Name __________________________________________________________________ Period ____________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6 Part 2
Logarithms
6.13
I can convert between logarithmic and
exponential notation.
6.14
I can apply the properties of
logarithms.
6.15
-
17
I can solve using logarithms and
exponents.
6.18
-
19
I can graph logarithms.
My goal for this unit: _____________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
What I need to do to reach my goal: ________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.13
Logs and Exponents
A logarithm is just another way to write an exponent!
Exponential Form Logarithmic Form
3
2
= 9
4
3
= 64
2
7
= 128
Note: If there is no number written as a subscript next to log, it is assumed to be a 10:
log a = b means log
10
a = b
Directions: Write each exponential equation in logarithmic form.
1.
6
2 64
=
2.
2
1
4
16
−
=
3.
27
1
3
1
3
=
4.
3
7
=
2187
5.
12
2
=
144 6.
5
3
=
125
Directions: Write each logarithmic equation in exponential form.
7.
7
log 49 2
=
8.
2
1
log 4
16
= −
9.
8
log 48
x
=
10.
log
10
100,000
=
5
11.
log
4
1024
=
5 12.
log
9
729
=
3

Directions: Simplify without a calculator.
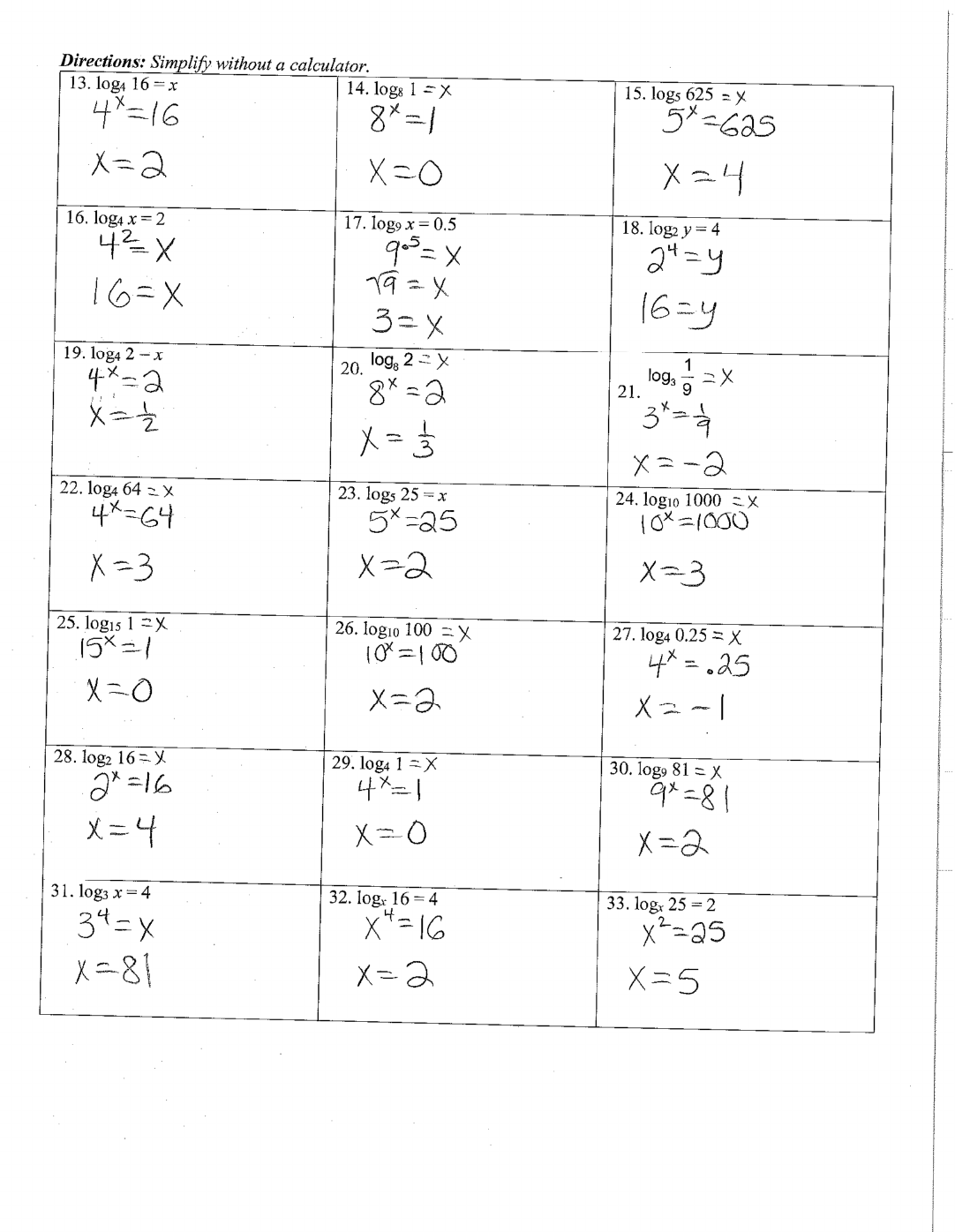
13.
log
4
16 =
x
14.
log
8
1 15.
log
5
625
16.
log
4
x
= 2 17.
log
9
x
= 0.5 18.
log
2
y
= 4
19.
log
4
2 =
x
20.
8
log 2
21.
3
1
log
9
22.
log
4
64
23.
log
5
25 =
x
24.
log
10
1000
25.
log
15
1
26.
log
10
100 27.
log
4
0.25
28.
log
2
16
29.
log
4
1 30.
log
9
81
31.
log
3
x
= 4 32.
log
x
16 = 4 33.
log
x
25 = 2

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.14
Properties of Logs
Product Property of Logarithms log
b
(mn) = log
b
m + log
b
n
Quotient Property of Logarithms
nm
n
m
bbb
logloglog −=
Power Property of Logarithms log
b
m
n
= n log
b
m


Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.15
Solving Using Logs and Exponents (Day 1)
One way to solve exponential equations, is to write both sides of the equation with the same base.
2
x + 6
= 2
5
same base
⇒
exponents are equal
x
+ 6 = 5
x
=
−
1
Check: 2
−
1 + 6
= 2
5
9
2x
−
3
= 27 different bases
(3
2
)
2x
−
3
= 3
3
rewrite with the same base
3
4x
−
6
= 3
3
simplify
4
x
−
6 = 3 same base
⇒
exponents are equal
4
x
= 9
x
= 2.25
Check: 9
2(2.25)
−
3
= 27
Directions: Solve each equation for the unknown value showing all work using the method of writing each side
of the equation using the same base. Check your answer.
1.
6
2 4
x+
=
2.
3 6
16 8
x x
+
=
3.
2 4
9 27
x x
+
=
4.
0.5 2 5
256 64
x x
+
=
5.
2
1
16
2
x
=
6.
2
1
64
32
x
=
7.
6
1
27
27
x−
=
8.
2 3
3
216 36
x
x
+
=
9.
3
1
27
9
x
=
10.
3 9
16 64
x x
+
=
11.
2
81 243
x x
+
=
12.
3
2
1
8
2
x
=

Another way to solve exponential equations, is to take the log of both sides.
5
2x
−
3
= 18 cannot use same base
log 5
2x
−
3
= log 18 take log of both sides
2
x
−
3(log 5) = log 18 power property
2
x
−
3 =
5log
18log
isolate
x
x
=
2)3
5log
18log
( ÷+
x
≈
2.40
Check: 5
2(2.40)
−
3
= 18
e
4x
−
9
= 56 cannot use same base
ln
e
4x
−
9
= ln 56 take ln of both sides
4
x
−
9 (ln
e
) = ln 56 power property
4
x
−
9 = ln 56 ln
e
= 1
x
= (ln 56 + 9)
÷
4 isolate
x
x
≈
3.26
Check:
e
4(3.26)
−
9
= 56
Directions: Solve each equation for the unknown value showing all work using the method of taking the log of
both sides. Check your answer.
13.
2
5 20
x
=
14.
2 8
12 15
x−
=
15.
1 2
12 20
x −
=
16.
2 3
3 4 78
x
e
−
− =
17.
10 8
6 4 34
x
e
−
− =
18.
(
)
7 6
8 10 8 59
x−
− =
19.
4 1
6 3 37
x
e
− −
− + = −
20.
2 5
8 48
x −
=
21.
2
4 20
x +
=
22.
2
4 6
x
=
23.
5 6
5 50
x −
=
24.
4
e
x
+ 3
= 22

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.16
Solving Using Logs and Exponents (Day 2)
Solve logarithmic equations by applying the properties (if needed), then writing as an exponent. Solve
resulting equation. Check.
log
2
(5
x
+ 7) = 5
2
5
= 5
x
+ 7 write as an exponent
32 = 5
x
+ 7 solve for
x
25 = 5
x
solve for
x
x
= 5
log
4
x
+ log
4
(
x
−
12) = 3
log
4
(
x
(
x
−
12)) = 3 properties of logs
4
3
=
x
2
−
12
x
write as an exponent
x
2
−
12
x
−
64 = 0 set equal to 0
(
x
+ 4)(
x
−
16) = 0 factor
x
=
−
4
x
= 16
x
≠
−
4
Directions: Solve by applying the properties, writing as an exponent, then solving.
1.
log
3
(9
x
+ 2) = 4
2.
log
4
x
+ log
4
(
x
−
6) = 2 3.
log (5
x
−
11) = 2
4.
ln (4
x
−
1) = 3 5.
log
2
(
x
+ 1)
−
log
2
(
x
−
4) = 3
6.
ln (3
x
+ 11) = 4
7.
log
6
x
+ log
6
(
x
+ 5) = 2
8.
log
4
(4
x
−
9) = 3
9.
log
5
(4
x
+ 11) = 2
Solve logarithmic equations by applying the properties then dropping the logs on each side, then solve.
Check.
log
3
(7
x
+ 3) = log
3
(5
x
+ 9)
7
x
+ 3 = 5
x
+ 9 drop the logs
2
x
= 6 solve for
x
x
= 3
log
7
(
x
−
2) + log
7
(
x
+ 3) = log
7
14
log
7
((
x
−
2)(
x
+ 3)) = log
7
14 properties of logs
(
x
−
2)(
x
+ 3) = 14 drop the logs
x
2
+ 3
x
−
2
x
−
6 = 14 FOIL
x
2
+
x
−
20 = 0 set equal to 0
(
x
+ 5)(
x
−
4) = 0 factor
x
=
−
5
x
= 4
x
≠
−
5
Directions: Solve by applying the properties, dropping the logs on each side, then solving.
10.
log 5
x
= log (2
x
+ 9)
11.
log
4
(2
x
+ 1) = log
4
(
x
+ 2)
−
log
4
3
12.
log
8
x
+ log
8
(
x
+ 6)
=
log
8
(5
x
+ 12)
13.
ln
(2
x
−
1)
+ ln
(
x
+ 3) = ln
(
x
2
+
x
−
7)
14.
log (
x
−
2)
−
log (2
x
−
3) = log 2 15.
log (10
−
4
x
) = log (10
−
3
x
)
16.
log
6
(
x
+ 4) + log
6
(
x
−
2) = log
6
4
x
17.
log
9
(3
x
+ 5) = log
9
(7
x
−
12)
18.
log
9
(
−
11
x
+ 2) = log
9
(
x
2
+ 30) 19.
log
12
(
x
2
+ 35) = log
12
(
−
12
x
−
1)

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.17
Solving Using Logs and Exponents (Day 3)
Solve each equation. Use one of the 4 methods you have practiced the last few days:
1.
Write exponents using the same base
2.
Take the log of both sides
3.
Use properties of logs then write as an exponent
4.
Use properties of logs then drop the log on both sides
1.
(
)
4
3 10 4 91
x−
− − = −
2.
4
−
x
= 32
3.
log (4
x
−
2) = log (
−
5
x
+ 5) 4.
log
6
x
+ log
6
(
x
−
9) = 2
5.
5 2 1
3 27
x x
+
=
6.
5
2
1
8
16
x +
=
7.
5
x
− 3
= 600
8.
ln (6
x
−
5) = 3

9.
(
)
8 10
7 10 9 4
x−
− + =
10.
ln (
x
−
3)
−
ln (
x
−
5) = ln 5
11.
log
5
6 + log
5
2
x
2
= log
5
48
12.
3
4
x
= 90
13.
8 1
10 3 70
x
e
+
− =
14.
log
4
(3
x
−
2)
−
log
4
(4
x
+ 1) = 2
15.
In the year 2010, the population of a city was 22
million and was growing at a rate of about 2.3%
per year. The function
p
(
t
) = 22(1.023)
t
gives the
population, in millions,
t
years after 2010. Use
the model to determine in what year the
population will reach 30 million. Round to the
nearest year.
16.
A sample of bacteria began with a population of
100 and grows over time at a rate of 35% per
hour. Write a function to model this growth.
How long before the population doubles?
17.
In 2005, an orchard had 24,000 blueberries and
the number has been growing at a rate of about
5% per year. The function
b
(
t
) = 24(1.05)
t
gives
the number of blueberries, in thousands,
t
years
after 2005. Use the model to determine in what
year the number will reach 55,000. Round to the
nearest year.
18.
A sample of cancer cells began with 400 cells
and grows at a rate of 60% per hour. Write a
function to model this growth.
How long before the number of cells triples?

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.18
Graphs of Logarithms
Complete the table of values for each of the following (use a graphing calculator or desmos) the use that to
graph (on same graph, but different colors).
y = 2
x
y = log
2
x
What relationship did you notice in the table of
values?
What relationship did you notice on the graph?
What is the domain and the range for the first graph
equation?
What is the domain and the range for the second
equation?
( ) log
b
f x x
=
==
=
(
((
(
)
))
)
( ) log
b
g x a x h k
= − +
= − += − +
= − +
Graph
a
|a| > 1 →vertical stretch by |a|
|a| < 1 →vertical compression by |a|
a < 0 →reflection over x-axis
h
shift right h units
shift left h units
k
shift up k units
shift down k units
Vertical Asymptote
x = 0 x = h
Reference Point (1, 0) (1 + h, k)
Reference Point
(b, 1)
(b + h, a + k)
0h
> →
0h
< →
0
k
> →
0k
< →
x y
−
3
−
2
−
1
0
1
2
3
x y
8
1
4
1
2
1
1
2
4
8

Directions: Graph each function. Tell how the graph is transformed from the graph of its parent function.
1.
f
(
x
) = log
2
x
+ 4
2.
f
(
x
) = 3log
4
(
x
+ 6)
3.
f
(
x
) = log (
x
+ 5)
4.
f
(
x
) = 3
+ ln
x
5.
f
(
x
) =
−
log
4
x
6.
f
(
x
) = log
4
x
+ 2
7.
f
(
x
) =
−
log
4
x
+ 2
8.
f
(
x
) = log
4
x
−
2

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.19
Graphs of Logarithms (Day 2)
Directions: Write each transformed function.
1.
The function
f
(
x
) = log (
x
+ 1) is reflected across
the
x
-axis and translated down 4 units.
2.
The function
f
(
x
) = log
8
(
x
−
3) is compressed
vertically by a factor of
2
5
and translated up 11
units.
3.
The function
f
(
x
) =
−
log
9
(
x
+ 4) is translated 4
units right and 1 unit down and vertically
stretched by a factor of 7.
4.
The function
f
(
x
) = 3 ln (2
x
+ 8) is vertically
stretched by a factor of 3, translated 7 units up,
and reflected across the
x
-axis.
5.
The function
f
(
x
) =
−
log (5
−
x
)
−
2 is translated 6
units left, vertically compressed by a factor of
1
3
,
and reflected across the
x
-axis.
6.
The function
f
(
x
) = 8log
7
x
−
5 is compressed
vertically by a factor of 0.5, translated right 1
unit, and reflected across the
x
-axis.
7.
What transformations does the function
f
(
x
) =
−
ln (
x
+ 1)
−
2 undergo to become the
function
g
(
x
) = ln (
x −
1)?
8.
The function
f
(
x
) = ln
x
is reflected across the
x
-axis.
9.
The function
f
(
x
) = log
8
x
is vertically
compressed by a factor of 0.5.
10.
The function
f
(
x
) = log
3
x
is vertically stretched
by a factor of 4.
11.
The function
f
(
x
) = log
x
is shifted 3 units left
and reflected across the
x
-axis.
12.
The graph of the function
f
(
x
) = log
3
x
is
transformed by reflecting across the
x
-axis,
translating 2 units left, and 4 unit down.

Directions: Describe the transformation from the parent function to the given function.
13.
(
)
= + −
2
( ) 5log 2 1
g x x
14.
(
)
= − + +
( ) log 5 2
g x x
15.
(
)
= − −
6
( ) 3log 4 2
g x x
16.
(
)
= − + +
8
( ) 2log 9 3
g x x
Given the following data about the heights of chair seats and table tops for children, create scatterplots of the
ordered pairs (age of child, chair seat height) (age of child, table top height).
17.
Explain if a logarithmic model would be appropriate for each data set.
18.
Perform logarithmic regression for each data set.
19.
Use your regression equation to predict the chair seat height for a child 14 years old and 50 years old.
Explain if each is reasonable or not.
20.
Use your regression equation to predict the table top height for a child 14 years old and 50 years old.
Explain if each is reasonable or not.

Name ____________________________________________________________ Period __________________
Algebra 3-4 Unit 6.20
Are You Ready for Unit 6 Part 2 Assessment?
I can apply logarithmic properties and rules.
1.
Write as an exponent: ln
x
= 8
2.
Write as an exponent: log
x
= 3
3.
Write as a logarithm:
x
4
= 25
4.
Write as a logarithm:
e
3
=
x
5.
Write as an exponent: log
3
x
= 4
6.
Write as a logarithm: 10
x
= 7
7.
Write as a single logarithm: log
3
8 + log
3
7
8. Write as a single logarithm: log
9
x
− log
9
y
9.
Write as a single logarithm:
log
2
x
+ log
2
y
− log
2
z
10.
Expand using the properties of logarithms.
4
2
log
c
ba
11.
Expand using the properties of logarithms.
log
xy
3
12.
Expand using the properties of logarithms.
cba
xy
23
3
3
log
I can graph logarithmic equations.
13.
Describe the transformatio
ns from
f
(
x
) = log
2
(
x
) to
g
(
x
) = −log
2
(
x
− 3)
14.
Describe the transformations from
f
(
x
) = log
2
(
x
) to
g
(
x
) = 3 log
2
(
x
+ 5) − 2
15.
Describe the transformations from
f
(
x
) = log
2
(
x
) to
g
(
x
) = −0.5 log
2
(
x
) − 9
16.
Describe the transformations from
f
(
x
) = log
2
(
x
) to
g
(
x
) = log
2
(−
x
) + 6
17.
The graph of
f
(
x
) = log
2
x
is transformed by
translating up 2 units and left 4 units. What
is the function of the transformed graph?
18.
The graph of
f
(
x
) = log
2
x
is transformed by
reflecting over the
x
-axis, translating down 3
units and right 1 unit. What is the function
of the transformed graph?

19.
The graph of
f
(
x
) = log
2
x
is transformed by
a vertical stretch by a factor of 3 and
translating down 5 units. What is the
function of the transformed graph?
20.
The graph of
f
(
x
) = log
2
x
is transformed by
a reflection over the
x
-axis and a vertical
stretch by a factor of 5. What is the function
of the transformed graph?
I can solve equations with logarithms and exponents.
21. Solve: 3
2
x
− 1
− 4 = 239
22.
Solve: 2
3
x
+ 4
+ 5 = 133
23.
Solve: 3
e
x
= 11
24.
Solve: 9 + 2
e
x
+ 7
= 22
25. Solve: −8 + 4
x
− 9
= 92
26.
Identify
x
in each:
ln (
x
) = 1.7
ln (12) =
x
e
3.5
=
x
e
x
= 92
27.
The population of a town was 2,500 people
in the year 2000. If it is growing
exponentially at a rate of 8% per year, write
an equation to model the growth.
Use your model to determine in what year
the population will double what it was in the
year 2000.
28.
The population of a town was 2,500 people
in the year 2000. If it is decreasing
exponentially at a rate of 8% per year, write
an equation to model the decay.
Use your model to determine in what year
the population will reach 1,000 people.
29.
The value of
a painting can be modeled by
the equation
V
(
t
) = 250(0.93)
t
where
t
= 0
in the year 2010 and the value is in
thousands of dollars. What will the value of
the painting be in the year 2020?
30.
The value of a painting can be modeled by
the equation
V
(
t
) = 250(1.28)
t
where
t
= 0
in the year 2010 and the value is in
thousands of dollars. In approximately what
year will the painting be valued at
$400,000?