
Steps to creating your Intelligent Mail
®
Barcode
The Intelligent Mail barcode is a 65-bar Postal Service
™
barcode used to sort and track letters and flats. It allows
mailers to use a single barcode to participate in multiple Postal Service programs simultaneously, expands mailers’
ability to track individual mailpieces, and provides greater mail stream visibility.
The Intelligent Mail barcode can be applied on Priority Mail
®
pieces,
First-Class
Mail
®
pieces,
Standard Mail
®
pieces,
Periodicals, letters and flats, and Bound
Printed Matter flats. The Intelligent Mail barcode can be used for IMb Tracing
®
service, and it can be used for address correction services: manual address
correction notices, ACS
™
, OneCode ACS
®
,
and Intelligent Mail Full-Service
ACS
™
. IMb Tracing
®
service provides information about when and where the
Postal Service sorts a mailpiece on mail-processing equipment. Traditional ACS,
OneCode ACS, and Full-Service ACS provide mailers with electronic address-
correction information when a mailpiece cannot be delivered as addressed.
STEP 1: DOWNLOAD AND INSTALL THE ENCODER AND FONT
The Intelligent Mail barcode consists of a 20-digit tracking code (Barcode
Identifier, Service Type Identifier, Mailer Identifier, and Serial Number) and a
Routing Code (ZIP Code
™
) field of up to 11 digits. An encoder is required to
convert the digits into a 65-character string representing the bars of the IMb
®
tracking code, and a special font is required to convert the 65-character string into
the IMb
®
tracking code itself. Users can download a library of IMb tracking code fonts and computer source code from
the Fonts and Encoders Download page at ribbs.usps.gov. The Intelligent Mail Barcode Resource Download page on
RIBBS provides many useful links and answers to frequently asked questions.
STEP 2: APPLY FOR A MAILER IDENTIFIER
A Mailer Identifier (Mailer ID or MID) is required for the IMb
®
tracking code. New Mailer IDs are assigned through
centralized USPS
®
processes, generally through the Mailer ID system at gateway.usps.com (Business Customer
Gateway). Refer to the User Access to Electronic Mailing Information and Reports Guide on RIBBS for step-by-step
instructions for using the Mailer ID system. Mail owners and mail preparers will be assigned their six- or nine-digit MIDs
based on criteria established by the Postal Service. For the RIBBS web site, go to https://ribbs.usps.gov/index.
cfm?page=mailingpromotions. The Intelligent Mail Mailer ID Application page on the RIBBS
®
site explains the few
exceptions to using the Business Customer Gateway to obtain new Mailer IDs, such as when requesting multiple Mailer
IDs or Mailing Agents acting on behalf of Mail Owners.
STEP 3: POPULATE THE BARCODE FIELDS
The five IMb fields are the Barcode Identifier, the Service Type Identifier, the Mailer ID, the Serial Number, and the
Routing Code (ZIP Code). The Barcode Identifier field should be “00” (zero-zero) with one exception: automation-price
eligible flat mail bearing a printed optional endorsement line (OEL). When mailers prepare flat-size pieces using IMb
®
tracking codes to meet automation-price eligibility requirements, the IMb
®
tracking codes on any pieces bearing printed
OELs must contain the Barcode Identifier corresponding to the printed OEL used. See the Barcode ID Reference Table
on RIBBS
®
to determine the correct Barcode Identifier.
The attributes that determine which Service Type Identifier (STID) should appear in an IMb
®
tracking code are the
class of mail, the ACS service desired, and whether IMb Tracing service is desired. See the Service Type ID Reference
Table on the RIBBS site to determine the correct Service Type Identifier.
The Mailer Identifier (MID) is explained in Step 2, above. All Intelligent Mail
®
barcodes must contain a valid MID,
except in the case of Origin IMb Tracing barcodes, where the Mailer ID and Serial Number fields are combined to
provide the full 15 digits for customer use.
Information about OneCode ACS is available in
Publication 8b, OneCode ACS Technical Guide.
Information on IMb Tracing is available in the
IMb Tracing User Guide. Users should also read
A Guide to Intelligent Mail for Letters and Flats,
which provides in-depth information about the
Intelligent Mail program. For information about
address quality, go to: https://www.usps.com/
business/manage-address-quality.htm.
Once the encoder and font are installed,
verify the print quality by producing samples,
as instructed in the encoder package.
The Intelligent Mail Barcode Specification
USPSB-3200 and The Intelligent Mail Barcode
Technical Resource Guide provide extensive
technical information about Intelligent Mail
barcodes.
(continued on back)
The Serial Number, in conjunction with the MID and class of mail, can uniquely identify the mailpiece. Currently,
Serial Number uniqueness is not required to qualify for basic automation prices. The Intelligent Mail
®
Full-Service
option requires that mailpieces be uniquely identified, and the tracking code cannot be reused for a period of 45 days.
Depending on the length of the MID, the Serial Number is either a nine- or six-digit number.
The Routing Code can contain a 5-digit ZIP Code
™
, 9-digit ZIP+4
®
code, or 11-digit delivery-point code. To obtain
automation discounts, a Delivery-Point ZIP Code from CASS™ -certified (Coding Accuracy Support System) software
is required. Mailers may opt not to populate the ZIP Code and use the IMb
®
tracking code only for tracking the
mailpiece. If populated, it must never be padded with leading or trailing zeros that are not part of a valid 5-, 9-, or
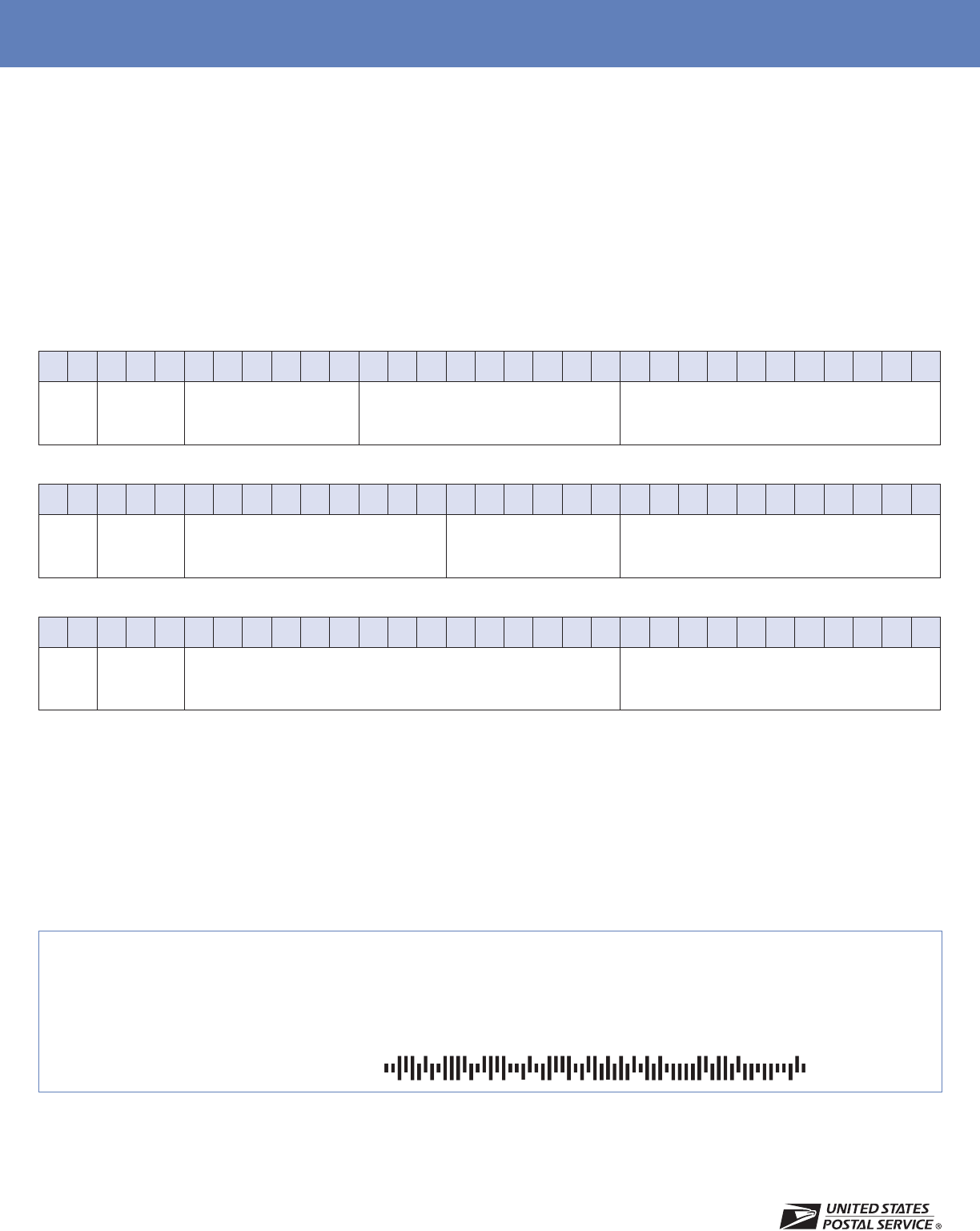
11-digit ZIP Code. The Intelligent Mail barcode concatenates the five fields in this way:
Six Digit Mailer Identifier
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Barcode
ID
[2N]
Service
Type ID
[3N]
Mailer ID
[6N]
Serial Number
[9N]
Routing Code (ZIP)
[none,5,9, or 11N]
Nine-Digit Mailer Identifier
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Barcode
ID
[2N]
Service
Type ID
[3N]
Mailer ID
[9N]
Serial Number
[6N]
Routing Code (ZIP™)
[none,5,9, or 11N]
Origin IMb Tracing
®
Intelligent Mail Barcode Format
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Barcode
ID
[2N]
Service
Type ID
[3N]
Original IMb Tracing Customer Number
(Available to the mailer to use for their own identification purposes)
[15N]
Routing Code (ZIP)
(Serves as “Subscriber ID” for Origin IMb Tracing)
[9 or 11N]
STEP 4: PUT EVERYTHING TOGETHER
Once mailers have selected service(s), received a MID, and devised a unique serial number strategy, they are ready to
put the five fields together to form the 20- to 31-digit string, encode it to 65 characters, and convert the 65-character
string using the IMb font to form the 65-bar Intelligent Mail barcode as in the example below. On letters, the Intelligent
Mail barcode can be placed in the address block or in the barcode clear zone. On flats, it can be placed on the
address side at least 1/8 inch from the edge of the piece.
Learn more about the Intelligent Mail barcode at ribbs.usps.gov
©2014 United States Postal Service®. All Rights Reserved.
The Eagle Logo is among the many trademarks of the U.S. Postal Service®.
EXAMPLE: Service Type ID of 270 (First-Class Mail
®
, Intelligent Mail Full-Service option, with IMb Tracing
®
service, no address correction), Mailer ID 123456,
uniquely identified by Serial Number 200800001, going to ZIP Code 98765-4321(01), is encoded like this:
Digit String: 0027012345620080000198765432101
Æ Intelligent Mail barcode encoder Æ Encoded string (T=Tracker, F=Full Bar, A=Ascender, D=Descender):
TTFAFDADTFFFADTAFAFTTDATDFAAFTDAFDFDFDATFDFTDDDDFADFFDADDTDDTTDAT
Æ Intelligent Mail barcode font Æ Intelligent Mail barcode:
