
Regulation 61-7
Emergency Medical Services
Disclaimer
DPH provides this copy of the regulation for the convenience of the
public and makes every effort to ensure its accuracy. However, this
is an unofficial version of the regulation. The regulation's most
recent final publication in the South Carolina State Register presents
the official, legal version of the regulation.
2100 Bull Street
Columbia, SC 29201

S.C. Code Sections 44-61-10 et seq., 44-78-10 et seq., and
44-80-10 et seq.
SECTION 100 – DEFINITIONS, LICENSURE, AND CERTIFICATION ..................................................... 1
101. Definitions. ...................................................................................................................................... 1
102. Licensure. ......................................................................................................................................... 6
103. EMS Agency License Application. .................................................................................................. 7
104. Emergency Medical Technicians. .................................................................................................. 9
105. Initial EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certification. .............................................................. 9
106. Issuance and Terms of Certification. ........................................................................................... 9
107. EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Certification Renewal. .......................................................... 10
108. Special Purpose EMT. ................................................................................................................... 10
109. Reciprocity. .................................................................................................................................... 10
110. Certification Examinations. ......................................................................................................... 11
111. Training Programs. (II) .................................................................................................................. 12
112. Certified EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Instructors. ......................................................... 12
113. Continuing Education (CE) Program. (II) .................................................................................... 13
114. Continuing Education Units (CEUs). ........................................................................................... 14
115. Pilot Programs. .............................................................................................................................. 14
116. Endorsement of Specialty Credentials. ...................................................................................... 14
117. Certification Patches. ................................................................................................................... 16
118. Variance. ........................................................................................................................................ 16
SECTION 200 – ENFORCEMENT OF REGULATIONS .......................................................................... 16
201. Inspections and Investigations. (I) .............................................................................................. 16
202. Plan of Correction. ........................................................................................................................ 16
203. Consultations. ............................................................................................................................... 17
SECTION 300 – ENFORCEMENT ACTIONS ........................................................................................ 17
301. General. .......................................................................................................................................... 17
302. Enforcement Actions against EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics. ..................................... 17
303. Investigative Review Committee. ................................................................................................ 19
304. Violation Classifications. .............................................................................................................. 19
305. Monetary Penalties. ...................................................................................................................... 20
May 22, 1981
-
5
11
June 27, 1986
624
10
6
February 26, 1988
812
12
2
July 28, 1995
1848
19
7
June 27, 1997
2161
21
6, Part 2
June 23, 2006
3000
30
6
June 24, 2016
4610
40
6
May 27, 2022
5055
46
5
SECTION 400 – POLICIES AND PROCEDURES (II) ............................................................................. 20
SECTION 500 – PERSONNEL REQUIREMENTS .................................................................................. 21
501. General. (I) ..................................................................................................................................... 21
502. Medical Control Physician. (I) ...................................................................................................... 22
503. Driver. (II) ....................................................................................................................................... 22
504. Emergency Medical Responder Agency. (II) .............................................................................. 23
505. Ambulance Service Agency. (II) ................................................................................................... 24
506. Special Response Vehicle (SRV). .................................................................................................. 24
507. Tiered Response System. (II) ....................................................................................................... 24
508. Volunteer EMS Agencies. ............................................................................................................. 25
SECTION 600 – REPORTING ............................................................................................................... 25
601. Adverse Incident Reporting. ........................................................................................................ 25
602. Collisions. ....................................................................................................................................... 26
603. Administration Changes. ............................................................................................................. 27
604. Accounting of Controlled Substances. (I) ................................................................................... 27
605. Agency Closure. ............................................................................................................................. 27
SECTION 700 – PATIENT CARE .......................................................................................................... 27
701. General. .......................................................................................................................................... 27
702. Data Manager. ............................................................................................................................... 28
703. Content. ......................................................................................................................................... 28
704. Report Maintenance. .................................................................................................................... 29
705. Do Not Resuscitate (DNR) Order. (II) .......................................................................................... 29
706. Physician Orders for Scope of Treatment (POST). (II) .............................................................. 30
SECTION 800 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................... 30
SECTION 900 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................... 30
SECTION 1000 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 30
SECTION 1100 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 30
SECTION 1200 – MEDICATIONS ........................................................................................................ 30
1201. General. (I) ................................................................................................................................... 30
1202. Medication Orders. (I) ................................................................................................................ 30
1203. Administering Medication and/or Treatments. (I) .................................................................. 31
1204. Medication Storage. ................................................................................................................... 31
1205. Disposition of Controlled Substances...................................................................................... 31
SECTION 1300 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 32
SECTION 1400 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 32
SECTION 1500 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 32
SECTION 1600 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 32
SECTION 1700 – SANITATION AND INFECTION CONTROL ............................................................. 32
1701. General......................................................................................................................................... 32
1702. Exterior Ambulance Surfaces. ................................................................................................... 32
1703. Interior Ambulance Surfaces Patient Compartment. ............................................................ 32
1704. Linen. ............................................................................................................................................ 33
1705. Oxygen Administration Apparatus. (II) .................................................................................... 33
1706. Resuscitation Equipment. (II) .................................................................................................... 34
1707. Suction Unit. (II) ........................................................................................................................... 34
1708. Splints. (II) .................................................................................................................................... 34
1709. Spinal Motion Restriction Device. (II) ....................................................................................... 35
1710. Bandages and Dressings. (II) ..................................................................................................... 35
1711. Obstetrical (OB) Kits. (II) ............................................................................................................. 35
1712. Oropharyngeal Appliances. (II) ................................................................................................. 35
1713. Communicable Diseases. (II) ..................................................................................................... 36
1714. Equipment. .................................................................................................................................. 36
1715. Equipment and Materials Storage Areas................................................................................. 36
1716. Personnel. .................................................................................................................................... 36
SECTION 1800 – AMBULANCE PERMITS. (I) ...................................................................................... 36
1801. General......................................................................................................................................... 36
1802. Temporary Ambulance Permit. ................................................................................................ 37
SECTION 1900 – AMBULANCES. (II) .................................................................................................. 37
1901. Ambulance Design...................................................................................................................... 37
1902. Ambulance Re-mounted Design and Equipment................................................................... 42
SECTION 2000 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 42
SECTION 2100 – MEDICAL EQUIPMENT ........................................................................................... 42
SECTION 2200 – AIR AMBULANCE .................................................................................................... 52
2201. Permitting. (I) ............................................................................................................................... 52
2202. Aircraft. ........................................................................................................................................ 53
2203. Aircraft Flight Crew. .................................................................................................................... 55
2204. Medical Supplies and Equipment. (II) ...................................................................................... 58
2205. Medication and Fluids for Advanced Life Support Air Ambulances. (II) .............................. 59
2206. Rescue Exception. (II) ................................................................................................................. 59
SECTION 2300 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 60
SECTION 2400 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 60
SECTION 2500 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 60
SECTION 2600 – [RESERVED] ............................................................................................................. 60
SECTION 2700 – SEVERABILITY ......................................................................................................... 60
SECTION 2800 – GENERAL ................................................................................................................. 60

1 | Regulation 61-7
SECTION 100 – DEFINITIONS, LICENSURE, AND CERTIFICATION
101. Definitions.
A. Abandoned. For the purpose of Section 302.B.3.h, unilateral termination by the EMS Personnel
of the provider-Patient relationship when continuing care was still needed. This includes the
termination of care without the Patient’s consent or without assurance that a level of care meeting the
assessed needs of the Patient’s condition is present and available. The provider-patient relationship
must have been established for abandonment to occur and the event must be without extenuating
circumstances such as provider safety or patients who act against medical advice (AMA).
B. Abuse. Physical Abuse or Psychological Abuse.
1. Physical Abuse. The act of intentionally inflicting or allowing infliction of physical injury on
a Patient by an act or failure to act. Physical Abuse includes, but is not limited to, slapping, hitting,
kicking, biting, choking, pinching, burning, actual or attempted sexual battery, use of medication
outside the standards of reasonable medical practice for the purpose of controlling behavior, and
unreasonable confinement. Physical Abuse also includes the use of a restrictive or physically intrusive
procedure to control behavior for the purpose of punishment except that of a therapeutic procedure
prescribed by a licensed physician or other legally authorized healthcare professional. Physical Abuse
does not include altercations or acts of assault between Patients.
2. Psychological Abuse. The deliberate use of any oral, written, or gestured language or depiction
that includes disparaging or derogatory terms to a Patient or within the Patient’s hearing distance,
regardless of the Patient’s age, ability to comprehend, or disability, including threats or harassment
or other forms of intimidating behavior causing fear, humiliation, degradation, agitation, confusion,
or other forms of serious emotional distress.
C. Advanced Emergency Medical Technician (AEMT). An advanced level emergency medical
services provider certified by the Department to provide basic and limited advanced emergency
medical care and transportation for Patients.
D. Advanced Life Support (ALS). An advanced level of prehospital, interhospital, and emergency
service care, which includes Basic Life Support functions, cardiac monitoring, cardiac defibrillation,
telemetered electrocardiography, administration of antiarrhythmic agents, intravenous therapy,
administration of specific medications, drugs and solutions, use of adjunctive ventilation devices,
trauma care, and other techniques and procedures authorized by the Department.
E. Adverse Incident. An unexpected event, including any accidents, that could potentially cause
harm, injury, or death to Patients, EMS Personnel, or third-party individuals.
F. Air Ambulance. Any aircraft that is intended to be used and is maintained or operated for
transportation of persons who are sick, injured, or otherwise incapacitated.
1. Fixed Wing. Any aircraft that uses fixed wings to allow it to take off, fly, and land.
2. Rotorcraft. A helicopter or other aircraft that uses a rotary blade to allow vertical and
horizontal flight without the use of wings.
G. Ambulance. A vehicle maintained or operated by a Licensed Agency that has obtained the
necessary permits and licenses for the transportation of persons who are sick, injured, wounded, or
otherwise incapacitated.

2 | Regulation 61-7
H. Attendant. A trained and qualified individual responsible for the operation of an Ambulance and
the care of Patients, regardless of whether the Attendant also serves as the Driver.
I. Attendant-driver. A person who is qualified as an Attendant and a Driver.
J. Basic Life Support (BLS). A basic level of prehospital care, which includes Patient stabilization,
airway clearance, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, hemorrhage control, initial wound care and fracture
stabilization, and other techniques and procedures authorized by the Department pursuant to
regulation.
K. Certificate. An official acknowledgment by the Department that an individual has completed
successfully one of the appropriate Emergency Medical Technician training programs, successfully
completed the requisite examinations, and which entitles that individual to perform the functions and
duties as delineated by the classification for which the Certificate was issued.
L. Condition Requiring an Emergency Response. The sudden onset of a medical condition
manifested by symptoms of such sufficient severity, including severe pain, which a prudent layperson
who possesses an average knowledge of health and medicine could reasonably expect without medical
attention, to result in:
1. Serious illness or disability;
2. Impairment of a bodily function;
3. Dysfunction of the body; or
4. Prolonged pain, psychiatric disturbance, or symptoms of withdrawal.
M. Continuing Education Program. A Department-approved program offered by an EMS Agency
that provides Continuing Education for the recertification of South Carolina certified EMT-basics,
AEMTs, and Paramedics.
N. Department. The South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control.
O. Do Not Resuscitate Bracelet (“Bracelet”). A standardized identification bracelet that:
1. Meets the specifications established under S.C. Code Section 44-78-30(B) or that is approved
by the Department under S.C. Code Section 44-78-30(B);
2. Bears the inscription "Do Not Resuscitate"; and
3. Signifies that the wearer is a Patient who has obtained a Do Not Resuscitate Order that has not
been revoked.
P. Do Not Resuscitate Order for Emergency Services (“DNR Order”). A document made pursuant
to the Emergency Medical Services Do Not Resuscitate Order Act, S.C. Code Sections 44-78-10, et
seq., to prevent Emergency Medical Services personnel from employing resuscitation measures or
any other medical process that would only extend the Patient’s suffering with no viable medical reason
to perform the procedure.
Q. Driver. An individual who drives or otherwise operates an Ambulance.

3 | Regulation 61-7
R. Electronic Patient Care Reports (ePCR). Patient care reports authored and submitted
electronically into the Department’s EMS data system.
S. Elopement. An instance when a Patient who wanders, walks, runs away, escapes, or otherwise
leaves unsupervised or unnoticed from the scene, transport unit, or prior to care being assumed by the
receiving facility.
T. Emergency. A situation in which a prudent layperson has identified a potential medical threat to
life or limb such that the absence of immediate medical attention could reasonably be expected to
result in placing the individual’s health in serious jeopardy, serious impairment of bodily functions,
or serious dysfunction of bodily organs.
U. Emergency Medical Responder Agency. An Agency licensed by the Department to provide
medical care at the EMT-basic level or above, as a nontransporting emergency medical responder.
May also be referred to as an EMT Rapid Responder Agency.
V. Emergency Medical Service Agency. An Agency licensed by the Department to provide
nontransport and/or transport emergency medical services in South Carolina, including public,
private, volunteer, fire departments, or other type of Ambulance services and Emergency Medical
Responder Agencies. May also be referred to as EMS Agency or Agency.
W. Emergency Medical Services Personnel. Persons trained and certified or licensed to provide
emergency medical care, whether on a paid or volunteer basis, as part of a Basic Life Support or
Advanced Life Support prehospital Emergency Medical Services, in an emergency department,
pediatric critical care, or specialty unit in a licensed hospital. May also be referred to as EMS
Personnel.
X. Emergency Medical Technician (EMT). An individual possessing a valid EMT-basic, Advanced
EMT (AEMT), or Paramedic Certificate issued by the Department.
Y. Emergency Transport. Services and transportation provided after the sudden onset of a medical
condition manifesting itself by acute symptoms of such severity, including severe pain, that the
absence of medical attention could reasonably be expected to result in the following:
1. Placing the Patient’s health in serious jeopardy;
2. Causing serious impairment of bodily functions or serious dysfunction of bodily organ or part;
or
3. A situation resulting from an accident, injury, acute illness, unconsciousness, or shock, for
example, requiring oxygen or other emergency treatment, or requiring the Patient to remain immobile
because of a fracture, stroke, heart attack, or severe hemorrhage.
Z. EMT-basic. An EMT certified by the Department at the basic level.
AA. Endorsement. A provision added to a Certificate, pursuant to approval by the Department,
enhancing the scope of practice or authorization of specific activities within the EMS system.
BB. Exploitation. 1) Causing or requiring a Patient to engage in an activity or labor that is improper,
unlawful, or against the reasonable and rational wishes of a Patient; 2) an improper, unlawful, or
unauthorized use of the funds, assets, property, power of attorney, guardianship, or conservatorship

4 | Regulation 61-7
of a Patient by an individual for the profit or advantage of that individual or another individual; or 3)
causing a Patient to purchase goods or services for the profit or advantage of the seller or another
individual through undue influence, harassment, duress, force, coercion, or swindling by
overreaching, cheating, or defrauding the Patient through cunning arts or devices that delude the
Patient and cause him or her to lose money or other property.
CC. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). The agency of the federal government that governs
aircraft design, operations, and personnel requirements.
DD. Flight Nurse. A licensed registered nurse who is trained in all aspects of Emergency care.
EE. Investigative Review Committee. A professional peer review committee that may be convened
by the Department, in its discretion, when the findings of an official investigation against an entity or
an individual regulated by the Department may warrant suspension or revocation of a License or
Certificate.
FF. License. An authorization issued by the Department to a person, firm, corporation, or
governmental division or agency to provide emergency medical services.
GG. Licensee. Any person, firm, corporation, or governmental division or agency possessing a
License to provide emergency medical services in South Carolina.
HH. Medical Control. Medical Control is provided by a licensed Agency’s physician who is
responsible for the care of the Patient by the Agency’s medical Attendants. Actual Medical Control
may be direct by two-way voice communications (on-line) or indirect by Protocols (off-line) control.
1. Off-Line Medical Control. An Agency’s Medical Control Physician assists in development
and implementation of Protocols and Patient care guidelines.
2. On-Line Medical Control. The physician directly communicates with EMS Personnel
regarding Patient care en-route or on-scene.
II. Medical Control Physician. A physician with a current unrestricted license to practice medicine
by the South Carolina Board of Medical Examiners, retained by an EMS Agency to provide Off-line
Medical Control, who participates in the review or evaluation of the services provided, and who
maintains quality control of the Patient care provided by the EMS Agency. May also be referred to as
EMS Medical Director.
JJ. Moral Turpitude. Behavior that is not in conformity with and is considered deviant by societal
standards.
KK. National Emergency Medical Services Information System (NEMSIS). The national database
that is used to store EMS data from the U.S. States and Territories. NEMSIS is a collaborative system
to improve Patient care through the standardization, aggregation, and utilization of point of care EMS
data at a local, state, and national level.
LL. National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT). A national certification
agency that provides a valid and uniform process to assess the knowledge and skills required for
competent practice by EMS professionals throughout their careers and maintains a registry of
certification status.

5 | Regulation 61-7
MM. Nonemergency Transport. Services and transportation provided to a Patient whose condition
is considered stable, including prearranged transports scheduled at the convenience of the service, the
Patient, or medical facility. A stable Patient is one whose condition by caregiver consensus can
reasonably be expected to remain the same throughout the transport and for whom none of the criteria
for Emergency Transport has been met.
NN. Palliative Treatment. The degree of treatment that must be provided to a Patient in the routine
delivery of emergency medical services, which assures the comfort and alleviation of pain and
suffering to all extents possible, regardless of whether the Patient has executed a document as
provided for in Chapter 78, Title 44 of the S.C. Code of Laws. May also be referred to as Palliative
Care.
OO. Paramedic. The highest level of EMT certified by the Department.
PP. Patient. An individual who is sick, injured, wounded, or otherwise incapacitated or helpless.
QQ. Permit. An authorization issued by the Department for an Ambulance which meets the
standards of this regulation.
RR. Physician Orders for Scope of Treatment (POST) Form. A designated document designed for
use as part of advance care planning, the use of which must be limited to situations where the Patient
has been diagnosed with a serious illness or, based upon medical diagnosis, may be expected to lose
capacity within twelve (12) months and consists of a set of medical orders signed by a Patient’s
Physician or other Authorized Healthcare Provider addressing key medical decisions consistent with
Patient goals of care concerning treatment at the end of life that is portable and valid across health
care settings.
SS. Prehospital Care: Assessment, stabilization, and care of a Patient, including, but not limited to,
the transportation to an appropriate receiving facility.
TT. Protocols. Written orders signed, dated, and issued by a Medical Control Physician that allow
EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics to administer particular medications and perform treatment
modalities in specific situations without On-line Medical Control. May also be referred to as Standing
Orders.
UU. Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP). A communications facility operated on a twenty-four
(24) hour basis which first receives 911 calls from persons in a 911 service area and which may
directly dispatch public safety services or extend, transfer, or relay 911 calls to appropriate public
safety agencies.
VV. Resuscitative Treatment. Artificial stimulation of the cardiopulmonary systems of the human
body, through either electrical, mechanical, or manual means including, but not limited to,
cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
WW. Revocation. An action by the Department to cancel or annul a License, Permit, or Certificate
by recalling, withdrawing, or rescinding the Agency’s or individual’s authorization to operate or
practice.
XX. Special Purpose EMT. A South Carolina licensed registered nurse (RN) or a Nurse Licensure
Compact (NLC) State RN who works in a critical care hospital setting, and is an EMT certified by
the Department to provide a continuance of critical care during transport while aboard Ambulances
equipped for their specialty area.

6 | Regulation 61-7
YY. “Star of Life”. A six (6) barred blue cross outlined with a white border of which all angles are
sixty (60) degrees, and upon which is superimposed the staff of Aesculapius in white. This is a
registered trademark of the United States Department of Transportation.
ZZ. Suspension. An action by the Department requiring a Licensee, Permit or Certificate holder to
cease operations or providing Patient care until such time as the Department rescinds that restriction.
AAA. Variance. An alternative method that ensures the equivalent level of compliance with the
standards in this regulation.
BBB. Volunteer EMS Agency. A not-for-profit EMS Agency that serves its local community with
emergency medical service coverage at any level and is staffed by at least ninety percent (90%)
non-paid staff. For the purpose of this regulation, token stipends received by volunteer EMS Agencies
are not considered paid remuneration or a primary wage.
102. Licensure.
A. No person, firm, corporation, association, county, district, municipality, or metropolitan
government or agency, either as owner, agent, or otherwise, shall furnish, operate, conduct, maintain,
advertise, or otherwise engage in or profess to engage in the business or service of providing
emergency medical response or Ambulance service, or both, without obtaining a License and
Ambulance Permit issued by the Department. When it has been determined by the Department that
services are being provided and the owner, agent, or otherwise has not been issued a License from the
Department, the owner, agent, or otherwise shall cease operation immediately and ensure the safety,
health, and well-being of Patients. Current and/or previous violations of the South Carolina Code
and/or Department regulations may jeopardize the issuance of a License or the licensing of any
party(ies) to provide emergency medical response or Ambulance service or both that is
owned/operated by the applicable party(ies). An EMS Agency shall not operate or advertise that it
provides a level of life support above the level for which it is licensed. (I)
B. An EMS Agency that applies to the Department for any additional initial or amended EMS
Agency Licenses shall be in substantial compliance with this regulation to obtain any additional initial
or amended EMS Agency Licenses.
C. Issuance and Terms of License.
1. The EMS Agency shall ensure the License issued by the Department is posted in a conspicuous
place in a public area.
2. The EMS Agency’s License is not assignable or transferable and is subject to Revocation at
any time by the Department for the EMS Agency’s failure to comply with the laws or regulations of
this state.
3. A License shall be effective for a specified EMS Agency, at a specific location, and for a
period of two (2) years following the date of issue. A License shall remain in effect until the
Department notifies the EMS Agency of a change in that status.
D. EMS Agency Name. Proposed and existing EMS Agencies shall not have the same or similar
name of any other EMS Agency licensed in South Carolina.

7 | Regulation 61-7
E. Amended License. An EMS Agency shall request issuance of an amended License by application
to the Department prior to any of the following circumstances:
1. Change of level of services provided;
2. Change of EMS Agency headquarters location from one geographic site to another; or
3. Changes in EMS Agency’s name or address (as notified by the post office).
F. Change of Licensee. An EMS Agency shall request issuance of a new License by application to
the Department prior to any of the following circumstances:
1. A change in the controlling interest even if, in the case of a corporation or partnership, the
legal entity retains the identity and name; or
2. A change in the legal entity, for example, sole proprietorship to or from a corporation or
partnership to or from a corporation, even if the controlling interest does not change.
103. EMS Agency License Application.
A. Application. Applicants for licensure as an EMS Agency shall submit to the Department a
complete and accurate application on a form prescribed and furnished by the Department prior to
initial licensing. The EMS Agency shall ensure the application is signed by the owner(s) if an
individual or partnership; by two (2) officers if a corporation; or by the head of the governmental
department having jurisdiction if a governmental unit. Corporations or limited partnerships, limited
liability companies, or any other organized business entity shall be registered with the South Carolina
Secretary of State’s Office if required to do so by state law.
B. The EMS Agency shall include the following with the application:
1. The name and address of the owner of the EMS Agency or proposed EMS Agency;
2. The name under which the EMS Agency applicant is doing business or proposes to do
business;
3. A copy of the business license, if applicable, of the EMS Agency or proposed EMS Agency
for the location of the service;
4. The number of Ambulances and/or emergency medical responder service vehicles and a
description of each vehicle including the make, Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), aircraft tail
number, model, year of manufacture, and other distinguishing characteristics to be used to designate
the applicant’s vehicles;
5. The location and description of the place or places, including substations, from which the EMS
Agency is intending to operate;
6. Personnel roster representing all employees, members, volunteers, and affiliates associated
with the service including, but not limited to, EMT-basics, AEMTs, Paramedics, Drivers, pilots,
registered nurses, certification numbers, and expiration dates of their South Carolina and NREMT
credentials, if applicable;

8 | Regulation 61-7
7. EMS Agency type(s) and the levels of capability for each type pursuant to Sections 504 and
505 to be provided at each location;
8. Name, email address, and phone number of the following, if applicable;
a. EMS Director;
b. EMS Assistant Director;
c. Training Officer;
d. Data Manager;
e. Infection Control Officer;
f. Pediatric Emergency Care Coordinator, if applicable; and
g. Medical Control Physician.
9. A copy of current Protocols and an authorized medication list both signed and dated by the
Medical Control Physician;
10. Records for each Driver, pursuant to Section 503;
11. Liability insurance information, to include name of insurance company, agent, phone
number, and type of coverage. A copy of insurance policies shall be furnished to the Department upon
request. The minimum limits of coverage shall be six hundred thousand dollars ($600,000.00) liability
and three hundred thousand dollars ($300,000.00) malpractice per occurrence. Applicants that claim
“self-insured” status shall provide documentation showing the specific coverages as outlined above;
12. A copy of the EMS Non-Dispensing Drug Outlet Permit from the South Carolina Board of
Pharmacy, when applicable;
13. A copy of the EMS Agency’s current registration Certificate from the Department’s Bureau
of Drug Control and registration Certificate from the United States Drug Enforcement Administration,
when applicable;
14. A copy of the EMS Agency’s Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)
Certificate of Waiver from the federal Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), when
applicable;
15. A copy of the EMS Agency’s Infectious Waste Generator Registration issued by the
Department, or if an out of state EMS Agency, the respective home state equivalent; and
16. Additional information if requested by the Department, such as affirmative evidence of the
applicant’s ability to comply with this regulation.
C. License Renewal. The EMS Agency shall submit a complete and accurate application on a form
prescribed and furnished by the Department prior to the License expiration date and shall not have
pending enforcement actions by the Department. If the License renewal is delayed due to enforcement
actions, the renewal License shall be issued only when the matter has been resolved by the
Department, or when the adjudicatory process is completed, whichever is applicable.

9 | Regulation 61-7
104. Emergency Medical Technicians.
A. No person may hold himself or herself out as an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic, or provide
Patient care that is within the scope of an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic as defined in South
Carolina Code Section 44-61-20 and this regulation without obtaining a proper Certificate from the
Department. When it has been determined by the Department that an individual is engaged as an
EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic, and the individual has not been issued a Certificate from the
Department, the individual shall cease engaging as an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic immediately.
Current and/or previous violation(s) of the South Carolina Code of Laws or Department regulations
may jeopardize the issuance of an EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certificate. (I)
B. No person shall provide Patient care within the scope of an Emergency Medical Technician
(EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic) without a current Certificate from the Department. The EMT
shall: (I)
1. Engage only in those practices for which he or she has been trained, within the scope of the
Department-issued Certificate, and as authorized by the EMS Agency’s Medical Control Physician;
and
2. Perform procedures only under the direction and oversight of a Medical Control Physician.
105. Initial EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certification.
A. Applicants for an initial EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Certificate shall submit to the
Department a completed application on a form prescribed, prepared, and furnished by the Department
prior to issuance of an initial Certificate. The applicant shall submit, along with the application, the
following:
1. Documentation that he or she has successfully passed the National Registry of Emergency
Medical Technicians (NREMT) examination for the level of certification desired and possesses a
current NREMT credential. In lieu of the NREMT credential, the Special Purpose EMT applicant
shall submit documentation demonstrating that he or she is a licensed registered nurse who works in
a critical care hospital setting;
2. A Criminal History Background Check. A person seeking EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic
certification shall undergo a state criminal history background check supported by fingerprints by the
South Carolina Law Enforcement Division (SLED) and a national criminal history background check
supported by fingerprints by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and report the results of the
criminal history background check to the Department; and (I)
3. The Department may require additional information including affirmative evidence of the
applicant’s ability to comply with this regulation.
106. Issuance and Terms of Certification.
A. The EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certificate is issued pursuant to South Carolina Code
Sections 44-61-80 et seq. and this regulation.
B. The EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certificate is not assignable or transferable and shall be
subject to Denial, Suspension, or Revocation by the Department for failure to comply with the South
Carolina Code of Laws and this regulation.

10 | Regulation 61-7
C. The EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certificate shall be valid for a period not exceeding four
(4) years from the date of issuance. A Certificate shall remain in effect until the Department notifies
the EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic of a change in that status.
D. EMS Personnel shall at all times while on duty or otherwise rendering Patient care have the
Department-issued identification on their person and available for view upon request. Patches from
other certifying or licensing agencies are not an acceptable substitute.
E. The EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic shall maintain current information in the Department’s
credentialing system.
107. EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Certification Renewal.
A. To renew his or her EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Certificate, the EMT-basic, AEMT, or
Paramedic shall submit a complete application with the Department, on a form prescribed, prepared,
and furnished by the Department, at least thirty (30) calendar days prior to the expiration date of his
or her Certificate and shall not have pending enforcement actions by the Department. If the Certificate
renewal is delayed due to enforcement actions, the Certificate renewal shall be issued only when the
matter has been resolved satisfactorily by the Department or when the adjudicatory process is
completed, whichever is applicable. The EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic shall submit, along with
the renewal application, the following:
1. Documentation of current NREMT credentials for the appropriate level of certification,
EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic, or documentation that the EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic was
certified by the Department prior to October 1, 2006, and has continuously maintained Certification.
In lieu of the NREMT credential, the Special Purpose EMT shall submit documentation
demonstrating he or she is a licensed registered nurse who works in a critical care hospital setting;
2. A state and national criminal history background check pursuant to S.C. Code Section
44-61-80 (D); and
3. Department-approved CPR credential for all EMTs and Department-approved Advanced
Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) credential for all Paramedics.
108. Special Purpose EMT.
A. A Special Purpose EMT certified by the Department prior to the effective date of the most recent
regulatory amendment shall be considered grandfathered in terms of their Certification and shall be
recognized as a Special Purpose EMT so long as he or she possesses a current Certificate issued by
the Department, renews his or her Certificate pursuant to Section 107 of this regulation, and maintains
employment in an EMS Agency.
B. The Special Purpose EMT shall only engage in those practices for which he or she has been
trained.
109. Reciprocity.
A. Candidates seeking reciprocity in South Carolina as an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic shall:
1. Hold either an NREMT credential or a current certification from another state for the level for
which they are applying; and

11 | Regulation 61-7
2. Complete the criminal history background check in accordance with S.C. Code Section
44-61-80(D) and pursuant to Section 105.A.2.
B. Candidates seeking reciprocity who hold a current and valid NREMT certification may apply
for direct reciprocity at the level of the NREMT credential they hold by creating an up-to-date profile
in the Department’s credentialing system and submitting a complete reciprocity application in a
format as determined by the Department. The candidate shall submit the following with the
application:
1. A properly completed out-of-state certification verification form;
2. A copy of their current NREMT certification for the level of reciprocity for which they are
applying; and
3. All other requirements as established by the Department.
C. Candidates not certified in South Carolina who hold a current and valid EMT-basic, AEMT, or
Paramedic certification from other states and do not hold a current NREMT certification may apply
for a one (1) year provisional certification at the level they hold. Candidates for provisional
certification shall create an up-to-date profile in the Department’s credentialing information system
and submit a complete reciprocity application in a format as determined by the Department. The
candidate shall submit the following with the application:
1. A copy of their current state certification identification card for the level for which he or she
is applying that includes the certification expiration date. All candidates with provisional Certificates
shall have no less than six (6) months remaining on their out-of-state certification by the time the
Department receives all required documentation necessary for certification; and
2. All other documentation and requirements as established by the Department.
D. South Carolina provisional Certificates for all levels of certification shall expire one (1) year
from the date of issue. Provisional certifications are non-renewable, and extensions are not permitted.
An active military service member deployed outside of South Carolina may submit a written request
in a format as determined by the Department for an extension on his or her provisional Certification
and submit a copy of the active duty orders with the request.
E. To convert a South Carolina provisional certification to a conventional South Carolina
Certification, the provisional Certificate holder shall obtain a NREMT certification and complete the
recertification requirements pursuant to Section 107 prior to expiration.
110. Certification Examinations.
Applicants for an EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Certificate shall successfully complete a
Department-approved training program that meets or exceeds the NREMT standards for the desired
level of certification. After completion of the training program and prior to certification, the applicant
shall successfully pass the NREMT cognitive and the Department-approved psychomotor
examinations.

12 | Regulation 61-7
111. Training Programs. (II)
A. Training programs are offered in approved technical colleges, other colleges and universities,
vocational schools, and State Regional EMS training offices. No training program shall advertise as
an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic training program or conduct EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic
training prior to approval as a training program from the Department. The training program applicant
shall:
1. Submit a complete application to the Department in a format determined by the Department.
Training program applicants shall submit documentation of accreditation as required by the NREMT
with their application to the Department;
2. Designate one (1) person as the EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic program coordinator; and
3. Have equipment for training purposes as approved by the Department available and in working
condition.
4. The provisions of this Section shall not affect training programs approved by the Department
as of the date of this regulation.
B. Departmental approval of a training program is granted for four (4) years. The training program
shall complete a renewal application, in format as determined by the Department, prior to the
expiration date to be re-approved. The training program shall not conduct courses with an expired
Department approval.
C. The training program shall ensure all courses are taught by Department-certified EMT-basic,
AEMT, and Paramedic instructors and shall not conduct class without equipment pursuant to Section
111.A.3. The training program may utilize specialty instructors, such as physicians, nurses,
anatomists, and other subject matter experts, for portions of instruction as determined by the training
program.
D. The training program shall retain a Medical Control Physician to provide medical oversight for
their program.
E. The training program shall maintain a seventy percent (70%) first time pass rate as defined by
NREMT, calculated using a three (3) year rolling history, on the cognitive and psychomotor portions
of the NREMT Examination.
112. Certified EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic Instructors.
A. All EMT-basic, AEMT, and Paramedic instructors shall be certified by the Department prior to
providing any instruction in a training program and meet the following requirements:
1. Submit a complete and signed certified EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic instructor
application in a format as determined by the Department;
2. Have three (3) years’ experience at the level for which he or she intends to teach;
3. Possess a high school diploma or GED;
4. Possess a current state EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Certificate. The certified EMT-basic,
AEMT, or Paramedic instructor shall only teach at or below the level of his or her Certificate level;

13 | Regulation 61-7
5. Successfully complete a forty (40) hour instructor methodology course offered by the National
Association of EMS Educators (NAEMSE), International Fire Service Accreditation Congress
(IFSAC), ProBoard or Department of Defense (DOD) fire instructor, South Carolina Criminal Justice
Academy, or other Department-approved course; and
6. Possess a current and valid CPR instructor credential.
B. Instructor Candidates. Instructor candidates may provide instruction in a training program under
the supervision of a Department-certified instructor.
C. Instructor Certification Renewal. The certified instructor shall submit a complete and signed
renewal application certification prior to the last day of the month in which his or her state EMT
certification expires. The renewal application shall include:
1. A copy of a current South Carolina and NREMT EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic
certification; and
2. A copy of a current and valid CPR instructor credential.
D. The Department may suspend or revoke an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic instructor
certification for any of the following reasons:
1. Any act of misconduct as outlined in Section 303.B.;
2. Suspension or Revocation of the holder’s South Carolina or NREMT certification;
3. Failure to maintain required credentials necessary for instructor designation;
4. Any act of sexual or other harassment toward another instructor or candidate;
5. Conducting classes while under the influence of drugs that negatively impair the ability to
instruct (prescribed, non-prescribed, or illegal); and
6. Falsification of any documents pertaining to the course (such as attendance logs, equipment
checklist).
113. Continuing Education (CE) Program. (II)
A. No EMS Agency shall begin or conduct a CE Program prior to receiving approval by the
Department. EMS Agencies seeking approval for a CE program shall file an application with the
Department in a format as determined by the Department.
B. The EMS Agency’s CE Program approval shall be effective for no more than four (4) years. The
CE Program shall submit a renewal application in a format as determined by the Department prior to
the expiration date of the Department’s approval.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure all CE Programs meet the requirements established by the
NREMT for recertification.

14 | Regulation 61-7
D. CE Programs may verify skills for currently credentialed state and NREMT personnel on their
roster. Provisional credentialed EMTs must have their NREMT skills verified at a
Department-approved NREMT testing site.
114. Continuing Education Units (CEUs).
A. The Department may approve additional CEUs on a case-by-case basis from medical schools,
hospitals, simulation centers, formal conventions, seminars, workshops, educational classes,
symposiums, and other Department approved continuing education events.
B. Applicants for CEUs shall submit requests in writing for approval from the Department at least
thirty (30) calendar days prior to the scheduled event.
C. The written requests for approval shall include the following:
1. Date, time, and agenda of the event;
2. Topics covered; and
3. List of speakers and their credentials.
115. Pilot Programs.
A. The EMS Agency that wishes to initiate a pilot program shall provide in writing to the
Department a detailed proposal of the program and any supporting materials requested by the
Department. The South Carolina Medical Control Committee and the South Carolina EMS Advisory
Council shall provide a written recommendation to the Department.
B. The EMS Agency shall not initiate a pilot program without prior written approval by the
Department. (I)
C. The EMS Agency, approved by the Department to initiate a pilot program, shall ensure
participating EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics perform the pilot procedures under their Medical
Control Physician’s oversight during the period of the pilot program.
D. The EMS Agency shall present a detailed report to the Medical Control Committee and EMS
Advisory Council upon the conclusion of the pilot program which includes all information requested
by the approving committees.
116. Endorsement of Specialty Credentials.
A. A Department-endorsed specialty credential may include, but is not limited to, the following
areas of specialized training:
1. Community Paramedic;
2. Critical Care Paramedic; and
3. Tactical Paramedic.

15 | Regulation 61-7
B. The applicant for Endorsement shall meet the minimum educational and clinical guidelines as
established by the Department and submit a complete application in a format as determined by the
Department that includes:
1. Documentation of the Department-required training;
2. Documentation that he or she is currently employed by an EMS Agency in one of the
specialized training areas pursuant to Section 116.A; and
3. Documentation that he or she has successfully passed the International Board of Specialty
Certification examination or other Department-approved national certifying board requirements.
C. Endorsement Renewal. The Department-endorsed Paramedic shall complete twenty-four (24)
hours of Department-approved continuing education above the NREMT certification requirements.
The Department-endorsed Paramedic shall submit documentation of the continuing education with
each Certificate renewal application.
D. Endorsement Reciprocity. A Paramedic seeking Endorsement through reciprocity shall submit
a complete application in a format as determined by the Department that includes:
1. Documentation of training and/or certification in his or her current state. The Department may
issue a one (1) year provisional Endorsement provided the Paramedic meets the minimum educational
and clinical guidelines as established by the Department prior to expiration of the provisional specialty
Endorsement; and
2. Documentation that the applicant is currently employed by or has a conditional employment
offer from a Licensed Agency to provide the level of service.
E. The Endorsement shall only be granted by the Department to Paramedics that are currently
certified by the Department. If a Paramedic’s Certification is expired, suspended, or revoked by the
Department, the Endorsement follows the same status as their certification.
F. The specialty endorsed Paramedic shall only practice their skills within the scope of practice of
their Department-approved agency, under a South Carolina licensed Medical Control Physician.
Specialty endorsed Paramedics are not independent healthcare practitioners.
G. The types of care rendered by specially endorsed Paramedics shall include, but are not limited
to, critical care interfacility services, prehospital services, preventative care, social service referrals,
chronic care support, follow-up care and maintenance, and tactical medical support of law
enforcement.
H. Licensed Agencies providing these specialized services shall:
1. Be licensed at the ALS level and provide Community Paramedic, Critical Care Paramedic, or
Tactical Paramedic services;
2. Have specific Protocols approved by the Department;
3. Develop and implement a Department-approved written training plan for training new
employees and providing continuing education for each specialty endorsed Paramedic; and

16 | Regulation 61-7
4. Ensure at least one (1) crew member on each ground Ambulance providing Critical Care is a
certified EMT and two (2) advanced level personnel (Paramedic, RN, Physician, or Respiratory
Therapist) are in the Patient compartment during transport.
117. Certification Patches.
A. An individual initially certified in South Carolina at any level shall receive a complimentary
patch for the level which he or she received his or her certification.
B. Additional patches may be purchased for individuals for services which meet the following
criteria:
1. The individual holds a current South Carolina certification; or
2. The individual is an EMS agency director, logistics officer, or training officer and is
purchasing patches in bulk for his or her service.
118. Variance.
An EMS Agency, EMT-basic, AEMT, Paramedic, training program, or instructor may request a
Variance to a provision or provisions of this regulation in a format specified by the Department.
Variances shall be considered on a case-by-case basis by the Department. The Department may revoke
issued Variances as determined to be appropriate by the Department.
SECTION 200 – ENFORCEMENT OF REGULATIONS
201. Inspections and Investigations. (I)
A. The EMS Agency is subject to Department inspections prior to initial licensing and subsequently
as deemed appropriate by the Department.
B. All EMS Agencies, permitted Ambulances, equipment, and vehicles, EMTs, training programs,
and instructors are subject to inspection by individuals authorized by the Department at any time
without prior notice. The EMS Agency, EMT, training program, and instructor shall provide the
Department all requested records and documentation in the manner and within the timeframe specified
by the Department.
C. The EMS Agency shall maintain records that include approved Patient care report forms,
employee or member rosters, or both, and training records. The EMS Agency shall grant individuals
authorized by the Department access to all properties and areas, objects, requested records, and
documentation at the time of the inspection or investigation. The EMS Agency shall provide the
Department with photocopies of documentation and records required in the course of inspections or
investigations for the purpose of enforcement of regulations. The Department shall maintain
confidentiality of the documentation in accordance with South Carolina Code Section 44-61-160.
202. Plan of Correction.
When the Department cites a violation of this regulation, the EMS Agency, EMT-basic, AEMT, or
Paramedic, Training Program, or EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Instructor shall submit an
acceptable plan of correction in a format determined by the Department. The EMS Agency,
EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic, Training Program, or EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic Instructor
shall ensure:

17 | Regulation 61-7
A. The plan of correction is signed by the EMS Agency administrator or individual and returned
by the date specified on the report of inspection or investigation.
B. The plan of correction describes: (II)
1. The actions taken to correct each cited deficiency;
2. The actions taken to prevent recurrences (actual and similar); and
3. The actual or expected completion dates of those actions.
203. Consultations.
Consultations may be provided by the Department as requested by the Licensee or Certificate
holder, or as deemed appropriate by the Department.
SECTION 300 – ENFORCEMENT ACTIONS
301. General.
The Department may suspend a License pending an investigation of an alleged violation or
complaint. The Department may impose a civil monetary penalty up to five hundred dollars ($500.00)
per offense per day to a maximum of ten thousand dollars ($10,000.00), revoke, or Suspend the
License if the Department finds that an EMS Agency has:
1. Allowed uncertified personnel to perform Patient care;
2. Falsified forms or documentation as required by the Department;
3. Failed to maintain required equipment as evidenced by past compliance history;
4. Failed to maintain a Medical Control Physician;
5. Failed to maintain equipment in working order; or
6. Failed to respond to a call within the EMS Agency’s service area without providing for
response by an alternate service provider.
302. Enforcement Actions against EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics.
A. General. When the Department determines that a Certificate holder is in violation of any
statutory provision, rule, or regulation, the Department, upon proper notice to the Certificate holder,
may deny, suspend, or revoke the Certificate or assess a monetary penalty in accordance with Section
305.A or both.
B. The Department may take enforcement action, including suspending or revoking a certification
and/or assessing a monetary penalty, against the holder of a Certificate at any time it is determined
that the certification holder:
1. No longer meets the prescribed qualifications set forth by the Department;

18 | Regulation 61-7
2. Has failed to provide to Patients emergency medical treatment of a quality deemed acceptable
by the Department, including failure to meet generally accepted standards for provision of care; or
3. Is guilty of Misconduct. Misconduct, constituting grounds for an enforcement action by the
Department, means that while holding a Certificate, the holder:
a. Used a false, fraudulent, or forged statement or document or practiced a fraudulent,
deceitful, or dishonest act in connection with the certification requirements or official documents
required by the Department;
b. Was convicted of or currently under indictment for a felony or another crime involving
Moral Turpitude, drugs, or gross immorality. The Certificate holder shall report in writing any arrest
to the Department as soon as possible but not to exceed five (5) business days following the arrest or
release from custody;
c. Is addicted to alcohol or drugs to such a degree as to render him or her unfit to perform as
an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic;
d. Sustained a mental or physical disability that renders further practice by him or her
dangerous to the public;
e. Obtained fees or assisted another in obtaining fees under dishonorable, false, or fraudulent
circumstances;
f. Disregarded an appropriate order by a physician concerning emergency treatment, including
protocol violations without appropriate justification;
g. At the scene of an accident or illness, refused to administer emergency care based on the
age, sex, race, religion, creed, or national origin of the Patient;
h. After initiating care of a Patient at the scene of an accident or illness, discontinued care or
Abandoned the Patient without the Patient’s consent or without providing for the further
administration of care by an equal or higher medical authority;
i. Revealed confidences entrusted to him or her in the course of medical attendance, unless
this revelation was required by law or is necessary to protect the welfare of the individual or the
community;
j. By action or omission and without mitigating circumstance, contributed to or furthered the
injury or illness of a Patient under his or her care;
k. Was careless, reckless, or irresponsible in the operation of an emergency vehicle;
l. Performed skills above the level for which he or she was certified or endorsed or performed
skills that he or she was not trained to do;
m. Observed the administration of substandard care by another EMT-basic, AEMT,
Paramedic, or other medical provider without documenting the event and notifying a supervisor;
n. By his or her actions or inactions, created a substantial possibility that death or serious
physical harm could result;

19 | Regulation 61-7
o. Did not take or complete remedial training or other courses of action as directed by the
Department as a result of an investigation or inquiry;
p. Was found to be guilty of the falsification of documentation as required by the Department;
q. Breached a section of the Emergency Medical Services Act of South Carolina or a
subsequent amendment of the Act or any rules or regulations published pursuant to the Act;
r. Has acted to disrespect, demean, disparage the Patient; has used profane, vulgar, or obscene
language to or directed at the Patient; or has derogated from standard professional conduct; or
s. Was found guilty of a violent crime as defined in S.C. Code Section 16-1-60.
C. The Department may suspend a Certificate pending the investigation of any complaint or
allegation regarding the commission of an offense including those listed in Section 302.B.
303. Investigative Review Committee.
The Department may convene, at its discretion, the Investigative Review Committee when the
findings of an official investigation against an entity or an individual regulated by the Department
may warrant Suspension or Revocation of a License or Certificate. This committee shall consist of
the State Medical Control Physician, three (3) regional EMS office representatives, at least one (1)
Paramedic, and at least one (1) emergency room physician who is also a Medical Control Physician.
304. Violation Classifications.
Violations of standards in this regulation are classified as follows:
A. Class I violations are those that the Department determines to present an imminent danger to the
health, safety, or well-being of the persons being served, other employees, or the general public; or a
substantial probability that death or serious physical harm could result therefrom. A physical
condition or one or more practices, means, methods, operations, or lack thereof may constitute such
a violation. Each day such violation exists may be considered a subsequent violation.
B. Class II violations are those other than Class I violations the Department determines to have a
negative impact on the health, safety or well-being of those being served, other employees, or the
general public. A physical condition or one or more practices, means, methods, operations, or lack
thereof may constitute such a violation. Each day such violation exists may be considered a
subsequent violation.
C. Class III violations are those that are not classified as Class I or II in these regulations or those
that are against the best practices as interpreted by the Department. A physical condition or one or
more practices, means, methods, operations, or lack thereof may constitute such a violation. Each day
such violation exists may be considered a subsequent violation.
D. Class IV violations are those that are specific to vehicle reinspection failures. These violations
can escalate based on frequency and point value accrued per deficiency identified in the vehicle
inspections conducted by the Department.
E. The notations “(I)” or “(II)”, placed within sections of this regulation, indicate that those
standards are considered Class I or II violations, if they are not met, respectively. Standards not so
annotated are considered Class III violations. Class IV violations are specific to vehicle reinspections

20 | Regulation 61-7
which may escalate to Class III violations.
F. In arriving at a decision to take enforcement actions, the Department shall consider the following
factors: specific conditions and their impact or potential impact on the health, safety, or well-being of
those being served, other employees and the general public, efforts by the EMT-basic, AEMT,
Paramedic, EMS Agency, training program or EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic instructor to correct
cited violations; behavior of the entity in violation that reflects negatively on that entity’s character,
such as illegal or illicit activities; overall conditions; history of compliance; and any other pertinent
factors that may be applicable to current statutes and regulations.
305. Monetary Penalties.
A. When imposing a monetary penalty against an EMS Agency, EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic
the Department may utilize the following schedule to determine the dollar amount:
FREQUENCY OF VIOLATION
CLASS I
CLASS II
CLASS III
1
st
$300 - 500
$100 - 300
$50 – 100
2
nd
$500 - 1,500
$300 - 500
$100 – 300
3
rd
$1,000 - 3,000
$500 - 1,500
$300 – 800
4
th
$2,000 - 5,000
$1,000 - 3,000
$500 -1,500
5
th
$5,000 - 7,500
$2,000 - 5,000
$1,000 - 3,000
6
th
or more
$10,000
$7,500
$2,000 - 5,000
B. When a licensed Agency fails a vehicle reinspection, a Class IV penalty may be levied upon the
agency. Pursuant to S.C. Code Section 44-61-70, the following Class IV penalty schedule shall be
used when a permitted Ambulance or licensed Emergency Medical Responder Agency loses points
upon reinspection:
FREQUENCY OF VIOLATION
CLASS IV Points
Penalty
1
st
0-24
$25-50
2
nd
25-50
$50-100
3
rd
51-100
$100-300
4
th
101-500
$300-500
5
th
501-1,000
$500-1,500
6
th
or more
Over 1,000
$1,000-3,000
SECTION 400 – POLICIES AND PROCEDURES (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall implement and be in full compliance with its policies and procedures.
B. The EMS Agency shall maintain written policies and procedures to include at least:
1. Staffing patterns to ensure compliance with en route times pursuant to Sections 504.B.2 and
505.A.2;
2. If electing to participate in a tiered response system, policies and procedures and, if necessary,
mutual aid agreements in place to identify the acuity of the incoming EMS requests in order to
properly triage the response and dispatch the appropriate level of Ambulance;
3. Continuing Patient transport if a vehicle becomes disabled;

21 | Regulation 61-7
4. Employee records retention and conducting background checks for credentialed and
non-credentialed personnel;
5. Governing the identification of EMS Personnel while providing care or while responding that
includes level of certification;
6. Reporting and investigating Adverse Incidents pursuant to Section 601;
7. Infection control and prevention;
8. Addressing the clean appearance of the EMT-basics, AEMTs, Paramedics, and Drivers;
9. Ensuring all EMS Personnel receive annual blood-borne pathogen training and maintain
documentation of the training;
10. Smoking Policy, including prohibiting the use of tobacco products or tobacco-like products
(such as electronic cigarettes) in the Patient compartment, the operator compartment of Ambulances,
or within twenty (20) feet of the Ambulance or any other apparatus in which oxygen is carried;
11. Recognizing out-of-service vehicles, which includes a highly visible mechanism at the
Driver’s position;
12. Defining, implementing, and reviewing Quality Assurance and/or process improvement
practices with regard to medical care provided by its EMS Personnel;
13. Medication Management to include written Protocols for storage and maintenance of
controlled substances; periodic inspection and inventory of maintained controlled substances by the
EMS Agency Director, EMS Agency Assistant Director, Medical Control Physician and/or Assistant
Medical Control Physician; and
14. Maintaining service in the event of the sudden or unexpected loss of the primary Medical
Control Physician.
C. The EMS Agency shall establish a time period for review, not to exceed two (2) years, of all
policies and procedures, and such reviews shall be documented and signed by the EMS Agency
director. The EMS Agency shall ensure all policies and procedures are accessible to the EMS Agency
personnel, printed or electronically, at all times.
SECTION 500 – PERSONNEL REQUIREMENTS
501. General. (I)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic is in the Patient
compartment at all times during Patient transport.
B. The EMS Agency may utilize registered nurses and physicians from a transferring or receiving
medical facility as Ambulance Attendants to assist EMTs in the performance of their duties during
transport when any of the following requirements are met:
1. The required medical care of the Patient is beyond the scope of practice for the certification
level of the EMT; or

22 | Regulation 61-7
2. The responsible physician, transferring or receiving, assumes responsibility of the Patient or
provides appropriate written orders to the registered nurse for Patient care.
502. Medical Control Physician. (I)
A. The EMS Agency shall retain a Medical Control Physician, who shall have independent
authority to execute his or her duties and responsibilities, to:
1. Provide oversight to ensure that all EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics for which he or she
provides direction are properly educated and certified pursuant to this regulation;
2. Provide oversight to ensure that an effective method of quality assurance and improvement,
with assistance of the EMS Agency Director, Data Manager, and other EMS Personnel, is integrated
into the emergency medical provider services for which he or she provides Medical Control; and
3. Provide off-line Medical Control by Protocols.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure that Protocols and authorized medication lists updated by the
Medical Control Physician are submitted to the Department within five (5) business days of the
updates in a manner prescribed by the Department.
C. The EMS Agency’s primary Medical Control Physician may designate medical oversight
authority to assistant or associate Medical Control Physicians. The EMS Agency’s Medical Control
Physician may withdraw, at his or her discretion, the authorization for EMS Personnel to perform any
or all Patient care procedure(s) or responsibilities. The EMS Agency shall notify the Department when
the Medical Control Physician withdraws the authorization to perform any or all Patient care
procedure(s) or responsibilities within three (3) calendar days. The EMS Agency’s Medical Control
Physician may respond to scene calls to render care, function as medical providers, provide medical
direction, and/or exercise their medical oversight authority.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure all initial Medical Control Physicians attend a Medical Control
Physician Workshop conducted by the Department within twelve (12) months of being designated as
Medical Control Physician and complete all Department mandated continuing education updates.
E. The EMS Agency shall not engage in EMS response without a Medical Control Physician.
503. Driver. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall:
1. Ensure each Ambulance Driver is at least eighteen (18) years of age;
2. Ensure each Ambulance Driver has in their possession at the time of vehicle operation a valid
driver’s license issued by the South Carolina Department of Motor Vehicles or from the state of his
or her residence;
3. Conduct a state criminal background check from the South Carolina Law Enforcement
Division (SLED) prior to the date of hire on each Ambulance Driver;
4. Secure and review a certified copy of each Ambulance Driver’s three (3)-year driving record;

23 | Regulation 61-7
5. Not employ an Ambulance Driver who is registered or required to be registered as a sex
offender with the South Carolina Law Enforcement Division (SLED) or any national registry of sex
offenders;
6. Ensure each Ambulance Driver has documentation of completion of a nationally accredited
driving safety course specific to Ambulances, which includes practical skill evolutions, within six (6)
months of hire; and
7. Ensure each Ambulance Driver has a current Department-approved CPR credential and First
Aid training.
B. The EMS Agency shall maintain documentation to ensure the EMS Agency meets the
requirements pursuant to Section 503.A and submits to the Department upon request.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure all Patients are transported with certified EMS Personnel in
addition to the Driver.
D. In emergencies that may require a third crew member, such as multiple casualty incidents
(MCIs), disasters, or where immediate local EMS resources are taxed, an Ambulance may, out of
necessity, be driven to the hospital by a member of a fire department, law enforcement agency, or
rescue squad. These out-of-necessity Drivers are exempt from Section 503.A, B, and C.
504. Emergency Medical Responder Agency. (II)
A. The Emergency Medical Responder Agency shall ensure the Emergency Medical Responder
vehicles are not used for the transportation of Patients.
B. Personnel. The Emergency Medical Responder Agency shall ensure and document in its
employee records that each of its EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics holds a current Certificate
from the Department. The Emergency Medical Responder Agency shall:
1. Ensure that vehicles are staffed in accordance with Section 504.B.2 and en route to all
emergent calls within five (5) minutes from the time the call is dispatched and en route within ten (10)
minutes for non-emergency calls. If the Emergency Medical Responder Agency is requested to
respond, an EMT-basic must respond on calls for a BLS Agency and a Paramedic must respond for
an ALS Agency eighty percent (80%) of the time.
2. Meet the staffing required for each response level as follows:(I)
a. BLS, at least one (1) EMT-basic or higher; and
b. ALS, at least one (1) Paramedic.
3. Documentation. The Emergency Medical Responder Agency shall maintain the following
documentation available as requested by the Department:
a. Staffing patterns to ensure compliance with en route times;
b. Approved Patient care report forms, employee and member rosters, time sheets, call rosters,
training records; and

24 | Regulation 61-7
c. Dispatch logs that show at least the time the call was received, the type of call, and en route
times.
505. Ambulance Service Agency. (II)
A. Personnel. The EMS Agency shall ensure all Ambulance Attendants have a valid EMT-basic,
AEMT, or Paramedic Certificate. The EMS Agency shall maintain documentation that each of its
EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics holds a current certification from the Department. The
Ambulance Service Agency shall:
1. Ensure that vehicles are staffed in accordance with Section 505.A.2 and en route to all
emergent calls within five (5) minutes from the time the call is dispatched and en route within ten (10)
minutes for non-emergency calls.
2. Have equipment and staff on all Ambulances to ensure the level of trained and qualified
personnel coincide with the requirements for its vehicle classification:(I)
a. BLS level service shall provide care and transport with at least one (1) EMT and one (1)
Driver.
b. ALS level service shall provide care and transport with at least one (1) EMT and one (1)
Paramedic. The EMS Agency shall ensure Ambulances transporting Patients requiring ALS level
service are fully equipped as an ALS unit with a Paramedic, physician, or RN in the Patient
compartment at all times.
3. If the Ambulance Service Agency only has one (1) EMT available to staff the Ambulance, the
Ambulance Service Agency shall ensure that the EMT is the Patient care provider and supervise the
care being provided.
B. The EMS Agency shall maintain documentation that demonstrates compliance with all en route
requirements and make it available to the Department upon request.
506. Special Response Vehicle (SRV).
The EMS Agency may utilize a non-permitted Special Response Vehicle (SRV) as a first response
vehicle. The EMS Agency shall ensure each SRV is staffed with a minimum of one (1) EMT that is
credentialed at the BLS or ALS level as determined by the Medical Control Physician. The EMS
Agency shall ensure the SRV is equipped as authorized by the Medical Control Physician.
507. Tiered Response System. (II)
A. An EMS Agency utilizing a tiered response system shall have a dispatch process in place to
specifically and reliably identify the acuity of the incoming EMS request to properly triage the
response and dispatch the appropriate level of care.
B. The EMS Agency may operate an ALS level-equipped Ambulance with BLS level personnel
provided an ALS credentialed responder intercepts the Ambulance.
C. If an ALS responder intercepts a BLS Ambulance, the EMS Agency shall ensure equipment and
personnel needed to provide ALS care is transferred and onboard the Ambulance prior to commencing
Patient transport.

25 | Regulation 61-7
508. Volunteer EMS Agencies.
A. A Volunteer EMS Agency shall have an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic attending to the
Patient at the scene and in the Ambulance while transporting the Patient to the hospital.
B. Volunteer Emergency Medical Responder Agencies without onsite EMT-basics, AEMTs, or
Paramedics shall be en route with at least one (1) EMT to all emergent calls within ten (10) minutes
from the time the call is dispatched.
C. If the Volunteer EMS Agency service has a written response policy in place in which an EMT
is allowed to respond directly to the scene from home or work, the EMS Agency may respond to the
scene of the Emergency even if an EMT is not on board the Ambulance. The EMS Agency shall make
the response policy available for inspection by the Department upon request.
D. If the Volunteer EMS Agency’s EMT responding directly to the scene is delayed and another
EMS Agency is immediately available with the required EMS Personnel, the Patient shall be
transported by that Agency. If no other service is immediately available, the volunteer EMS Agency
shall not transport a Patient without at least one (1) EMT on board.
E. If only one (1) EMT is available to staff the Ambulance crew, the Volunteer EMS Agency shall
ensure that the EMT is the Patient care provider and/or supervises the Patient care being provided.
The volunteer EMS Agency shall ensure a sole EMT is not the Driver of the Ambulance when a
Patient is being transported.
F. The Volunteer EMS Agency shall preplan for the lack of staffing by written mutual aid
agreements with neighboring agencies and by alerting the local Public Safety Answering Point
(PSAP) as early as possible when it is known that EMT level staffing is not available. The Volunteer
EMS Agency shall ensure sufficient staffing through preplanning, mutual aid agreements, and
continual recruitment programs.
G. The Volunteer EMS Agency shall ensure in all cases where the level of care is either EMT-basic,
AEMT, or Paramedic, the transporting unit is fully equipped to perform at that level of care.
SECTION 600 – REPORTING
601. Adverse Incident Reporting.
A. The requirements of Section 601 will take effect (1) year following the date of publication of
this regulation in the State Register.
B. The EMS Agency shall maintain a record of each Adverse Incident. The EMS Agency shall
retain all documented Adverse Incidents reported pursuant to this section two (2) years after the
Patient contact or transport.
C. The EMS Agency shall report Adverse Incidents to the Department via the Department’s
electronic reporting system or other format as determined by the Department as soon as possible, but
not to exceed seventy-two (72) hours from becoming aware of the Adverse Incident. Failure to report
the following Adverse Incidents may result in a Class II violation: (II)
1. Confirmed or suspected Abuse, Neglect, or Exploitation against a Patient by EMS Personnel;
2. Crimes committed against Patients by any EMS Personnel;

26 | Regulation 61-7
3. Unexpected or unexplained death of a Patient while under the care of the EMS Agency;
4. Any suspected overdose reversal administered to on duty EMS Personnel;
5. Elopement of Patient;
6. Any injury caused by EMS Personnel, including injuries involving the use of physical and/or
chemical restraints;
7. Medication error with adverse effects or that would cause potential harm to the Patient;
8. Suicide and/or attempted suicide while under the EMS Agency’s care;
9. Any Patient that is dropped or falls while under the care of an EMS Agency, including where
no injury occurs, to include stretcher drops due to malfunction or operator error; and
10. Any suspected or confirmed use of illicit or un-prescribed medications or alcohol by a crew
member while on duty, to include providing Patient care and/or the operation of an EMS Agency
vehicle.
D. The EMS Agency shall submit a separate written investigation report within five (5) calendar
days of every Incident required to be immediately reported to the Department pursuant to Section
601.C via the Department’s electronic reporting system or in a format as determined by the
Department. The EMS Agency’s report of investigation to the Department shall include the following
information: (II)
1. EMS Agency name, License number, type of Adverse Incident, the date the accident and/or
Adverse Incident occurred;
2. Number of Patients, staff, or by-standers directly injured or affected;
3. ePCR number, if applicable;
4. Patient name, age, and gender;
5. Witness(es) name(s); and
6. Identified cause of the Adverse Incident, internal investigation results if cause unknown, a
brief description of the Adverse Incident including location where occurred, treatment of injuries, and
cause of errors or omission in Patient care rendered, if applicable.
602. Collisions.
The EMS Agency shall notify the Department within seventy-two (72) hours of any collision
involving any EMS Agency’s vehicle or aircraft used to provide emergency medical services that
results in any degree of injury to personnel, pedestrians, Patients, passengers, observers, students, or
other persons. The EMS Agency shall submit the Ambulance Permit, if applicable, to the Department
if the damage renders the Ambulance out of service for more than two (2) weeks. The EMS Agency
shall submit the investigating law enforcement agency’s accident report regarding the collision to the
Department upon the EMS Agency’s receipt.

27 | Regulation 61-7
603. Administration Changes.
A. The EMS Agency shall notify the Department in writing within seventy-two (72) hours of any
expansion or contraction of the service, level of care, upgrade or downgrade, or if the physical
locations are changed.
B. The EMS Agency shall notify the Department in writing or a means as otherwise determined by
the Department within seventy-two (72) hours of any change in status of the EMS Director or EMS
Training Officer. The EMS Agency shall provide the Department in writing within ten (10) calendar
days the name of the person(s) appointed or hired into those positions and the effective date of the
appointment or hire.
C. The EMS Agency shall within twenty-four (24) hours notify the Department of any change in
status to the Medical Control Physician. The EMS Agency shall notify the Department in writing or
other means as determined by the Department the name of the newly appointed Medical Control
Physician, the effective date, the authorized medication list, Protocols, and standing orders within ten
(10) calendar days after the change.
604. Accounting of Controlled Substances. (I)
Any EMS Agency registered with the Department’s Bureau of Drug Control and the United States
Drug Enforcement Administration shall report any theft or loss of Controlled Substances to local law
enforcement and to the Department’s Bureau of Drug Control within seventy-two (72) hours of the
discovery of the loss and/or theft. Any Agency permitted by the South Carolina Board of Pharmacy
shall report the loss or theft of drugs or devices in accordance with S.C. Code Section 40-43-91.
605. Agency Closure.
A. Prior to the permanent closure of an EMS Agency, the Licensee shall notify the Department in
writing of the intent to close and the effective closure date. Within ten (10) calendar days of the
closure, the EMS Agency shall notify the Department of the provisions for the maintenance of all
records including the custodian of the Patient care reports. On the date of closure, the EMS Agency
shall return its License and all Ambulance Permits to the Department.
B. In instances where an EMS Agency temporarily closes, the Licensee shall notify the Department
in writing within fifteen (15) calendar days prior to temporary closure. In the event of temporary
closure due to an emergency, the EMS Agency shall notify the Department within twenty-four (24)
hours of the closure via telephone or email. At a minimum, this notification shall include, but not be
limited to, the reason for the temporary closure, the manner in which the records and Patient care
reports are being stored, and the anticipated date for reopening.
C. If the EMS Agency is closed for a period longer than six (6) months and there is a desire to
reopen, the EMS Agency shall reapply to the Department for licensure and shall be subject to all
licensing requirements at the time of that application.
SECTION 700 – PATIENT CARE
701. General.
A. The EMS Agency shall create and submit an ePCR for each Patient contact regardless of Patient
transport decision.

28 | Regulation 61-7
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure the primary Attendant documents all ePCRs within twenty-four
(24) hours of the completion of the call.
C. The EMS Agency shall submit all completed ePCRs into the Department’s EMS data system
within seventy-two (72) hours of the completion of the call.
D. The EMS Agency shall make available each ePCR to the receiving facility within sixty (60)
minutes of the completion of the call. The EMS Agency may substitute a paper information sheet,
provided the ePCR is made available to the receiving facility no later than twenty-four (24) hours
from completion of the call. The EMS Agency may use a custom Preliminary Patient Transfer Form
as long as the following minimum components are documented:
1. Incident type, date, location, and tracking number;
2. EMS Agency name;
3. Ambulance identifier;
4. EMS personnel name(s) and certification number(s);
5. Time of Dispatch, at-patient time, scene departure time, and destination arrival time;
6. Patient information to include Patient name, address, and date of birth;
7. Assessment and/or Treatment information to include the chief complaint; vital signs, including
Rapid Artery oCclusion Evaluation (RACE), Glascow Coma Score (GCS), and Revised Trauma
Score (RTS) if applicable; signs, symptoms, procedures, and interventions with pertinent times;
medications with times; and a brief narrative; and
8. Transfer of care information to include the receiving nurse, physician, or EMS Personnel with
signature.
702. Data Manager.
The EMS Agency shall appoint a Data Manager to ensure accuracy, HIPAA compliance, security,
and timely submission of ePCRs and to ensure the ePCRs reflect all the Attendants, including Drivers.
The EMS Agency shall notify the Department of any change in the Data Manager within ten (10)
calendar days.
703. Content.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure each ePCR reflects services, treatment, and care provided directly
to the Patient including information required to properly identify the Patient, a narrative description
of the call from time of first Patient contact to final destination, all EMS Personnel and non-EMS
responders on the call, and other information as determined by the Department.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure all ePCRs are coherently written, authenticated by the author,
and time stamped.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure EMS Personnel complete ePCRs involving refusals that include
the following: details of any assessment performed; information regarding the Patient’s capacity to
refuse; information regarding an informed refusal by the Patient; information regarding EMS

29 | Regulation 61-7
Personnel’s efforts to convince the Patient to accept care; and any efforts by the EMS Personnel to
protect the Patient after the refusal if the Patient becomes incapacitated.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure all data submissions from the ePCR software maintain a
minimum quality score as determined by the Department. The EMS Agency shall have ninety (90)
calendar days from the Department’s notification to successfully correct data quality.
704. Report Maintenance.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure data submissions from ePCR software into the Department’s
EMS data system meet the Department’s requirements.
B. The EMS Agency shall provide accommodations and equipment for the protection, security, and
storage of Patient care reports.
C. The EMS Agency shall maintain a copy of the original data, all attachments, and appended
versions of each ePCR for no less than ten (10) years for all adult Patients and thirteen (13) years for
minor Patients. The EMS Agency shall ensure attachments to ePCRs include EKGs, waveform
capnography records, code summaries, short reports, and other forms of recorded media.
D. In the event of a change of ownership, the EMS Agency shall ensure Patient care reports are
transferred to the new Licensee.
E. The EMS Agency shall ensure the ePCRs are made available only to individuals authorized by
the Licensee and/or state and federal laws.
705. Do Not Resuscitate (DNR) Order. (II)
A. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics shall not use any Resuscitative Treatment when called to
render emergency medical services if the Patient has a DNR Order and the document is presented to
the EMT, AEMT, or Paramedic upon their arrival or if the Patient is wearing a Bracelet.
B. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics shall provide the degree of Palliative Care called for
under the circumstances that exist at the time treatment is rendered.
C. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics shall give full resuscitative measures as are medically
indicated in all cases in the absence of a DNR Order or a Bracelet.
D. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics shall follow the request of the Patient and shall not
provide resuscitative measures when the Patient has a DNR Order or is wearing a Bracelet, except
where the:
1. DNR Order is revoked pursuant to S.C. Code Section 44-78-60; or
2. Bracelet, when applicable, appears to have been tampered with or removed.
E. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics who cannot honor the DNR Order or Bracelet shall
immediately transfer care of the Patient pursuant to S.C. Code Section 44-78-45.

30 | Regulation 61-7
706. Physician Orders for Scope of Treatment (POST). (II)
A. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics shall deem a POST form executed in South Carolina as
provided in the POST Act or a similar form executed in another jurisdiction in compliance with the
laws of that jurisdiction. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics shall accept a completed, executed,
and signed POST form deemed as valid expression of a Patient’s wishes as to health care.
B. EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics may accept a properly executed POST form as a valid
expression of whether the Patient consents to the provision of health care in accordance with Section
44-66-60 of the Adult Health Care Consent Act.
C. An EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic who is unwilling to comply with an executed POST form
based on policy, religious beliefs, or moral convictions shall contact the Patient’s health care
representative, health care agent, or the person authorized to make health care decisions for the Patient
pursuant to Section 44-66-30 of the Adult Health Care Consent Act, and the EMT-basic, AEMT, or
Paramedic shall allow the transfer of the Patient pursuant to S.C. Code Section 44-80-40.
SECTION 800 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 900 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1000 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1100 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1200 – MEDICATIONS
1201. General. (I)
The EMS Agency shall manage medications, including controlled substances, medical supplies,
and those items necessary for the rendering of first aid, in accordance with federal, state, and local
laws and regulations. The EMS Agency shall ensure such medication management includes securing,
storing, administering, and disposal of discontinued or expired drugs, including controlled substances.
1202. Medication Orders. (I)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure medications are administered to Patients only upon orders of a
physician. All verbal and written orders for controlled substances shall be signed and dated by a
physician no later than fourteen (14) days after the order is given. A physician’s signature shall be
present on all controlled substance administrations or if an electronic record is utilized the controlled
medication section must have a separate and distinct approval utilizing electronic digital signatures,
separate from the ePCR content.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure all orders for controlled substances are documented, signed, and
dated by the approving physician. EMS Agencies employing electronic signatures or computer-
generated signature codes shall ensure orders for controlled substances are authenticated by the
prescribing Physician. The EMS Agency shall ensure each ePCR includes either the emergency room
physician or local Medical Control Physician approval using electronic digital signatures. The EMS
Agency shall not utilize a phrase such as “Per Protocol” in lieu of the approving physician’s signature.

31 | Regulation 61-7
1203. Administering Medication and/or Treatments. (I)
The EMS Agency shall ensure doses of medication, including controlled substances, are
administered by the same EMS Personnel who prepared them for administration. The EMS Agency
shall maintain records of receipt, administration, and disposition of all medications, including
controlled substances, to enable an accurate reconciliation including:
A. The first and last name of the EMS personnel who administered the medication using either of
the following methods:
1. An electronic signature in a computerized recordkeeping system; or
2. A legible manual signature of a hard copy record.
B. The name of the EMS Agency;
C. The Patient name and run number;
D. The name and strength of the medication administered;
E. The date of administration;
F. The time of administration;
G. The amount of the dose administered in milliliters (ml);
H. The amount of waste; and
I. The name of physician ordering the medication.
1204. Medication Storage.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure all medications are stored at the temperature range established
by the manufacturer.
B. The EMS Agency shall store all medications in accordance with applicable state and federal
laws. The EMS Agency shall maintain an inventory of the stock and distribution of all controlled
substances in a manner that the disposition of any particular item is readily traced and pursuant to
Regulation 61-4, Controlled Substances.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure controlled substances listed in Schedules II, III, IV, and V shall
be stored in a double locked system and kept in a manner consistent with Regulation 61-4 and federal
Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) regulations. The EMS Agency shall ensure medications are
monitored and attended to prevent access by unauthorized individuals. The EMS Agency shall ensure
expired or discontinued medications are not to be stored with current medications.
1205. Disposition of Controlled Substances.
A. The EMS Agency shall dispose and destroy Controlled Substance in accordance with
requirements of the federal Drug Enforcement Administration.

32 | Regulation 61-7
B. The EMS Agency shall upon closure notify the federal Drug Enforcement Administration and
the Department’s Bureau of Drug Control and surrender controlled substances registrations.
SECTION 1300 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1400 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1500 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1600 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 1700 – SANITATION AND INFECTION CONTROL
1701. General.
A. The EMS Agency shall maintain and implement personnel practices that promote conditions
that prevent the spread of infectious, contagious, or communicable diseases, including but not limited
to standard precautions, transmission-based precautions, contact precautions, airborne precautions,
and isolation techniques. The EMS Agency shall ensure proper disposal of toxic and hazardous
substances. The EMS Agency shall ensure the preventive measures and practices are in compliance
with applicable guidelines of the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard of the Occupational Safety and
Health Act of 1970; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; R.61-105, Infectious Waste
Management; and other applicable federal, state, and local laws and regulations.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure the practice of hand hygiene to prevent the hand transfer of
pathogens, and the use of barrier precautions such as gloves in accordance with established guidelines.
1702. Exterior Ambulance Surfaces.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure the exterior of the vehicle has a reasonably clean appearance.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure exterior lighting is kept clear of foreign matter (insects, road
grime, or other) to ensure adequate visibility.
1703. Interior Ambulance Surfaces Patient Compartment.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure interior surfaces of each Ambulance are of a nonporous material
to allow ease of cleaning and that carpet-type materials are not used on any surface of the patient
compartment.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. The floors of each Ambulance are free from sand, dirt, and other residue that may have been
tracked into the compartment;
2. The wall, cabinet, and bench surfaces of each Ambulance are kept free of dust, sand, grease,
or any other accumulated surface matter;
3. The interiors of cabinets and compartments of each Ambulance are kept free from dust,
moisture, or other accumulated foreign matter;

33 | Regulation 61-7
4. Bloodstains, vomitus, feces, urine, and other similar matter are cleaned from each Ambulance
and all equipment after each call, using an agent or sodium hypochlorite solution described in Section
1703.C;
5. Window glass and cabinet doors of each Ambulance are clean and free from foreign matter;
6. Each Ambulance is equipped with a receptacle provided for the deposit of trash, litter, and all
used items; and
7. A container specifically designed for the safe deposit and secure retainment of contaminated
needles or syringes and a second container for contaminated or infectious waste is provided on each
Ambulance that is easily accessible from the Patient compartment.
C. The EMS Agency shall utilize an Environmental Protection Agency-recommended germicidal
and viricidal agent or a hypochlorite solution of ninety-nine (99) parts water and one (1) part bleach
to clean Patient contact areas. The agency shall utilize alcohol or sodium hypochlorite solution for
surfaces where such an EPA solution is recommended; however, alcohol should not be used for
disinfection of large surfaces. The EMS Agency shall ensure the contact time for the hypochlorite
solution is in accordance with the respective EPA registration for the select pathogen.
D. EMS Agencies shall clean all vehicles after each call.
1704. Linen.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure that each Ambulance stores and maintains dry, clean linen.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance is equipped with at least six (6) sets of freshly
laundered or disposable linens to be used on cots and pillows and changed after each Patient is
transported.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure soiled linen is transported on the Ambulance in a closed plastic
bag or container and removed from the Ambulance as soon as possible.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance maintains blankets and towels that are intact, in
good repair, and cleaned or laundered after each Patient use. The EMS Agency shall ensure that the
blankets are a hypoallergenic material designed for easy maintenance.
1705. Oxygen Administration Apparatus. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure oxygen administration devices such as masks, cannulas, and
delivery tubing are disposable and only used once.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure all masks, cannulas, and delivery tubing are individually wrapped
and unopened until used on a Patient.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure oxygen humidifiers are only filled with distilled or sterile water
upon use and cleaned after each use. The EMS Agency may utilize disposable single-use oxygen
humidifiers in lieu of multi-use types.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance that carries portable oxygen tanks maintains a
non-sparking oxygen wrench for use with the oxygen tanks.

34 | Regulation 61-7
1706. Resuscitation Equipment. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure bag mask assemblies and masks are free from dust, moisture, and
other foreign matter and stored in the original container, jump kit, or a closed compartment on the
Ambulance. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance maintains additional equipment needed
to facilitate the use of a bag valve mask, such as a syringe, stored with the bag mask assembly. The
EMS Agency shall ensure all masks, valves, reservoirs, and other items or attachments for bag mask
assemblies are clean and manufacturer’s recommendations on single-use equipment are followed
where indicated.
B. The EMS Agency shall utilize an EPA-recommended germicidal and viricidal agent or a sodium
hypochlorite solution of ninety-nine (99) parts water and one (1) part bleach to clean resuscitation
equipment not specifically addressed as single-use. The EMS Agency shall utilize alcohol or sodium
hypochlorite solution to clean resuscitation equipment surfaces where such an EPA solution is
recommended.
1707. Suction Unit. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure suction hoses are clean and free from foreign matter and
manufacturers’ recommendations on single-use equipment are followed where indicated.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure the suction reservoir of each suction unit is clean and dry.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure suction units are clean and free from dust, dirt, or other foreign
matter.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure tonsil tips and suction catheters are of the single-use disposable
type and stored in sealed sterile packaging until used.
E. The EMS Agency shall ensure suction units with attachments are cleaned and sanitized after
each use.
1708. Splints. (II)
The EMS Agency shall ensure:
A. Padded splints are neatly covered with a non-permeable material and clean, and when the outside
cover of the splint becomes soiled, they are thoroughly cleaned or replaced;
B. Commercial splints are free of dust, dirt, or other foreign matter;
C. Traction splints with commercial supports are clean and free from accumulated material;
D. All splinting materials are stored in such a manner as to promote and maintain cleanliness;
E. Splints are in functional working order with the recommended manufacturer’s attachments; and
F. Manufacturer’s recommendations on single-use splint equipment are followed where indicated.

35 | Regulation 61-7
1709. Spinal Motion Restriction Device. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure all pillows, mattresses, and spinal motion restriction devices
(SMRDs) that are not single-use items are covered with a non-permeable material and in good repair.
The EMS Agency shall remove any compromised stretcher or spine board from service.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure
1. All stretchers, cots, pillows, SMRDs, and spine boards are clean and free from foreign
material;
2. Canvas or neoprene covers on portable-type stretchers are in good repair;
3. All restraint straps and/or devices are kept clean and washed immediately if soiled;
4. Spinal motion restriction devices are manufactured from an appropriate material to facilitate
cleaning; and
5. All spinal motion restriction devices are free from rough edges or areas that may cause injury.
1710. Bandages and Dressings. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure all bandages are clean and individually wrapped or stored in a
closed container or cabinet. The EMS Agency shall ensure triangular bandages are single-use
disposable type.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure dressings are sterile, individually packaged and sealed, stored in
a closed container or compartment, and if the seal is broken or wrap is torn, the dressing is discarded.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure burn sheets are sterile and single-use only.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure all bandages or dressings that have been exposed to moisture or
soiled are replaced.
1711. Obstetrical (OB) Kits. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure all OB kits are sterile and wrapped with cellophane or plastic,
and if the wrapper is torn or the kit is opened but not used, the items in the kit that are not individually
wrapped are discarded and replaced.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure all OB kits are single-use only.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure all items in each OB kit past the expiration date are replaced
individually if other items are individually sealed and sterile.
1712. Oropharyngeal Appliances. (II)
The EMS Agency shall ensure single-use instruments inserted into a Patient’s mouth or nose are
individually wrapped and stored properly. The EMS Agency shall ensure all instruments inserted into
a Patient’s mouth that are not intended for single-use only are cleaned and decontaminated following
manufacturer’s guidelines.

36 | Regulation 61-7
1713. Communicable Diseases. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure that when an Ambulance has been contaminated with blood, body
fluids, or other potentially infectious material (OPIM), to include potential contamination from
respiratory droplets if transporting a Patient with signs or symptoms consistent with a respiratory
illness of an infectious cause, the vehicle is taken out of service until decontamination is completed.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure all linen used during any transport is removed from the cot and
properly disposed of, or immediately placed in a designated, leak-proof bag or container and sealed
until cleaned. The EMS agency shall ensure all used linen is treated as contaminated and handled as
per standard precautions.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure all Patient contact areas, equipment, and any surface soiled during
the call is cleaned and disinfected pursuant to Section 1703.C.
1714. Equipment.
The EMS Agency shall ensure all reusable equipment used for direct Patient care is in good repair
and cleaned as it becomes soiled, and kept free from foreign matter.
1715. Equipment and Materials Storage Areas.
The EMS Agency shall ensure all equipment not used in direct Patient care is in storage spaces or
compartments to prevent contamination or damage to direct Patient care equipment or materials.
1716. Personnel.
The EMS Agency shall ensure uniforms and clothing are clean or changed if they become soiled,
contaminated, or exposed to vomitus, blood, or other potentially infectious material (OPIM).
SECTION 1800 – AMBULANCE PERMITS. (I)
1801. General.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure that each Ambulance for which the Permit is issued meets all
requirements as to design, medical equipment, supplies, and sanitation as set forth in this regulation.
The EMS Agency shall have each Ambulance inspected by the Department prior to issuance of the
initial permit.
B. The EMS Agency shall display the Permit decal for each specific Ambulance on the rear door
or rear window of the Ambulance or aircraft portfolio, as applicable.
C. The EMS Agency shall not make an entry on, deface, alter, remove, or obliterate an Ambulance
Permit.
D. The EMS Agency shall return an Ambulance Permit to the Department within ten (10) business
days when the vehicle chassis is sold, removed from service, or when the window is replaced due to
damage.

37 | Regulation 61-7
1802. Temporary Ambulance Permit.
A. The EMS Agency may request in writing, and the Department grant at its discretion, a temporary
Permit in cases where a temporary asset or short-term solution to an Ambulance is needed. The EMS
Agency shall ensure these temporary assets meet all Ambulance permitting and equipment
requirements for the level of service of its intended use.
B. The EMS Agency shall be issued a temporary Ambulance Permit for a period not to exceed
ninety (90) calendar days and may only be extended in extenuating circumstances at the Department’s
discretion.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance with a temporary Permit, twith the exception of
Air Ambulances, has the following minimum exterior markings:
1. Illumination devices pursuant to Sections 1901.G;
2. Emblems and markings pursuant to Section 1901.B affixed on vehicles with temporary
markings; and
3. The name on the face of the EMS Agency’s License affixed with temporary lettering not less
than three (3) inches in height.
SECTION 1900 – AMBULANCES. (II)
1901. Ambulance Design.
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure all Ambulances meet the design requirements established by the
Department for Ambulances permitted and utilized in South Carolina and are effective with the
publication of this regulation. The EMS Agency shall ensure all equipment, lighting, interior and
exterior doors, and environmental equipment operates as designediered* at all times when the
Ambulance is in service.
*Presented as printed in State Register Volume 46, Issue 5, Document No. 5055. The correct word is “designated.”
B. Base Unit. The EMS Agency shall ensure the chassis of each Ambulance is at least three-quarter
ton. In the case of modular or other type body units, the EMS Agency shall ensure the Ambulance
chassis is proportionate to the body unit, weight, and size; power train is compatible and matched to
meet the performance criteria listed in the Federal KKK-A-1822 F Specification, NFPA 1917 or
Commission on Accreditation of Ambulance Services Ground Vehicle Standard for Ambulances
version 2.0. After updates are released to the Federal KKK-A- 1822 F Specification, NFPA 1917 or
Commission on Accreditation of Ambulance Services Ground Vehicle Standard for Ambulances
version 2.0, the EMS Agency shall make applicable safety-related upgrades to each Ambulance on
timetables as determined by the Department.
C. Emblems and Markings. The EMS Agency shall ensure all items in this section are of reflective
quality and in contrasting color to the background on which it is applied. The EMS Agency shall
ensure:
1. There is a continuous stripe, of not less than three (3) inches on cab and six (6) inches on
Patient compartment, to encircle the entire Ambulance with the exclusion of the hood panel. The EMS
Agency shall ensure reflective chevrons, Battenberg patterns, or other markings are at least six (6)
inches in height and meet the requirements of this section; and

38 | Regulation 61-7
2. Emblems and markings are of the type, size and location as follows:
a. Side: Each side of the Patient compartment has the “Star of Life,” not less than twelve (12)
inches in height, the word “AMBULANCE”, not less than six (6) inches in height, under or beside
each star, and the name of the EMS Agency as stated on the EMS Agency’s License, of lettering not
less than three (3) inches in height; and
b. Rear: The word “AMBULANCE”, not less than six (6) inches in height, two (2) “Star of
Life” emblems of not less than twelve (12) inches in height, and the name of the EMS Agency as
stated on the EMS Agency’s License, of lettering not less than three (3) inches in height.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure that prior to private sale of Ambulances to the public, all emblems
and markings in Section 1901.C are removed.
E. Interior Patient Compartment Dimensions. The EMS Agency shall ensure the interior Patient
compartment has the following dimensions:
1. Length: A minimum of twenty-five (25) inches clear space at the head, ten (10) inches at the
foot of a seventy-six (76) inch cot, and a minimum inside length of one hundred twenty-two (122)
inches;
2. Width: A minimum inside width of sixty-nine (69) inches;
3. Height: A minimum dimension of sixty (60) inches from floor to ceiling; and
4. A minimum of twelve (12) inches of clear aisle walkway between the edge of the primary
Patient cot and base of the nearest vertical feature measured along the floor.
F. Access to Ambulance.
1. Driver Compartment.
a. The EMS Agency shall ensure the Driver’s seat has an adjustment to accommodate the fifth
(5
th
) percentile to ninety fifth (95
th
) percentile adult male.
b. The EMS Agency shall ensure there is a functional door on each side of the Ambulance in
the Driver’s compartment.
c. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance provides separation between the Driver
compartment and the Patient compartment to provide privacy for radio communication and to protect
the Driver from an unruly Patient. The EMS Agency shall ensure provision for both verbal and visual
communication between Driver and Attendant by a sliding shatter resistant material partition or door.
The EMS Agency shall ensure the bulkhead of each Ambulance is strong enough to support an
Attendant’s seat in the Patient area at the top of the Patient’s head and to withstand deceleration forces
of the Attendant in case of accident.
2. Patient Compartment.
a. The EMS Agency shall ensure there is a functional door on the right side of the Patient
compartment near the Patient’s head area of the compartment. The EMS Agency shall ensure the side

39 | Regulation 61-7
door allows EMT-basics, AEMTs, and Paramedics to position themselves at the Patient’s head and
quickly remove the Patient from the side of the vehicle if the rear door is jammed.
b. The EMS Agency shall ensure the rear doors of the Patient compartment swing clear of the
opening to allow full access to the Patient’s compartment.
c. The EMS Agency shall ensure the Patient compartment doors incorporate a holding device
to prevent the door closing unintentionally from wind or vibration. The EMS Agency shall ensure that
when Patient compartment doors are open, the holding device shall not protrude into the access area.
d. The EMS Agency shall ensure that Ambulances carrying spare tires position the spare tire
to be removed without disturbing the Patient.
G. Interior Lighting.
1. Driver Compartment: The EMS Agency shall ensure lighting is available for both the Driver
and an Attendant, if riding in the Driver compartment, to read maps, records, etc. The EMS Agency
shall ensure there is shielding of the Driver’s area from the lights in the Patient compartment.
2. Patient Compartment: The EMS Agency shall ensure illumination provides an intensity of
forty (40)-foot candles at the level of the Patient. The EMS Agency shall ensure lights are controllable
from the entrance door, the head of the Patient, and the Driver’s compartment. The EMS Agency may
utilize a rheostat control of the compartment lighting or by a second system of low intensity lights to
reduced lighting levels.
H. Illumination Devices.
1. Flood and load lights. The EMS Agency shall ensure there is least one (1) flood light mounted
not less than seventy-five (75) inches above the ground and unobstructed by open doors located on
each side of the vehicle. The EMS Agency shall ensure a minimum of one (1) flood light, with a
minimum of fifteen (15) foot candles, is mounted above the rear doors of the vehicle.
2. Warning Lights. The EMS Agency shall ensure the Ambulance emergency warning light
system contains a minimum of twelve (12) fixed red lights, one (1) fixed clear light, and one (1) fixed
amber light. The EMS Agency shall ensure the upper body warning lights are mounted at the extreme
upper corner areas of the Ambulance body, below the horizontal roofline. The EMS Agency shall
ensure the single clear light is centered between the two (2) front-facing, red, upper corner lights. The
EMS Agency shall ensure doors or other ancillary equipment do not obstruct the standard warning
lights. The EMS Agency shall ensure the amber light is symmetrically located between the two (2)
rear-facing red lights. The EMS Agency shall ensure there are two (2) red grille lights. The EMS
Agency shall ensure the lateral facing intersection lights are mounted as close as possible to the front
upper edge of each front fender and may be angled forward a maximum of thirty degrees (30°).
I. Seats:
1. Driver Compartment. The EMS Agency shall ensure a seat for both Driver and Attendant is
provided in the Driver’s compartment and that each seat shall have armrests on each side of the
Driver’s compartment.
2. Patient Compartment. The EMS Agency shall ensure two (2) fixed seats that are padded,
eighteen (18) inches wide by eighteen (18) inches high to head of Patient behind the Driver; the other
seat may be a square-bench type located on the curb (right) side of the vehicle.

40 | Regulation 61-7
J. Safety Factors for Patient Compartment.
1. Cot Fasteners. The EMS Agency shall ensure crash-stable fasteners are provided to secure
cot(s).
2. Cot Restraint. If the cot is floor-supported on its own support wheels, the EMS Agency shall
provide a means to secure it in position under all conditions. The EMS Agency shall ensure all untitled
Ambulances purchased for use in South Carolina after July 1, 2017, meet all seating and cot restraint
mandates outlined in the Federal KKK-A-1822F, all change notices included.
3. Patient Restraint. The EMS Agency shall ensure a restraining device is provided to prevent
longitudinal or transverse dislodgement of the Patient during transit or to restrain an unruly Patient to
prevent further injury or aggravation to the existing injury.
4. Safety Belts for Drivers and Attendants. The EMS Agency shall ensure quick-release,
retractable, and self-adjustable safety belts are provided for the Driver, the Attendants, and all seated
Patients.
5. Mirrors.
a. The EMS Agency shall ensure there are two (2) exterior rear view mirrors, one (1) mounted
on the left side of the vehicle and one (1) mounted on the right side. The EMS Agency shall ensure
the location of mounting provides maximum rear vision from the Driver’s seated position.
b. The EMS Agency shall ensure there is an interior rear view mirror or rear view camera to
provide the Driver with a view of occurrences in the Patient compartment.
6. Windshield Wipers and Washers. The EMS Agency shall ensure each vehicle is equipped with
two (2) electrical windshield wipers and washers in addition to defrosting and defogging systems.
7. Sun Visors. The EMS Agency shall ensure there is a sun visor for both Driver and Attendant.
8. Exterior Visual Lighting. The EMS Agency shall ensure there are operational headlights (high
and low beam), taillights, brake lights, and turn signals that can be operated by the Driver of the
vehicle.
K. Environmental Equipment: Driver/Patient Compartment.
1. Heating. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Ambulance has the capability to heat the Patient
and Driver compartments to a temperature of seventy-five degrees Fahrenheit (75°F) within a
reasonable period while driving in an ambient temperature of zero degrees Fahrenheit (0°F). The EMS
Agency shall ensure the heating system is designed to recirculate inside air and is capable of
introducing twenty percent (20%) of outside air with minimum effect on inside temperature. Fresh air
intake shall be located in the most practical contaminant-free air space on the vehicle.
2. Heating Control. The EMS Agency shall ensure heating is thermostatically or manually
controlled and the heater blower motors are at least a three (3) speed (high, medium, and low) design.
The EMS Agency shall ensure separate switches are installed in the Patient compartment.
3. Air Conditioning. The EMS Agency shall ensure the air conditioning in each Ambulance has
a sufficient capacity to lower the temperature in the Driver’s and Patient’s compartment to

41 | Regulation 61-7
seventy-five degrees Fahrenheit (75°F) within a reasonable period and maintain that temperature
while operating in an ambient temperature of ninety-five degrees Fahrenheit (95°F). The EMS
Agency shall ensure each air conditioning unit is designed to deliver twenty percent (20%) of fresh
outside air of ninety-five degrees Fahrenheit (95°F) ambient temperature while holding the inside
temperature specified. The EMS Agency shall ensure all parts, equipment, and workmanship are in
keeping with accepted air conditioning practices.
4. Air Conditioning Controls. The EMS Agency may utilize manual or thermostatic air delivery
controls to operate the unit. The EMS Agency is not required to have a reheat type system in the
Driver’s compartment unit. The EMS Agency shall ensure switches or other controls are within easy
reach of the Driver in his normal driving position. The EMS Agency shall ensure air delivery fan
motors are at least a three (3) speed design. The EMS Agency shall ensure switches and other control
components exceed in capacity the amperage and resistance requirements of the motors.
5. Environmental Control and Medications. The EMS Agency shall ensure the temperature in
the Patient compartment or anywhere medications are stored (SRVs, fire apparatus, rapid response
vehicles, carry-in bags, and other) is monitored for temperature extremes to prevent drug adulteration.
The EMS Agency shall ensure medications (excluding oxygen) and IV fluids are removed and
discarded if the temperatures reach or exceed one hundred degrees Fahrenheit (100°F), or thirty-eight
degrees Celsius (38°C). The EMS Agency shall ensure medications and IV fluids are removed and
discarded if temperatures in the drug storage area drop below twenty degrees Fahrenheit (20°F), or
negative seven degrees Celsius (-7°C).
6. Insulation. The EMS Agency shall ensure the entire body, side, ends, roof, floor, and Patient
compartment doors are insulated to minimize conduction of heat, cold, or external noise entering the
vehicle’s interior. The EMS Agency shall ensure the insulation is vermin- and mildew-resistant,
fireproof, non-hygroscopic, non-setting type. The EMS Agency may consider plywood floor when
undercoated sufficient insulation for the floor area.
L. Storage Cabinets. The EMS Agency shall ensure all cabinets meet the criteria as stated in the
most current edition of the Federal KKK-A-1822 Specification, NFPA 1917, or similar specification
standards accepted by the Department as to types of surfaces, design, and storage. The EMS Agency
shall ensure cabinets are of a size and configuration to store all necessary equipment and all equipment
in interior cabinets is accessible to Attendants at all times.
M. Two-Way Radio Mobile. The EMS Agency shall include on each vehicle two-way radio mobile
equipment that will provide a reliable system operating range of at least a twenty (20) mile radius
from the base station antenna. The EMS Agency shall ensure the mobile installation provides
microphones for transmitting to at least Medical Control and receiving agencies, at both the Driver’s
position and in the Patient compartment. The EMS Agency shall ensure selectable speaker outputs,
singly and in combination are provided at the Driver’s position, in the Patient’s compartment, and
through the public address system.
1. The EMS Agency shall provide the Department with all radio frequencies utilized by the EMS
Agency as requested by the Department.
2. In the event technological advancements render the above components obsolete, the
Department may make determinations as to the efficacy of proposed technology on an individual basis
prior to allowing its use. The EMS Agency may utilize cell phones with hand-held radios that are able
to reach Medical Control, dispatch center, and receiving facilities as backup.

42 | Regulation 61-7
N. Siren-Public Address. The EMS Agency shall ensure all siren and public address systems
provide a power output with a minimum one hundred (100) watts, and in voice operation the power
output is at least forty-five (45) watts through two (2) exterior mounted speakers. The EMS Agency
shall ensure the public address amplifier is independent of the mobile radio unit.
O. Antenna. The EMS Agency shall mount each antenna with coaxial or other cable if a radio
system is installed.
P. Glass Windows. The EMS Agency shall ensure all windows, windshield, and door glass are
shatter resistant.
Q. The EMS Agency shall establish a means to immediately identify that a vehicle is out of service
for any operator who might have reason to use the vehicle. The EMS Agency shall ensure any vehicle
that is “out of service”, whether for mechanical or staffing issues, is readily identifiable to the public
and the Department. The EMS Agency shall identify out of service vehicles by one (1) of the
following means:
1. A sign on the outside of the Driver’s door near the door handle, minimum eight and one half
inches by eleven inches (8.5” × 11”) and red in color;
2. A special bag that covers the steering wheel, red in color, and labeled “Out of Service”; or
3. A large sign on the Driver’s window, red in color, reading “Out of Service,” laminated, or a
permanent, commercially manufactured type, minimum eight and one half inches by eleven inches
(8.5” × 11”). If the unit is being driven and is out of service, the sign may be placed in the far right
hand corner of the front window so as to not obstruct the Driver’s vision but so as to be visible from
the exterior of the vehicle.
1902. Ambulance Re-mounted Design and Equipment.
After July 1, 2022, EMS Agencies choosing to utilize Ambulance Re-mounts shall ensure these
units are compliant with the Commission on Accreditation of Ambulance Services (CAAS) “Ground
Vehicle Standards for Ambulances” or other nationally recognized standards as approved by the
Department.
SECTION 2000 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 2100 – MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure the following equipment is maintained on all in-service vehicles
in accordance with the response:
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
Personal Protective Equipment
1.
Eye protection or face
shield for each medical
crew member
R
R
R
R
R
R

43 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
One (1)
2.
Labeled Non-sterile,
latex-free exam gloves
– two (2) sizes
Five (5) pairs each
R
R
R
R
R
R
3.
Mask/Face shield for
each Crew Member
One (1) each
R
R
R
R
R
R
4.
Protective clothes
covering
R
R
R
R
R
R
Automatic External Defibrillator (AED)
5.
AED: secured and
positioned for easy
access to Attendants
One (1)
R
R
R
R
N/A
N/A
6.
Paddles or pads and
cables, Adult and
Pediatric, compatible
with AED
R
R
R
R
R
R
Monitor/Defibrillator
7.
Four (4) lead wave
form, twelve (12)
lead/EKG, SpO2
waveform with numeric
reading, waveform
capnography, and
invasive pressure ports
for adult and pediatric,
and neonate, if
applicable. Printable
and transmittable and
secured and positioned
so displays are visible to
Attendants. All
components are
required, but not all on
one device.
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
8.
ECG Electrodes
Twenty (20)
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
R
R
9.
Extra roll of compatible
printer paper
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
MCO
R
R
10.
Internal rechargeable
battery pack
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
MCO
R
R
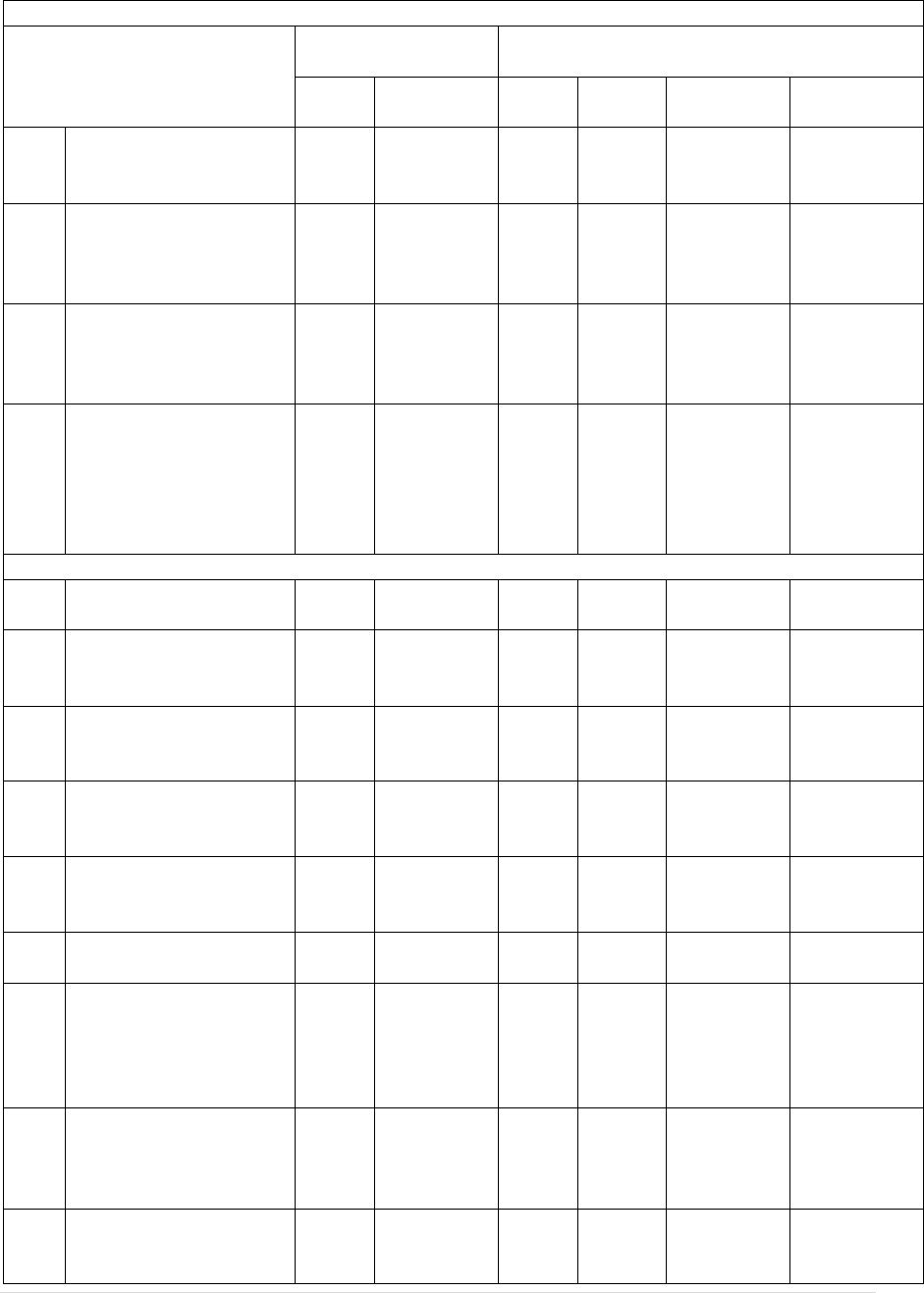
44 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
11.
Extra battery or AC
adapter and cord
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
MCO
R
R
12.
Defibrillator: May be
integrated into cardiac
monitor module.
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
MCO
R
R
13.
Pads – Pediatric and
Adult (Neonatal sizes if
transports are
conducted)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
14.
Transcutaneous Pace –
Adult and Pediatric
capabilities
(stand-alone unit or
integrated into cardiac
monitor modular)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
Oxygen Delivery
15.
Nasal Cannulas – Adult
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
16.
Nasal
Cannula- Pediatric
Two (2)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
17.
Non-Rebreather Mask –
Adult
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
18.
Non-Rebreather Mask –
Infant
Two (2)
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
R
19.
Non-Rebreather Mask –
Pediatric
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
20.
Disposable Nebulizer
Two (2)
MCO
R
MCO
R
R
R
21.
NPA 16 French through
34 French
(12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32,
36)
One (1) each
MCO
R
R
R
R
R
22.
Nonmetallic
oropharyngeal airways
(OPAs): sizes 0-5.
One (1) each
R
R
R
R
R
R
23.
Positive Pressure
Airway device
One (1)
MCO
R
MCO
R
R
R

45 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
24.
Individual use circuit
for Positive pressure
device compatible with
the device
Two (2)
MCO
R
MCO
R
R
R
25.
Portable Oxygen
Cylinder (min 1000
PSI) with working
regulator
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
26.
Spare Portable Oxygen
Cylinder
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
27.
On-Board Oxygen
Cylinder (min 2000L)
With working regulator
One (1)
N/A
N/A
R
R
R
R
Bag Valve Mask Ventilation Units (BVM)
28.
Adult BVM
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
29.
Pediatric BVM
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
30.
Neonate BVM
One (1)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
Bandage Material
31.
ABD pad at least five by
nine inches (5” x 9”)
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
32.
Adhesive bandages
Five (5)
R
R
R
R
R
R
33.
Individually wrapped
four by four inch (4” x
4”) Sterile Gauze Pads
Fifteen (15)
R
R
R
R
R
R
34.
Individually wrapped
Sterile Gauze bandage
rolls two (2) different
Sizes Required
One (1) each size
R
R
R
R
R
R
35.
Four by four inch (4” x
4”) Commercial Sterile
Occlusive Dressing or
Chest Seal
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R

46 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
36.
Hypoallergenic
Adhesive Tape – One
inch (1”)
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
37.
Hypoallergenic
Adhesive Tape – Two
Inch (2”)
One (1)
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
38.
Hypoallergenic
Adhesive Tape – Three
Inch (3”)
One (1)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
39.
Large Trauma Bandage
Shears
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
40.
Sterile Water or Normal
Saline for irrigation
Minimum of 250 ml.
R
R
R
R
R
R
41.
Arterial Tourniquet
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
42.
Hemostatic Agent or
Bandage (non-granular)
Two (2)
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
Assessment Tools
43.
Thermometer
One (1)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
44.
Sphygmomanometer,
cuff, bladder, and
tubing in sizes for each
age and size (Minimum
of 3 sizes)
One (1) each size
R
R
R
R
R
R
45.
Adult Stethoscope
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
46.
Pediatric Capable
Stethoscope
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
47.
Pulse Oximeter with
numeric reading with
Adult and Pediatric
capabilities
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
48.
Penlight
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
Miscellaneous

47 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
49.
Commercial
antimicrobial and
waterless hand cleanser
R
R
R
R
R
R
50.
EPA recommended
Germicidal/viricidal
agent or sodium
hypochlorite
solution - ninety-nine
(99) parts water and one
(1) part bleach for
cleaning equipment.
R
R
R
R
R
R
51.
Portable Suction
R
R
R
R
R
R
52.
Wall Mounted Suction
N/A
N/A
R
R
R
R
53.
Suction Tubing
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
54.
Rigid suction Tip
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
55.
Flexible Suction Tip
Four (4) sizes
MCO
R
R
R
R
R
56.
Naloxone
Administration Kit
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
57.
Epinephrine
Administration Kit
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
58.
Sharps container (fixed
with locking
mechanism)
One (1)
N/A
N/A
R
R
R
R
59.
Portable Sharps
Container
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
60.
Current color-coded
Pediatric weight and
length-based drug dose
chart
One (1)
MCO
R
MCO
R
R
R
61.
Antiseptic pads for
injection sites
Twenty-four (24)
R
R
R
R
R
R
62.
18-20g needles at least
one and one-half inch (1
½”) length
Two (2) sets
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R
63.
23g-25g needles at least
one and one-half inch (1
½”) length
Two (2) sets
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R
64.
1 ml Syringes
Two (2)
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R

48 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
65.
3-5 ml Syringes
Two (2)
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R
66.
10-20 ml Syringes
Four (4)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
67.
Sterile burn sheet
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
68.
Triangular Bandages
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
69.
Traction-type, lower
extremity splint
(Bi-polar or Uni-polar
type is acceptable)
One (1)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
MCO
70.
Padded splints: 15” x 3”
(or other approved
commercially available
splints for arm or leg
fractures)
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
MCO
71.
Padded Splints: 36” x 3”
(or other approved
commercially available
splints for arm or leg
fractures)
Two (2)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
MCO
72.
Pelvic Splint
One (1)
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
73.
Long Spine Board: at
least 16” x 72”. (A
folding backboard may
be used as a substitute.)
One (1)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
MCO
74.
Cervical collars:
Adjustable or available
in sizes of short, regular,
or tall. Adult and
Pediatric
Minimum of one (1)
each
R
R
R
R
R
MCO
75.
Commercially or
Premade Head
Immobilization Device
– Adult and Pediatric
One (1) each
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
MCO

49 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
76.
Nine (9) foot straps (one
(1) set 10-point spider
straps may be used)
Minimum of three (3)
each
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
77.
Triage Tag (Compatible
with the state system)
R
R
R
R
R
MCO
78.
Patient Restraints
one (1) set
N/A
N/A
R
R
R
R
79.
Obstetrical Kit: Sterile,
latex free. (Contains the
following: gloves,
scissors or surgical
blades, umbilical cord
clamps or tapes,
dressing, towels,
perinatal pad, bulb
syringe and a receiving
blanket)
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
80.
Glucometer or Blood
Glucose Measuring
Device
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
81.
Emesis basin or bag
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
82.
Bedpan and urinal
One (1) each
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
83.
ABC Fire Extinguisher
(minimum of 5 LBS,
properly mounted)
One (1)
R
R
R
R
R
R
84.
Battery Operated
Flashlight
(non-penlight)
Two (2)
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
MCO
85.
High Visibility vest or
reflective clothing
Two (2)
R
R
R
R
R
R
86.
Protective Work Gloves
2 Pair
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
87.
Protective Helmet
Two (2)
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
MCO
R
88.
Flameless Flare, Glow
Sticks, Cones, or
Reflective Triangles
R
R
R
R
R
MCO

50 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
Three (3)
89.
Blankets/ Linen
Three (3) each
MCO
MCO
R
R
R
R
Advanced Airway and Ventilatory Support
90.
Laryngoscope handle
with extra set of
batteries and bulbs
(Compatible with
Blades)
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
91.
Laryngoscope blades –
0-4 Miller, 1-4
Macintosh - Adult/
Pediatric/Neonate sizes
(Compatible with
handle)
One (1) each
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
92.
Video Laryngoscope
One (1)
N/A
MCO
N/A
N/A
MCO
MCO
93.
Disposable ET tube
sizes 2.5 through 8mm
with stylets sized for
each tube
One (1) each
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
94.
Bougie type device
One (1)
N/A
MCO
N/A
N/A
MCO
MCO
95.
ET Placement Detector
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
96.
Water soluble
lubricating jelly
Four (4) each
R
R
R
R
R
R
97.
Blind Insertion Airway
Device (BIAD) – Age
and weight sizes as
defined by FDA.
Syringe(s) needed to
inflate bulbs shall be
included in packaging,
if not, appropriate
size(s) carried by
provider.
R
R
R
R
R
R
98.
Mucosal Atomizer
Device
One (1)
N/A
MCO
N/A
N/A
MCO
MCO
99.
Positive End-Expiratory
Pressure (PEEP) valve
R
R
R
R
R
R

51 | Regulation 61-7
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
(may be incorporated
into BVMs) – age
appropriate
100.
Mechanical ventilator
and circuit - age/weight
appropriate, including
neonate, if applicable,
includes measurement
of: Fraction of inspired
oxygen (FiO2); Tidal
volume (Vt);
Respiratory rate (RR) or
frequency; and PEEP.
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
MCO
R
101.
Continuous Positive
Airway Pressure
(CPAP), able to be
incorporated within the
mechanical ventilator
mechanical and with
appropriate setting and
attachments for adult,
pediatric, and neonate
Patients, if applicable
N/A
N/A
N/A
MCO
MCO
R
102.
Bi-level Positive
Airway Pressure
(BiPap), able to be
incorporated within the
mechanical ventilator
mechanical and with
appropriate setting and
attachments for adult,
pediatric, and neonate
Patients, if applicable
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
MCO
MCO
103.
Chest Decompression
Kit
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
104.
Printable waveform
End-tidal CO2
continuous monitoring
capabilities. May be
incorporated within
cardiac monitor
modular
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
R
R
Venous Access
105.
Intravenous catheters
14g-20g
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R

52 | Regulation 61-7
B. The EMS Agency shall maintain the equipment used in the provision of Patient care clean, in
good repair, and operating condition, within the manufacturer expiration date, and in accordance with
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standard 1910.1030.
C. Local Medical Control Option (MCO). The EMS Agency shall ensure all local MCO medical
equipment is incorporated into its Protocols pursuant to Section 502.B.
SECTION 2200 – AIR AMBULANCE
2201. Permitting. (I)
A. No EMS Agency, Ambulance service provider, agent or broker shall secure or arrange for Air
Ambulance service originating in South Carolina unless the Air Ambulance service meets the
provisions of S. C. Code Sections 44-61-10, et seq. and these regulations. The EMS Agency providing
Air Ambulance services that transport Patients in the prehospital setting shall be permitted as
Required (R); Medical Control Option (MCO); Not Applicable (N/A)
Item, and Quantity
EMERGENCY
RESPONSE
AMBULANCE
EMT-
Basic
Paramedic
EMT-
Basic
AEMT
Paramedic
Air/Critical
Care
Two (2) each
106.
Intravenous catheters
22g-24g for
pediatric/neonate
transport
Two (2) each
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R
107.
Intraosseous needles –
15mm, 25mm, 45mm
One (1) each
N/A
MCO
N/A
R
R
R
108.
Macro drip sets, 10-20
gtts/ml
Two (2)
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R
109.
Micro drip set
One (1)
N/A
R
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
110.
IV start kits containing
latex free tourniquet,
antiseptic solution, and
latex free catheter
dressing.
Three (3)
N/A
R
N/A
R
R
R
111.
Intravenous fluids: may
be combination of
sizes100mL-1000mL
variety such as Lactated
Ringers, Normal Saline,
D5W. Capability to be
administered warm.
4000 ml total
N/A
R
(2000 ml
total)
N/A
R
R
R
112.
IV Pressure Infuser
One (1)
N/A
MCO
N/A
MCO
R
R

53 | Regulation 61-7
Advanced Life Support. The EMS Agency shall have each Air Ambulance inspected prior to issuance
of the initial Permit and inspected thereafter at a frequency as determined by the Department.
B. The EMS Agency shall submit an application to the Department, in a format as determined by
the Department, prior to being issued an initial Air Ambulance Permit and Air Ambulance Permit
renewals. The EMS Agency shall submit the following documentation with the application:
1. A copy of current FAA operational certificate including designation for Air Ambulance
operations;
2. Proof of accreditation from the Commission on Accreditation of Medical Transport Systems
(CAMTS). After updates are released to the CAMTS Air Ambulance Standards, the EMS Agency
shall make applicable safety related upgrades to each Air Ambulance on timetables as determined by
the Department; and
3. A letter of agreement verifying each aircraft meets the specifications of this regulation if the
aircraft is leased from a pool.
C. The EMS Agency shall ensure that prior to issuance of an initial or renewal Air Ambulance
Permit that the Air Ambulance for which the Permit is issued meets all requirements as set forth in
this regulation. Each Permit shall be issued for a specific Air Ambulance and is not transferrable to
another vehicle.
D. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Air Ambulance conforms to all federal and state laws and
regulations, including Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR) part 135.
E. Out-of-State Air Ambulances.
1. EMS Agencies from out of state with Air Ambulances transporting Patients from locations
originating in South Carolina shall obtain an EMS Agency License from the Department prior to
engaging in operations and shall have applicable current and valid licenses and permits in their home
state, except where exempt pursuant to S.C. Code Section 44-61-100(D).
2. EMS Agencies from out of state operating Air Ambulances in a state where no license and/or
permit is available shall obtain a EMS Agency License in South Carolina and meet all requirements
in Section 1200.
3. EMS Agencies from out of state with Air Ambulances transporting Patients from locations
originating in South Carolina shall submit ePCRs to the Department within seventy-two (72) hours
of completing the transport.
2202. Aircraft.
The EMS Agency shall ensure all operations comply with all federal aviation regulations which are
adopted by reference, FAA Part 135. The EMS Agency shall ensure each aircraft meets the following
specifications:
A. Configured in such a way that the medical Attendants have adequate access for the provision of
Patient care within the cabin to give cardiopulmonary resuscitation and maintain the Patient’s life
support. The EMS Agency shall ensure:

54 | Regulation 61-7
1. The aircraft has an entry that allows loading and unloading without excessive maneuvering
(no more than forty-five (45) degrees about the lateral axis and thirty (30) degrees about the
longitudinal axis) of the Patient; and
2. The configuration does not compromise functioning of monitoring systems, intravenous lines,
and manual or mechanical ventilation.
B. Has at least one (1) stretcher or cot that can be carried to the Patient and allow loading of a
supine Patient by two (2) Attendants. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. The maximum gross weight allowed on the stretcher or cot (inclusive of Patient and
equipment) as consistent with manufacturer’s guidelines;
2. The aircraft stretchers and cots, and the means of securing them in-flight, are consistent with
federal aviation regulations;
3. The stretcher or cot is sturdy and rigid enough that it can support cardiopulmonary
resuscitation;
4. The head of the cot is capable of being elevated at least thirty (30) degrees for Patient care and
comfort; and
5. The Patient placement allows for safe personnel egress.
C. Has appropriate communication equipment to ensure both internal crew and air to ground
exchange of information between individuals and agencies appropriate to the mission, including at
least Medical Control, air traffic control, emergency services (EMS, law enforcement agencies, and
fire), and navigational aids;
D. Is equipped with radio headsets that ensure internal crew communications and transmission to
appropriate agencies;
E. The pilot is able to control and override radio transmissions from the cockpit in the event of an
Emergency situation;
F. Lighting. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Air Ambulance has a supplemental lighting system
installed in the aircraft which includes standard lighting and is sufficient for Patient care; The EMS
Agency shall ensure:
1. The lighting system includes a self-contained lighting system powered by a battery pack or a
portable light with a battery source is available;
2. That red lighting or low intensity lighting may be used in the Patient care area if not able to
isolate the Patient care area from effects on the cockpit or on a pilot; and
3. For those flights meeting the definition of “long range,” the EMS Agency shall have additional
policies in place to address how cabin lighting will be provided during fueling and/or technical stops
to ensure proper Patient assessment can be performed and adequate Patient care provided.
G. Has hooks and/or devices for hanging intravenous fluid bags;
H. Rotor Wing Aircraft must have an external landing light and tail-rotor position light;

55 | Regulation 61-7
I. Design does not compromise Patient stability in loading, unloading, or in-flight operations;
J. Temperature. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. The interior of the Air Ambulance is climate controlled to avoid adverse effects on Patients
and personnel on board;
2. The thermometer is mounted inside the Air Ambulance cabin; and
3. The Air Ambulance cabin temperatures are measured and documented every fifteen (15)
minutes during a Patient transport until temperatures are maintained within the range of fifty degrees
Fahrenheit (50°F) to ninety-five degrees Fahrenheit (95°F), or ten degrees Celsius (10° C) to
thirty-five degrees Celsius (35° C) for aircraft.
K. Electric power outlet. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Air Ambulance aircraft is equipped
with an inverter or appropriate power source of sufficient output to meet the requirements of the
complete specialized equipment package without compromising the operation of any electrical
aircraft or Ambulance equipment. The EMS Agency shall ensure each Air Ambulance maintains extra
batteries onboard for critical Patient care equipment.
2203. Aircraft Flight Crew.
A. Rotorcraft Pilot. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. Each Rotorcraft pilot possess at least a commercial Rotorcraft-helicopter and instrument
helicopter rating of 05.04.03;
2. Prior to an assignment with a medical service, the Rotorcraft pilot in command possesses two
thousand (2,000) total flight hours, or total flight hours of at least fifteen hundred (1,500) hours, and
recent experience that exceeds the operator’s pre-hire qualifications such as current air medical and/or
search and rescue experience or Airline Transport Pilot (ATP) rated that include the following:
a. At least twelve hundred (1,200) helicopter flight hours;
b. At least one thousand (1,000) of those hours must be as Pilot-in-Charge (PIC) in Rotorcraft;
c. One hundred (100) hours unaided, if the pilot is not assigned to a Night Vision Goggles
(NVG) base or aircraft;
d. Fifty (50) hours unaided as long as the pilot has one hundred (100) hours aided, if assigned
to an NVG base or aircraft; and
e. A minimum of five hundred (500) hours of turbine time.
3. The pilot is readily available within a defined call-up time to ensure an expeditious and timely
response; and
4. ATP certificate and instrument currency is strongly encouraged.
B. Rotorcraft Mechanic. The EMS Agency shall ensure:

56 | Regulation 61-7
1. The mechanic primarily assigned to a specific Air Ambulance is factory schooled or equivalent
in an FAA approved program on the type of specific airframe, the power plant and all related systems.
The EMS Agency shall ensure the primarily assigned mechanic provides direct (on-site during
maintenance) supervision to other mechanics assisting with maintenance that may not have this level
of experience or training;
2. All mechanics receive formal training on human factors and maintenance error reduction;
3. A policy is written that grants the mechanic permission without fear of reprisal to decline
performing any maintenance critical to flight safety that he has not been appropriately trained for,
until an appropriately trained mechanic is available to directly supervise or assist;
4. There is a documented annual review of infection control, medical systems, and installations
on the aircraft, Patient loading and unloading procedures for all mechanics;
5. At least one (1) technician is available for each service with formal training on the aircraft
electrical system and formal training on the autopilot system; and
6. Training related to the interior modification of the aircraft:
a. Prepares the mechanic for inspection of the installation as well as the removal and
reinstallation of special medical equipment; and
b. Includes supplemental training on service and maintenance of medical oxygen systems and
a policy as to who maintains responsibility for refilling the medical oxygen systems;
C. Fixed Wing Pilot. The EMS Agency shall ensure the pilot-in-command (PIC) possesses the
following qualifications:
1.Possesses the following flight hours:
a. Prior to assignment with an EMS Agency and if the aircraft is to be operated using a single
PIC, with no Second in Command (SIC):
TYPE OR
CLASS OF
AIRCRAFT
TOTAL
FLIGHT
HOURS
MULTI-ENGINE
HOURS
PIC HOURS
TYPE RATE
HOURS
Single Engine
Turbo-Prop
2500
N/A
1000
50
Multi-Engine
Piston
2500
500
1000
50
Multi-Engine
Turbo Prop
2500
500
1000
100
b. If the aircraft is to be operated with two (2) fully trained and qualified pilots:
TYPE OR
CLASS OF
AIRCRAFT
PIC TOTAL
FLIGHT
HOURS
MULTI-ENGINE
HOURS
PIC HOURS
SIC TOTAL
HOURS
Single Engine
Turbo-Prop
2000
N/A
1000
500

57 | Regulation 61-7
Multi-Engine
Piston
2000
500
1000
500
Multi-Engine
Turbo Prop
2000
500
1000
800
Multi-Engine
Turbo Prop
3000
500
1500
1000
2. The PIC is Airline Transport Pilot (ATP) rated within five (5) years of hire;
3. In aircraft that requires two (2) pilots, both pilots shall be type-rated for the make and model,
and both pilots shall hold first class medical Certificates if the Certificate holder operates
internationally. Both pilots shall have training on Crew Resource Management (CRM) or Multi-pilot
Crew Coordination (MCC); and
4. When operating an Air Ambulance with two (2) pilots, the EMS Agency shall maintain
policies procedures that address avoidance of a “green on green” situation, where a lower experienced
PIC is paired with a lower experienced SIC. The EMS Agency shall ensure the two (2) pilots
combined have completed a minimum combined flight experience of two hundred fifty (250) hours
in make and model.
D. Fixed-Wing Mechanic. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. The mechanic primarily assigned to a specific Air Ambulance possess a minimum of two (2)
years of airplane experience as a certified airframe and power plant mechanic prior to assignment, or,
in the case of a repair station, the Maintenance Repair Organization (MRO) shall hold a FAA issued
Certificate under FAA 14 CFR Part 145, or the national equivalent, and hold the ratings and/or
limitations within its Operations Specifications for the make/model upon which it is performing
scheduled maintenance;
2. The primary mechanic performing scheduled maintenance to a specific Air Ambulance is
factory-schooled or equivalent in an approved program on the type-specific airframe, the power plant,
and all related systems within eighteen (18) months of employment by the operator;
3. All mechanics must receive formal training on human factors and maintenance error reduction;
4. If not working for a maintenance organization certified under FAA 14CFR Part 145 or national
equivalent, the EMS Agency implements a written policy that grants the mechanic permission,
without fear of reprisal, to decline from performing any maintenance critical to flight safety that he
or she has not been appropriately trained for, until an appropriately trained mechanic is available to
directly supervise;
5. There is an annual review of infection control, medical systems, and installations on the
aircraft, Patient loading and unloading procedures for all mechanics;
6. There will be at least one (1) technician or MRO available for each service with formal training
on the aircraft electrical system and formal training on avionics; and
7. Training related to the interior modifications of the aircraft:
a. Training must prepare the mechanic for inspection of the installation as well as the removal
and reinstallation of special medical equipment; and

58 | Regulation 61-7
b. There is supplemental training on service and maintenance of medical oxygen systems and
a policy as to who maintains responsibility for refilling the medical oxygen system.
E. The EMS Agency shall ensure that each Patient is evaluated prior to a flight for the purpose of
determining that appropriate Air Ambulance, flight and medical crew, and equipment are provided to
meet the Patient’s needs.
F. The EMS Agency shall ensure that all medical crew members are adequately trained to perform
in flight duties prior to functioning in an inflight capacity.
G. Aircraft Medical Crew. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. Each Advanced Life Support Air Ambulance is staffed with at least one (1) currently certified
Paramedic or Flight Nurse as may be required by the Patient’s condition;
2. Each crew member wears a flame retardant uniform with reflective striping; and
3. Each crew member displays, upon request, a legible photo identification with first name and
certification level (for example, pilot, RN, or other) while Patient care is anticipated to be rendered.
H. Orientation Program. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. All medical flight crew members complete a base level flight orientation program supervised
by the EMS Agency’s Medical Control Physician; and
2. The flight orientation program is documented and of a duration and substance to cover all
Patient care procedures, including altitude physiology, and flight crew requirements.
2204. Medical Supplies and Equipment. (II)
A. Delivering Oxygen. The EMS Agency shall ensure that oxygen is installed according to federal
aviation regulations (FAA Part 135.91). The EMS Agency shall ensure that medical transport
personnel determine how oxygen is functioning by use of pressure gauges mounted in the Patient care
area. The EMS Agency shall ensure:
1. Each gas outlet shall be clearly identified;
2. “No Smoking” sign shall be included;
3. Oxygen flow must be stoppable at or near the oxygen source from inside the aircraft or
Ambulance;
4. The following indicators shall be accessible to medical transport personnel while en route;
a. Quantity of oxygen remaining; and
b. Measurement of liter flow.
5. Adequate amounts of oxygen for anticipated liter flow and length of transport with an
emergency reserve must be available for every mission; and

59 | Regulation 61-7
6. When the Air Ambulance is in motion, all oxygen cylinders shall be affixed to a wall or floor
with crash stable, quick release fittings.
B. Sanitation. The EMS Agency shall ensure that the floor, sides, ceiling, and equipment in the
Patient cabin of the Air Ambulance are a nonporous surface capable of being cleaned and disinfected
in accordance with Section 1700.
C. Each EMS Agency shall maintain on each Air Ambulance all medical equipment pursuant to
Section 2100.
2205. Medication and Fluids for Advanced Life Support Air Ambulances. (II)
A. The EMS Agency shall ensure medications and fluids approved by the Department for
possession and administration by Paramedics and specified by the Medical Control Physician are
carried on the Air Ambulance. The EMS Agency shall ensure that medications not included on the
approved medication list for Paramedics are only carried on board the Air Ambulance if the EMS
Agency has a written Protocol that includes delineation of administration only by a registered nurse
or physician.
B. The EMS Agency shall ensure on each Air Ambulance:
1. All Medications are easily accessible;
2. Controlled substances are in a double locked system and kept in a manner consistent with state
and federal controlled substances laws and regulations;
3. Storage of medications allows for protection from extreme temperature changes within the
U.S. Pharmacopeia guidelines, if environment deems it necessary; and
4. If there is a refrigerator on the Air Ambulance for medications, a temperature monitoring and
tracking policy is established and implemented, and the refrigerator is used and labeled “for
medication use only.”
2206. Rescue Exception. (II)
The EMS Agency may utilize an aircraft or SRV without a Permit for occasional non-routine
missions, such as the rescue and transportation of victims or Patients who may or may not be ill or
injured from structures, depressions, water, cliffs, swamps or isolated scenes when the rescuers or
EMS Agency present at the scene determines the preferred method of rescue and transportation
incident thereto due to the nature of the entrapment, condition of the victim, existence of an immediate
life threatening condition, roughness of terrain, time element and/or other pertinent factors. The EMS
Agency shall ensure:
A. After the initial rescue, an EMT-basic, AEMT, or Paramedic accompanies the victim or Patient
en route with the necessary and appropriate EMS supplies and equipment needed for the en route care
of the specific injuries or illness involved;
B. The aircraft or SRV is of adequate size and configuration to effectively make the rescue and to
accommodate the victim or Patient, Attendant(s), and equipment;
C. Reasonable space is available inside the aircraft or SRV for continued victim or Patient comfort
and care;

60 | Regulation 61-7
D. A permitted Air Ambulance or Ambulance is not available within a reasonable distance response
time; and
E. Provided the Patient is transferred to a higher level of EMS ground transportation for
stabilization and transport if such ground unit is available at a reasonably safe landing area.
SECTION 2300 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 2400 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 2500 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 2600 – [RESERVED]
SECTION 2700 – SEVERABILITY
In the event that any portion of this regulation is construed by a court of competent jurisdiction to
be invalid, or otherwise unenforceable, such determination shall in no manner affect the remaining
portions of this regulation, and they shall remain in effect as if such invalid portions were not
originally a part of this regulation.
SECTION 2800 – GENERAL
Conditions that have not been addressed in this regulation shall be managed in accordance with the
best practices as interpreted by the Department.
