present value (Consolidated)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 155 / 240
Allowance for Bad Debt (Roll Forward)
(Unit: KRW million)
2016 2015 2014
1. Allowance for bad debts
(beginning balance)
383,194 294,157 329,853
2. Net Bad Debt Expense
(①-②±③)
29,843
11,373 49,349
① Bad Debt Expense
(Write-off)
31,334
14,149 50,705
② Bad Debt Recovered
1,491 2,776 1,356
③ Others
- - -
3. Bad debts expense 104,606
100,410 13,653
4. Allowance for bad debts
(Ending balance)
457,957
383,194 294,157
※ Based on consolidated financial statements.
- The guideline for Bad Debts Allowances
(1) Calculation of Bad Debts Allowances
Bad Debts are calculated based on write-off experiences and future expected bad debts.
(2) Calculation Method for Write-Off Experience Rate:
Experience rate of write-off: the actual write-off rate for the average receivables balance of previous three (3) years
Future expected bad debts: Cases of debtor bankruptcy, compulsory execution, death, or disappearance are reflected
in the bad debt allowance, ranging from 1% ~ 100% of the balance of trade-other receivable
[Bad Debt Allowance]
Situation Rate of Allowance
Dispute or Conflict 25%
Receivable through utilization of third party collection agency 50%
Receivable under litigation 75%
Customer filed or in the process of filing bankruptcy 100%

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 156 / 240
(3) Instruction: Write-off is recorded when trade receivables contain the following characteristics:
ㆍ Objective proof of bad debts, such as bankruptcy, compulsory execution, discontinuance of business, debtor’s death
or disappearance
ㆍ Legal action has failed or the right of collection is extinguished.
ㆍ When the collection agency gives as notice that collection is not possible.
ㆍ When the collateral is sold or insurance is received.
ㆍ The collection expenses exceed the amount of receivables.
The outstanding period of trade receivables
(Unit : KRW million)
Less than
6 months
6 months ~
1 year
1 year ~
3 years
More than
3 years
Total
Amount
24,480,590 31,331
156,425
36,178 24,704,524
Ratio
99.1% 0.1%
0.6%
0.2% 100.0%
* Receivables amount on net present value (consolidated)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 157 / 240
C. Inventory
- The inventory status by Division over the last three years is as follows:
(Unit: KRW million)
Division Category 2016 2015 2014 Note
CE
Finished Goods 2,182,776
1,851,491
1,946,482
Work In Process 116,636
77,940
80,122
Raw Material 1,887,460
1,697,398
1,566,121
Material In Transit 2,022,321
1,672,192
1,694,448
Total 6,209,193
5,299,021
5,287,173
IM
Finished Goods 2,032,004
1,924,116
2,210,160
Work In Process 531,628
347,780
279,861
Raw Material 2,851,438
2,471,314
2,751,331
Material In Transit 594,955
492,149
488,877
Total 6,010,025
5,235,359
5,730,229
DS
Semi-
Conductor
Finished Goods 871,428
1,598,617
777,450
Work In Process 3,796,746
4,740,937
3,677,543
Raw Material 541,573
505,226
419,398
Material In Transit 62,078
109,333
121,477
Total 5,271,825
6,954,113
4,995,868
DP
Finished Goods 299,208
398,342
409,516
Work In Process 444,831
483,084
244,324
Raw Material 375,611
265,206
281,223
Material In Transit 69,782
49,957
55,176
Total 1,189,432
1,196,589
990,239
DS
Total
Finished Goods 1,203,332
2,014,630
1,228,783
Work In Process 4,412,185
5,353,650
4,105,675
Raw Material 977,020
804,420
750,929
Material In Transit 135,230
162,897
178,218
Total 6,727,767
8,335,597
6,263,605
Total
Finished Goods 5,905,339
5,769,460
5,773,448
Work In Process 5,017,384
5,779,303
4,465,071
Raw Material 6,494,166
5,859,262
5,957,006
Material In Transit 936,614
1,403,769
1,121,979
Total 18,353,503
18,811,794
17,317,504
Inventory Ratio (%)– Total Assets
[Inventory ÷ Total Assets]
7.0%
7.8%
7.5%
Inventory Turn-over
[ Yearly CGS ÷{(Beginning of Inventory End of
Inventory)÷2}]
6.5
6.8
7.0
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 158 / 240
Inventory Counts
(1) Inspection Date
ㆍ End of May and November (twice a year)
ㆍ Performed check of the existence of inventories included in an accounting books and records on the inspection date
(2) Inspection Method
ㆍ Internal warehouse: Closed & Total Inspection
※ Sample check in semiconductor and DP inventory, SVC materials
ㆍ Outside warehouse
Performed check of the possession confirmation documents and sample tests at third party warehouse and Inventory in
transit
ㆍ External auditors join and observe the inspection and carry out sample test to check the existence and completeness.
Inventory Aging and Valuation
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Inventory as of December 31, 2016 is as follows:
(Unit : KRW million)
Category
Acquisition
Cost
Inventory
Valuation Reserve
Balance Note
Finished Goods
7,982,850 2,077,511 5,905,339
Work In Process
5,334,607 317,223 5,017,384
Raw Material
7,526,608 1,032,442 6,494,166
Material In Transit
936,614 - 936,614
Total
21,780,679 3,427,176 18,353,503
※ Prepared on a consolidated basis
D. Fair Value Estimation
Refer to 3. Financial Instruments by Category and 24. Financial Risk Management in 『Ⅲ. Financial Affairs』.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 159 / 240
E. List of Issued Debt Securities
Issued Debt Securities
(As of December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million, %)
Issuing
Company
Type of
Securities
Issuance
Method
Date of
Issuance
Total Nominal
Amount
Interest
Rate
Rating
(Rating Institution)
Maturity Date Payment Status
Management
Company
Samsung
Electronics
Corporate
Bonds
Public
Offering
1997.10.02 120,850 7.7 A+(S&P), A1(Moody's) 2027.10.01 Partial Redemption
Goldman Sachs
et al.
SEA
Corporate
Bonds
Public
Offering
2012.04.10 1,208,500 1.8 A+(S&P), A1(Moody's) 2017.04.10 Unredeemed
Goldman Sachs
et al.
Total - - - 1,329,350 - - - - -
Details and Compliance of the Bond Management Contract (Samsung Electronics)
(Base Date of Preparation: December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million, %)
Name of Security Date of Issuance Maturity Date Issued Amount
Settlement Date of
Bond Management
Contract
Debenture Management Company
US$ 100,000,000
7.7% Debenture
1997.10.02 2027.10.01 120,850 1997.10.02
The Bank of New York Mellon
Trust Company, N.A.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 160 / 240
Base Date of Implementation: December 31, 2016
Financial Ratios
Contract Details
Not applicable
Implementation Status Not applicable
Constraint on Collaterals
Contract Details
Less than 10% of net tangible assets
Implementation Status Compliant (there is no collateral for the relevant assets)
Constraint on Disposal of Assets
Contract Details
Certain requirements, such as transfer of obligations on the bond, must be satisfied to dispose all or
most of an asset
Implementation Status Compliant (disposal of assets accounted for 3.1% of the total during ’16)
Submission of Implementation Report Implementation Status Not applicable
※ The date of the bond management contract was signed on the same day as the Fiscal Agency Agreement; accordingly, the Bank of New York Mellon Trust
Company, N.A. is under the authority of the Fiscal Agent.
※ The exchange rate as of the base date has been applied.
※ The net tangible assets subjected to the limitation of collaterals are production facilities and stocks owned by the Company.
Main Details and Compliance of the Bond Management Contract (SEA)
(Base Date of Preparation : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million, %)
Name of Security
Date of
Issuance
Maturity Date Issued Amount
Date of Bond
Management
Contract
Debenture Management Company
US$1,000,000,000
1.75% Notes
2012.04.10 2017.04.10 1,208,500 2012.04.10 Citi Bank,.N.A., London branch

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 161 / 240
Base Date of Implementation: December 31, 2016
Financial Ratios
Contract Details
Not applicable
Implementation Status Not applicable
Constraint on Collaterals
Contract Details
Less than 10% of net tangible assets
Implementation Status Compliant (there is no collateral for the relevant assets)
Constraint on Disposal of Assets
Contract Details
Certain requirements, such as transfer of obligations on the bond, must be satisfied by the
guarantor to dispose all or most of an asset
Implementation Status Compliant (disposal of assets accounted for 3.1% of the total during ’16)
Submission of Implementation Report Implementation Status Not applicable
※ The date of the bond management contract was signed on the same day as the Fiscal Agency Agreement; accordingly, Citi Bank, N.A. London branch is under
the authority of the Fiscal Agent.
※ The exchange rate as of the base date has been applied.
※ The net tangible assets subjected to the limitation of collaterals are production facilities and stocks owned by the Company.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 162 / 240
Commercial Paper Balance
(Base Date : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million)
Maturity
Under 10
Days
Above 10 Days /
Under 30 Days
Above 30 Days /
Under 90 Days
Above 90 Days /
Under 180 Days
Above 180 Days /
Under 1 Year
Above 1 Year /
Under 2 Years
Above 2 Years /
Under 3 Years
Above 3
Years
Total
Balance
Public - - - - - - - - -
Private - - - - - - - - -
Total - - - - - - - - -
Asset-Backed Short Term Bond Unredeemed Balance
(Base Date : December 31, 2016)
Maturity
Under 10
Days
Above 10 Days /
Under 30 Days
Above 30 Days /
Under 90 Days
Above 90 Days /
Under 180 Days
Above 180 Days /
Under 1 Year
Total Issue Limit Balance Limit
Balance
Public- --- ----
Private- --- ----
Total - --- ----

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 163 / 240
Corporate Bond Unredeemed Balance
(Base Date : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million)
Maturity Under 1 Year
Above 1 Year /
Under 2 Years
Above 2 Years /
Under 3 Years
Above 3 Years /
Under 4 Years
Above 4 Years /
Under 5 Years
Above 5 Years /
Under 10 Years
Above 10 Years Total
Balance
Public 1,214,543 6,043 6,043 6,043 6,043 30,213 6,043 1,274,971
Private- -------
Total 1,214,543 6,043 6,043 6,043 6,043 30,213 6,043 1,274,971
※ The exchange rate as of the base date has been applied.
- Corporate Bond Unredeemed Balance (Samsung Electronics)
(Base Date : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million)
Maturity Under 1 Year
Above 1 Year /
Under 2 Years
Above 2 Years /
Under 3 Years
Above 3 Years /
Under 4 Years
Above 4 Years /
Under 5 Years
Above 5 Years /
Under 10 Years
Above 10
Years
Total
Unredeemed
Balance
Public 6,043 6,043 6,043 6,043 6,043 30,213 6,043 66,471
Total 6,043 6,043 6,043 6,043 6,043 30,213 6,043 66,471
※ The exchange rate as of the base date has been applied.
- Corporate Bond Unredeemed Balance (SEA)
(Base Date : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million)
Maturity
Under 1
Year
Above 1 Year /
Under 2 Years
Above 2 Years /
Under 3 Years
Above 3 Years /
Under 4 Years
Above 4 Years /
Under 5 Years
Above 5 Years /
Under 10 Years
Above 10
Years
Total
Unredeemed
Balance
Public 1,208,500 - - - - - - 1,208,500
Total 1,208,500 - - - - - - 1,208,500
※ The exchange rate as of the base date has been applied.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 164 / 240
Hybrid Bond Outstanding Balance
(Base Date : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million)
Maturity Under 1 Year
Above 1 Year /
Under 5 Years
Above 5 Years
/ Under 10
Years
Above 10
Years / Under
15 Years
Above 15
Years / Under
20 Years
Above 20
Years / Under
30 Years
Above 30
Years
Total
Unredeemed
Balance
Public --------
Private --------
Total --------
Contingent Convertible Bond Outstanding Balance
(Base Date : December 31, 2016) (Unit : KRW Million)
Maturity
Under 1
Year
Above 1
Year / Under
2 Years
Above 2
Years /
Under 3
Years
Above 3
Years /
Under 4
Years
Above 4
Years /
Under 5
Years
Above 5
Years /
Under 6
Years
Above 10
Years /
Under 20
Years
Above 20
Years /
Under 30
Years
Above 30
Years
Total
Unredeemed
Balance
Public - ---------
Private - ---------
Total - --------

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 165 / 240
IV. Auditor’s Report
1. Introduction
Samil PwC has audited the financial year end consolidated/separate financial position of the Company as of December 31,
2016, and the related financial year end consolidated/separate statements of income and comprehensive income for the
year ended December 31, 2016, and the consolidated/separate statements of changes in equity and cash flows for the year
ended December 31, 2016. Nothing has come to attention that causes them to believe the accompanying year end
consolidated/separate financial statements are not presented fairly, in all material respects, in accordance with the K-IFRS.
Samil PwC also conducted audits on the consolidated/separate financial statement of financial position of the Company as
of December 31, 2014 and 2015, and the related consolidated/separate statements of income, comprehensive income,
changes in equity and cash flows for the year then ended and expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial
statements. There are 169 subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016. There are 13 newly incorporated/acquired entities, and 11
of them, such as Stellus Technologies, appointed PwC as the auditor and 2 of them, such as SVIC #32, appointed Deloitte
Anjin as external auditor at their own decision.
Period end Group Auditor Audit(Review) Opinion Remarks
31 December 2016 Samil PwC Not applicable Not applicable
31 December 2015 Samil PwC Unqualified Not applicable
31 December 2014 Samil PwC Unqualified Not applicable
< Audit(Review) plan for the year ended December 31, 2016 >
Review Period Planned dates
2016 1Q
Pre-review 2016.03.07 ~ 2016.03.25
Review 2016.04.07 ~ 2016.05.13
2016 2Q
Pre-review 2016.06.07 ~ 2016.06.24
Review 2016.07.07 ~ 2016.08.12
2016 3Q
Pre-review 2016.09.07 ~ 2016.09.23
Review 2016.10.07 ~ 2016.11.14
System and Internal Control Audit
2016.06.22 ~ 2016.07.29
Audit Procedures
2016.12.05 ~ 2016.12.23
Completion of final audit procedures
2017.01.04 ~ 2017.02.27

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 166 / 240
[Audit Contract Description] (In millions of Korean won)
Fiscal Year Group Auditor Description Compensation Total Hours
Year ended
December 31,
2016
Samil PwC - Review of the interim consolidated/separate financial statements 3,690
43,999
Year ended
December 31,
2015
Samil PwC
- Review of the interim consolidated/separate financial statements
- Audit on consolidated/separate financial statements
3,690
43,928
Year ended
December 31,
2014
Samil PwC
- Review of the interim consolidated/separate financial statements
- Audit on consolidated/separate financial statements
3,690
43,411
Samil PwC has performed non-audit services and has been paid KRW 1,353 million by the Company for the year ended
December 31, 2016.
[Non-Audit Service Contract Description] (In millions of Korean won)
Fiscal Year Contract Date Non-audit Service Description Period for Service Compensation
Note
Year ended
December
31, 2016
December 2016 Tax Advisory 2016.12~2016.12 220
February 2016 Custom Tax Advisory 2016.01~2016.12 1,133
Subtotal 1,353
Year ended
December
31, 2015
June 2014 Incorporation, M&A and Divestiture Advisory 2015.01~2015.12 503
May 2014 Tax Advisory 2015.01~2015.12 47
Subtotal 550
Year ended
December
31, 2014
September 2013 Incorporation, M&A and Divestiture Advisory 2014.01~2014.12 1,161
August 2013 Custom Tax Advisory 2014.01~2014.12 533
October 2013 Process Improvement Advisory 2014.01~2014.12 996
Others 297
Subtotal 2,987
2. Regarding Internal Control
Samil PwC has reviewed management's report on the operations of the Internal Accounting Control System ("IACS") of
the Company as of December 31, 2016 and nothing has come to attention that causes them to believe that management's
report on the operations of the IACS is not presented fairly, in all material respects, in accordance with IACS standards.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 167 / 240
V. Management Discussion and Analysis
1. Note on Forward-Looking Statements
This annual report includes forward-looking statements that relate to future events and can be generally identified by
phrases containing words such as “believes,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “foresees,” “forecasts,” “estimates” or other words
or phrases of similar meaning. These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and may
involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may affect our actual results, performance,
achievements or financial position, making them materially different from the actual future results, performance,
achievements or financial position expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. Unless otherwise specified,
all data presented in this report is from our consolidated financial statements.
Uncertain events that could positively or negatively affect the Company’s management condition and financial
performance include:
• Trends of financial markets domestically and abroad, including changes in exchange rates and interest rates
• The Company’s strategic decision making, including disposals and purchases of businesses
• Unexpected sudden changes in core businesses such as CE, IM, Semiconductor, and DP
• Other changes domestically and abroad that can affect management condition and financial performance
The Company assumes no obligation to revise or update this report to reflect risks or uncertainties that arise after the
reporting period.
2. Overview
In 2016, the global economy continued to slow down and faced heightened uncertainties due to U.S. interest rate hikes
and the impact of Brexit. Under these circumstances, South Korea’s economic slowdown continued, with sluggish exports
and domestic consumption hindering growth.
Despite intensified competition over major products, the Company achieved solid earnings driven by the support of our
shareholders and tireless efforts of all of our executives and employees. We recorded sales of KRW 202 trillion and
operating profit of KRW 29 trillion on a consolidated basis. On a stand-alone basis, SEC posted sales of KRW 134 trillion
and operating profit of KRW 14 trillion.
In financial terms, the debt-to-equity ratio is 35.9%, the capital adequacy ratio is 73.6%, and ROE is 12.2% on a
consolidated basis. On a stand-alone basis, SEC’s debt-to-equity ratio is 27.1%, the capital adequacy ratio is 78.7%, and
ROE is 8.5%. Therefore, we have maintained a solid financial structure. Our company’s brand value reached USD 51.8
billion in 2016, a 14% increase, and was ranked the world’s 7th largest company for its third consecutive year (Oct ’16
Interbrand).
In terms of business, we solidified our industry leadership and maintained a dominant market share by building on our
technological competence and launching the world’s first 10nm-class DRAM and by expanding sales of SUHD TVs and
Curved TVs based on our differentiated image quality and design strengths.
In 2017, we expect that the uncertainties weighing on the global economy will continue to increase, caused by further
interest rate increases in the U.S. this year, the impact of Brexit on the EU, as well as rising protectionism under the new
U.S. government. Under these circumstances, we project that competition in our main product markets will become even
fiercer. Also, competitors’ heavy investments and their aggressive moves to reduce the technology gap pose a greater
challenge to our company.
In a response to such ongoing changes within business conditions and a challenging environment, we will work to
strengthen the technological competitiveness of our business. We will save no effort to lay the strong base for seizing
future opportunities, by developing new businesses with great potential through strategic M&A and R&D investment.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 168 / 240
3. Financial Position and Performance (Consolidated)
A. Financial Position
(Unit: KRW million)
Classification 2016 2015 Increase/decrease % change
Total assets
262,174,324 242,179,521 19,994,803 8.3%
Current assets
141,429,704 124,814,725 16,614,979 13.3%
- Cash and cash equivalents
32,111,442 22,636,744 9,474,698 41.9%
- Short-term financial instruments
52,432,411 44,228,800 8,203,611 18.5%
- Available-for-sale financial assets
3,638,460 4,627,530
△989,070 △21.4%
- Trade and other receivables
24,279,211 25,168,026
△888,815 △3.5%
- Inventories
18,353,503 18,811,794
△458,291 △2.4%
- Other current assets
10,614,677 9,341,831 1,272,846 13.6%
Non-current assets
120,744,620 117,364,796 3,379,824 2.9%
- Available-for-sale financial assets
6,804,276 8,332,480
△1,528,204 △18.3%
- Associates and joint ventures
5,837,884 5,276,348 561,536 10.6%
- Property, plant and equipment
91,473,041 86,477,110 4,995,931 5.8%
- Intangible assets
5,344,020 5,396,311
△52,291 △1.0%
- Other non-current assets
11,285,399 11,882,547
△597,148 △5.0%
Total liabilities
69,211,291 63,119,716 6,091,575 9.7%
Current liabilities
54,704,095 50,502,909 4,201,186 8.3%
Non-current liabilities
14,507,196 12,616,807 1,890,389 15.0%
Total equity
192,963,033 179,059,805 13,903,228 7.8%
Total liabilities and equity
262,174,324 242,179,521 19,994,803 8.3%
Capital adequacy ratio
73.6% 73.9%
△0.3%
-
Debt-to-equity ratio
35.9% 35.3% 0.6% -
Inventory turnover
6.5 6.8
△0.3
-
※ Presented in accordance with Korean International Financial Reporting Standards (“K-IFRS”)
[ᇞ represents negative (-) balance]

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 169 / 240
- Samsung Electronics’ total assets in 2016 were KRW 262.174 trillion, an increase of KRW 19.995 trillion (8.3%) from
the previous year. This includes an increase of KRW 5.0 trillion in property, plant and equipment from large-scale
facilities investment, as well as an increase of KRW 9.5 trillion in cash and cash equivalents.
- Total liabilities were KRW 69.211 trillion, an increase of KRW 6.092 trillion (9.7%) from the previous year. This
includes an increase of KRW 4.201 trillion (8.3%) in current liabilities and an increase of KRW 1.890 trillion (15.0%) in
non-current liabilities.
- Total equity was KRW 192.963 trillion, an increase of KRW 13.903 trillion (7.8%) from the previous year. Retained
earnings increased by KRW 7.954 trillion primarily from net income of KRW 22.726 trillion.
- In terms of financial ratios, the Company maintained the financial structure of a world-class company as the capital
adequacy ratio decreased by 0.3% from the previous year to 73.6% and the debt-to-equity ratio increased by 0.6% from
the previous year to 35.9%.
B. Performance
(Unit: KRW million)
Classification 2016 2015 Increase/decrease % change
Sales
201,866,745 200,653,482 1,213,263 0.6%
Cost of sales
120,277,715 123,482,118
△3,204,403 △2.6%
Gross profit
81,589,030 77,171,364 4,417,666 5.7%
Selling and administrative expenses
52,348,358 50,757,922 1,590,436 3.1%
Operating profit
29,240,672 26,413,442 2,827,230 10.7%
Other revenue
3,238,261 1,685,947 1,552,314 92.1%
Other expenses
2,463,814 3,723,434
△1,259,620 △33.8%
Gain on valuation using the equity method of accounting
19,501 1,101,932
△1,082,431 △98.2%
Financial revenue
11,385,645 10,514,879 870,766 8.3%
Financial expenses
10,706,613 10,031,771 674,842 6.7%
Income before income tax expense
30,713,652 25,960,995 4,752,657 18.3%
Income tax expense
7,987,560 6,900,851 1,086,709 15.7%
Net income
22,726,092 19,060,144 3,665,948 19.2%
※ Presented in accordance with Korean International Financial Reporting Standards (“K-IFRS”)
[ᇞ represents negative (-) balance]

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 170 / 240
- In 2016, revenue increased by 0.6% to KRW 202 trillion. This strong result was made possible by increased sales of
semiconductors such as memory products, despite stopping the sales and production of Galaxy Note 7.
- Operating profit increased by 10.7% to KRW 29.241 trillion, income before income tax expense increased by 18.3% to
KRW 30.714 trillion, and net income increased by 19.2% to KRW 22.726 trillion.
Performance by division
[Unit: KRW million]
Classification Division Business
2016 2015
% change
Amount Share Amount Share Amount (%)
Revenue
CE 47,045,423 23.3% 46,895,411 23.4% 150,012 0.3%
IM 100,302,112 49.7% 103,554,255 51.6%
△3,252,143 △3.1%
DS
Semiconductor 51,157,002 25.3% 47,586,752 23.7% 3,570,250 7.5%
DP 26,928,644 13.3% 27,486,861 13.7%
△558,217 △2.0%
Total 78,148,203 38.7% 75,026,114 37.4% 3,122,089 4.2%
Overall revenue
201,866,745 100.0% 200,653,482 100.0% 1,213,263 0.6%
Operating profit
CE 2,638,002 9.0% 1,254,187 4.7% 1,383,815 110.3%
IM 10,807,569 37.0% 10,142,022 38.4% 665,547 6.6%
DS
Semiconductor 13,595,004 46.5% 12,787,297 48.4% 807,707 6.3%
DP 2,226,626 7.6% 2,295,367 8.7%
△68,741 △3.0%
Total 15,850,986 54.2% 14,887,262 56.4% 963,724 6.5%
Overall operating profit
29,240,672 100.0% 26,413,442 100.0% 2,827,230 10.7%
[ᇞ represents negative (-) balance]
[CE Division]
- The CE division’s 2016 revenue increased by 0.3% from the previous year to KRW 47.045 trillion. Consolidated
operating profit increased by KRW 1.384 trillion compared to the previous year to KRW 2.638 trillion.
- The CE division is on the path of stable growth, focusing on our strategic products equipped with our industry leading
premium technologies, such as high picture quality SUHD TVs, Family Hub refrigerators, Active/AddWash washing
machines, and Breeze-free air conditioners.
Our TV business maintained the top position in the overall TV market for the 11th consecutive year, based on our
outstanding technology and design strengths. We continued to widen the gap with our competitors and, as a result,
solidified our market leading position.
In 2017, we will continue to maintain our market leadership in the industry by leading the premium market with our
QLED TV product which provides superior image quality.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 171 / 240
[IM Division]
- The IM division’s revenue for 2016 was KRW 100.302 trillion, decreased by 3.1% compared to the previous year, but
operating profit increased by 6.6% to KRW 10.808 trillion.
- In terms of the IM division business, global shipments of our flagship Galaxy S7 smartphone increased and our mid to
low-range products Galaxy A and J series were well received in the market. Unfortunately, we had to halt sales of our
premium Note 7 smartphone launched in the second half of the year due to quality issues.
In 2017, we will focus on strengthening the premium market leadership based on our unique form factor as well as
differentiated design/UX, and constantly strengthen our position in the mid to low-range markets by offering a diverse
line-up of products. In addition, we will work hard to meet the different needs of consumers with better usability and
more convenient user experience through accessories and wearable devices like Gear S3 and VR.
Along with these efforts, we will continue to invest in new growth engines to differentiate our products and services, in
areas such as Cloud, Intelligence, Mobile B2B, as well as Mobile Payment such as Samsung pay. We will build on the
industry’s Top R&D capability and grow as a global leading company which constantly delivers new value to our
consumers. While constantly pursuing product innovation, we will make sure that consumer safety is our top priority. By
implementing multi-layer safety measures, conducting a thorough pre-safety check, and establishing an organization
devoted to safety verification, we will strive to ensure that a similar quality-related issue does not happen again. We will
be committed to building trust from the market and our consumers.
[Semiconductor]
- The semiconductor business’s 2016 revenue increased by 7.5% from the previous year to KRW 51.157 trillion.
Operating profit increased by 6.3% compared to the previous year to KRW 13.595 trillion.
- The memory business achieved a record high result by enhancing process technology, reducing cost, and expanding
shipments of more profitable products, based on stable demands from major mobile and server customers. Also, we
are focused on securing next-generation technological leadership through continuous investment.
- The The DRAM business environment gradually turned into a supply shortage period from a state of oversupply, as
overall demand increased with the launch of new mobile products and other suppliers were slow in developing high-
performance and high-quality products. Under these circumstances, a heavy demand on the Company is likely to
continue for an extended period of time. We unveiled the industry’s first 10nm-class DRAM products in the fourth
quarter of 2016 and secured a competitive position at least a year ahead of competitors in terms of technology
development capability. Furthermore, we are making various efforts to solidify the leadership position in the DRAM
market through methods such as the ongoing work on the differentiated products based on 10nm-class technology and
the development of next-generation DRAMs.
The demand for NAND is expected to increase as more NAND is included in new smartphones and the ever-increasing
adoption of SSDs (solid state drives) continues, and as a resultwe expect the chip market to experience a supply shortage
as suppliers are reaching the limits in migrating to finer processes and competitors are slow in expanding Vertical
NAND production. We are mass producing both planar and vertical NANDs in order to address the customer demand for
various NAND products in a timely manner. In particular, the Company is mass producing the 3rd generation of Vertical
NAND, which is ahead of its competitors in terms of technology and simultaneously entering the premium market by
applying the products to high-performance SSDs. we are also expanding high-quality 3bit MLC products to maximize
cost competitiveness
In 2017, growth in the memory semiconductor market is expected to continue. In order to continue to lead as the No. 1
memory maker, the Company will expand on differentiated products based on advanced processes and address demands
from each application’s market by taking advantage of our diverse product line-ups.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 172 / 240
- For the System LSI business, the growth has mostly come from mobile products, but we expect the markets for mobile
products such as smartphones and tablets to slow down in 2017. However, the overall demand is projected to stay flat,
due to an increased demand from newly forming markets, such as IoT, wearable, automotive electronics components,
health care and others.
We are also witnessing an increasing demand for high-resolution, high-quality and differentiated image sensors from
companies seeking to differentiate their mobile products. Based on our advanced technologies like dual pixels, we are
leading the CIS product markets for mobile devices.
We have advanced processes and manufacturing technology over our competitors that enable us to lead the foundry
industry. Production demand from fabless customers continue to increase.
[DP]
- The DP division’s revenue in 2016 decreased by 2.0% from the previous year to KRW 26.929 trillion. Operating profit
decreased by 3.0% compared to the previous year to KRW 2.227 trillion.
- We are focused on strengthening the competitiveness of the OLED business through increasing production yields,
improving cost competitiveness and enhancing collaboration with customers. In the mobile display market, the demand
for OLED panel is projected to continuously increase, driven by the demand from smartphone makers who seek to
differentiate their products. Further, the growing trend towards large-sized and high-resolution screens will continue and
demand for flexible displays will further increase. We will diversify the product line-ups of mid- to small-sized OLED
panels and expand our customer base. At the same time, we will expand shipments of flexible products.
This year, we will strive to develop new technologies and make strategic investments in order to respond quickly to
paradigm shifts of the emerging IT industries including IoT, AI, and automotive electronics while securing a leading
position in the next-generation markets.
Along with our efforts to strengthen our business competitiveness, we will undertake a thorough review on the existing
systems and practices in all areas of our business in order to build a robust risk management system.
We expect various uncertainties to persist throughout this year, but we will continue our effort to widen the gap with
competitors through continuous technology innovation and business advancement while striving to better understand the
market and our customers’ needs through in-depth reviews and creating new values. By doing so, we hope to make 2017
another year for strong growth.
C. New businesses
N/A
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 173 / 240
D. Changes in Organizational Structure
In December 2009, following an organizational change, the Company was reorganized from a two-divisional system
(DMC and DS) to a system of seven independent business units. Additionally, the total number of regional headquarters
increased to 10, as the Africa regional headquarters was newly established.
In April 2010, the Digital Imaging business unit was added through a merger with Samsung Digital Imaging, increasing
the total number of business units to eight. In December 2010, an overseas semiconductor division was changed from a
subsidiary to a regional headquarters.
In July 2011, the Company established the DS business headquarters to reinforce synergies in the component business. In
December 2011, following an organizational change, the DMC division was re-established and the Company returned to a
two-divisional system (DMC and DS).
In April 2012, the LED business unit was added through a merger with Samsung LED.
In May 2012, the Japan regional headquarters was established under the DS division.
In December 2012, following an organizational change, the CE and IM businesses were upgraded to individual division
status, and the IT Solution business was divided into the Printing Solution and Computer businesses. The Printing
Solution business was incorporated into the CE division, and the Computer business was integrated into the Mobile
business under the IM division. The Medical Device business team was upgraded to a business unit within the CE
division.
In December 2013, the Digital Imaging business was changed to a team unit, and then was integrated with the Mobile
business.
In December 2015, the LED business was reorganized and converted into a team unit.
(Refer to 『2. Company History』 of 『I. Corporate Overview』 for more details about changes in the organizational
structure.)
E. Foreign Exchange Risk
The Company is exposed to foreign exchange risks of currencies, including USD, in carrying out business activities.
Uncertainty related to exchange rates could influence business transactions, assets and liabilities in the future. In particular,
as the Company exports more than it imports, won cash flow can be negatively impacted when the won is strong. As such,
the Company focuses on minimizing foreign exchange risk by matching foreign currency income and expenditure and
does not hedge foreign currencies using derivatives. In particular, macroeconomic factors such as a fall in KRW/USD
exchange rate and global policies to move away from ultra-low interest rates can negatively impact the Company’s
profitability.
F. Recognition of Asset Impairment Loss
The Company conducts an annual review of asset impairment loss, and the determination of recoverable amount of a
CGU (cash generating unit) was based on the calculation of value in use. The use of value was calculated on assumption
regarding BTCF (before tax cash flow), based on the financial budget for the next five years approved by the management
committee. In calculating terminal-year cash flow for period that exceeds the term, assumption of fixed average growth
(does not exceed industry average) was used.
(Refer to 『2. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements』 of 『III. Financial Affairs』 for more details about asset
impairment loss)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 174 / 240
4. Liquidity, Financing, and Expenditure
As of the end of 2016, the Company has KRW 88.182 trillion of liquid funds.
These liquid funds include i) cash and cash equivalents, ii) short-term financial instruments, and iii) short-term available-
for-sale securities. This balance increased by KRW 16.689 trillion from KRW 71.493 trillion at the end of the previous
period.
The Company’s short-term borrowings (including alternatives for liquidity) are KRW 13.980 trillion, an increase of KRW
2.603 trillion from KRW 11.377 trillion of the end of the previous year. Long-term borrowings are KRW 1.303 trillion, a
decrease of KRW 194 billion from KRW 1.497 trillion of the end of the previous year.
The Company’s net cash (liquid funds - borrowings) is KRW 72.900 trillion, which is an increase of KRW 14.281 trillion
from KRW 58.619 trillion of the end of the previous period.
The Company has ample liquidity according to the liquidity assessment index of the global credit rating agency Moody’s.
The Company’s cash coverage (liquid funds/borrowings), which is a major liquidity index that Moody’s uses, corresponds
to the highest level, Aaa.
2016 2015 Note
Cash Coverage
(Liquid funds/borrowings)
577% 555%
Moody's rating
Aaa : >100%
5. Other Information for Investment Decision Making
A. Significant accounting policies and estimation
- Refer to 『2. Note to Consolidated Financial Statements』 in 『III. Financial Affairs』 for significant accounting
policies and estimates.
B. Environment and employees
- Refer to 『5. Sanctions and others』 in 『XI. Other information』 for environmental sanctions or administrative actions.
- No significant changes in employee positions during this period.
C. Legal regulations
- Refer to 『5. Sanctions and others』 of 『XI. Other information』 for major legal regulations on the Company’s
businesses.
D. Derivatives and risk management policy
- To manage exchange rate risk, overseas companies enter into currency forwards which are denominated in the trading
currency of a foreign currency position as opposed to the companies’ reporting currencies. Overseas offices buy or sell
currency forwards with less than one year maturity via a bank to avert risk.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 175 / 240
VI. Corporate Governance
1. Board of Directors
A. Overview of Board of Directors
As of December 31, 2016, the Board of Directors (BOD) consists of nine (9) directors, four (4) of whom are executive
directors (Oh-Hyun Kwon, Boo-Keun Yoon, Jong-Kyun Shin, and Jae-Yong Lee) and five (5) independent directors (In-
Ho Lee, Han-Joong Kim, Kwang-Soo Song, Byeong-Gi Lee, and Jae-Wan Bahk).
The Board has six (6) committees as follows: Management Committee, Audit Committee, Independent Director
Recommendation Committee, Related Party Transactions Committee, Compensation Committee, and CSR Committee.
B. The BOD Agendas considered and voting results
Date Agenda Results
Independent directors
In-Ho
Lee
Han-
Joong
Kim
Kwang-
Soo
Song
Byeong
-Gi
Lee
Eun-
Mee
Kim
Jae-
Wan
Bahk
Jan 28,
2016
① Approval of FY2015 financial statements and annual business
report
② Buyback and cancellation of treasury stocks
③ Disposal of Samsung Card shares
④ Approval of FY2016 business plan
⑤ Appointment of compliance officer
※
Reported Item
① Report on the internal accounting management system
② Assessment of the internal accounting management system
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
Absent
Absent
Absent
Absent
Absent
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
-
-
Feb 12,
2016
① Decision to convene the 47
th
(FY2016) AGM
② Decision of the 47th AGM agenda items
- report items:
1) FY2015 annual audit report
2) FY2015 annual business report
- Item 1: Approval of FY2015 financial statements, including
balance sheet, income statement, and the statement
of appropriation of retained earnings, etc.
-Item 2: Appointment of Directors
Item 2-1: Appointment of Independent Directors
Item 2-1-1: Appointment of In-ho Lee as an Independent
Director
Item 2-1-2: Appointment of Kwang-soo Song as an
Independent Director
Item 2-1-3: Appointment of Jae-wan Bahk as an Independent
Director
Item 2-2: Appointment of Executive Directors
Item 2-3: Appointment of Audit Committee members
- Item 3: Approval of remuneration limit for Directors
- Item 4: Approval of amendments to the Articles of Incorporation
③ Approval of changes in large-scale goods and services
transactions in 2016
※
Reported Item
① Report on the results of compliance review
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
Mar 11,
2016
① Revision to BOD regulations
② Appointment of BOD Chairman
③ Appointment of CEO and Directors
④ Appointment of BOD Committee members
⑤ Setting the remuneration of directors
⑥ Cancellation of real estate lease contracts with Samsung Life Insurance
⑦ Donation
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
Absent
Absent
Absent
Absent
Absent
Absent
Absent
For
For
For
For
For
For
For

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 176 / 240
Apr 28,
2016
① Approval of the 48th 1Q16 financial statements and business report
② Buyback and cancellation of treasury stocks
③ Property leasing contract with Samsung Life Insurance
④ Acquisition of Samsung Biologics shares
⑤ Donation to Sungkyunkwan University
⑥ Approval of holding a concurrent position as Executive Director in
Samsung Display
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
-
-
-
For
For
For
For
For
For
May 20,
2016
① Property leasing contract with Samsung Display
② Approval of Greenhouse gas emissions trading with Samsung
Display
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
For
For
Jul 28,
2016
① Approval of the 48th 1H16 financial statements, half-year business
report and June quarterly dividend
② Buyback and cancellation of treasury stocks
③ Revision to management committee regulations
④ Revision to CSR committee regulations
⑤ Application for property insurance
⑥ Application for Venture Capital Union
A
pproved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
-
-
-
For
For
For
For
For
For
Sep 12,
2016
① Disposal of Printing Solutions Business
② Approval of the Printing solutions business Spin-off
③ Decision to convene the Extraordinary General Shareholders
Meeting (EGM)
④ Decision of the EGM agenda items
- report item: audit report
- Item 1: Approval of the Printing solutions business Spin-off
- Item 2: Appointment of Jae-Yong Lee as an Executive director
⑤ Closing of shareholder register and the record date for EGM
⑥ Disposal of Samsung Biologics shares
A
pproved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
-
-
-
For
For
For
For
For
For
Oct 27,
2016
① Approval of the 3Q16 financial statements and business report
② Participation in Samsung Heavy Industries rights offering
③ Purchase of shares of Cheil Worldwide
④ A property leasing contract with Samsung Securities
⑤ Sale of real estate to Samsung Life Insurance
⑥ Establishment and operation of Lifelong Learning center
⑦ Application for Venture Capital Union
⑧ Donation to Samsung Life Public Welfare Foundation
A
pproved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
Nov 2,
2016
① Report and disclosure of Spin-off Completion of Printing Solutions
Business
② Revision to BOD regulations
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
For
For
Nov 14,
2016
① Acquisition of Harman
Approved
For For For For - For
Nov 29,
2016
① Approval of transactions with affiliate person(s)
② Payment of retirement pensions
③ Approval of mid to long-term shareholder value enhancement plans
④ Purchase of facility of Samsung Display
※
Reported Item
① Report on the results of compliance review
A
pproved
Approved
Approved
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
-
-
-
-
For
For
For
For

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 177 / 240
C. The Committees of BOD
(1) Composition of the BOD Committees as of December 31, 2016
Committee Name Members Member Name
Responsibility and
Authority
Management
3 Executive
Directors
Oh-Hyun Kwon, Boo-Keun Yoon,
Jong-Kyun Shin
See description below
Related Party
Transactions
3 Independent
Directors
In-Ho Lee, Han-Joong Kim,Kwang-Soo Song
Compensation
3 Independent
Directors
Kwang-Soo Song, In-Ho Lee, Byeong-Gi Lee
CSR
5 Independent
Directors
Byeong-Gi Lee, In-Ho Lee, Han-Joong Kim,
Kwang-Soo Song, Jae-Wan Bahk
※ The Audit Committee and Independent Director Recommendation Committee were excluded according to Corporate Disclosure
Guidelines set forth by the Financial Supervisory Service Authority of South Korea.
i) The Management Committee
- Responsibility: The Management Committee deliberates and decides on matters specified by the BOD regulations and
resolutions or specifically delegated by the BOD. The composition and operation of the management
committee are determined by the BOD.
- Authority
The Management Committee deliberates and decides on the following matters:
(A) General management
1. Annual or mid to long-term management policy and strategy
2. Key management strategy
3. Business planning and restructuring
4. Establishment, relocation, and withdrawal of overseas branch and corporation
5. Initiating cooperation such as strategic partnership with foreign companies
6. Acquisition or disposal of domestic and overseas subsidiaries
(Provided that the value of transaction exceeds 0.1% of total equity)
7. Other major management matters
8. Establishment, relocation, and withdrawal of branches and operations
9. Appointment or dismissal of supervisors
10. Suspension or shutdown of production over 5% of the total production in the recent year
11. Licensing agreements and technology transfer, partnership in regards to technology of over 0.5% of the total equity
12. Acquisitions and transfers of patents related to new material and new technology of over 0.5% of the total equity
13. Collection and destruction of products corresponding to over 5% of the total sales in the recent business year
14. Contracting for over 5% of the total sales in the recent business year
15. Contracting or canceling of single sales agency and suppliers over 5% of the total sales in the recent business year
16. Set basic principles of organization management
17. Decision making on basic principles and any changes related to wages, bonus, and fringe benefits
18. Appointments, dismissals and changes of transfer agent
19. Closing of shareholder register and setting reference date
20. Establishing corporate guidelines for business and management related activities
21. Donations over KRW 50 billion per donation. Donation to related parties between KRW 3 billion and KRW 5 billion
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 178 / 240
(B) Matters related to Finance
1. Acquisitions or disposals of equity investments with a value between 0.1% and/or less than 2.5% of the total equity
2. Direct overseas investments with a value of over 0.1% and/or less than 2.5% of the total equity
3. New debt guarantee (excluding extension of period) or collateral issuance with a value of over 0.1% and/or less
than 2.5% of the total equity
A. Collateral: Only in the case of providing collateral for others
B. Guarantee: Excludes performance guarantee (e.g., bid, contract, defect, difference guarantee) and tax
payment guarantee
4. New credit agreement contract (excluding extension of period) with a value of over 0.1% and/or less than 5% of
the total equity
5. Approval of related party transactions:
Related party transactions with affiliates involving cash (loans and payments), equity (stocks and bonds) or
assets (such as real estate and intangible property rights) with a value between KRW 3 billion and/or less than
KRW 5 billion, as defined in the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act
※ Excluding cases where existing contracts are renewed without significant change.
6. Issuance of Corporate Bond
7. Acquisition and disposal of real estate with a value of over 0.1% of the total equity, provided that the transaction
is with the third party
8. Any matters that the CEO deems necessary and important for the business (e.g., CAPEX)
(C) All other matters except for those delegated to the BOD and other committees in accordance with BOD regulations
ii) Related Party Transactions Committee
- Responsibility: Improve management transparency through establishment of a voluntary compliance system
- Authority
1) Right to receive reports on related party transactions:
The Committee can request reports on related party transactions with affiliates
※ According to the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act, the Related Party Transactions committee is
permitted to conduct preliminary reviews and approves on related party transactions over KRW 5 billion and
other transactions that are deemed as significant.
2) Right to order ex officio investigation of related party transactions
3) Right to propose corrective measures for related party transactions
iii) Compensation Committee
- Responsibility: Provide transparent and objective decision making process related to remuneration of directors
- Authority
1) Propose remuneration limit of directors at annual general shareholders’ meeting
2) Establish the director remuneration system
3) Other matters delegated by the Board
iv) CSR Committee
- Responsibility: Address social responsibilities of the Company and make contributions to public interest
- Authority
1) Matters related to social responsibility of the Company
2) Matters related to establishment, composition and management of organizations (e.g. research groups or council
under the committee)
3) Other matters delegated by the Board

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 179 / 240
(2) The BOD Committee Activities
※ The Audit Committee and Independent Director Recommendation Committee were excluded according to Corporate
Disclosure Guidelines set forth by the Financial Supervisory Service Authority of South Korea.
The Management Committee
Date Agenda Voting Results
Attendance/Voting Results of
Independent Directors
Jan 28, 2016
① Greenhouse gases emissions trading
② Liquidation of a subsidiary
③ Establishment of regional office
Approved
Approved
Approved
N/A
(All comprised of
executive directors)
Feb 17, 2016
① Patent license agreement
② Memory investment
Approved
Approved
Mar 30, 2016
① Establishment of regional office
② Additional investment in Pyeongtaek complex
Approved
Approved
Apr 28, 2016
① Memory investment
Approved
May 20, 2016
① Stake acquisition of regional office
② Establishment of a subsidiary
Approved
Approved
Jun 9, 2016
① Stake acquisition of regional office
② Memory investment
③ Closing of shareholder register for June quarterly dividend
Approved
Approved
Approved
Jun 29, 2016
① Patent license agreement
② Establishment of regional office
③ Real estate contract
Approved
Approved
Approved
Jul 28, 2016
① Memory investment and investment in a subsidiary
② Liquidation of a subsidiary
③ Liquidation of a marketing corporate entity
Approved
Approved
Approved
Aug 11, 2016 ① Stake acquisition of subsidiary Approved
Sep 1, 2016 ① Disposal of assets Approved
Sep 28, 2016
① Establishment of a subsidiary
② Stake acquisition of subsidiary
③ Real estate contract
Approved
Approved
Approved
Oct 24, 2016
① Liquidation of a subsidiary
② Memory investment
Approved
Approved
Nov 29, 2016
① Additional investment in Pyeongtaek complex
② S.LSI investment
Approved
Approved
Dec 20, 2016
① Memory investment
※
Reported Item
① Proposals from investors
Approved
-

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 180 / 240
The Related Party Transactions Committee
Date Agenda
Voting
Results
Name of independent directors
In-Ho Lee
(Attendance:
100%)
Han-Joong Kim
(Attendance:
100%)
Kwang-Soo Song
(Attendance:
100%)
For/against
Jan 27,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Disposal of Samsung Card shares
- Report on 4Q15 related party transactions
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Feb 12,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Approval of changes in large-scale goods and services
transactions in 2016
-
-
-
-
Mar 11,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1)
Cancellation of real estate lease contracts with Samsung
Life Insurance
2) Donation
-
-
-
-
Apr 27,
2016
- Approval items
1) Appointment of the head of Related Party Transactions
Committee
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Acquisition of Samsung Biologics shares
2) Donation to Sungkyunkwan University
3) Property leasing contract with Samsung Life Insurance
- Report on 1Q16 related party transactions
Approved
-
-
For
-
-
For
-
-
For
-
-
May 20,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Property leasing contract with Samsung Display
2) Approval of Greenhouse gas emissions trading with
Samsung Display
-
-
-
-
Jul 27,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Application for property insurance
2) Application for Venture Capital Union
- Report on 2Q16 related party transactions
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Sep 12,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Disposal of Samsung Biologics shares
-
-
-
-
Oct 26,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Participation in Samsung Heavy Industries rights offering
2) Purchase of shares
3) Property leasing contract with Samsung Securities
4) Sale of real estate to Samsung Life Insurance
5) Application for Venture Capital Union
6) Donation to Samsung Life Public Welfare Foundation
- Report on 3Q16 related party transactions
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Nov 29,
2016
- Prior review on large-scale related party transactions
1) Approval of large-scale goods and services transactions in
2017
2) Payment of retirement pensions
-
-
-
-

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 181 / 240
The Compensation Committee
Date Agenda
Voting
Results
Name of Independent Directors
Kwang-Soo Song
(Attendance: 100%)
In-Ho Lee
(Attendance: 100%)
Byeong-Gi Lee
(Attendance: 100%)
For/Against
Feb 5,
2016
① Prior review on 2016 remuneration
ceiling for Directors
Approved For For For
The CSR Committee
Date Agenda
Voting
Results
Name of Independent Directors
Byeong-Gi Lee
(Attendance:
100%)
In-Ho Lee
(Attendance:
100%)
Han-Joong Kim
(Attendance:
100%)
Kwang-Soo
Song
(Attendance:
100%)
Jae-Wan Bahk
(Attendance:
100%)
For/Against
Apr 28,
2016
① Review on establishment of risk
management council
-
-
-
-
-
-
May 20,
2016
① Review on risk management plans
② Research results and findings of the
2nd term research committee for the
advancement of corporate ecosystem
Approved
-
For
-
For
-
For
-
For
-
For
-
Jul 28,
2016
① Establishment of CSR risk
management council
Approved
For
For
For
For
For
Nov 29,
2016
※ Reported Item
① Report on 4Q16 results of CSR risk
management council
- - - - - -

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 182 / 240
D. Director Independence
(1) Appointment of Directors
Directors are appointed by shareholders at the general meeting of shareholders. The Board is responsible for nominating
candidates for Executive Directors, and the Independent Director Recommendation Committee nominates independent
director candidates, who are presented to shareholders as separate agendas and voted on at the annual general meeting.
The Board submits shareholders’ proposal for appointment of Directors at the annual general shareholder meeting as a
separate agenda if the proposal satisfies related laws and regulations.
The composition of the Board of Directors, as appointed by shareholders, is as follows:
[As of December 31, 2016]
Position Name Nominated by Responsibility
Transactions with
the Company
Relation with the
controlling
shareholder
Executive
Director
Oh-Hyun Kwon BOD
Chairman of BOD
Head of DS Division
N/A
N/A
Executive
Director
Boo-Keun Yoon
BOD
Head of CE Division
Executive
Director
Jong-Kyun Shin
BOD
Head of IM Division
Executive
Director
Jae-Yong Lee
BOD
Overall management of the
Company's operations
Affiliate
Independent
Director
In-Ho Lee
Independent
Director
Recommendation
Committee
Overall management
of the Company
N/A
Independent
Director
Han-Joong Kim
Independent
Director
Recommendation
Committee
Overall management
of the Company
Independent
Director
Kwang-Soo Song
Independent
Director
Recommendation
Committee
Overall management
of the Company
Independent
Director
Byeong-Gi Lee
Independent
Director
Recommendation
Committee
Overall management
of the Company
Independent
Director
Jae-Wan Bahk
Independent
Director
Recommendation
Committee
Overall management
of the Company
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 183 / 240
(2) Independent Director Recommendation Committee
The Independent Director Recommendation Committee assesses the independence and ability of potential candidates and
recommends selected candidates to be appointed at the annual general meeting of shareholders. The committee is
composed of three Independent Directors (Han-Joong Kim, Byeong-Gi Lee, and Jae-Wan Bahk) and one Executive
Director (Oh-Hyun Kwon) based on related laws that states more than a majority of members should be independent
directors in accordance with clause 4 of Article 542-8 of the Commercial Law.
(3) Professionalism of Independent Directors
The Company provides the independent directors with access to support staff so they are able to perform their duties
professionally in the BOD and the Board committees. The support staff provides the Directors with reference materials
corresponding to the meeting agendas well in advance so Directors will have the ample opportunity thoroughly review the
topics to be discussed before the Board and committee meetings. If necessary, the Directors are provided with separate
information sessions on any item on the agenda and they are also frequently provided updates on other key management
issues. In addition, the support staff conducts internal education programs which allow Independent Directors to visit and
conduct inspect domestic and overseas business sites and receive reports of the current state of business operation.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 184 / 240
2. Audit System
A. Profile of the member of the Audit Committee
As of December 31, 2016, SEC operates an Audit Committee consisting of three (3) Independent Directors.
Name Career Note
In-Ho Lee
- Corporate Advisor, Shinhan Bank (2009-2011)
- Chief Executive Officer, Shinhan Financial Group (2005-2009)
- President & CEO, Shinhan Bank (1999-2003)
Independent director
Han-Joong Kim
- Professor Emeritus, Yonsei University (2012-Present)
- President, Yonsei University (2008-2012)
- Professor, Dept. of Preventive Medicine & Public Health (1982-2012)
Independent director
Kwang-Soo Song
- Advisor, Kim & Chang Law Office (2007-Present)
- Prosecutor General, Supreme Prosecutors’ Office (2003-2005)
- Chief Prosecutor, Daegu High Prosecutors’ Office (2002-2003)
Independent director
B. Audit Committee Independence
Pursuant to related laws and the Articles of Incorporation, SEC has prepared internal audit regulations which encompass
composition, operation, authority, and responsibility of the Audit Committees to carry out audit related activities.
The Audit Committee is exclusively composed of Independent Directors appointed at the general shareholder meeting and
includes audit and financial experts. Also, the Audit Committee satisfies requirements of relevant laws.
(e.g., The stipulation that the role of head of the committee be held by an Independent Director.)
Requirements Satisfied the requirement Applicable Acts, etc.
- The audit committee shall consist of at least three directors Satisfied (three directors) Article 415-2 (2) of the
Commercial Act,
Article 2 of the Company’s Audit
Committee Regulation
- The ratio of independent directors shall exceed two thirds of the
total number of members.
Satisfied (all members are independent
directors)
- At least one member of the committee shall be an accounting or
financing expert.
Satisfied (In-ho Lee)
Article 542-11 (2) of the
Commercial Act,
Article 3 of the Company’s Audit
Committee Regulation
- The representative of the committee shall be an independent
director.
Satisfied
- Other conditions (affiliates of majority shareholder, etc.)
Satisfied (n/a)
Article 542-11 (3) of the
Commercial Act
The Audit Committee reviews accounting documents including financial statements and audit process related documents
presented by the external auditor, and if needed, requests the external auditor to perform additional reviews on accounting
books and records. To ensure the reliability of accounting related disclosures, the audit committee receives and reviews a
report on internal accounting control systems prepared by internal accounting managers. In addition, the Committee
attends the BOD meetings and other significant meetings. The Committee receives reports on deliberations of the
Management Committee and on business performance from Directors and requests additional reviews and
supplementation of data as needed.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 185 / 240
C. Major Activities of the Audit Committee
See the table below for major activities of the Audit Committee by reporting date.
Date Agenda Voting Results
Name of independent directors
In-Ho Lee
(Attendance: 100%)
Han-Joong Kim
(Attendance: 100%)
Kwang-Soo Song
(Attendance: 100%)
For/Against
Jan 27,
2016
- Report on 2015 financial statement and business report
- Report on 2015 internal accounting management
system activities
- Report on 4Q15 non-audit activities
- Report on 2015 audit activities
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Feb 12,
2016
- Review of the 2016 AGM agenda
- Assessment of 2015 activities of internal compliance
system
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Apr 27,
2016
-
A
ppointment of the head of Audit Committee
- Report on 1Q16 financial statement and business report
- Report on 1Q16 non-audit activities
A
pproved
-
-
For
-
-
For
-
-
For
-
-
Jul 27,
2016
- Report on 1H16 financial statement and hal
f
-year
business report
- Report on 2Q16 non-audit activities
- Report on 1H16 audit activities
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Sep 12,
2016
- Review of the 48th EGM agenda
-
-
-
-
Oct 26,
2016
- Report on 3Q16 financial statement and business report
- Report on 3Q16 non-audit activities
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
D. Compliance Officer
1. Compliance Officer
Name Sang-joo Lee
Age 46
Academic Background
Doctor of Laws (Korea University College of Law) / Master of Public Administration (Graduate
School of Public Administration, Harvard University)
Current Position Corporate Compliance Team leader at Samsung Electronics Legal Affairs Office
Career
- Dec ’12: Senior vice president/Team leader of Samsung Electronics Global Legal Affairs Team
- Dec ’15: Senior vice president/Team leader of Samsung Electronics Compliance Team
- Feb ’16: Senior vice president/Concurrently Chief privacy officer of Samsung Electronics Global
Privacy Office
2. Date of BOD resolution Jan 28, 2016
3. Disqualifications N/A
4. Others N/A
3. Voting Rights of Shareholders
A. Voting Method
The Company has not adopted a concentrated voting system, voting in writing, or an electronic voting system.
B. Minority Shareholder Right
No minority shareholder right was exercised during the reporting period.
C. Competition over Management Right
No competition over management rights occurred during the reporting period.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 186 / 240
VII. Information on Shareholders
1. Ownership of Shares by the Major Shareholder and Related Parties
The following table presents changes in shares held by the major shareholder and related parties as of the beginning and
end of the reporting period.
[As of December 31, 2016] (Unit: Shares, %)
Name Relationship
Type of
share
Number of Shares owned
Note Beginning of period End of period
# shares owned
% # shares owned %
Kun-Hee Lee
Major
shareholder
Common 4,985,464
3.38
4,985,464
3.54 -
Kun-Hee Lee
Major
shareholder
Preferred 12,398
0.05
12,398
0.06 -
Samsung C&T Affiliate Common 5,976,362
4.06
5,976,362
4.25 -
Samsung Welfare
Foundation
Affiliate Common 89,683
0.06
89,683
0.06 -
Samsung Foundation
Of Culture
Affiliate Common 37,615
0.03
37,615
0.03 -
Ra-Hee Hong Affiliate Common 1,083,072
0.74
1,083,072
0.77 -
Jae-Yong Lee Affiliate Common 840,403
0.57
840,403
0.60 -
Samsung Life
Insurance
Affiliate Common 10,622,814
7.21
10,622,814 7.55 -
Samsung Life
Insurance
Affiliate Preferred 879
0.00
879
0.00 -
Samsung Life
Insurance
(special accounts)
Affiliate Common 493,350
0.33
467,320
0.33 Open market sales
Samsung Life
Insurance
(special accounts)
Affiliate Preferred 45,457
0.20
51,614
0.25 Open market sales
Samsung Fire &
Marine Insurance
Affiliate Common 1,856,370
1.26
1,856,370
1.32 -
Oh-Hyun Kwon Affiliate Common 1,700
0.00
1,300
0.00 Open market sales
Sang-Hoon Lee Affiliate Common 1,473
0.00
0
0
Resigned from the director
position
Tot al
Common 25,988,306
17.64
25,960,403 18.45 -
Preferred 58,734
0.26
64,891
0.32 -
※ The definition of ‘major shareholder’ is as defined in the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act of Korea.
※ The changes in percentage of shares owned reported herein (excluding open market sales) resulted from the purchase of treasury
stock.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 187 / 240
[The major shareholder]
○ Name of the major shareholder: Kun-Hee Lee
○ Career (recent 5 years): Chairman of Samsung Electronics (2010.3 ~)
Member of the International Olympic Committee (1996 ~)
- The major shareholder of record has not changed during the reporting period.
2. Ownership of Shares
As of December 31, 2016, the date of Suspension of Entry in the Register of Shareholders, shareholders with over 5%
voting shares, excluding the major shareholder, are as follows:
[As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: Shares)
Classification Name Number of shares owned Share ratio Note
Shareholders with
over 5% voting
shares
National Pension Service 12,976,838
9.22 -
Samsung Life Insurance 11,090,134
7.88 -
Employee Stock Ownership Association - - -
※ Note: According to the shareholder register, as of December 31, 2016.
※ The number of shares owned and share ratio of Samsung Life Insurance includes special accounts.
3. Minority Shareholders
[
As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: Person, Shares, %)
Classification
Shareholder Shares owned
Note
# of shareholders Portion # of shares Portion
Minority
shareholder
66,719
99.98 76,998,715
54.73
Shareholders with shares less than 1/100 of
total issued stocks
Total 66,799
100.00 140,679,337
100.00
※ Note: According to the shareholder register, as of December 31, 2016.
※ Based on the number of common stock with voting rights.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 188 / 240
4. Stock Affairs
Preemptive Rights in the
Articles of Incorporation
1. New shares to be issued by the Company shall be allocated to the shareholders in proportion to their
respective shareholdings in accordance with Paragraph 6, Article 8. If shares are not subscribed for as a
result of waiver or loss of the preemptive right of the shareholders to subscribe for new shares, or if
fractional shares remain at the time of allocation of new shares, such shares may be disposed of by a
resolution of the Board of Directors in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.
2. Notwithstanding the above Paragraph 1, new shares may be allocated to persons other than
shareholders in the following cases:
a. If the Company issues new shares or causes underwriters to underwrite new shares by a resolution of
the Board of Directors in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including the Financial
Investment Services and Capital Markets Act;
b. If the Company allocates new shares preferentially to members of the Employee Stock Ownership
Association by a resolution of the Board of Directors in accordance with applicable laws and
regulations including the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act;
c. If the Company issues new shares for the issuance of depositary receipts (DR) by a resolution of the
Board of Directors in accordance with the applicable laws and regulations including the Financial
Investment Services and Capital Markets Act;
d. If the Company issues new shares by public offering in accordance with Article 11-3;
e. If new shares are issued by the exercise of stock options in accordance with Article 11-4;
f. If the Company issues new shares to the extent of 20% of the total issued and outstanding shares to
domestic or foreign financial institutions for the purpose of obtaining financing urgently or to the relevant
partner company for the purpose of inducing technology therefrom, etc., by a resolution of the Board of
Directors; provided that the issue price of the new shares shall not be less than the price prescribed by
the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act and other applicable laws and regulations.
☞ (Note) Paragraph 6, Article 8
In the case of rights issue, bonus issue or stock dividend, the holders of common shares shall be entitled to
common shares, and the holders of preferred shares shall be entitled to preferred shares, in proportion to their
respective shareholdings; provided that in the case of rights issue and stock dividend the Company may, if
necessary, issue only one kind of shares, where all the shareholders shall be entitled to such kind of shares to be
issued.
☞ (Note) Article 11-3 (Public Offering)
1. The Company may issue new shares by public offering to the extent that the new shares do not exceed 20% of
the total number of issued and outstanding shares by a resolution of the Board of Directors, pursuant to Article
165-6, Paragraph 1, Item 3 of the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act.
2. If the Company issues new shares by public offering, the type, quantity and issue price of the shares to be newly
issued shall be determined by a resolution of the Board of Directors; provided that the issue price of such new
shares shall not be less than the price prescribed by the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act
and other applicable laws and regulations.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 189 / 240
Preemptive Rights in the
Articles of Incorporation
☞ (Note) Article 11-4 (Stock Options)
1. The Company may grant stock options to its officers and employees (including officers and employees of the
related companies as set forth in Article 542-3, Paragraph 1 of the Commercial Code; the same shall apply for
the purpose of this Article) by a special resolution of the general meeting of shareholders pursuant to Article 542-
3 of the Commercial Code, to the extent permitted by the Commercial Code; provided, however, that the
Company may grant the stock options to its officers and employees (except for the directors of the Company) by
a resolution of the Board of Directors to the extent determined by the relevant laws and regulations.
2. The person to whom stock options may be granted are the officers and employees who have contributed or have
the capacity to contribute to the establishment, management, overseas business, technical innovation, etc. of the
Company; provided, however, that the officers and employees who may not be entitled to stock options under the
relevant laws and regulations shall be excluded.
3. The shares to be issued to the officers or employees by the exercise of their stock options (in case the Company
pays, either in cash or treasury shares, the difference between the exercise price of stock options and the market
price, they refer to the shares which are the basis for such calculation) shall be common shares in registered
form or preferred shares in registered form.
4. Total number of shares to be delivered in accordance with the exercise of stock options shall be up to the extent
permitted by the relevant laws and regulations.
5. The stock options may be exercised until an expiry date determined by a resolution of the general meeting of
shareholders or the Board of Directors and such expiry date shall be determined within a period not exceeding
eight (8) years from the date when two (2) years have elapsed from the date of the general meeting of
shareholders or the date of the Board of Directors' meeting at which a resolution to grant such stock options is
adopted; provided, however, that the person to whom a stock option is granted should serve the Company for at
least two (2) years after the date of such resolution in order to exercise such stock option, unless otherwise set
forth by relevant laws and regulations.
6. The terms and conditions for stock options, such as the contents and exercise price thereof shall be determined
by a special resolution of the general meeting of shareholders or by a resolution of the Board of Directors in
accordance with the relevant laws and regulations and the Articles of Incorporation; provided, however, that such
matters which are not provided for as matters reserved for resolutions of the general meeting of shareholders or
the Board of Directors' meeting under the relevant laws and regulations or the Articles of Incorporation may be
determined by the Board of Directors or a committee authorized by the Board of Directors.
7. The Company may cancel the grant of stock options by a resolution of the Board of Directors in any of the
following cases:
a. In case the relevant officer or employee voluntarily retires from his/her office or leaves the Company after the
grant of stock options;
b. In case the relevant officer or employee causes substantial damages to the Company due to his/her willful
misconduct or negligence;
c. In case any of the causes for cancellation set forth in the stock option agreement occurs.
Settlement date December 31
Annual General
Meetings of
Shareholders
Within 3 months after the end of every business year
Shareholder register closing period One month from January 1
Stock type 1,5,10,50,100,500,1000,10000(8 types)
Transfer agent Korea Securities Depository(T: +82-2-3774-3000): 23, Yeouinaru-ro 4-gil, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul, Korea
Shareholder benefit n/a Published on Joongang Daily

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 190 / 240
5. Stock Price and Stock Transactions
A. Domestic Stock Market
(Unit: KRW, Shares)
Type
July ‘16 August September October November December
Common
stock
Stock price
Highest
1,543,000
1,687,000
1,643,000
1,706,000 1,746,000
1,812,000
Lowest 1,421,000
1,517,000
1,465,000
1,535,000 1,539,000
1,718,000
Average 1,497,810
1,595,545
1,583,474
1,606,750 1,625,045
1,777,190
Volume
Highest (day)
334,983
410,644
529,987
781,771 570,704
329,251
Lowest (day) 126,701
139,177
153,203
185,799 108,349
93,069
Monthly 4,470
5,037
5,218
6,910 5,105
3,922
Preferred
stock
Stock price
Highest
1,265,000
1,400,000
1,355,000
1,379,000 1,356,000
1,438,000
Lowest 1,180,000
1,252,000
1,178,000
1,251,000 1,209,000
1,355,000
Average 1,219,762
1,318,136
1,292,632
1,304,000 1,278,000
1,401,381
Volume
Highest (day) 82,134
126,128
65,293
65,540 102,488
58,063
Lowest (day) 17,649
22,252
16,503
10,300 19,312
8,252
Monthly 932
995
791
504 705
708
※ Monthly trading volume in 1,000 shares

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 191 / 240
B. Overseas Stock Market
□ Name of Stock Exchange: London Stock Exchange (Common stock)
(Unit: USD, KRW, DR)
Type
July ‘16 August September October November December
Common
stock
Stock
price
Highest
686.50
750.50
745.50
763.00 733.50
767.00
(Converted to KRW)
772,793
830,353
823,778
847,922 857,095
896,930
Lowest
602.00
671.50
666.00
670.50 660.00
731.50
(Converted to KRW)
694,106
744,626
732,267
744,926 768,504
857,757
Average
650.55
713.43
706.57
708.90 695.30
749.70
Volume
Highest (day)
125,764
72,419
75,048
184,917 94,563
59,094
Lowest (day)
16,374
11,052
13,065
14,293 4,062
3,276
Monthly
896
732
794
1,198 569
477
※ Monthly volume in 1,000 Depository Receipt (DR) shares.
※ Stock price converted to KRW is based on the closing price of the KRW/USD exchange rate of the applicable trading day.
Ratio: Common one (1) share equals DR two (2) shares
□ Name of Stock Exchange: Luxembourg Stock Exchange (Preferred stock)
(Unit: USD, KRW, DR )
Type
July ‘16 August September October November December
Preferred
stock
Stock
price
Highest
564.00
621.00
615.00
609.00 576.00
606.00
(Converted to KRW)
634,895
698,811
686,832
676,782 673,056
708,717
Lowest
504.00
560.00
532.00
545.00 518.00
574.00
(Converted to KRW)
581,112
620,984
584,934
605,495 605,956
670,604
Average
531.14
588.14
577.64
573.67 546.73
590.00
Volume
Highest (day)
81,517
24,881
23,993
20,447 20,661
13,261
Lowest (day)
614
573
829
490 761
212
Monthly
194
164
97
107 100
74
※ Monthly volume in 1,000 DR shares.
※ Stock price converted to KRW is based on KRW/USD exchange rate of closing price of trading day.
Ratio: Preferred one (1) share equals DR two (2) shares

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 192 / 240
VIII. Executives and Employees
1. Executives and Employees
A. Registered Executives
[As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: # of shares)
Name Gender
Date of
birth
Position
Registered
executive
Full/
part-
time
Responsibility
Major career
Numbe
r
of shares
owned
Length of
Service
Term expiration
Common
Preferred
Oh-
Hyun
Kwon
M 1952.10 CEO
Registered
executive
Full time
Chairman of BOD
Head of DS
Division
Head of DS
Division
1,300 0 58 mo. 2018.03.16
Boo-
Keun
Yoon
M 1953.02 CEO
Registered
executive
Full time
Head of CE
Division
Head of CE
Division
0 0 46 mo. 2019.03.15
Jong-
Kyun
Shin
M 1956.01 CEO
Registered
executive
Full time
Head of IM
Division
Head of IM
Division
0 0 46 mo. 2019.03.15
Jae-
Yong
Lee
M 1968.06
Executive
Director
Registered
executive
Full time
Overall
management of
the Company's
operation
Vice Chairman
840,403
0 3 mo. 2019.10.27
In-Ho
Lee
M 1943.11
Independent
Director
Registered
executive
Part time
Overall
management of
the Company
Former
President &
CEO of
Shinhan
Bank
0 0 82 mo. 2019.03.19
Han-
Joong
Kim
M 1948.11
Independent
Director
Registered
executive
Part time
Overall
management of
the Company
Former
President of
Yonsei
University
0 0 58 mo. 2018.03.18
Kwang-
Soo
Song
M 1950.01
Independent
Director
Registered
executive
Part time
Overall
management of
the Company
Advisor at Kim
& Chang Law
Office
0 0 46 mo. 2019.03.15
Byeong-
Gi Lee
M 1951.05
Independent
Director
Registered
executive
Part time
Overall
management of
the Company
Professor
Emeritus at
Seoul National
University
0 0 58 mo. 2018.03.16
Jae-
Wan
Bahk
M 1955.01
Independent
Director
Registered
executive
Part time
Overall
management of
the Company
Professor
o
f
Public
Administration
at
Sungkyunkwan
University
0 0 10 mo. 2019.03.11
※ On March 11, 2016, Jae-Wan Bahk was newly appointed as an Independent Director at the annual general meeting
of shareholders and Independent Director Eun-Mee Kim retired upon the expiration of her term.
※ Jae-Yong Lee was newly appointed as Executive Director at the Extraordinary General Meeting of Shareholders
on October 27, 2016, and Executive Director Sang-Hoon Lee resigned.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 193 / 240
B. Concurrent Position with Other Companies
[As of December 31, 2016]
Concurrent office holder Company
Name Position Name of company Position
Kwang-Soo Song Independent director Doosan Corp. Independent director
Jae-Wan Bahk Independent director Lotte Shopping co., Ltd Independent director
Oh-Hyun Kwon Executive director, CEO Samsung Display Executive director, CEO
Jae-Yong Lee Executive director EXOR N.V Independent director
C. Employees
[As of December 31, 2016] (Unit: KRW million)
Division Gender
No. of employees
Average length
of service
(years)
Total
Compensation
Average
Compensation
per employee
Regular
Contract-
based
Others Total
CE M 11,058 109 - 11,167 12.9 - -
CE F 2,159 19 - 2,178 7.9 - -
IM M 19,358 215 - 19,573 11.1 - -
IM F 6,793 32 - 6,825 8.6 - -
DS M 31,281 123 - 31,404 10.5 - -
DS F 12,856 22 - 12,878 9.8 - -
Others M 7,305 139 - 7,444 13.4 - -
Others F 1,702 29 - 1,731 8.8 - -
Gender Total M 69,002 586 - 69,588 11.4 8,277,739 116
Gender Total F 23,510 102 - 23,612 9.2 1,962,847 81
Total 92,512 688 - 93,200 10.8 10,240,586 107
※ Total compensation and average compensation per employee were calculated before income tax and other deductions based on the
earned income payment record submitted to the district tax office in accordance with Article 20 of the Income Tax Law.
※ The number of employees represent domestic employees resident in Korea, excluding four executive directors.
※ Average compensation per employee was calculated based on total average employee figure of 95,460
(male: 71,084; female: 24,375)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 194 / 240
2. Remuneration for Directors
A. Summary on Total Remuneration
(1) Remuneration approved at the annual general meetings of shareholders
(Unit: KRW million)
Number of Persons
Amount Approved at
Shareholders’ Meeting
Note
Executive Directors 4
-
-
Independent Directors 2
-
-
Audit Committee member or Auditor 3
-
-
Total 9
39,000
-
※ Number of persons as of the Reporting Date.
※ The amount approved at shareholders’ meeting is the remuneration limit for directors registered pursuant to Article 388 of the
Korean Commercial Act (“Registered Directors”). It includes compensation for Registered Directors who retired this fiscal year
and in past years.
(2) Remuneration Paid
[Remuneration paid for directors and audits]
(Unit: KRW million)
Number
of Persons
Total amount of
remuneration
Average remuneration per
Director
Note
9 20,194
2,203
Remuneration for resigned director is included
※ Number of persons is as of the Reporting Date.
※ The total amount is the income based on the Income Tax Law that incumbent or retired executive directors, independent directors,
and members of audit committee in the fiscal year received as a Registered Director in accordance with Article 159 of the
Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act and Article 168 of the enforcement decree of the same law.
※ Average remuneration per Director was calculated by dividing total remuneration by annual average number of persons.
※ There is no recognized expenses (compensation expenses) in this term from granting stock options.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 195 / 240
[Remuneration paid by type of director]
(Unit: KRW million)
Number
of Persons
Total amount of
remuneration
Average
remuneration
per Director
Note
Executive Director
(not including independent directors
and audit committee members)
4 19,750
4,837
Remuneration for resigned director is included
Independent Director
(not including audit committee
members)
2 188
90
Remuneration for resigned director is included
Audit Committee member 3 256
85
-
Auditor - -
-
-
※ Number of persons is as of the Reporting Date.
※ The total amount is the income based on the Income Tax Law that incumbent or retired executive directors, independent directors,
and members of audit committee in the fiscal year received as a Registered Director in accordance with Article 159 of the
Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act and Article 168 of the enforcement decree of the same law.
※ Average remuneration per Director was calculated by dividing total remuneration by annual average number of persons.
※ There is no recognized expenses (compensation expenses) in this term from granting stock options.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 196 / 240
3. Remuneration for Individual Executive Directors
(1) Summary on Remuneration by Executive
(Unit: KRW million)
Name position
Total amount of
remuneration
Remuneration not included
in total amount
Oh-Hyun Kwon CEO 6,698
-
Boo-Keun Yoon CEO 5,030
-
Jong-Kyun Shin CEO 3,986
-
Jae-Yong Lee Executive Director 1,135
-
Sang-Hoon Lee Executive Director 2,901
-
(2) Criteria and Methodology
(Unit: KRW million)
Name
Type of
remuneration
Total amount Criteria and methodology
Oh-Hyun
Kwon
(CEO)
Earned
Income
Salary 1,944
In accordance with internal regulation for executive treatment (Board resolution),
Remuneration is determined based on position (vice president), responsibilities, and
performance results. He was paid KRW 174 million per month from January to April
and KRW 156 million per month from May to December.
Bonus 4,635
- Traditional holiday bonus: 100% of monthly wage
- Target Achievement Incentive: Paid biannual basis within the range of 0~200% of monthly
wage
* CEO decides the amount according to the level of target achieved
- Performance Incentive: When performance exceeds the Company’s goal; CEO
decides the amount based on 20% profit. Paid once a year within 0~50% of salary.
(Adjusted according to individual performance)
- Long-term incentive: Calculated within the director remuneration limit, based on the
average salary of 3 years, using ROE, stock performance, and EBIT margin as criteria.
Paid over the course of 3 years.
※ Bonus awarded based on his contributions and consideration for his performance;
As the Company’s CEO, he laid the foundation for the Company’s continuous growth.
He expanded cutting-edge processes and increased sales of high value-added
products for semiconductor and DP business, and he also improved productivity of
OLED panels. Under his leadership, the Company achieved KRW 202 trillion in
revenue and KRW 29 trillion in operating profit.
Profit from
exercising
stock
option
- n/a
Other
Income
119
Fringe benefits are provided in line with the internal regulation for executive treatment
(Board resolution)
Retirement Income - n/a
Other Income - n/a
(Unit: KRW million)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 197 / 240
Name
Type of
remuneration
Total amount Criteria and methodology
Boo-Keun
Yoon (CEO)
Earned
Income
Salary 1,728
In accordance with internal regulation for executive treatment (Board resolution),
Remuneration is determined based on his position (president), responsibilities, and
performance results. He was paid KRW 144 million per month.
Bonus 3,216
- Traditional holiday bonus: 100% of monthly wage
- Target Achievement Incentive: Paid biannual basis within the range of 0~200% of monthly
wage
* CEO decides the amount according to the level of target achieved
- Performance Incentive: When performance exceeds the Company’s goal; CEO
decides the amount based on 20% profit. Paid once a year within 0~50% of salary.
(Adjusted according to individual performance)
- Long-term incentive: Calculated within the director remuneration limit, based on the
average salary of 3 years, using ROE, stock performance, and EBIT margin as criteria.
Paid over the course of 3 years.
※ Bonus awarded based on his contributions and consideration for his performance;
He strengthened the Company’s leading position in the market by expanding
shipments of premium products such as Chef Collection kitchen appliances and Add
Wash washing machines, and strengthened business competitiveness by increasing
B2B investment and launching innovative products including QLED TV and Family
Hub 2.0 refrigerator. Under his leadership, the Company’s TV business maintained the
top position (in terms of market share) in the overall TV market for the 11th
consecutive year.
Profit from
exercising
stock
option
- n/a
Other
Income
86
Fringe benefits are provided in line with the internal regulation for executive treatment
(Board resolution)
Retirement Income - n/a
Other Income - n/a
(Unit: KRW million)
Name
Type of
remuneration
Total amount Criteria and methodology
Jong-Kyun
Shin (CEO)
Earned
Income
Salary 1,728
In accordance with internal regulation for executive treatment (Board resolution),
Remuneration is determined based on his position (president), responsibilities, and
performance results. He was paid KRW 144 million per month.
Bonus 2,154
- Traditional holiday bonus: 100% of monthly wage
- Target Achievement Incentive: Paid biannual basis within the range of 0~200% of monthly
wage
* CEO decides the amount according to the level of target achieved
- Performance Incentive: When performance exceeds the Company’s goal; CEO
decides the amount based on 20% profit. Paid once a year within 0~50% of salary.
(Adjusted according to individual performance)
- Long-term incentive: Calculated within the director remuneration limit, based on the
average salary of 3 years, using ROE, stock performance, and EBIT margin as criteria.
Paid over the course of 3 years.
※ Bonus awarded based on his contributions and consideration for his performance;
Despite many challenges such as the Galaxy Note 7 issue, he expanded sales of
flagship products such as Galaxy S7 and S7 Edge, strengthening the Company’s
leading position in the global market. Also, he expanded service regions of Samsung
Pay and Cloud.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 198 / 240
Profit from
exercising
stock
option
- n/a
Other
Income
104
Fringe benefits are provided in line with the internal regulation for executive treatment
(Board resolution)
Retirement Income - n/a
Other Income - n/a
(Unit: KRW million)
Name
Type of
remuneration
Total amount Criteria and methodology
Jae-Yong
Lee
(Executive
Director)
Earned
Income
Salary 476
In accordance with internal regulation for executive treatment (Board resolution),
Remuneration is determined based on his position (vice chairman), responsibilities,
and performance results. He was paid KRW 159 million per month from October to
December.
Bonus 635
- Traditional holiday bonus: 100% of monthly wage
- Target Achievement Incentive: Paid biannual basis within the range of 0~200% of monthly
wage
* CEO decides the amount according to the level of target achieved
- Performance Incentive: When performance exceeds the Company’s goal; CEO
decides the amount based on 20% profit. Paid once a year within 0~50% of salary.
(Adjusted according to individual performance)
- Long-term incentive: Calculated within the director remuneration limit, based on the
average salary of 3 years, using ROE, stock performance, and EBIT margin as criteria.
Paid over the course of 3 years.
※ Bonus awarded based on his contributions and consideration for his performance;
As a registered director, he successfully made a large-scale strategic M&A deal since
he sat on the Board, contributing to securing future growth engines of the Company.
Profit from
exercising
stock
option
- n/a
Other
Income
24
Fringe benefits are provided in line with the internal regulation for executive treatment
(Board resolution)
Retirement Income - n/a
Other Income - n/a

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 199 / 240
(Unit: KRW million)
Name
Type of
remuneration
Total amount Criteria and methodology
Sang-Hoon
Lee
(Executive
Director)
Earned
Income
Salary 1,080
In accordance with internal regulation for executive treatment (Board resolution),
Remuneration is determined based on his position (president), responsibilities, and
performance results. He was paid KRW 108 million per month from January to
October.
Bonus 1,719
- Traditional holiday bonus: 100% of monthly wage
- Target Achievement Incentive: Paid biannual basis within the range of 0~200% of monthly
wage
* CEO decides the amount according to the level of target achieved
- Performance Incentive: When performance exceeds the Company’s goal; CEO
decides the amount based on 20% profit. Paid once a year within 0~50% of salary.
(Adjusted according to individual performance)
- Long-term incentive: Calculated within the director remuneration limit, based on the
average salary of 3 years, using ROE, stock performance, and EBIT margin as criteria.
Paid over the course of 3 years.
※ Bonus awarded based on his contributions and consideration for his performance;
Despite many challenges such as the low growth of the global economy, he
strengthened internal stability by efficiently managing resources and creating synergy
among businesses, as the president of Corporate Management Office. Also, he greatly
contributed to creating an organizational culture which fosters creativity and
reengineering the organization.
Profit from
exercising
stock
option
- n/a
Other
Income
102
Fringe benefits are provided in line with the internal regulation for executive treatment
(Board resolution)
Retirement Income - n/a
Other Income - n/a
B. Stock Options Granted and Exercised
(1) Status of Stock Options Granted to Registered Directors
There have been no stock options granted to, or exercised by, the executive BOD or Audit Committee members during the
reporting period.
(2) Status of Stock Options Granted to Non-Registered Executives
As of December 31, 2016, there is no accumulated-basis unexercised stock option.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 200 / 240
IX. Affiliates and Subsidiaries
1. Affiliates & Subsidiaries
A. Affiliates
- Name of affiliated group: Samsung Group
As at December 31, 2016, Samsung Group had a total of fifty-eight (58) domestic affiliates, where seven (7) affiliates
(Nuri Solution, Samsung Fine Chemicals, S-EnPol, Hantok Chemicals, SDI-Chemical Co., Ltd., Jeongahm Wind Power,
Allat) were excluded and three (3) affiliate (SDI- Chemical Co., Ltd., Samsung Fire & Marine Financial Service, S-
Printing Solution) were added. Among the Samsung Group’s fifty-eight (58) domestic affiliates, sixteen (16) affiliates
including Samsung Electronics are listed, and forty-two (42) affiliates are unlisted.
[As of December 31, 2016]
No. of
affiliates
Name of affiliates
Listed 16
Samsung C&T, Samsung Electronics, Samsung SDI, SEMCO, Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance,
Samsung Heavy Industries, Samsung Life Insurance, MULTICAMPUS,
Samsung Securities, Samsung SDS, Samsung Card, Samsung Engineering, S1,
Cheil Worldwide, Hotel Shilla, Samsung Biologics
Unlisted 42
Seoul Lakeside CC, Samwoo Architects & Engineers, CVnet Corporation,
Samsung Bioepis, Samsung Display, Samsung Corning Advanced Glass, SU Materials,
STECO, SEMES, Samsung Electronics Service, Samsung Electronics Sales,
Samsung Electronics Logitech, Suwon Samsung Bluewings FC, Samsung Medison,
Samsung Claim Adjustment Service, Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Service,
Samsung Fire & Marine Financial Service, Daejung Offshore Wind Power Co., Ltd., Samsung Futures,
Samsung Asset Management, Saengbo, Samsung Life Service, Samsung SRA Asset Management, Samsung
Life Financial Service, SD Flex, Cheil Fashion Retail, Natural9, Samsung Welstory,
S-Printing Solution, SECUI, STM, S-Core, OpenHands, Miracom,
Samsung Card Customer Service, Human TSS, S-1CRM, Shilla Stay,
HDC Shilla Duty Free LTD, SERI, Samsung Lions, Samsung Venture Investment Corporation
Total 58
※ Effective March 11, 2016, CREDU changed its name to Multicampus Co., Ltd..
※ Effective April 1, 2016, Colombo Korea changed its name to Cheil Fashion Retail Co., Ltd.
※ Allat was excluded from the Company group on December 15, 2016 (sold its shares on September 30, 2016)
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 201 / 240
B. Ownership Status of Affiliates and Subsidiaries
1) Domestic
Investee
Investor
Samsung
C&T Corp
Samsung
Electronics
Samsung
SDI
Samsung
Electro-
Mechanics
Samsung
Heavy
Industries
Hotel
Shilla
Samsung
Engineering
Cheil
Worldwide
S1
Corpo
ration
Samsung
SDS
Samsung
Lions
SERI STECO
Samsung C&T
Corporation
4.2 0.1 7.0
17.1 1.0
Samsung
Electronics
19.6 23.7 16.9
5.1 25.2
22.6 29.8 70.0
Samsung SDI
2.1 0.4 0.1 11.7 11.0 29.6
Samsung Electro-
mechanics
2.6 2.3
23.8
Samsung Heavy
Industries
1.0
Cheil Worldwide
0.1 67.5
Hotel Shilla
S1 Corporation
SERI
Samsung SDS
Samsung Life
Insurance
0.1 7.9 0.1 0.1 3.3
7.4
0.0
0.1
5.6 0.1 14.8
Samsung Fire &
Marine Insurance
1.4 1.3 0.2 1.0
Samsung
Securities.
3.1 1.3
Samsung Card
1.3 3.0 1.9
SDC
Samsung
BioLogics
Miracom
Tota l
6.3 13.5 19.6 23.8 23.2
17.0
18.9 28.4
20.8 39.7 67.5 100.0 70.0
※ (% of Ownership; As of December 31, 2016; Based on Common shares)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 202 / 240
Investee
Investor
SEMES
Samsung
Electronics
Service
Samsung
Electronics
Sales
Suwon
Samsung
Bluewings
FC
Samsung
Electronics
Logitech
Samsung
Display
Samsung
Medison
Samsung
BioLogics
Samsung
BioEpis
Samsung
Corning
Advanced
Glass
SU
Materials
CVnet
Seoul
Lakeside
CC
Samsung C&T
Corporation
43.4
40.1
100.0
Samsung
Electronics
91.5 99.3 100.0 100.0 84.8 68.5 47.8
Samsung SDI
15.2
Samsung Electro-
mechanics
Samsung Heavy
Industries
Cheil Worldwide
100.0
Hotel Shilla
S1 Corporation
SERI
Samsung SDS
9.4
Samsung Life
Insurance
0.0
Samsung Fire &
Marine Insurance
Samsung
Securities.
Samsung Card
SDC
50.0 50.0
Samsung
BioLogics
93.3
Miracom
Tota l
91.5 99.3 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 68.5 75.0
93.3
50.0 50.0 49.5
100.0
※ (% of Ownership; As of December 31, 2016; Based on Common shares)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 203 / 240
Investee
Investor
Samwoo
Architects &
Engineers
SD Flex
Cheil
Fashion
Retail
Natural9
Samsung
Welstory
Daejung
Offshore
Wind
Power
SECUI Human TSS
S-1CRM STM
MULTI
CAMPUS
S-Core
Open
Hands
Samsung C&T
Corporation
100.0 100.0 51.0 100.0 8.7
Samsung
Electronics
Samsung SDI
50.0 100.0
Samsung Electro-
mechanics
Samsung Heavy
Industries
50.1
Cheil Worldwide
5.2
Hotel Shilla
S1 Corporation
100.0 100.0 0.6
SERI
15.2
Samsung SDS
56.5 47.2 81.8 100.0
Samsung Life
Insurance
0.0
Samsung Fire &
Marine Insurance
Samsung
Securities.
Samsung Card
SDC
Samsung
BioLogics
Miracom
0.5
Tota l
100.0 50.0 100.0 51.0 100.0 50.1 65.2 100.0 100.0 100.0 62.4 88.1 100.0
※ (% of Ownership; As of December 31, 2016; Based on Common shares)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 204 / 240
Investee
Investor
Miracom
Shilla
Stay
HDC
Shilla
Duty
Free
LTD
Samsung
Life
Insurance
Saengbo
Samsung
Life
Service
Samsung
SRA
Asset
Managem
ent
Samsung
Life Financial
Service
Samsung
Fire &
Marine
Insurance
Samsung
Claim
Adjustmen
t Service
Samsung
Fire &
Marine
Insurance
Service
Samsung Fire
& Marine
Financial
Service
Samsung
Securities
Samsung C&T
Corporation
19.3
Samsung
Electronics
Samsung SDI
Samsung Electro-
mechanics
Samsung Heavy
Industries
Cheil Worldwide
5.4
Hotel Shilla
100.0 50.0
S1 Corporation
0.6
SERI
Samsung SDS
83.6
Samsung Life
Insurance
50.0 99.8 100.0 100.0 15.0 30.2
Samsung Fire &
Marine Insurance
100.0 100.0 100.0
Samsung
Securities.
Samsung Card
SDC
Samsung
BioLogics
Miracom
Tota l
89.6 100.0 50.0 19.3 50.0 99.8 100.0 100.0 15.0 100.0 100.0 100.0
30.2
※ (% of Ownership; As of December 31, 2016; Based on Common shares)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 205 / 240
Investee
Investor
Samsung
Card
S-Printing
Solution
Samsung
Card
Customer
Service
Samsung
Asset
Management
Samsung
Futures
Samsung
Venture
Investment
Samsung C&T
Corporation
16.7
Samsung
Electronics
100.0 16.3
Samsung SDI
16.3
Samsung Electro-
mechanics
17.0
Samsung Heavy
Industries
17.0
Cheil Worldwide
Hotel Shilla
S1 Corporation
SERI
Samsung SDS
Samsung Life
Insurance
71.9 100.0
Samsung Fire &
Marine Insurance
Samsung
Securities.
100.0
16.7
Samsung Card
100.0
SDC
Samsung
BioLogics
Miracom
Tota l
71.9 100.0 100.0 100.0
100.0
100.0
※ (% of Ownership; As of December 31, 2016; Based on Common shares)

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 206 / 240
2) Overseas
Investor Investee
Ownership
Samsung C&T America Inc. Meadowland Distribution
100.0
Samsung C&T America Inc. SAMSUNG OIL & GAS USA CORP
10.0
Samsung C&T America Inc. Samsung Green repower, LLC
100.0
Samsung C&T America Inc. Samsung Solar Construction Inc.
100.0
Samsung C&T America Inc. QSSC, S.A. de C.V.
20.0
Samsung C&T America Inc. S-print Inc
24.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE GRW EPC GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE GRW EPC LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE SKW EPC GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE SKW EPC LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE GRW LP Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE SKW LP Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE WIND PA GP INC.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE WIND PA LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE GRS Holdings GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE GRS Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE K2 EPC GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE K2 EPC LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE KS HOLDINGS GP INC.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE KS HOLDINGS LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Belle River LP Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Armow EPC GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Armow EPC LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Armow LP Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE North Kent 1 LP H.LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Wind GP Holding Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE North Kent 2 LP Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Solar Development GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Solar Development LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Windsor Holdings GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Windsor Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Southgate Holdings GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Southgate Holdings LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Solar Construction Management GP Inc.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Solar Construction Management LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE DEVELOPMENT GP INC.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE DEVELOPMENT LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE BRW EPC GP INC.
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE BRW EPC LP
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE North Kent 1 GP Holdings Inc
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE North Kent 2 GP Holdings Inc
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE Belle River GP Holdings Inc
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE NK1 EPC GP Inc
100.0
Samsung Renewable Energy Inc. SRE NK1 EPC LP
100.0
Samsung Green repower, LLC SOLAR PROJECTS SOLUTIONS,LLC
50.0
SP Armow Wind Ontario GP Inc SP Armow Wind Ontario LP
0.0
Samsung C&T Oil & Gas Parallel Corp. PLL Holdings LLC
83.6
Samsung C&T Oil & Gas Parallel Corp. PLL E&P LLC
90.0
SRE GRW EPC GP Inc. SRE GRW EPC LP
0.0
SRE SKW EPC GP Inc. SRE SKW EPC LP
0.0
PLL Holdings LLC Parallel Petroleum LLC
61.0
SRE GRW LP Holdings LP Grand Renewable Wind LP Inc.
45.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 207 / 240
SRE SKW LP Holdings LP South Kent Wind LP Inc.
50.0
SRE WIND PA GP INC. SRE WIND PA LP
0.0
SRE GRS Holdings GP Inc. Grand Renewable Solar GP Inc.
50.0
SRE GRS Holdings GP Inc. SRE GRS Holdings LP
0.0
SRE K2 EPC GP Inc. SRE K2 EPC LP
0.0
SRE KS HOLDINGS GP INC. KINGSTON SOLAR GP INC.
50.0
SRE KS HOLDINGS GP INC. SRE KS HOLDINGS LP
0.0
SOUTHGATE SOLAR GP INC. SOUTHGATE SOLAR LP
0.0
WINDSOR SOLAR GP INC. WINDSOR SOLAR LP
0.0
SRE Belle River LP Holdings LP SP Belle River Wind LP
42.5
SP Belle River Wind GP Inc SP Belle River Wind LP
0.0
SRE Armow EPC GP Inc. SRE Armow EPC LP
0.0
SRE Armow LP Holdings LP SP Armow Wind Ontario LP
50.0
SRE North Kent 1 LP H.LP North Kent Wind 1 LP
50.0
SRE Wind GP Holding Inc. SP Armow Wind Ontario GP Inc
50.0
SRE Wind GP Holding Inc. SRE GRW LP Holdings LP
0.0
SRE Wind GP Holding Inc. SRE SKW LP Holdings LP
0.0
SRE Wind GP Holding Inc. SRE Armow LP Holdings LP
0.0
SRE Wind GP Holding Inc. South Kent Wind GP Inc.
50.0
SRE Wind GP Holding Inc. Grand Renewable Wind GP Inc.
50.0
South Kent Wind GP Inc. South Kent Wind LP Inc.
0.0
Grand Renewable Wind GP Inc. Grand Renewable Wind LP Inc.
0.0
North Kent Wind 1 GP Inc North Kent Wind 1 LP
0.0
SRE North Kent 2 LP Holdings LP North Kent Wind 2 LP
50.0
North Kent Wind 2 GP Inc North Kent Wind 2 LP
0.0
SRE Solar Development GP Inc. SRE Solar Development LP
0.0
SRE Windsor Holdings GP Inc. WINDSOR SOLAR GP INC.
50.0
SRE Windsor Holdings GP Inc. SRE Windsor Holdings LP
0.0
SRE Windsor Holdings LP WINDSOR SOLAR LP
50.0
SRE Southgate Holdings GP Inc. SOUTHGATE SOLAR GP INC.
50.0
SRE Southgate Holdings GP Inc. SRE Southgate Holdings LP
0.0
SRE Southgate Holdings LP SOUTHGATE SOLAR LP
50.0
SRE Solar Construction Management GP Inc. SRE Solar Construction Management LP
0.0
SRE DEVELOPMENT GP INC. SRE DEVELOPMENT LP
0.0
SRE BRW EPC GP INC. SRE BRW EPC LP
0.0
SRE North Kent 1 GP Holdings Inc SRE North Kent 1 LP H.LP
0.0
SRE North Kent 1 GP Holdings Inc North Kent Wind 1 GP Inc
50.0
SRE North Kent 2 GP Holdings Inc SRE North Kent 2 LP Holdings LP
0.0
SRE North Kent 2 GP Holdings Inc North Kent Wind 2 GP Inc
50.0
SRE Belle River GP Holdings Inc SRE Belle River LP Holdings LP
0.0
SRE Belle River GP Holdings Inc SP Belle River Wind GP Inc
50.0
SRE NK1 EPC GP Inc SRE NK1 EPC LP
0.0
Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH SCNT Investment Atlantic SPRL
0.0
Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH POSS-SLPC, s.r.o
20.0
Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH Solluce Romania 1 B.V.
20.0
Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH Solluce Slovenia 1 B.V.
20.0
Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH S.C. Otelinox S.A
94.3
Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH KSI LLP
25.0
Samsung C&T U.K. Ltd. Samsung Nigeria Co., Ltd.
0.1
Solluce Romania 1 B.V. LJG GREEN SOURCE ENERGY ALPHA S.R.L.
78.0
Solluce Slovenia 1 B.V. ZE Solar 1 D.O.O.
70.0
Cassava Investment Korea Pte. Ltd. PT. Cahaya Borneo Sukses Agrosindo
49.0
Cassava Investment Korea Pte. Ltd. PT. Cassava Borneo Sukses Plantation
49.0
Samsung C&T Thailand Co., Ltd Samsung Development (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
67.0
Cheil Holding Inc. Samsung Const. Co. Phils.,Inc.
75.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 208 / 240
Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd. Samsung Chemtech Vina LLC
48.3
Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd. S-print Inc
16.0
Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd. Cassava Investment Korea Pte. Ltd.
12.7
Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd. PT. INSAM BATUBARA ENERGY
10.0
Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd. Malaysia Samsung Steel Center Sdn.Bhd
30.0
Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd. S&G Biofuel PTE.LTD
12.6
S&G Biofuel PTE.LTD PT. Gandaerah Hendana
95.0
S&G Biofuel PTE.LTD PT. Inecda
95.0
Samsung C&T Hongkong Ltd. Samsung C&T Thailand Co., Ltd
13.2
Samsung C&T Hongkong Ltd. SAMSUNG (TIANJIN) INTERNATIONAL TRADING CO., LTD
100.0
Samsung C&T Hongkong Ltd. SAMSUNG TRADING (SHANGHAI) CO., LTD
100.0
Samsung C&T Hongkong Ltd. Samsung Precision Stainless Steel(pinghu) Co.,Ltd.
45.0
Samsung C&T Hongkong Ltd. Samsung Corporation (Guangzhou) Limited.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Japan Corporation
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung R&D Institute Japan Co. Ltd
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics America, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Canada Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Mexico S.A. De C.V.
63.6
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics (UK) Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Holding GmbH
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Iberia, S.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics France S.A.S
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Hungarian RT.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Italia S.P.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Europe Logistics B.V.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Overseas B.V.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Polska, SP.Zo.o
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Portuguesa S.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Nordic Aktiebolag
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Austria GmbH
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Slovakia s.r.o
55.7
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Display (M) SDN.Bhd.
75.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics(M) SDN.BHD.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Vina Electronics Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Asia Private Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung India Electronics Private Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung R&D Institute India-Bangalore Private Limited
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Australia Pty. Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics PT Samsung Electronics Indonesia
100.0
Samsung Electronics Thai Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
91.8
Samsung Electronics Samsung Malaysia Electronics(SME) Sdn.Bhd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Hong Kong Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Suzhou Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
69.1
Samsung Electronics Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Suzhou Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics (Shandong) Digital Printing Co., Ltd.
87.1
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Huizhou Co., Ltd.
89.6
Samsung Electronics Tianjin Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
48.2
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Taiwan Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Tianjin Samsung Telecom Technology Co., Ltd.
90.0
Samsung Electronics Shanghai Samsung Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Suzhou Computer Co., Ltd.
73.7

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 209 / 240
Samsung Electronics Shenzhen Samsung Electronics Telecommunication Co., Ltd.
95.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Semiconductor (China) R&D Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung (China) Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung SemiConductor Xian
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Gulf Electronics Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Egypt S.A.E
0.1
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics South Africa(Pty) Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica (Zona Libre)
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronica da Amazonia Ltda.
87.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Argentina S.A.
98.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Chile Limitada
4.1
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Rus Company LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Rus Kaluga LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics Samsung SDI Brasil Ltda.
0.1
Samsung Electronics Tianjin Samsung LED Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Tianjin Samsung Opto-Electronics Co., Ltd.
82.0
Samsung BioEpis SAMSUNG BIOEPIS UK LIMITED
100.0
Samsung BioEpis Samsung Bioepis CH GmbH
100.0
Samsung BioEpis SAMSUNG BIOEPIS AU PTY LTD
100.0
Samsung BioEpis Samsung Bioepis TR Pharmaceutical Distributor LLC
100.0
Samsung BioEpis SAMSUNG BIOEPIS BR PHARMACEUTICAL LTDA
100.0
Samsung Display Intellectual Keystone Technology LLC
41.9
Samsung Display Samsung Display Slovakia s.r.o.
100.0
Samsung Display Samsung Display Vietnam Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Display Samsung Suzhou Module Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Display Samsung Suzhou LCD Co., Ltd.
60.0
Samsung Display Samsung Display Dongguan Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Display Samsung Display Tianjin Co., Ltd.
95.0
Samsung Display Novaled GmbH
9.9
SEMES SEMES America, Inc.
100.0
SEMES SEMES (XIAN) Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Medison Samsung Medison India Private Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. NexusDX, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. NeuroLogica Corp.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Samsung Receivables Corporation
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Dacor Holdings, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Quietside LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. SmartThings, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Samsung Oak Holdings, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Joyent Inc
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. SamsungPay, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Prismview, LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Samsung Semiconductor, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Samsung Research America, Inc
100.0
Samsung Electronics America, Inc. Samsung International, Inc.
100.0
Dacor Holdings, Inc. Dacor
100.0
Dacor Holdings, Inc. EverythingDacor.com, Inc.
100.0
Dacor Holdings, Inc. Distinctive Appliances of California, Inc.
100.0
Dacor Dacor Canada Co.
100.0
Samsung Oak Holdings, Inc. Stellus Technologies, Inc.
100.0
Joyent Inc Joyent Ltd
100.0
Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. Samsung Austin Semiconductor LLC.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Canada Inc. PrinterOn Corporation
100.0
Samsung Electronics Canada Inc.
A
dGear Technologies Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Canada Inc. NewNet Communication Technologies (Canada), Inc.
100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 210 / 240
PrinterOn Corporation PrinterOn America Corporation
100.0
PrinterOn Corporation PrinterOn Europe Limited
100.0
Samsung Research America, Inc SAMSUNG NEXT LLC
100.0
Samsung Research America, Inc VivLabs
100.0
SAMSUNG NEXT LLC SAMSUNG NEXT FUND LLC
100.0
Samsung International, Inc. Samsung Mexicana S.A. de C.V
100.0
Samsung Electronics Mexico S.A. De C.V. Samsung Electronics Digital Appliance Mexico, SA de CV
100.0
Samsung Electronics (UK) Ltd. Samsung Semiconductor Europe Limited
100.0
Samsung Electronics Holding GmbH Samsung Semicondu
c
tor Europe GmbH
100.0
Samsung Electronics Holding GmbH Samsung Electronics GmbH
100.0
Samsung Electronics Hungarian RT. Samsung Electronics Czech and Slovak s.r.o.
31.4
Samsung Electronics Hungarian RT. Samsung Electronics
Slovakia s.r.o
44.3
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Mexico S.A. De C.V.
36.4
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS BALTICS SIA
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics West Africa
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics East Africa
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Egypt S.A.E
99.9
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Israel Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Tunisia S.A.R.L
99.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Pakistan(Private) Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics South Africa Production (Propr
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Turkey
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Semiconductor Israel R&D Center,Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Levant Co.,Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Maghreb Arab
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Venezuela, C.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung
Electronica da Amazonia Ltda.
13.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Chile Limitada
95.9
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Peru S.A.C.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Rus
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Ukraine LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Ukraine Company LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung R&D Institute Rus LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics KZ and Central Asia LLP
100.0
Samsung Electronics Benelux B.V. Samsung Electronics Caucasus Co., Ltd
100.0
Samsung Electronics Nordic Aktiebolag Samsung
Nanoradio Design Center
100.0
Samsung Electronics Austria GmbH Samsung Electronics Switzerland GmbH
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung Electronics Czech and Slovak s.r.o.
68.6
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung Electronics Romania LLC
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Porta Nuova Varesine Building 2 S.r.l.
49.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung Electronics Poland Manufacturing SP.Zo.o
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung Electronics Greece S.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung Denmark Research Center ApS
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung France Research Center SARL
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Samsung Cambridge Solution Centre Limited
100.0
Samsung Electronics Europe Holding Cooperatief U.A. Novaled GmbH
40.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics Japan Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics Display (M) SDN.Bhd.
25.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics New Zealand Limited
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics Philippines Corporation
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung R&D Institute BanglaDesh
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics Vietnam Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electronics HCMC CE Complex Co. Ltd,.
100.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung SDI(Malaysia) Sdn, Bhd.
25.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 211 / 240
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. Samsung Electro-Mechanics(Thailand) Co., Ltd.
25.0
Samsung Asia Private Ltd. iMarket Asia Co., Ltd.
11.4
PT Samsung Electronics Indonesia PT Samsung Telecommunications Indonesia
100.0
Thai Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Laos Samsug Electronics Sole Co., Ltd
100.0
Samsung Electronics Hong Kong Co., Ltd. iMarket Asia Co., Ltd.
11.3
Suzhou Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Samsung Suzhou Electronics Export
Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Suzhou Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
19.2
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Mobile R&D Center China-Guangzhou
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Mobile R&D Center China -
Tianjin
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Network R&D Center China-Shenzhen
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Electronics (Shandong) Digital Printing Co., Ltd.
12.9
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Electronics Huizhou Co., Ltd.
10.3
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Tianjin Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
43.1
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Beijing Samsung Telecom R&D Center
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Electronics Suzhou Computer Co., Ltd.
26.3
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung R&D Institute China -
Nanjing
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Samsung Electronics (Beijing) Service Company Limited
100.0
Samsung (CHINA) Investment Co., Ltd. Tianjin Samsung Opto-Electronics Co., Ltd.
8.0
Samsung Gulf Electronics Co., Ltd. Samsung Electronics Egypt S.A.E
0.1
Samsung Electronics Maghreb Arab Samsung Electronics Tunisia S.A.R.L
1.0
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica (Zona Libre)
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica Miami, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica (Zona Libre)
Samsung Electronica Colombia S.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronics Latinoamerica (Zona Libre)
Samsung Electronics Panama. S.A
100.0
Samsung Electronica da Amazonia Ltda. Simpress Comercio, Locacao e Servicos S.A.
100.0
Samsung Electronica da Amazonia Ltda. Samsung Electronics Argentina S.A.
2.0
Samsung Electronics KZ and Central Asia LLP Samsung Electronics Caucasus Co., Ltd
0.0
Samsung SDI Intellectual Keystone Technology LLC
41.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Japan Co., Ltd.
89.2
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI America, Inc.
91.7
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Hungary Rt.
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Europe GmbH
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Battery Systems GmbH
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI(Malaysia) Sdn, Bhd.
68.6
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Vietnam Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Energy Malaysia Sdn, Bhd.
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI(Hong Kong) Ltd.
97.6
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI China Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI-
A
RN (Xi'An) Power Battery Co., Ltd.
50.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI-Sungrow Energy Storage Battery Co., Lt
65.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI (Changchun) Power Battery Co., Ltd.
50.0
Samsung SDI
Samsung SDI(Tianjin)Battery Co.,Ltd.
50.0
Samsung SDI Samsung SDI Brasil Ltda.
45.0
Samsung SDI Novaled GmbH
50.1
Samsung SDI SAMSUNG SDI WUXI CO.,LTD.
100.0
Samsung SDI Samsung Chemical Electronic Materials (SuZhou) Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDI iMarket Asia Co., Ltd.
8.7
Samsung SDI America, Inc. Samsung SDI Mexico, S.A. de C.V.
100.0
Samsung SDI America, Inc. Samsung SDI Brasil Ltda.
40.4
Samsung SDI(Hong Kong) Ltd. Tianjin Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
80.0
Samsung SDI(Hong Kong) Ltd. Samsung SDI Brasil Ltda.
14.5
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Machanics Japan Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics Japan Advanced Technology Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics America, Inc.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics SAMSUNG ELECTRO-MECHANICS GMBH
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Hungary Electro-Mechanics Private Limited Liability Company
100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 212 / 240
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics(Thailand) Co., Ltd.
75.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics Philippines, Corp.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Calamba Premier Realty Corporation
39.8
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics Pte Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics Vietnam Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Dongguan Samsung Electro-Mechanics Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Tianjin Samsung Electro-Mechanics Co., Ltd.
81.8
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung High-Tech Electro-Mechanics(Tianjin) Co., Ltd.
95.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Samsung Electro-Mechanics (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics Kunshan Samsung Electro-Mechanics Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Electro-Mechanics iMarket Asia Co., Ltd.
8.7
Samsung Electro-Mechanics America, Inc. Samsung Electro-Mechanics do Brasil Intermediacoes de Negocios Ltda.
100.0
Calamba Premier Realty Corporation Batino Realty Corporation
100.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance SAMSUNG FIRE & MARINE MANAGEMENT CORPORATION
100.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance SAMSUNG FIRE & MARINE INSURANCE COMPANY OF EUROPE
100.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance P.T. Asuransi Samsung Tugu
70.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Samsung Vina Insurance Co., Ltd
75.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance SAMSUNG REINSURANCE PTE. LTD
100.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Samsung Property & Casualty Insurance Company(China), Ltd
100.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance Samsung
Fire & Marine Insurance Management Middle East
100.0
Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance SAMSUNG FIRE & MARINE CONSULTORIA EM SEGUROS LTDA.
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. Camellia Consulting Corporation
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. Offshore 1 consulting Corporation
51.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. Samsung Heavy Industries India Pvt.Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. SAMSUNG HEAVY INDUSTRIES (M) SDN.BHD
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. Samsung Heavy Industries(Ningbo) Co., Ltd
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. Samsung Heavy Industries(Rongcheng) Co., Ltd
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. Rongcheng Gaya Heavy Industries Co., Ltd
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. SAMSUNG HEAVY INDUSTRIES NIGERIA LIMITED
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. SAMSUNG HEAVY INDUSTRIES BRASIL ASSESSORIA EM PROJETOS
EMPRESARIAIS LTDA.
100.0
Samsung Heavy Industries Co.,Ltd. SHI BRAZIL CONSTRUCTION
100.0
SAMSUNG HEAVY INDUSTRIES NIGERIA LIMITED SHI - MCI FZE
70.0
Samsung Life Insurance Porta Nuova Varesine Building 2 S.r.l.
51.0
Samsung Life Insurance 30 GRESHAM STREET(JERSEY) LIMITED
100.0
Samsung Life Insurance THAI SAMSUNG LIFE INSURANCE CO., LTD.
35.8
Samsung Life Insurance Beijing Samsung Real Estate Co.. Ltd
90.0
Samsung Asset Management Samsung Asset Management (New York), Inc.
100.0
Samsung Asset Management Samsung Asset Management(London) Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Asset Management Samsung Private Equity Manager I Co., Ltd
100.0
Samsung Asset Management Samsung Asset Management (Hong Kong) Ltd.
100.0
30 GRESHAM STREET(JERSEY) LIMITED 30 GRESHAM STREET (SINGAPORE) LIMITED
100.0
Samsung Asset Management (Hong Kong) Ltd. Samsung Asset Management (Beijing) Ltd.
100.0
CHEIL INDUSTRIES ITALY SRL COLOMBO VIA DELLA SPIGA S.R.L
100.0
Samsung Fashion Trading Co. ,Ltd Eight Seconds(Shanghai)Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation MYODO METAL CO., LTD.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Japan Corporation
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T America Inc.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Finance Corporation.
80.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung E&C America, INC.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SAMSUNG OIL & GAS USA CORP
90.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Renewable Energy Inc.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SCNT Power Norte S. De R.L. de C.V.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation QSSC, S.A. de C.V.
60.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Oil & Gas Parallel Corp.
100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 213 / 240
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Canada Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Deutschland GmbH
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T U.K. Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T ECUK Limited
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Whessoe engineering Limited
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SCNT Investment Atlantic SPRL
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation POSS-SLPC, s.r.o
50.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Solluce Romania 1 B.V.
80.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SAM investment Manzanilo.B.V
53.3
Samsung C&T Corporation Solluce Slovenia 1 B.V.
80.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Ecosolar OOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Ecoenergy Solar OOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation
A
grilplam EOOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Fishtrade EOOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Manageproject EOOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Solar Park EOOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Veselinovo Energy OOD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Construction Hungary Kft.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T (KL) Sdn.,Bhd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Malaysia SDN. BHD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Erdsam Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Chemtech Vina LLC
51.7
Samsung C&T Corporation S-print Inc
40.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Cassava Investment Korea Pte. Ltd.
29.7
Samsung C&T Corporation P.T. Samsung Development
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Development (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
33.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Thailand Co., Ltd
43.9
Samsung C&T Corporation Cheil Holding Inc.
40.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Const. Co. Phils.,Inc.
25.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Design Philippines Inc
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Oil & Gas Australia PTY. LTD
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation PT. INSAM BATUBARA ENERGY
90.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T India Pte., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Corporation India Private Limited
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Malaysia Samsung Steel Center Sdn.Bhd
70.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Singapore Pte., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation S&G Biofuel PTE.LTD
50.5
Samsung C&T Corporation SAMSUNG C&T Mongolia LLC.
70.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Eng.&Const. Mongolia LLC.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation S&WOO CONSTRUCTION PHILIPPINES,INC.
40.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Hongkong Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation GUANGDONG XINGPU STEEL CENTER CO.,LTD
51.6
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Taiwan Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Precision Stainless Steel(pinghu) Co.,Ltd.
55.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SAMSUNG C&T (SH
A
NGHAI) CO., LTD.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T (Xi'an) Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Nigeria Co., Ltd.
99.9
Samsung C&T Corporation SAMSUNG C&T CORPORATION SAUDI ARABIA
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SAM Gulf Investment Limited
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Chile Copper SpA
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation SCNT Power Kelar Inversiones Limitada
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T do Brasil Construtora LTDA.
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Corporation Rus LLC
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation KSI LLP
25.0
Samsung C&T Corporation JSC BALKHASH THERMAL POWER PLANT
50.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 214 / 240
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung SDI America, Inc.
8.3
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung SDI(Malaysia) Sdn, Bhd.
6.4
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung SDI(Hong Kong) Ltd.
2.4
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung SDI Brasil Ltda.
0.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Beijing Samsung Real Estate Co.. Ltd
10.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Cheil Industries Corp., USA
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation CHEIL INDUSTRIES ITALY SRL
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung Fashion Trading Co. ,Ltd
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation CHEIL INDUSTRIES INC. VIETNAM COMPANY LIMITED
100.0
Samsung C&T Corporation Samsung C&T Corporation UEM Construction JV Sdn Bhd
60.0
Samsung C&T Corporation iMarket Asia Co., Ltd.
19.3
Samsung Welstory WELSTORY VIETNAM COMPANY LIMITED
90.0
Samsung Welstory Shanghai Ever-Hongjun Business Mgt Service Co.,LTD
85.0
Samsung Welstory Shanghai Welstory Food Company Limited
70.0
MULTICAMPUS L
A
NGUAGE TESTING INTERNATIONAL, INC
82.4
Eight Seconds(Shanghai)Co., Ltd. Eight Seconds (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd.
100.0
PengTai Greater China Co., Ltd. PengTai China Co., Ltd.
100.0
PengTai Greater China Co., Ltd. PengTai Taiwan Co., Ltd.
100.0
PengTai Greater China Co., Ltd. PengTai Interactive Advertising Co.,Ltd.
100.0
PengTai China Co., Ltd. PengTai e-Commerce Co.,Ltd.
100.0
PengTai China Co., Ltd. PengTai Marketing Service Co., Ltd.
100.0
PengTai Interactive Advertising Co.,Ltd. MEDIALYTICS Inc.
51.0
iMarket Asia Co., Ltd. iMarket China Co., Ltd.
80.0
Samsung Securities Samsung Securities (America), Inc.
100.0
Samsung Securities Samsung Securities (Europe) Limited.
100.0
Samsung Securities Samsung Securities (Asia) Limited.
100.0
Samsung SDS iMarket Asia Co., Ltd.
40.6
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc.
100.0
Samsung SDS SAMSUNG SDS GSCL CANADA., LTD.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS America, Inc.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Europe Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Hungary Kft.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Slovakia,
s.r.o.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Poland Sp. Z.o.o.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Netherlands Cooperatief U.A
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Asia Pacific Pte. Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS India PVt. Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDS SAMSUNG SDS VIETNAM CO., LTD.
100.0
Samsung SDS SAMSUNG SDS GLOBAL SCL ASIA PACIFIC PTE. LTD.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS GSCL Vietnam Co Ltd
100.0
Samsung SDS PT. Samsung SDS Global SCL Indonesia
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Philippines Co., Ltd. Inc.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Thailand Co.,Ltd
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Malaysia SDN.BHD.
100.0
Samsung SDS SAMSUNG SDS GLOBAL SCL AUSTRALIA PTY., LTD.
100.0
Samsung SDS SDS-
A
CUTECH CO., LTD
50.0
Samsung SDS
A
LS SDS Joint Stock Company
51.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS China, Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung IT Services (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Hong Kong Ltd
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Egypt
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL South Africa (PTY) Ltd.
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Transport and Logistics Joint Stock Company
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global Supply Chain Logistics Middle East DWC-LLC
100.0
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Latin America Solucoes Em Tecnologia Ltda
99.7
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 215 / 240
Samsung SDS SAMSUNG SDS GLOBAL SCL LATIN AMERICA LOGISTICA LTD
99.7
Samsung SDS Samsung SDS Global SCL Rus Limited Liability Company
100.0
Miracom MIRACOM INC ASIA PACIFIC LTD
100.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. Samsung SDS Latin America Solucoes Em Tecnologia Ltda
0.3
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. Samsung SDS Mexico, S.A. DE C.V.
99.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. Samsung SDS Global SCL Panama S. A.
100.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. Samsung SDS Global SCL Chile Limitada
100.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. Samsung SDS Global SCL Peru S.A.C.
100.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. Samsung SDS Global SCL Colombia S.A.S.
100.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL America, Inc. SAMSUNG SDS GLOBAL SCL LATIN AMERICA LOGISTICA LTD
0.3
Samsung SDS Europe Ltd. Samsung SDS Global SCL Netherlands Cooperatief U.A
0.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL Netherlands Cooperatief U.A Samsung SDS Global SCL Poland Sp. Z.o.o.
0.0
Samsung SDS Global SCL Netherlands Cooperatief U.A Samsung SDS Global SCL Rus Limited Liability Company
0.0
Samsung SDS India PVt. Ltd. Samsung SDS India Private Limited
100.0
Samsung SDS China, Ltd. Samsung SDS Global Development Center Xi'an
100.0
Samsung SDS China, Ltd. Samsung SDS Global SCL Beijing Co., Ltd
100.0
MIRACOM INC ASIA PACIFIC LTD MIRACOM INC CHINA LTD
100.0
Samsung Engineering Offshore 1 consulting Corporation
49.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering America Inc.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering Hungary Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering (Malaysia) SDN.
BHD.
100.0
Samsung Engineering PT Samsung Engineering Indonesia Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
81.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering India Private Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering Vietnam
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering Construction(Shanghai) Co., Lt
100.0
Samsung Engineering SAMSUNG ENGINEERING CONSTRUCTION XIAN CO., LTD.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Saudi Arabia Company Limited.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Muharraq Wastewater Services Company W.L.L.
64.8
Samsung Engineering Muharraq STP Company B.S.C.
4.6
Samsung Engineering Muharraq Holding Company 1 Ltd.
45.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Ingenieria Mexico Construccion Y Operacion S.A. De C.V.
99.9
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering Trinidad Co., Ltd.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Ingenieria Manzanillo, S.A. De C.V.
99.9
Samsung Engineering Grupo Samsung Ingenieria Mexico, S.A. De C.V.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Ingenieria Energia S.A. De C.V.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering Bolivia S.A
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Ingenieria DUBA S.A. de C.V.
100.0
Samsung Engineering Samsung Engineering Kazakhstan LLP
100.0
Samsung Engineering America Inc. SEA Construction, LLC
100.0
Samsung Engineering America Inc. SEA Louisiana
Construction, L.L.C.
100.0
Samsung Engineering (Malaysia) SDN. BHD. Muharraq Wastewater Services Company W.L.L.
0.3
Samsung Engineering India Private Ltd. Samsung Saudi Arabia Company Limited.
0.0
Samsung Saudi Arabia Company Limited. Samsung EPC Company Ltd.
75.0
Muharraq Holding Company 1 Ltd. Muharraq Holding Company 2 Ltd.
100.0
Muharraq Holding Company 2 Ltd. Muharraq STP Company B.S.C.
89.9
S1 Corporation SOCM LLC
100.0
S1 Corporation Samsung Beijing Security Systems
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil USA Inc.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Central America Inc.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide IRIS Worldwide Holdings Limited
71.7
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Europe Ltd.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Germany GmbH
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil France SAS
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Nordic AB
100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 216 / 240
Cheil Worldwide Cheil India Pvt. Ltd.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil (Thailand) Ltd.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Singapore Pte. Ltd.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Vietnam Co. Ltd.
90.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Integrated Marketing Philippines, Inc.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Malaysia SDN BHD
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil China
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Hong Kong Ltd.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Bravo Asia Limited
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Bravo Asia-Shanghai
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil MEA FZ-LLC
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil South Africa Pty., Ltd.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide CHEIL KENYA LIMITED
99.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Communications Nigeria Ltd.
99.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Jordan LLC
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Ghana Limited
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Brazil Communications Ltda.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Mexico Inc. SA de CV
98.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Chile SpA.
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Rus LLC
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Ukraine LLC
100.0
Cheil Worldwide Cheil Kazakhstan LLC
100.0
Hotel Shilla Samsung Hospitality America Inc.
100.0
Hotel Shilla SAMSUNG HOSPITALITY U.K. Limited
100.0
Hotel Shilla SAMSUNG HOSPITALITY ROMANIA SRL
100.0
Hotel Shilla Shilla Travel Retail Pte.Ltd
100.0
Hotel Shilla SAMSUNG HOSPITALITY VIETNAM CO.,LTD
100.0
Hotel Shilla SHILLA HOSPITALITY PHILIPPINES INC.
100.0
Hotel Shilla SAMSUNG HOSPITALITY INDIA PRIVATE LIMITED
100.0
Hotel Shilla SHILLA LIMITED Macao
100.0
Hotel Shilla Samsung Shilla Business Service Beijing Co., Ltd.
100.0
Hotel Shilla SHILLA LIMITED Hong Kong
100.0
Iris Americas, Inc. Iris USA, Inc.
100.0
Iris Americas, Inc. Iris Atlanta, Inc.
100.0
Iris Americas, Inc. Iris Experience, Inc.
100.0
Iris Americas, Inc. Iris Latin America, Inc.
100.0
Iris Americas, Inc. Iris Worldwide San Diego, Inc.
100.0
Iris Latin America, Inc. Irisnation Latina No.2, S. de R.L. de C.V.
0.0
Iris Latin America, Inc. Irisnation Latina, S. de R.L. de C.V.
0.0
Cheil USA Inc. The Barbarian Group LLC
100.0
Cheil USA Inc. McKinney Ventures LLC
100.0
Cheil USA Inc. Cheil India Pvt. Ltd.
0.0
Cheil USA Inc. Cheil Mexico Inc. SA de CV
2.0
Samsung Hospitality America Inc. Samsung Hospitality Europe GmbH
100.0
IRIS Worldwide Holdings Limited Iris Nation Worldwide Limited
100.0
IRIS Worldwide Holdings Limited Josh & James Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Americas, Inc.
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Irisnation Latina No.2, S. de R.L. de C.V.
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Irisnation Latina, S. de R.L. de C.V.
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris London Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Promotional Marketing Ltd
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Ventures 1 Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Founded Partners Limited
76.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Products (Worldwide) Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Korea Limited
100.0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 217 / 240
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris PR Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Concise Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Digital Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Amsterdam B.V.
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Datalytics Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Ventures (Worldwide) Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Culture Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Concise Consultants Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Irisnation Singapore Pte Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Worldwide Integrated Marketing Pvt Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris Sydney PTY Ltd
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Iris (Beijing) Advertising Company Limited
100.0
Iris Nation Worldwide Limited Irisnation Hong Kong Limited
100.0
Iris London Limited Iris Partners LLP
100.0
Iris Promotional Marketing Ltd Holdings BR185 Limited
100.0
Iris Ventures 1 Limited Iris Germany GmbH
100.0
Founded Partners Limited Founded Partners, Inc.
100.0
Iris Germany GmbH Pepper NA, Inc.
100.0
Iris Germany GmbH Pepper Technologies Pte Limited
100.0
Cheil Europe Ltd. BEATTIE MCGUINNESS BUNGAY LIMITED
100.0
Cheil Europe Ltd. Cheil Italia S.r.l
100.0
Cheil Europe Ltd. CHEIL SPAIN S.L
100.0
Cheil Europe Ltd. CHEIL BENELUX B.V.
100.0
Cheil Germany GmbH Cheil Austria GmbH
100.0
Cheil Singapore Pte. Ltd. PengTai Greater China Co., Ltd.
95.0
Cheil Singapore Pte. Ltd. PT. CHEIL WORLDWIDE INDONESIA
100.0
Cheil Integrated Marketing Philippines, Inc. Cheil Philippines Inc.
30.0
Cheil Hong Kong Ltd. PengTai Greater China Co., Ltd.
3.1
Cheil MEA FZ-LLC One Agency FZ LLC
100.0
Cheil MEA FZ-LLC One RX Project Management Design and Production Limited Company
0.0
Cheil South Africa Pty., Ltd. CHEIL KENYA LIMITED
1.0
Cheil South Africa Pty., Ltd. Cheil Communications Nigeria Ltd.
1.0
One Agency FZ LLC One RX India PVT. LTD
100.0
One Agency FZ LLC One RX Project Management Design and Production Limited Company
100.0
One Agency FZ LLC One RX Interior Design LLC
100.0
One Agency FZ LLC One RX Printing LLC
100.0
One Agency FZ LLC One Agency South Africa Pty., Ltd.
100.0
One Agency FZ LLC One RX Russia LLC
99.9
One RX Interior Design LLC One RX India PVT. LTD
0.0
Holdings BR185 Limited Brazil 185 Participacoes Ltda
100.0
Brazil 185 Participacoes Ltda Iris Router Marketing Ltda
80.0
Cheil Rus LLC One RX Russia LLC
0.1
※ (% of Ownership; As of December 31, 2016; Based on Common shares)
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 218 / 240
C. Related Statute & Regulation
Restrictions on cross-holdings within Samsung Group in accordance with the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act
(1) Date of announcement by authorities of companies deemed Samsung Group companies for the current year:
April 1, 2016
(2) Summary of Regulation
- Restriction of cross-holdings
- Restriction of debt guarantee between affiliates
- Restriction of voting rights at financial affiliates, including insurance
- Decision by board committee and public disclosure of large-scale related party transactions
- Public disclosure of important matters of unlisted companies
- Other public disclosures related to Group status

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 219 / 240
D. Equity Investments in other corporations
(1) The
total book value of equity investments in other corporations as of December 31, 2016 is KRW 49,937 billion
[As of December 31, 2016]
(Unit: 1,000 shares, KRW million, %)
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisitio
n Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance Current Financial Stats
Qty
Ownershi
p (%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valu
ation
Qty
Owner
ship
(%)
Book Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Listed
Samsung
Electro-
Mechanics
1977.01 Business 250
17,693
23.69
445,244
0 0
17,693
23.69
445,244
7,269,453
20,643
Listed
Samsung
Card
1988.12 Business 10,000
43,393
37.45
1,455,485
-43,393
-
1,455,48
5
0
0
0.00
0
19,070,997
333,724
Unlisted STECO 1995.06 Management
24,000
2,590
70.00
35,861
0 0
2,590
70.00
35,861
73,744
2,273
Unlisted SEMES 1992.12 Management
1,000
2,173
91.54
71,906
0 0
2,173
91.54
71,906
717,229
76,299
Unlisted SERI 1991.05 Business 320
3,576
29.80
24,942
0 0
3,576
29.80
24,942
131,131
221
Listed
Samsung
SDS
1992.07 Business 6,160
17,472
22.58
560,827
0 0
17,472
22.58
560,827
6,331,679
469,831
Unlisted
Samsung
Lions
1986.08 Business 240
55
27.50
-102
-55 102
0
0
0.00
0
28,042
25,631
Unlisted
Samsung
Electronics
Service
1998.01 Management
30,000
6,000
99.33
48,121
0 0
6,000
99.33
48,121
296,104
1,388
Unlisted
Samsung
Electronics
Sales
2000.12 Management
3,100
1,767
100.00
247,523
0 0
1,767
100.00
247,523
550,655
2,062
Unlisted
Samsung
Electronics
Logitech
1999.04 Management
76
1,011
100.00
46,669
0 0
1,011
100.00
46,669
146,052
13,165
Unlisted
Samsung
Display
2012.04 Management
16,009,547
221,969
84.78
18,509,307
0 0
221,969
84.78
18,509,307
39,225,460
1,673,165
Unlisted SVIC #14 2009.05 Management
18,000
0
99.00
0
0 0
0
0.00
0
66,796
4,487

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 220 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance Current Financial Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted SVIC #21 2011.11 Management
19,800
2
99.00
164,692
-1 -67,122
0
1
99.00
97,570
181,200
9,646
Unlisted SVIC #22 2011.11 Management
19,800
2
99.00
159,558
-1 -12,276
0
1
99.00
147,282
163,503
-3,405
Unlisted SVIC #26 2014.11 Management
19,800
1
99.00
108,405
1 25,839
49,500
2
99.00
183,744
105,021
5,062
Unlisted SVIC #27 2014.09 Management
5,940
0
99.00
15,642
0 0
0
99.00
15,642
16,567
862
Unlisted SVIC #28 2015.02 Management
7,425
1
99.00
67,518
1 80,784
11,682
2
99.00
159,984
64,453
-5,020
Unlisted SVIC #32 2016.08 Management
19,800
0
0.00
0
0 40,194
0
0
99.00
40,194
0
0
Unlisted SVIC #33 2016.11 Management
4,950
0
0.00
0
0 4,950
0
0
99.00
4,950
0
0
Unlisted
Samsung
Medison
2011.02 Management
286,384
87,350
68.45
477,648
0 0
87,350
68.45
477,648
315,073
-19,902
Unlisted
S-Printing
Solution
2016.11 Business 218,370
0
0.00
0
10,000 218,370
0
10,000
100.00
218,370
0
0
Unlisted
Samsung
BioLogics
2011.04 Business 30,000
12,899
46.79
545,665
7,938 -102,472
0
20,837
31.49
443,193
5,974,295
1,874,243
Unlisted
Intellectual
Discovery
2011.05 Business 5,000
1,784
15.71
5,241
0 0
1,784
15.71
5,241
46,591
-5,479
Listed
Samsung
Heavy
Industries
1977.09 Business 125
40,676
17.61
441,331
25,255 215,428
-46,897
65,931
16.91
609,862
17,301,592
-
1,212,110
Listed
Samsung Fine
Chemicals
1995.05 Business 1,346
2,165
8.39
77,073
-2,165 -77,073
0
0
0.00
0
1,684,225
89,979
Listed Hotel Shilla 1979.12 Business 252
2,005
5.11
154,965
0 -58,438
2,005
5.11
96,527
2,176,705
18,482
Listed
Cheil
Worldwide
1988.09 Business 185
14,499
12.60
300,124
14,539 259,619
-68,144
29,038
25.24
491,599
1,866,862
81,741

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 221 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Listed A-Tech Solution 2009.11 Business 26,348
1,592
15.92
8,469
0
8,167
1,592
15.92
16,636
172,054
-3043
Listed iMarket Korea 2000.12 Business 1,900
647
1.80
16,377
0
-9,645
647
1.80
6,732
1,266,306
49,566
Listed KT Skylife 2001.12 Business 3,344
240
0.50
4,152
0
240
0.50
4,152
711,294
72,987
Listed Samsung SDI 1977.01 Business 304
13,463
19.58
1,534,745
0
-292,140
13,463
19.58
1,242,605
16,225,303
25,686
Listed Wonik IPS 2016.04 Business 16,214
0
0.00
0
1,851
20,545
27,950
1,851
4.48
48,495
0
0
Listed Wonik Holdings 2013.12 Business 15,411
3,610
4.48
40,975
-1,851
-20,545
-8,573
1,759
2.28
11,857
658,491
73,014
Unlisted SSLM 2012.04 Business 52,296
4,378
9.31
0
-4,158
0
220
0.39
0
137,633
-77,909
Unlisted
Kihyup
Technology
Banking
1995.01 Business 5,000
1,000
17.24
5,000
0
0
1,000
17.24
5,000
98,192
968
Unlisted Pusan Newport 1997.09 Business 590
1,135
0.98
5,677
-1,135
-5,677
0
0
0.00
0
641,380
45,221
Unlisted
The Korea
Economic Daily
1987.05 Business 150
72
0.39
365
0
0
72
0.39
365
324,848
27,122
Unlisted
Samsung
Venture
Investment
1999.11 Business 4,900
980
16.33
7,207
0
308
980
16.33
7,515
82,759
6,010
Unlisted Cyber Bank 2000.12 Business 8,000
1,083
7.46
0
0
0
1,083
7.46
0
0
0
Unlisted FineChips 2001.12 Business 10
2
3.81
10
0
0
2
3.81
10
3,626
41
Unlisted SK Telink 2010.11 Business 4,357
15
1.13
4,357
0
0
15
1.13
4,357
309,955
55,781
Unlisted Inkel 2006.11 Business 130
0
0.00
0
0
0
0
0.00
0
129,344
-1,694

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 222 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Listed
Yongpyong
Resort
2007.05 Business 1,869
400
1.05
1,869
0 1,563
400
0.83
3,432
970,651
11,573
Unlisted
Sambo
Computer
2012.09 Withdrawal 0
0
0.01
0
0 0
0
0.01
0
37,711
2,280
Unlisted Icube #1 2009.12 Business 4,000
0
16.23
4,000
0 0
0
16.23
4,000
20,747
-287
Unlisted KT Wibro 2010.07 Business 60,000
600
24.20
48,500
0 0
600
24.20
48,500
270,129
3,540
Unlisted
Shinsung Eng &
Construction
2010.07 Withdrawal 1
0
0.01
0
0 0
0
0.01
0
55,272
584
Unlisted Woobang 2010.07 Withdrawal 0
1
0.00
0
0 0
1
0.00
0
260,744
12,199
Unlisted
Heehoon
Design &
Global
2010.07 Withdrawal 0
2
0.02
0
0 0
2
0.02
0
42,516
-8,168
Unlisted
Daewoo
Development
2012.12 Withdrawal 0
0
0.02
0
0 0
0
0.02
0
131,773
953
Unlisted
Daewoo
Songdo
Development
2012.12 Withdrawal 0
9
0.02
0
0 0
9
0.02
0
1,216,605
-7,984
Unlisted
Zyle Motor
Sales
2012.12 Withdrawal 0
1
0.00
0
0 0
1
0.00
0
305,917
4,623
Unlisted
Woojung
Construction
2014.04 Withdrawal 0
5
0.35
0
0 0
5
0.35
0
23,920
-6,902
Unlisted Hyunjin 2014.04 Withdrawal 0
23
0.25
0
0 0
23
0.25
0
31,585
13,219
Unlisted
Sungwon
Construction
2014.04 Withdrawal 0
1
0.03
0
0 0
1
0.03
0
34,337
-1,733
Unlisted Inhee 2014.04 Withdrawal 0
2
0.17
0
0 0
2
0.17
0
10,698
-99
Unlisted
Samsung
Solution
2014.04 Withdrawal 0
4
6.70
0
0 0
4
6.70
0
8,925
55

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 223 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance Current Financial Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total
Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted
STX
Construction
2014.04 Withdrawal 0
0
0.01
0
0 0
0
0.01
0
117,512
-320
Unlisted Poonglim 2014.05 Withdrawal 0
52
0.37
0
0 0
52
0.37
0
340,165
-1,056
Unlisted JNT 2011.02 Business 1,800
0
24.00
3,120
0 -624
0
0
24.00
2,496
13,437
-35
Unlisted SV 2011.02 Business 1,850
0
14.85
3,188
0 -896
0
0
14.85
2,292
20,085
-85
Unlisted
Seoul
Investment
Partners
2011.1 Business 1,550
0
19.38
2,737
0 -48
0
0
19.38
2,689
12,061
6,955
Unlisted Daishin Aju IB 2011.08 Business 258
0
3.00
1,049
0 -323
0
0
3.00
726
44,139
11,675
Unlisted TS 2011.11 Business 1,700
0
20.32
2,682
0 -1,478
0
0
20.48
1,204
19,749
5,737
Unlisted IMM 2011.11 Business 760
0
7.60
1,964
0 -1,256
0
0
7.60
708
29,433
12,154
Unlisted L&S 2012.07 Business 848
0
7.46
2,773
0 -1,017
0
0
7.46
1,756
32,490
-545
Unlisted Maltani Corp. 2012.04 Business 16,544
45
15.00
15,860
0 0
410
45
15.00
16,270
68,704
382
Unlisted Pantech 2013.06 Business 53,000
53,000
10.03
0
0 0
53,000
10.03
0
86,122
-69,928
Unlisted KTCNP-GC 2013.12 Business 960
0
3.56
4,036
0 1,219
0
0
3.56
5,255
110,296
-622
Unlisted
Postech
Technology
Investment
2013.12 Business 600
0
10.00
600
0 0
0
10.00
600
296,670
95
Unlisted
AI Research
Institute
2016.07 Business 3,000
0
0.00
0
600 3,000
0
600
14.29
3,000
0
0
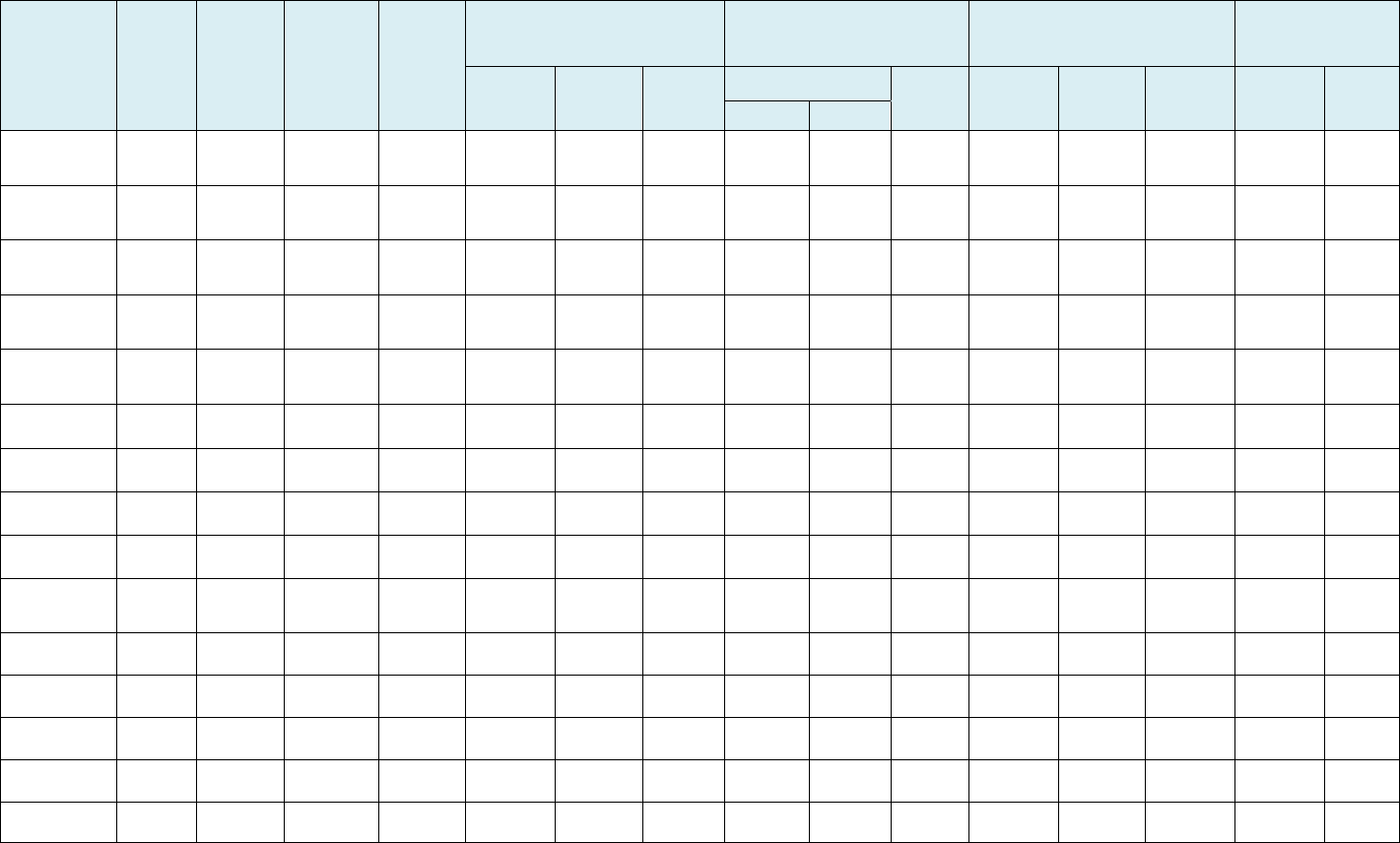
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 224 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted SECA 1992.08
Position
Security
3,823
0
100.00
90,922
0 0
0
100.00
90,922
465,801
30,182
Unlisted SEA 1978.07
Position
Security
59,362
492
100.00
5,651,195
0 4,411,886
0
492
100.00
10,063,081
14,875,687
268,083
Unlisted SELA 1989.04
Position
Security
319
40
100.00
86,962
0 0
40
100.00
86,962
327,557
-35,071
Unlisted SEM 1995.07
Position
Security
3,032
3,837
63.58
165,638
0 0
3,837
63.58
165,638
1,030,161
193,947
Unlisted SEASA 1996.06
Position
Security
4,696
21,854
98.00
6,779
0 0
21,854
98.00
6,779
40,459
6,572
Unlisted SEDA 1994.01
Position
Security
13,224
77,205,709
87.04
647,620
0 0
77,205,709
87.04
647,620
3,114,334
322,939
Unlisted SECH 2002.12
Position
Security
597
0
4.10
597
0 0
0
4.10
597
345,850
28,583
Unlisted SESA 1989.01
Position
Security
3,276
8,021
100.00
142,091
0 0
8,021
100.00
142,091
642,393
43,198
Unlisted SENA 1992.03
Position
Security
392
1,000
100.00
69,372
0 0
1,000
100.00
69,372
701,525
5,086
Unlisted SEH 1991.05
Position
Security
1,954
753
100.00
650,157
0 0
753
100.00
650,157
1,254,673
97,474
Unlisted SEP 1982.09
Position
Security
204
1,751
100.00
37,616
0 0
1,751
100.00
37,616
155,940
6,773
Unlisted SEF 1991.08
Position
Security
230
2,700
100.00
234,115
0 0
2,700
100.00
234,115
908,971
63,996
Unlisted SEUK 1995.07
Position
Security
33,908
109,546
100.00
433,202
0 0
109,546
100.00
433,202
1,133,512
106,413
Unlisted SEHG 1982.02
Position
Security
28,042
0
100.00
354,846
0 0
0
100.00
354,846
383,777
112,541
Unlisted SEAG 2002.01
Position
Security
40
0
100.00
32,162
0 0
0
100.00
32,162
289,807
16,498

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 225 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total
Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted SEI 1993.05
Position
Security
862
677
100.00
143,181
0 0
677
100.00
143,181
768,278
59,554
Unlisted SEBN 1995.07
Position
Security
236
539,138
100.00
914,751
0 0
539,138
100.00
914,751
1,264,497
42,790
Unlisted SELS 1991.05
Position
Security
18,314
1,306
100.00
24,288
0 0
1,306
100.00
24,288
1,894,614
-7,745
Unlisted SEPOL 1996.04
Position
Security
5,462
106
100.00
78,267
0 0
106
100.00
78,267
457,516
51,265
Unlisted SSA 1998.12
Position
Security
263
2,000
100.00
32,622
0 0
2,000
100.00
32,622
603,300
51,871
Unlisted SESK 2002.06
Position
Security
8,976
0
55.68
263,767
0 0
0
55.68
263,767
1,888,341
107,968
Unlisted SEEH 2008.01
Position
Security
4,214
0
100.00
1,369,992
0 0
0
100.00
1,369,992
6,989,207
-31,925
Unlisted SEO 1997.01
Position
Security
120
0
100.00
-10,043
0 0
0
100.00
-10,043
105,859
-134
Unlisted SRSC 1997.11
Position
Security
707
0
100.00
8,211
0 -8,211
0
0
0.00
0
22,414
186
Unlisted SERC 2006.01
Position
Security
24,877
0
100.00
180,079
0 8,211
0
0
100.00
188,290
598,708
11,598
Unlisted SERK 2007.07
Position
Security
4,600
0
100.00
204,555
0 0
0
100.00
204,555
608,200
52,030
Unlisted SEAU 1987.11
Position
Security
392
53,200
100.00
111,964
0 0
53,200
100.00
111,964
431,714
-22,370
Unlisted SEMA 1989.09
Position
Security
4,378
16,247
100.00
153,602
0 0
16,247
100.00
153,602
117,879
18,228
Unlisted SGE 1995.05
Position
Security
827
0
100.00
32,836
0 0
0
100.00
32,836
952,236
59,431
Unlisted SEEG 2012.07
Position
Security
23
0
0.05
39
0 0
0
0.05
39
539,155
48,358

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 226 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted SEIN 1991.08
Position
Security
7,463
46
99.99
118,909
0 0
46
99.99
118,909
964,021
53,205
Unlisted SDMA 1995.03
Position
Security
21,876
71,400
75.00
244,382
0 0
71,400
75.00
244,382
246,755
26,583
Unlisted SIEL 1995.08
Position
Security
5,414
216,787
100.00
75,263
0 0
216,787
100.00
75,263
3,723,127
326,462
Unlisted SRI-B 2005.05
Position
Security
7,358
17
100.00
31,787
0 0
17
100.00
31,787
147,149
-2,500
Unlisted SAVINA 1995.01
Position
Security
5,839
0
100.00
28,365
0 0
0
100.00
28,365
350,158
55,471
Unlisted TSE 1988.01
Position
Security
1,390
11,020
91.83
279,163
0 0
11,020
91.83
279,163
1,889,410
179,527
Unlisted STE 1996.01
Position
Security
4,206
2,499
49.00
0
0 0
2,499
49.00
0
6,568
0
Unlisted SME 2003.05
Position
Security
4,796
17,100
100.00
7,644
0 0
17,100
100.00
7,644
312,263
18,422
Unlisted SAPL 2006.07
Position
Security
793
877,133
100.00
981,483
0 0
877,133
100.00
981,483
4,227,798
957,734
Unlisted SEHK 1988.09
Position
Security
349
274,250
100.00
79,033
0 0
274,250
100.00
79,033
948,800
26,450
Unlisted SET 1994.11
Position
Security
456
27,270
100.00
112,949
0 0
27,270
100.00
112,949
1,253,480
44,025
Unlisted SESS 1994.12
Position
Security
18,875
0
100.00
504,313
0 0
0
100.00
504,313
836,562
78,202
Unlisted SCIC 1996.03
Position
Security
23,253
0
100.00
617,941
0 22,512
0
0
100.00
640,452
12,748,395
-77,629
Unlisted SEHZ 1992.12
Position
Security
792
0
89.56
255,535
0 0
0
89.56
255,535
6,192,974
722,700
Unlisted SSEC 1995.04
Position
Security
32,128
0
69.06
130,551
0 0
0
69.06
130,551
637,485
16,748

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 227 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted TSEC 1993.04
Position
Security
15,064
0
48.20
138,101
0 0
0
48.20
138,101
858,675
100,638
Unlisted SSDP 1993.08
Position
Security
4,446
0
87.10
65,319
0 0
0
87.10
65,319
853,982
87,004
Unlisted TSTC 2001.03
Position
Security
10,813
0
90.00
490,041
0 0
0
90.00
490,041
2,075,123
146,972
Unlisted SSTC 2001.11
Position
Security
15,799
0
100.00
22,512
0 -22,512
0
0
0.00
0
6,151
-898
Unlisted SSET 2002.02
Position
Security
6,009
0
95.00
121,624
0 0
0
95.00
121,624
118,697
15,839
Unlisted SESC 2002.09
Position
Security
5,471
0
73.70
34,028
0 0
0
73.70
34,028
886,593
62,565
Unlisted SSS 2001.01
Position
Security
1,200
0
100.00
19,189
0 0
0
100.00
19,189
3,792,437
141,232
Unlisted SSCR 2006.09
Position
Security
3,405
0
100.00
9,332
0 0
0
100.00
9,332
24,818
3,420
Unlisted TSOE 2010.04
Position
Security
33,837
0
82.00
93,154
0 -19,262
0
82.00
73,893
125,762
-29,078
Unlisted TSLED 2012.04
Position
Security
119,519
0
100.00
119,519
0 0
0
100.00
119,519
349,963
36,338
Unlisted SCS 2012.09
Position
Security
111,770
0
100.00
3,888,196
0 0
0
100.00
3,888,196
9,742,388
171,644
Unlisted SSCX 2016.04
Position
Security
1,141
0
0.00
0
0 1,141
0
0
100.00
1,141
0
0
Unlisted SJC 1975.12
Position
Security
273
1,560
100.00
370,647
0 0
1,560
100.00
370,647
656,101
80,912
Unlisted SRJ 1992.08
Position
Security
3,120
122
100.00
117,257
0 0
122
100.00
117,257
157,461
2,933
Unlisted TSST Japan 2004.03 Business 1,639
30
49.03
0
0 0
30
49.03
0
248,021
0

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 228 / 240
※ Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted SDIB 1996.09 Business 3,110
586
0.08
0
0 0
586
0.08
0
21,571
-6,735
Unlisted
Semiconductor
Portal
2002.12 Business 38
0
1.21
10
0 0
0
1.21
10
1,466
19
Unlisted FTS 2008.12 Business 1,952
116
100.00
563
-116 -563
0
0
0.00
0
950
-1
Unlisted Nanosys, Inc 2010.08 Business 4,774
1,747
1.43
2,387
0 0
1,747
1.43
2,387
24,502
-14,519
Unlisted
ONE BLUE
LLC
2011.07 Business 1,766
0
16.67
1,766
0 0
0
16.67
1,766
37,054
1,020
Unlisted TidalScale 2013.08 Business 1,112
2,882
8.87
1,112
0 0
2,882
8.87
1,112
8,590
-2,809
Unlisted Sentiance 2012.12 Business 3,422
7
9.79
3,422
0 0
7
10.85
3,422
6,084
-1,317
Unlisted Mantis Vision 2014.01 Business 1,594
355
2.94
1,980
0 0
355
2.93
1,980
8,919
-8,376
Unlisted
Argus Cyber
Security
2015.09 Business 356
10
0.39
356
0 0
10
0.39
356
31,839
-2,787
Unlisted INEDA 2014.04 Business 3,181
6,100
6.41
5,397
0 0
6,100
7.42
5,397
5,674
-2,220
Unlisted Leman 2014.08 Business 1,019
17
3.91
1,019
0 0
17
3.66
1,019
3,049
-3,608
Unlisted Alces 2014.09 Business 4,832
421
19.95
4,832
0 0
421
18.50
4,832
4,900
-3,353
Unlisted Keyssa 2016.01 Business 3,332
0
0.00
0
1,235 3,332
0
1,235
2.58
3,332
32,495
-20,671
Unlisted Zyomed 2016.01 Business 2,044
0
0.00
0
1,464 2,044
0
1,464
2.88
2,044
9,729
-2,212
Unlisted SensiFree 2016.01 Business 2,111
0
0.00
0
490 2,111
0
490
17.88
2,111
4,980
-2,226

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 229 / 240
*Account noted here reflects approved for sales securities.
* Based on separate financial statements
* Ownership percentage is calculated based on the number of common shares issued
Account
Name of
Company
Acquisition
Date
Objective
Acquisition
Cost
Beginning Balance Increase/Decrease Ending Balance
Current Financial
Stats
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Acquisition/Disposal
Valuation
Qty
Ownership
(%)
Book
Value
Total Asset
Net
Income
(Loss)
Qty Amount
Unlisted
Bot Home
Automation
2016.03 Business 2,307
0
0.00
0
540 2,307
0
540
0.89
2,307
37,886
-17,493
Unlisted Unispectral 2016.02 Business 1,112
0
0.00
0
115 1,112
0
115
8.83
1,112
0
0
Unlisted Quobyte 2016.04 Business 2,865
0
0.00
0
729 2,865
0
729
11.83
2,865
3,528
-9,949
Unlisted Afero 2016.05 Business 5,685
0
0.00
0
723 5,685
0
723
5.60
5,685
323
-1,350
Unlisted Graphcore 2016.06 Business 3,494
0
0.00
0
3,000 3,494
0
3,000
7.73
3,494
0
0
Unlisted Soundhound 2016.12 Business 7,059
0
0.00
0
306 7,059
0
306
1.24
7,059
18,445
19,269
Listed Rambus 2010.01 Business 185,363
4,788
4.11
65,039
-4,788 -65,039
0
0
0.00
0
843,259
247,747
Listed SEAGATE 2011.12 Business 788,454
12,539
4.19
538,766
-12,539
-
538,766
0
0
0.00
0
10,308,912
734,844
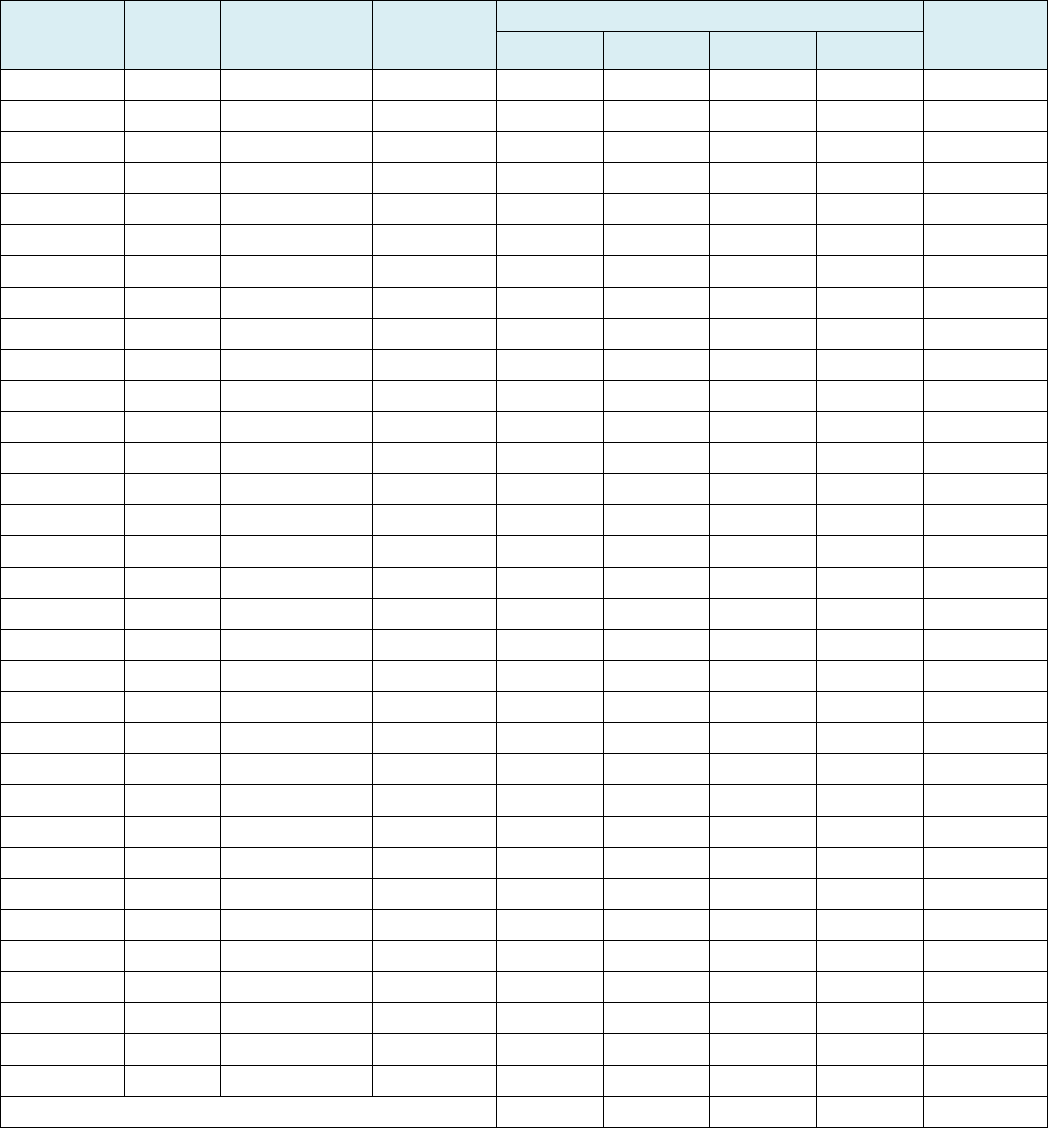
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 230 / 240
X. Related Party Transactions
1. Credit Offerings for Affiliates and Subsidiaries
A. Details on Debt Guarantee (as of December 31, 2016)
- Domestic: N/A
- Overseas:
(Unit: USD thousand)
Company Relationship Creditor
Guarantee Expiry
Date
Transactions
Limit of
Guarantee
Beginning of
period
Increase Decrease End of period
SEA Subsidiary SMBC, etc. 2017-12-16 1,000,000
-
- 1,000,000
2,425,000
SEM Subsidiary Santander, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
546,000
SAMCOL Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 66,333
17,252
- 83,585
156,000
SEDA Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-18 -
-
- -
769,000
SECH Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
178,000
SEPR Subsidiary BBVA, etc. 2017-12-16 58,033
10,706
- 68,739
180,000
SSA Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 126,001
-
91,674 34,327
335,000
SEMAG Subsidiary SocGen, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
110,000
SETK Subsidiary BTMU, etc. 2017-12-16 134,625
53,242
- 187,867
590,000
SECE Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 1,180
-
1,180 -
110,000
SEEG Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 -
-
- -
50,000
SEIN Subsidiary BNP, etc. 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
186,000
SJC Subsidiary Mizuho Bank, etc. 2017-12-16 107,656
-
107,656 -
900,040
SRJ Subsidiary SMBC 2016-02-28 20,734
-
20,734 -
-
SEUC Subsidiary Credit Agricole, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
175,000
SEDAM Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 110,408
-
9,082 101,326
391,000
SECA Subsidiary Nova Scotia 2017-10-10 -
-
- -
11,105
SELA Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
30,000
SEEH Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
727,000
SERK Subsidiary BNP, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
345,000
SELV Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
10,000
SAPL Subsidiary BOA, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
411,000
SEV Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
15,000
SAVINA Subsidiary SCB, etc. 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
71,000
SET Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
30,000
SCIC Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
350,000
SME Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
110,000
SAMEX Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
5,000
SEASA Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
1,000
SSAP Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 14,267
-
3,985 10,282
30,000
Simpress Subsidiary BNP 2017-11-08 36,356
8,173
- 44,529
60,000
SEHK Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 -
-
- -
2,000
SEPM Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 115,493
-
28,623 86,870
125,000
Total 1,791,086
89,373
262,934 1,617,525
9,434,145
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 231 / 240
SEC requires BOD approval for individual guarantees exceeding 2.5% of total equity. When the guarantee amount is
between 0.1% and/or less than 2.5%, the approval decision is delegated to the Management Committee.
B. Purchase and Sales of Securities
N/A

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 232 / 240
2. Acquisitions and Disposals of Assets with Affiliates and Subsidiaries
In 2016, the Company sold its stakes in Samsung Card to Samsung Life Insurance in order to focus on core business
competencies. The Company sold assets to various affiliates including SCS (Samsung China Semiconductor Co., Ltd.), to
increase the production capacity of such affiliates.
In addition, the Company acquired assets including facility equipment from affiliates to improve efficiency of domestic
production, and purchased shares of Cheil Worldwide owned by Samsung C&T for the purpose of strengthening the
strategic collaborative relationship.
(Unit: KRW million)
Company
Relation
ship
Transaction Type Transaction Date
Date based on Asset Amount
Samsung Life
Insurance
Affiliates Asset sale 2016.12.22 Date of sale Samsung card shares, etc. 1,557,499
Samsung C&T Affiliates Asset purchase 2016.10.27 Date of purchase Cheil Worldwide shares, etc. 267,524
SCS Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.12.17 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc.
83,096
SAS Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.12.31 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc.
65,905
SEHC Affiliates Asset sale 2016.11.16 Date of sale Machinery, etc.
30,370
SEVT Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.10.06 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc. 29,666
SESS Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.10.25 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc. 7,322
Samsung
Display
Affiliates Asset purchase 2016.12.01 Date of purchase Emission credits, etc. 6,957
TSTC Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.11.14 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc. 3,047
SEV Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.12.02 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc. 2,776
SIEL Affiliates Asset sale 2016.12.01 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 2,011
SEHZ Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.07.20 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc. 1,780
TSOE Affiliates Asset purchase 2016.08.16 Date of purchase Machinery, etc. 990
Samsung
Bioepis
Affiliates Asset sale 2016.04.15 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 853
SEDAM Affiliates Asset sale 2016.11.10 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 736
TSLED Affiliates Asset purchase 2016.11.30 Date of purchase Machinery, etc. 451
Samsung SDI Affiliates Asset sale 2016.10.25 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 397
SEMES Affiliates Asset sale 2016.12.22 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 381
SEPM Affiliates Asset sale 2016.04.22 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 213
TSE Affiliates Asset sale 2016.09.20 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 171
SEIN Affiliates Asset sale 2016.11.14 Date of sale Machinery, etc. 164
SEH Affiliates Asset sale/purchase 2016.06.17 Date of sale/purchase Machinery, etc. 111
※ Transaction amount was calculated by an appropriate method based upon market value assessment.
※ Acquisitions and disposals of assets with affiliates and subsidiaries listed above were not on the agenda of BOD. The sale of shares to Samsung
Life Insurance and the purchase of emission credits from Samsung Display proceeded with the approval of BOD.
※ Transaction date: most recent transaction
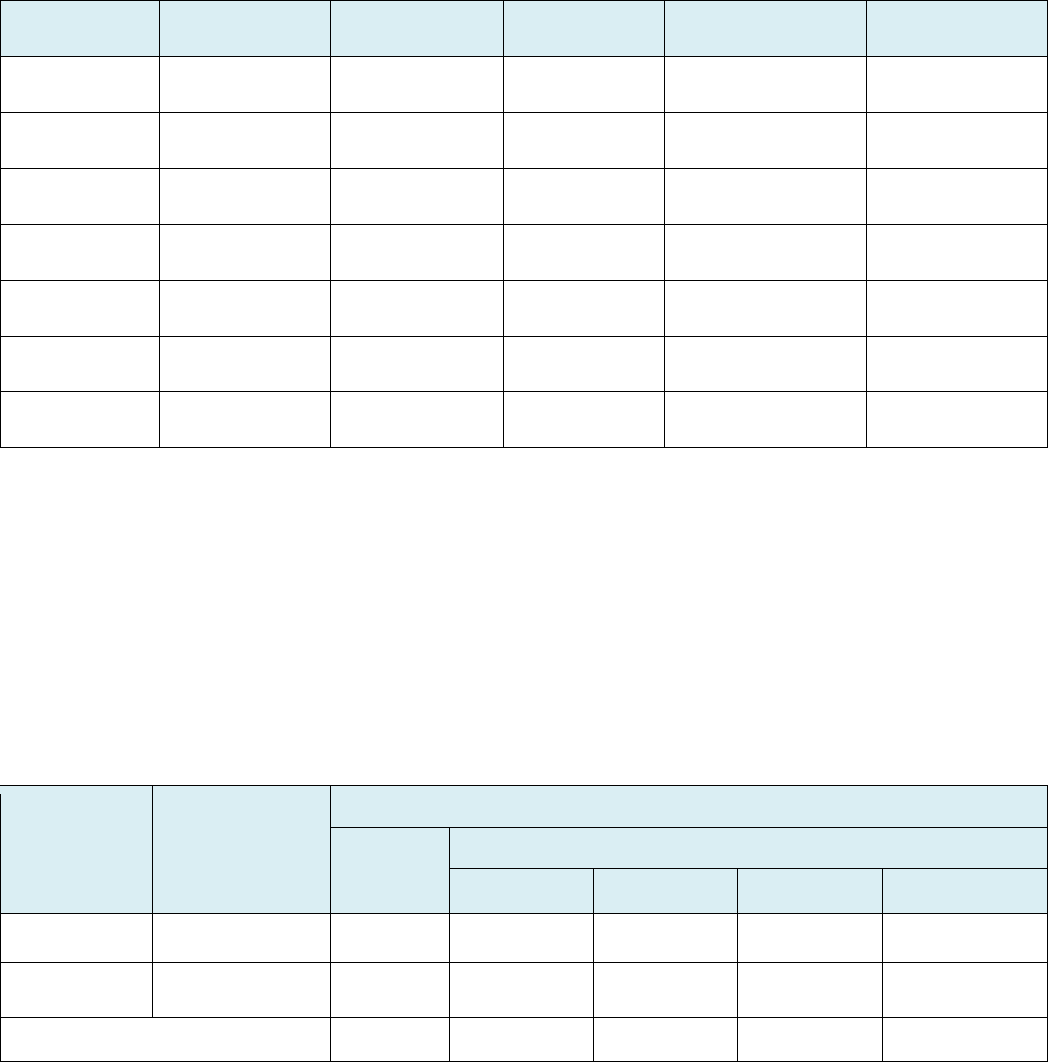
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 233 / 240
3. Business Transactions with Affiliates and Subsidiaries
(Unit: KRW million)
Company Relationship
Type of
Transaction
Date Details Amount
SEA Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Purchase/sales of HHP
and Home Appliance, etc.
27,469,787
SSI Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Purchase/sales of
semiconductors, etc
16,090,070
SEVT Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Purchase/sales of HHP,
etc
15,005,311
SSS Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Sales of semiconductors,
etc
13,574,341
SEV Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Purchase/sales of HHP
and Home Appliance, etc.
13,103,453
SEHZ Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Purchase/sales of HHP
and TV, etc.
9,472,646
SII Subsidiary Sales/Purchases 2016.01 - 2016.12
Purchase/sales of TV,
etc.
6,944,535
In 2016, SEC conducted business transactions with the following subsidiaries: SEA (Samsung Electronics America, Inc.)
4. Transactions with Stakeholders other than Affiliates and Subsidiaries
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s outstanding loan amount is KRW 115.7 billion related to support for supplier
companies for product competitiveness and mutual development as well as home loan and educational expenses for
employee welfare. In addition, the Company provides debt guarantees up to KRW 9.0 billion for employees’ loans from
financial institutions relating to housing rental.
(Unit: KRW million)
Company Relationship
Loans
Account title
Transaction
Beginning of period
(January 1, 2016)
Increase Decrease
End of period
(December 31, 2016)
SEST Co., Ltd., etc Partner company Short-term loans
31,042
1,120
892
31,271
Bumjin I&D, etc
Partner company and
employee
Long-term loans
85,368
38,372
39,357
84,383
To tal
116,410
39,492
40,248 115,653
※ The amount shown above reflects the discounted present value of debts before accounting for impaired debts.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 234 / 240
XI. Other Information
1. Public Disclosure
- N/A
2. Summary of Results of Shareholder Meetings
[As of December 31, 2016]
Date Agenda Results
FY2016 extraordinary general
meeting of shareholders ('16.10.27)
1. Approval of Printing solutions business Spin-off
2. Appointment of Executive director
- Nominee : Jae-Yong Lee
Approved
Approved
FY2016 annual general meeting of
shareholders ('16.3.11)
1. Approval of Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Statement of Appropriation of Retained
Earnings (Draft), etc. for FY2015
2. Election of Directors
2.1: Appointment of Independent Directors
2.1.1: In-Ho Lee
2.1.2: Kwang-Soo Song
2.1.3: Jae-Wan Bahk
2.2: Appointment of Executive Director
2.2.1: Boo-Keun Yoon
2.2.2: Jong-Kyun Shin
2.2.3: Sang-Hoon Lee
2.3: Appointment of Members of Audit Committee
2.3.1: In-Ho Lee
2.3.2: Kwang-Soo Song
3. Approval of the Remuneration Limit for the Directors for FY 2016
4. Approval of amendments to the Articles of Incorporation
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
FY2015 annual general meeting of
shareholders ('15.3.13)
1. Approval of Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Statement of Appropriation of Retained
Earnings (Draft), etc. for FY2014
2. Appointment of Directors
2.1: Appointment of Independent Directors
2.1.1: Han-Joong Kim
2.1.2: Byeong-Gi Lee
2.2: Appointment of Executive Director (Oh-Hyun Kwon)
2.3: Appointment of Member of Audit Committee (Han-Joong Kim)
3. Approval of the limit on the remuneration for Directors
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
Approved
FY2014 annual general meeting of
shareholders ('14.3.14)
1. Approval of Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Statement of Appropriation of Retained
Earnings (Draft), etc. for FY2013
2. Approval of the limit on the remuneration for Directors
Approved
Approved
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 235 / 240
3. Litigation
(1) The litigation with Apple Inc. (“Apple”) is ongoing in the United States as at the reporting date. On August 24, 2012,
the jury determined that the Group partially infringed Apple’s design and utility patent and should pay damages to
Apple. However, On March 1, 2013, the Judge ordered a new trial for a certain portion of the damages, ruling that it
was originally miscalculated. On November 21, 2013 a jury verdict was rendered on the recalculated damages
amount, and on March 6, 2014, the Judge made a final judgement to confirm the total damages and deny Apple’s bid
for a permanent injunction against the Group. The Group appealed the decision on the damages amount on March 7,
2014, and a hearing on the appeal was held on December 4, 2014. On May 18, 2015, the appeals court affirmed in
part and reversed in part a previous decision, and remanded it. On June 17, 2015, the Group petitioned for an en banc
rehearing regarding the design infringement, and on August 13, 2015, the federal court dismissed the Group’s
request. After the remand procedure, the Court of First Trial announced a partial final judgment on the appeals on
September 18, 2015. On October 13, 2015, the immediate appeal was dismissed and on November 19, 2015, the
Federal Circuit Court denied an en banc rehearing request. On December 11, 2015, the Group made payment for the
damages. On December 14, 2015, the Group filed an appeal to the Supreme Court regarding the design patent
infringement ruling. Thereafter, the two parties have submitted in writing to the District court details of supplemental
damages incurred in connection with the ruling. On March 21, 2016, the Supreme Court granted the design-related
appeals filed by the Group and on March 22, 2016, the Court of First Trial ordered all proceedings for review of
damages scheduled to commence March 28, 2016 suspended until the sentence rendered by the Supreme Court was
confirmed. On June 1, 2016, the Group submitted the draft document in the design-related appeal, and on June 28,
2016, several companies and organizations presented the document in support of the Group. Apple filed a dissenting
document on July 29, 2016, and on August 5, 2016, several companies and organizations presented an advocative
document. On August, 29, 2016, the Group submitted a rebuttal letter. Oral statements for the appeal were held at the
Supreme Court on October 11, 2016. On December 6, 2016, the Supreme Court issued a ruling citing the Group
appeal and returned the case to the Court of Appeals. On February 7, 2017, the Court of Appeals reversed the case to
the Court of First Trial.
Additionally, on May 5, 2014, the jury in another ongoing patent lawsuit determined that the Group partially
infringed Apple’s utility patent and should pay damages to Apple. On November 25, 2014, the first trial judgment
was pronounced to confirm the jury’s verdict. The Group appealed on November 25, 2014 and the rehearing was
held on January 5, 2016. On August 27, 2014, the Judge denied Apple’s request for a permanent injunction on the
Group’s product. However, on September 17, 2015, the appellate court reversed and remanded a previous decision
and on December 16, 2015, the Federal Circuit Court denied an en banc hearing request of the Group. On January
18, 2016, the Court of First instance ordered a permanent injunction on the Group’s product. The Group asserts that
the Group’s product was designed around the patent and thus has not infringed the patent. The final conclusion and
the effect of the patent lawsuits with Apple are uncertain as at the reporting date.
In August 2014, the Group and Apple reached an agreement to withdraw from ongoing litigation in all regions other
than the United States, and the Group has withdrawn all non-United States based lawsuits.
(2) The Group is involved in claims, disputes, and investigations conducted by regulatory bodies at the reporting date,
including civil claims from some overseas buyers for price-fixing related to the sale of TFT-LCD. Although the
outflow of resources and timing of these matters are uncertain, the Group believes the outcome will not have a
material impact on the financial condition of the Group.

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 236 / 240
(3) In addition, during the normal course of business with numerous companies, the Group has been involved in various
claims, disputes, and investigations conducted by regulatory bodies. Although the outflow of resources and timing of
these matters are uncertain, the Group believes the outcome will not have a material impact on the financial
condition of the Group.
4. Guarantees
- Domestic: As of December 31, 2016, the Company provided a debt guarantee of KRW 36,825 million to its
employees who took debt from financial institutions in order to finance employee housing rental. The Company’s
housing rental debt guarantee limit is KRW 56,752 million. The Company has provided guarantees for borrowings
executed by Medicapital from Dime Investment and two other companies in the amount of KRW 2,264 million.
- Overseas:
(Unit: USD thousand)
Company Relationship Creditor
Guarantee Expiry
Date
Transactions
Limit of
Guarantee
Beginning of
period
Increase Decrease End of period
SEA Subsidiary SMBC, etc. 2017-12-16 1,000,000
-
- 1,000,000
2,425,000
SEM Subsidiary Santander, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
546,000
SAMCOL Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 66,333
17252
- 83,585
156,000
SEDA Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-18 -
-
- -
769,000
SECH Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
178,000
SEPR Subsidiary BBVA, etc. 2017-12-16 58,033
10,706
- 68,739
180,000
SSA Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 126,001
-
91,674 34,327
335,000
SEMAG Subsidiary SocGen, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
110,000
SETK Subsidiary BTMU, etc. 2017-12-16 134,625
53242
- 187,867
590,000
SECE Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 1,180
-
1,180 -
110,000
SEEG Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 -
-
- -
50,000
SEIN Subsidiary BNP, etc. 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
186,000
SJC Subsidiary Mizuho Bank, etc. 2017-12-16 107,656
-
107,656 -
900,040
SRJ Subsidiary SMBC 2016-02-28 20,734
-
20,734 -
-
SEUC Subsidiary Credit Agricole, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
175,000
SEDAM Subsidiary Citibank, etc. 2017-12-16 110,408
-
9082 101,326
391,000
SECA Subsidiary Nova Scotia 2017-10-10 -
-
- -
11,105
SELA Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
30,000
SEEH Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
727,000
SERK Subsidiary BNP, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
345,000
SELV Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
10,000
SAPL Subsidiary BOA, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
411,000
SEV Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
15,000
SAVINA Subsidiary SCB, etc. 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
71,000
SET Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
30,000
SCIC Subsidiary HSBC, etc. 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
350,000
SME Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 -
-
- -
110,000
SAMEX Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
5,000

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 237 / 240
SEASA Subsidiary Citibank 2017-12-16 -
-
- -
1,000
SSAP Subsidiary SCB 2017-11-08 14,267
-
3985 10,282
30,000
Simpress Subsidiary BNP 2017-11-08 36,356
8,173
- 44,529
60,000
SEHK Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 -
-
- -
2,000
SEPM Subsidiary HSBC 2017-06-13 115,493
-
28,623 86,870
125,000
Total 1,791,086
89,373
262,934 1,617,525
9,434,145
※ SEC requires BOD approval for individual guarantees exceeding 2.5% of total equity. When the guarantee amount is between
0.1% and/or less than 2.5%, the approval decision is delegated to the Management Committee.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 238 / 240
5. Sanctions and Others
The Company is engaged in a lawsuit after being issued a corrective order and fine (KRW 14,126 million) on July 10,
2012 for violating Article 23 (Prohibition of Unfair Trade Practices) of the Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act. In
order to comply with relevant laws on fair trade, the Company has strengthened internal oversight and provides education
to executives and employees for the prevention of unfair trade practices.
The Company was ordered to pay a fine (KRW 26 million) on January 13, 2014 from the Fair Trade Commission for
violating Article 4 (Announcement of Critical Information and Integrated Notification) of the Fair Labeling and
Advertising Act, and has subsequently paid the fine. To comply with the Fair Labeling and Advertising Act, the Company
offers education and training to executives and employees regarding these laws.
The Company was ordered to pay a fine (KRW 267 million) on March 7, 2013, for violating the Occupational Safety and
Health Act in connection with a hydrofluoric acid gas leak that occurred on January 28, 2013, and has subsequently paid
the fine. The Company was issued an improvement order and ordered to pay a fine (KRW 2.2 million) on April 1, 2013,
for violating the Toxic Chemicals Control Act. The Company reported compliance with the improvement order and
subsequently paid the fine. As a result of this incident, three employees and executives (a director of chemicals supply
management with 20 years of continuous employment, a manager in charge of toxic chemicals with 8 years of continuous
employment, and a manager of chemicals supply management with 11 years of continuous employment) of SEC were
ordered to pay a fine (KRW 15 million) at the first trial (in Suwon District Court) on October 31, 2014. The Company
appealed the decision. In order to improve the capabilities of safety managers, the Company has implemented a relevant
education program, and is strengthening inspection on maintenance and management of dangerous facilities.
For the hydrofluoric acid gas leak occurred on May 2, 2013, SEC was ordered to pay a fine (KRW 4.5 million) on
February 27, 2014, for violating the Occupational Safety and Health Act and the Toxic Chemicals Control Act, and has
subsequently paid the fine. The Company has completely revamped theHealth & Safety Management Program, including
creating a new organization devoted to the prevention of leakage to avoid such accidents from reoccurring in the future.
The Company was ordered and paid a fine of KRW 166.7 million for not reporting the importation of certain chemicals in
August 2013, following a joint inspection by the Ministry of Environment and Gyeong-Gi Province. The Company has
improved the reporting process for imported chemicals to ensure proper notification of such chemicals.
Pursuant to the results of a joint inspection by the prosecutor’s office and the Ministry of Employment and Labor
conducted from June 16 through June 20 (2014), a current executive of SEC (Head director of safety & healthy
management with 32 years of continuous employment) and SEC were ordered and respectively paid a fine of KRW 2
million for violating the obligation of taking safety measures in accordance with the Occupational Safety and Health Act
on July 29, 2015 (in Suwon District Court).
To prevent recurrence, the Company has implemented its own Environment &
Safety Preliminary Evaluation System and conducts regular inspections.
Pursuant to the results of a regular inspection by the Ministry of Employment and Labor conducted from December 14
through December 16 (2015), SEC paid a fine of KRW 18.76 million for violating the obligation of implementing safety
measures in accordance with the Occupational Safety and Health Act on December 31, 2015 (The original amount was
KRW 23.45 million, but was reduced by 20%, as the company voluntarily paid the fine by the due date). Regarding this
matter, the Company has implemented its own safety inspection program for Hazardous Machineries and equipment to
reinforce compliance management.
Pursuant to the results of a Process Safety Management (PSM) inspection by the Ministry of Employment and Labor
conducted from December 5 through the December 9 (2016), the Company was ordered to pay a fine of KRW 3.52
million for violating the obligation of implementing safety measures in accordance with the Occupational Safety and
Health Act on December 14, 2016 and has subsequently paid the fine. In order to comply with relevant laws, the Company
is training process safety experts on site and conducting its own process safety evaluation.
Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 239 / 240
The years of continuous employment described herein is based on the date of order.
The Company (including Samsung Display) has joint responsibility for reimbursement of liabilities that Samsung Display
accrued before the separation.
On October 23, 2013, the Company signed a basic agreement on comprehensive business cooperation with Corning
Incorporated, etc. Inflow or outflow of resources can occur hereafter, as the agreement includes conditions for
compensation of loss. Projected disbursement as of the end of reporting term was counted as liabilities.
For information on the Company’s commitments and contingencies, refer to Commitments and Contingencies notes in the
Separate and Consolidated Financial Statements.
6. Return of Short-Swing Profits
The Company has not received any notification of short-swing profits from the Securities & Futures Commission (the
Governor of the Financial Supervisory Service) in the past three years and until the date of this report.
7. Subsequent Events
On January 24, 2017, the board of directors approved the share buyback and retirement of common and preferred stock,
with the estimated total number of shares to be repurchased of 1.28 million (common stock 1.02 million, preferred stock
0.26 million). All repurchased shares will be retired after the buyback is completed. The period of purchase is subject to
end on April 24, 2017.
Since the agreement to acquire Harman on November 14, 2016, the Company has completed all necessary procedures for
acquisition, including shareholders’ meeting and approval of antitrust review in 10 countries subject to examination,
including the United States. The Company has completed the acquisition of Harman on March 10, 2017 (March 11, 2017,
in Korea).
8. Acquisition and Divestments
A. Acquisitions and divestments (Separate only)
[Split of S-Printing Solution]
Company Name: S-Printing Solution Corp.
Location: 129 Samsung-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do
Purpose of split: S-Printing Solution competitiveness improvement
Approval of split: October 27, 2016 (temporary shareholders’ meeting)
Date of split: November 1, 2016

Samsung Electronics 2016 Business Report 240 / 240
(Unit: KRW million)
Company Account
Forecast Actual
1st Year 2nd Year
1st Year 2nd Year
Actual Difference Actual Difference
S-Printing
Solution
Sales 2,094 14,160 2,186 4.40% - -
Operating
Income
-29 -1,359 -61 111.48% - -
Net Income -67 -1,486 -10 -84.72% - -
Difference rate of operating income was more than 110% due to the year-end bonus payments and difference of net
income was more than 80% due to the foreign exchange differences and etc.
Details of the above statement can be found in the “Important Matters Report“, published in DART
(http://dart.fss.or.kr/).
Split of S-Printing Solution business is reported on a separate basis.
- Please refer to the Management Combination and Non-current Assets Held-for-Sale (Assets of disposal group) notes in
the Consolidated Financial Statements for acquisition and divestments on the consolidation basis.
9. Green Management
The Company is actively securing “Green Technology Certifications” to follow the Low Carbon Green Growth policy of
the Korean government.
(Green Technology Certification)
The Company is acquiring Green Technology Certifications in accordance with Clause 2, Article 32 of the Framework Act
on Low Carbon Green Growth. Green technology development is a part of our “Planet First” strategy, which strives to
conduct business activities in a manner that respect people and nature. Since the certification system was introduced in
2010, the Company has secured 14 valid Green Technology Certifications as of December 31, 2016. In addition, the
Company has acquired 50 ‘Green Technology’ product certificates (429 models), for commercialized products.
Certified Green Technologies as of December 31, 2016 are as follows:
Division Business Name of green technology and green projects No.
CE Low-power consumption SoC design technology for digital TVs, etc.
9
IM
Pentile display power-saving technology that adapts to level of illumination of the
surroundings, etc.
5
Tot al
14
※ The data reported above is with respect to Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. only.
※ See 『11. Other Information (B. Environmental regulations)』 in 『II. Businesses Overview』 for greenhouse gas emission and
energy use.
